A method for ultrasonic testing of austenitic stainless steel fillet welds
A technology for austenitic stainless steel and detection methods, which is applied in the analysis of solids using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, and measuring devices. It can solve problems such as inability to locate and large thickness differences. To achieve the effect of ensuring the quality of the weld seam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
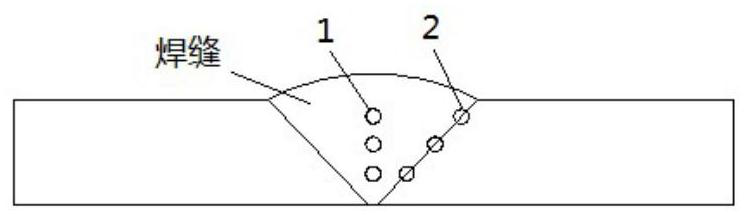
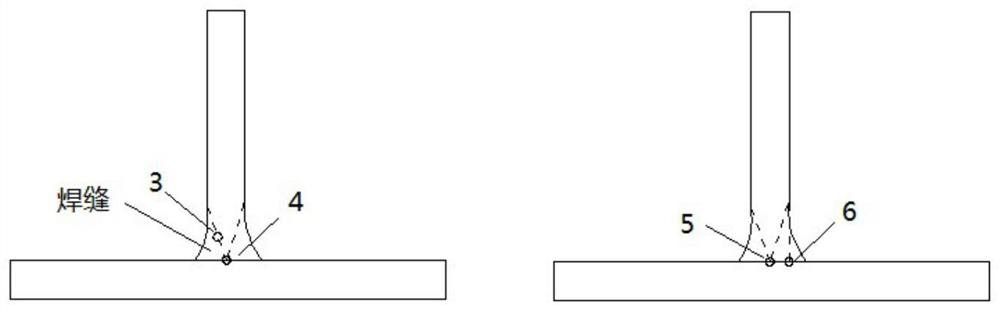
[0052] Defects in austenitic fillet welds are mainly pores and slag inclusions in the weld, lack of fusion on the flange side, lack of fusion on the web side and incomplete penetration at the root. Insufficient fusion and incomplete penetration are the main defect types in this type of fillet weld, and they must be detected first. In order to solve this problem, the present invention proposes a method for ultrasonic testing of austenitic stainless steel fillet welds, comprising the following steps:
[0053] Step 1: Select the instrument. A type A pulse reflection ultrasonic flaw detector is adopted, and the working frequency of the flaw detector includes at least 0.5MHz-5MHz.
[0054] Step 2: Select the detection probe. According to different detection locations and objects, three types of probes are required: 1) dual-element longitudinal wave straight probe; 2) dual-element longitudinal wave oblique probe; 3) creeping wave probe.
[0055] 1) Double crystal longitudinal wav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com