Treatment method of medium-alkaline azo dye-containing wastewater
A technology of azo dyes and treatment methods, applied in water/sewage treatment, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, degassed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of no degradation activity, reduced reduction activity, and low degradation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
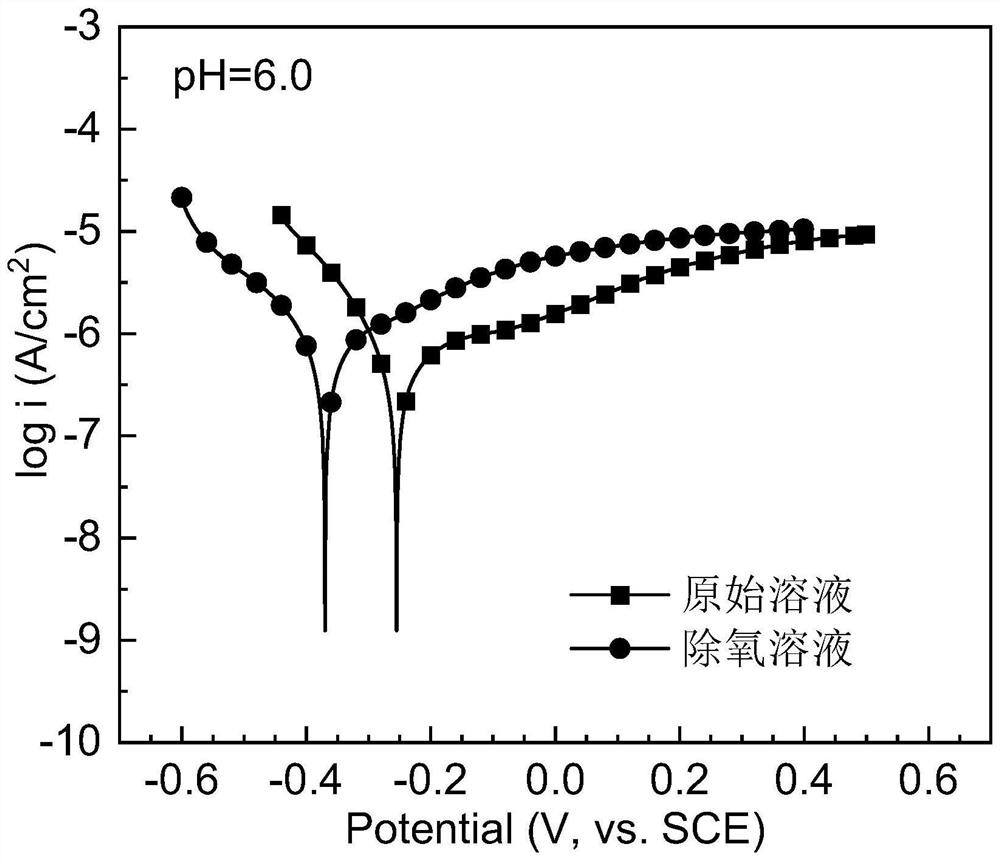
[0047] The surface of the pure iron sheet was polished to remove the scale, and the electrochemical experiments were carried out in the original and deoxidized golden orange II dye solutions. Nitrogen was exposed to the solution for 30 minutes to remove oxygen, the dye concentration was 25mg / L, pH=6.0, and the test temperature was 25°C. Test results such as figure 1 shown.
[0048] figure 1 Polarization curves of pure iron flakes in pristine and deoxygenated golden orange II dye solutions at pH = 6.0. It can be seen from the figure that when the dissolved oxygen in the solution is eliminated, the corrosion potential of the pure iron sheet drops from -0.255V to -0.370V, and the corrosion current density decreases from 5.4×10 -7 A / cm 2 up to 7.2×10 -7 A / cm 2 . The test results show that the reactivity of the pure iron sheet in the dye solution becomes stronger after oxygen removal.
Embodiment 2
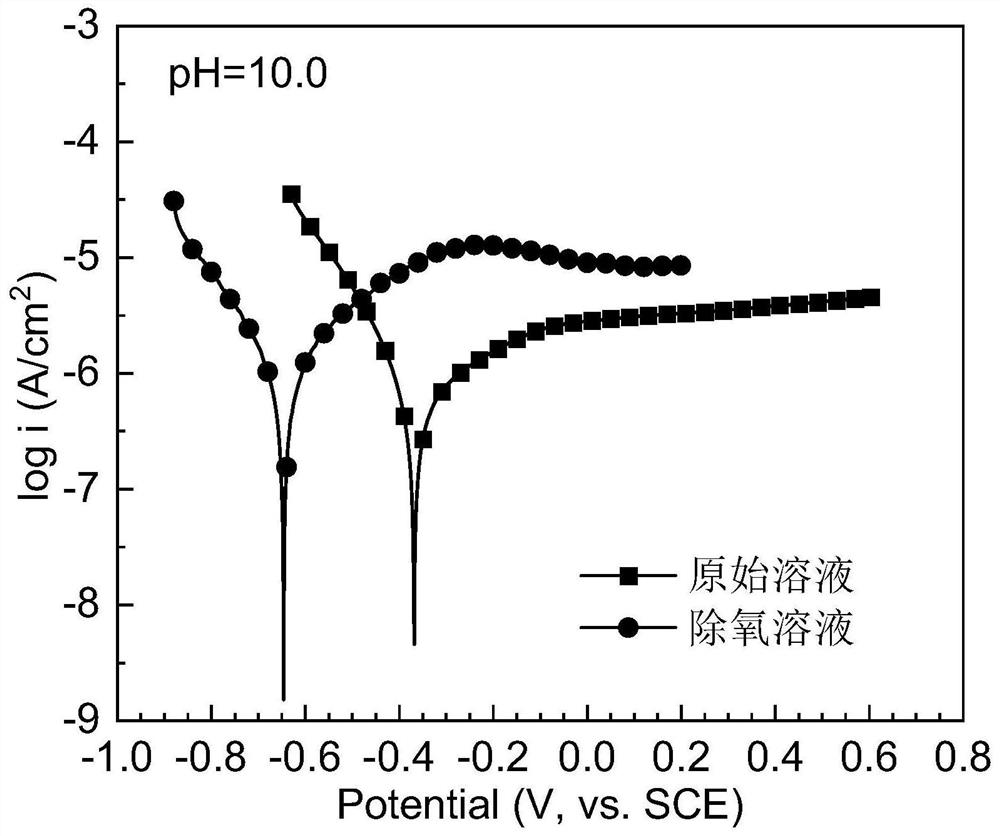
[0050] The surface of the pure iron sheet was polished to remove the scale, and the electrochemical experiments were carried out in the original and deoxidized golden orange II dye solutions. Nitrogen was exposed to the solution for 30 minutes to remove oxygen, the dye concentration was 25mg / L, pH=10.0, and the test temperature was 25°C. Test results such as figure 2 shown.
[0051] figure 2 Polarization curves of pure iron flakes in pristine and deoxygenated golden orange II dye solutions at pH = 10.0. It can be seen from the figure that when the dissolved oxygen in the solution is eliminated, the corrosion potential of the pure iron sheet drops significantly from -0.368V to -0.646V, and the corrosion current density decreases from about 6.4×10 -7 A / cm 2 Significantly increased to 1.1×10 -6 A / cm 2 . The test results show that after oxygen removal, the reactivity of the pure iron sheet in the highly basic dye solution is greatly enhanced.
Embodiment 3
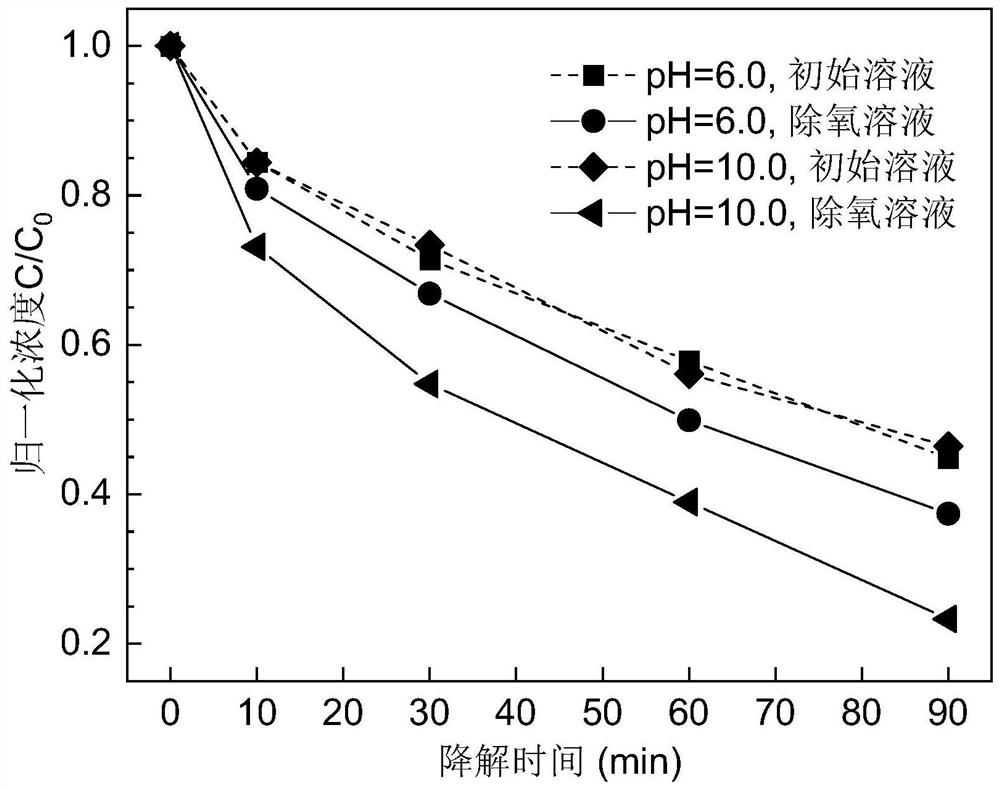
[0053] Clean the pure iron particles with an average particle size of 350 μm with hydrochloric acid of pH = 2.5 to remove surface oxides, and then fully wash with deionized water to remove residual acid. The cleaned pure iron is used to degrade golden oranges with a concentration of 25mg / L For solution II, the amount of pure iron used is 10g / L, the experimental temperature is 25°C, and the stirring speed is 240rpm. The test solution is divided into the original pH and deoxygenated solution, and the deoxygenated solution is obtained by aerating nitrogen for 30 minutes.
[0054] image 3 When pH=6.0 and 10.0, the normalized concentration of pure iron degraded original Golden Orange II solution and deoxygenated Golden Orange II solution varies with the degradation time. It can be seen from the figure that in the dye solution without oxygen removal, pure iron shows lower degradation performance at pH=6.0 and 10.0; in the dye solution with oxygen removal, the degradation rate of p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| corrosion potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| corrosion potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com