Positive electrode slurry comprising oxalic acid, method for manufacturing same, positive electrode for secondary battery, and secondary battery
A technology for positive electrode slurry and lithium secondary batteries, which can be used in secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, battery electrodes, etc., and can solve problems such as phase stability reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0078] Another embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing positive electrode slurry, the method comprising:
[0079] (a) a process of adding a positive electrode active material, a conductive material, and a binder to a solvent, and then mixing them with each other to prepare a mixture; and
[0080] (b) adding oxalic acid and an overcharge inhibitor to the mixture, and then mixing them with each other to prepare a positive electrode slurry; wherein, the positive electrode active material, conductive material and binder based on 100 parts by weight of the positive electrode slurry The total solid content of the overcharge inhibitor is 1 to 2 parts by weight, and the total solid content of the positive electrode active material, conductive material and binder based on 100 parts by weight of the positive electrode slurry, the addition amount of oxalic acid 0.1 to 0.7 parts by weight.
[0081] Here, descriptions of the positive electrode active material, ...
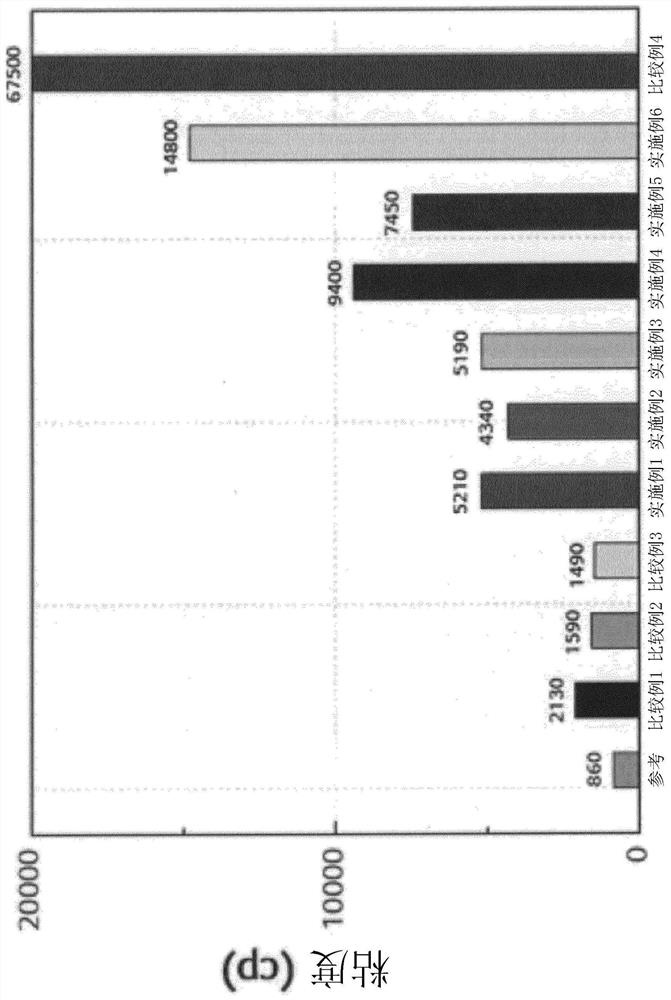
experiment example 1
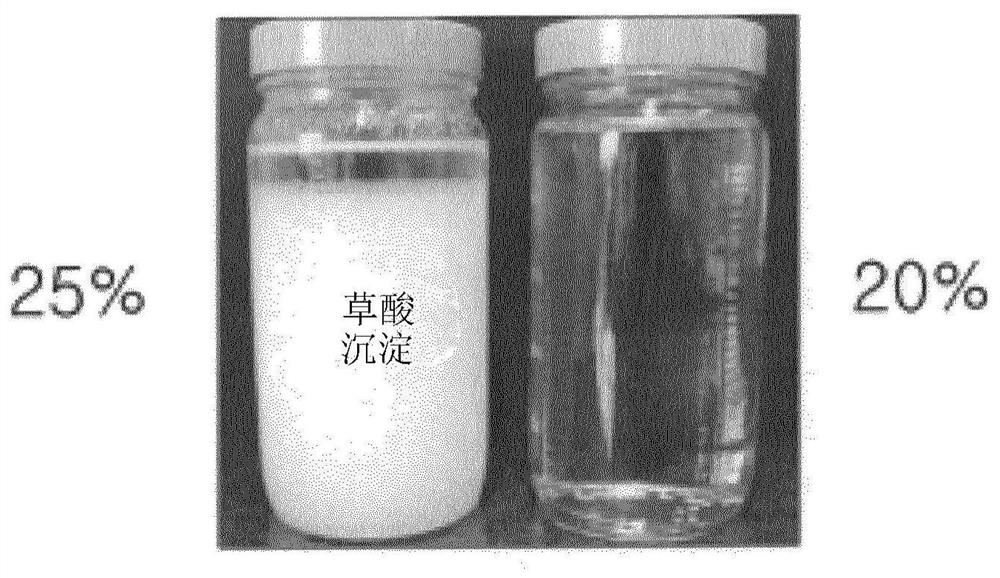
[0114] Dissolution tests were performed by changing the concentration of oxalic acid (weight of oxalic acid / weight of solution x 100) to 20% and 25% while dissolving oxalic acid in NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone), as figure 1 shown.
[0115] refer to figure 1 , complete dissolution was observed at a concentration of 20%, while at a concentration of 25% oxalic acid reached saturation and did not dissolve further, resulting in precipitation.
[0116] Therefore, in the present invention, an oxalic acid solution with a concentration of 20% is used.
experiment example 2
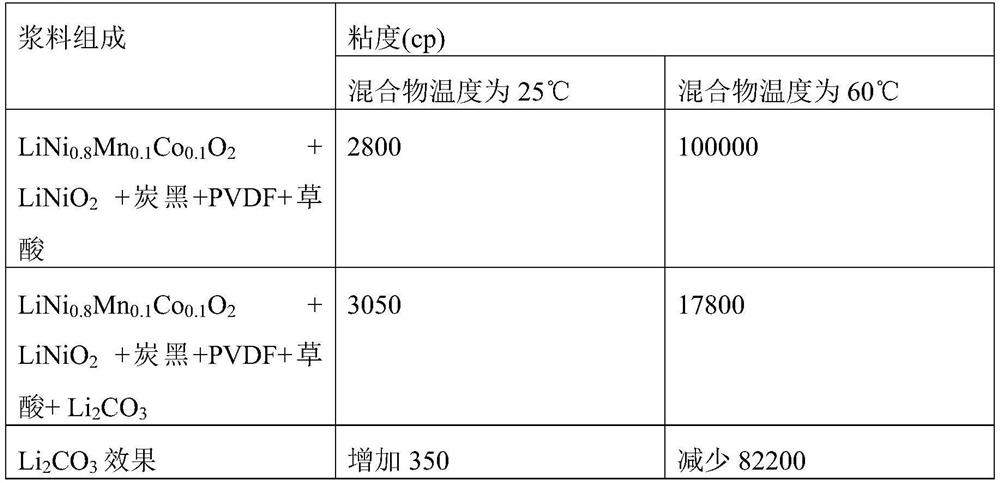
[0118] Add 96.865% by weight of active material LiNi in a weight ratio of 80:20 0.8 mn 0.1 co 0.1 o 2 and the active material LiNiO 2 active material, 1.9% by weight of carbon black as a conductive material (predispersed solution (16% solution of carbon black in NMP)), 1.235% by weight of PVDF as a binder (PVDF solution (PVDF in NMP 6% solution)) and mixed using a BTM mixer (INOUE Inc., 5 L volume, three-shaft mixer with a total of three blades including one low speed blade and two high speed blades)).
[0119] Mixtures were prepared as samples at 25°C and 60°C, respectively.
[0120] The oxalic acid solution (20% concentration) of Experimental Example 1 was mixed with each of the two mixtures using a homogenizing dispersing mixer (PRIMIX Corp., 500 ml volume, a high-speed dispersing machine), so that based on the active material, conductive material and The total weight of the binder, the amount of oxalic acid is 0.5 parts by weight, after that, 3 parts by weight (excess...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com