Fermented milk product and preparation thereof by using phospholipase
A technology for fermenting dairy products and phospholipase, applied in the direction of dairy products, bacteria used in food preparation, milk preparations, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and high energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
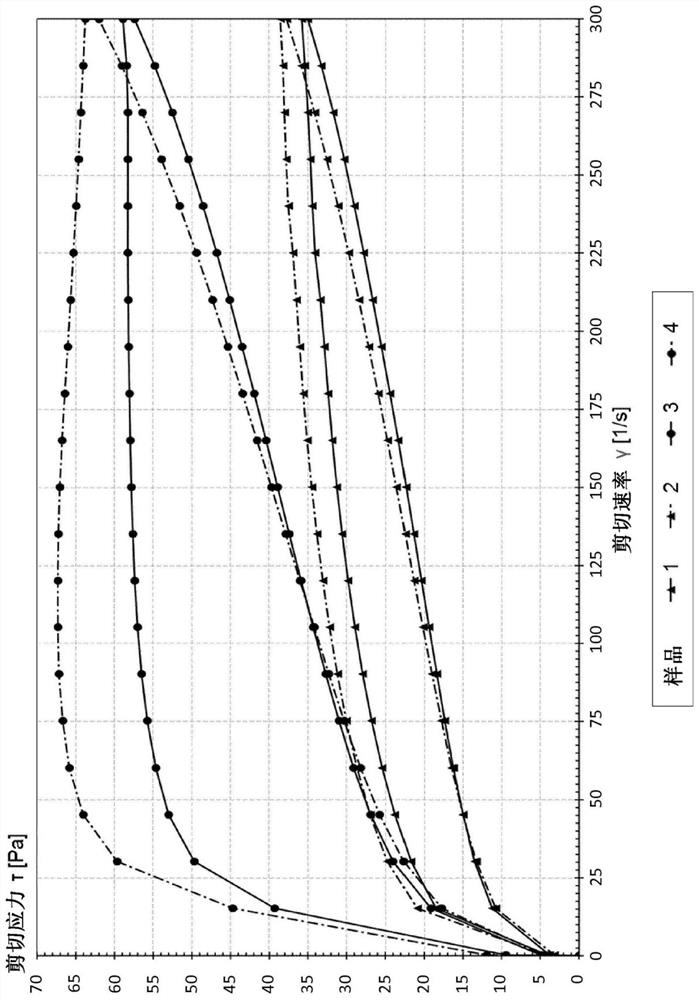
[0115] Yogurt products containing 1.5% or 5.0% fat were prepared. On days 7 and 30, the effect of phospholipase on rheological properties was assessed.
[0116] Preparation of milk base:
[0117] Skim milk powder and whole milk powder (Fonterra Co-operative Group Limited, New Zealand) were used to prepare the milk bases of the following examples.
[0118] Table 1. Composition of milk base (w / w)
[0119] sample Skim milk powder whole milk powder water 1 8.60% 5.30% 86.10% 2 8.60% 5.30% 86.10% 3 8.10% 9.00% 82.90% 4 8.10% 9.00% 82.90%
[0120] The ingredients were mixed with water using a Silverson mixer at 45°C-50°C. The hydration time was 20 minutes. In two stages (150 bar in the first stage, 50 bar in the second stage; 200 bar in total), the milk base was homogenized with a GEA Lab homogenizer and pasteurized at 85°C for 30 minutes and then cooled.
[0121] Starter cultures:
[0122] The starter culture consisted of Strept...
Embodiment 2
[0142] 1. Experimental Setup
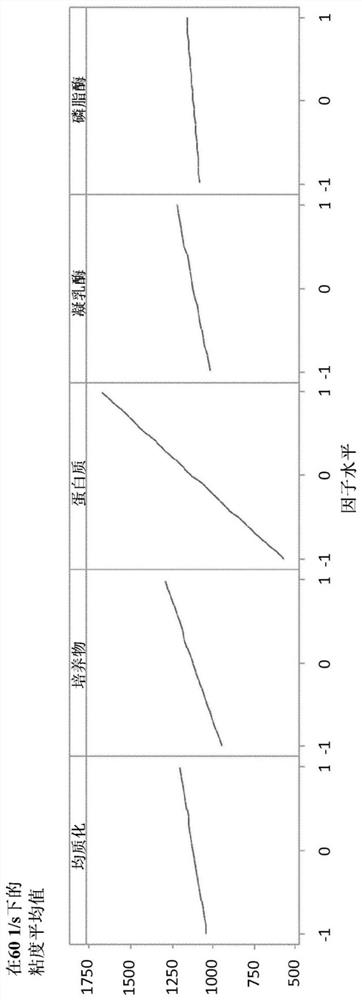
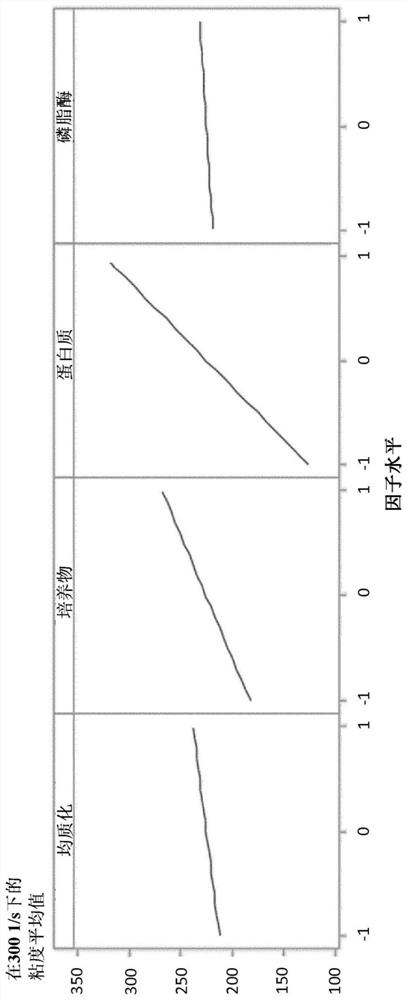
[0143] In 16 experiments, a factorial-fractional design was chosen to examine the following 5 factors. The aim was to confirm the effect of phospholipase on texture in a larger design and to examine significance, interaction with homogenization pressure level, interaction with rennet, and interaction with starter cultures.
[0144] Table 5. Experimental setup: Factors Factors are orthogonally coded:
[0145] factor -1 +1 1- Homogenization pressure 150 bar 300 bar 2- Starter cultures 1 2 3- Protein content 2.50% 4.50% 4-rennet none Yes 5-phospholipase none Yes
[0146] Table 6. Experimental Setup: Design
[0147]
[0148]
[0149] Table 7. Aliasing Structure
[0150] 1 2345 2 1345 3 1245 4 1235 12 345 13 245 14 235 23 145 24 135 34 125 123 45 124 35 134 25 234 15 1234 5
[0151] For third-order inte...
Embodiment 3
[0202] Soy yogurt containing 2.03% fat and 4.05% protein was prepared. The effect of phospholipase on rheological properties was assessed on day 7.
[0203] Table 12. Composition (w / w) used to prepare soy yogurt
[0204] Element Specification quantity(%) Chinese soybean meal Redman 22.50 sugar KSL, refined sugar 5.00 water Tap water, PUB 72.50
[0205] Table 13. Samples of Example 3
[0206]
[0207] Preparation and Fermentation:
[0208] Depending on the setting, the phospholipase is added before the fermentation period, at the beginning of the fermentation period, or during the fermentation period.
[0209] The method used in Example 3 is as follows. The compositions shown in Table 12 were mixed with a Silverson mixer. The mixing temperature / hydration time was 45°C-50°C / 20min. Homogenization was performed using a GEA Lab homogenizer, preheated at 65-70°C, with a pressure of 150 bar in the first stage and 50 bar in the second...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com