Food composition and pharmaceutical composition with strains of lactic acid bacteria for modulating blood glucose
A pharmaceutical composition and technology of lactic acid bacteria, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, lactobacillus, dairy products, etc., can solve problems such as differences in the ability to control fasting blood sugar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1: Morphological and general properties of the lactic acid bacteria strain of the present invention
[0055] The taxonomic characteristics of the strains will be confirmed according to the results of 16S rDNA sequence analysis and API bacterial identification system analysis. The morphological and general characteristics of the above strains are listed in Table 2:
[0056] Morphological and general property characteristics of the lactic acid bacteria strain of the present invention
[0057]
Embodiment 2
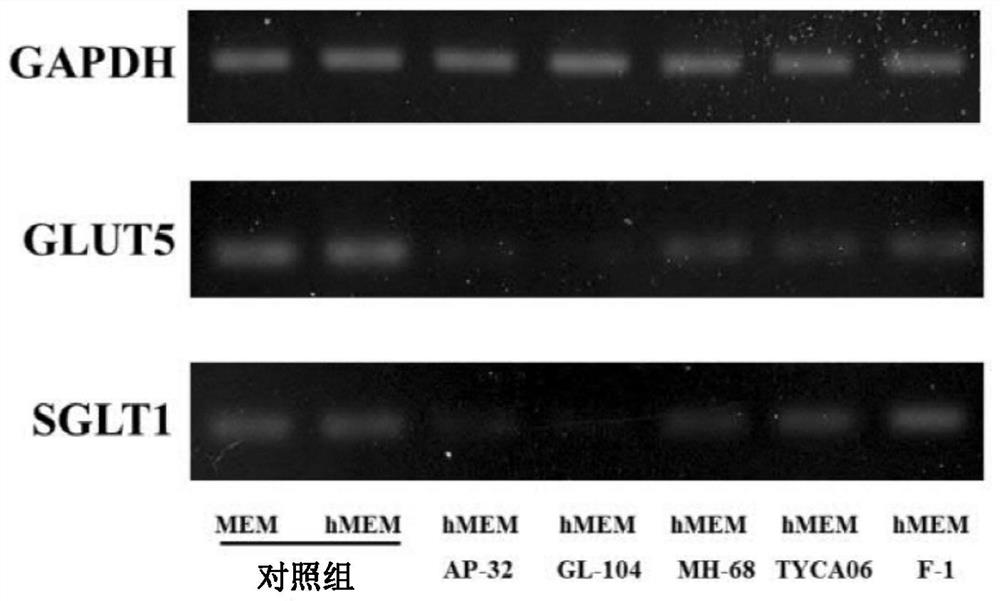
[0058] Example 2: Screening of lactic acid bacteria strains with monosaccharide metabolism ability by in vitro tests
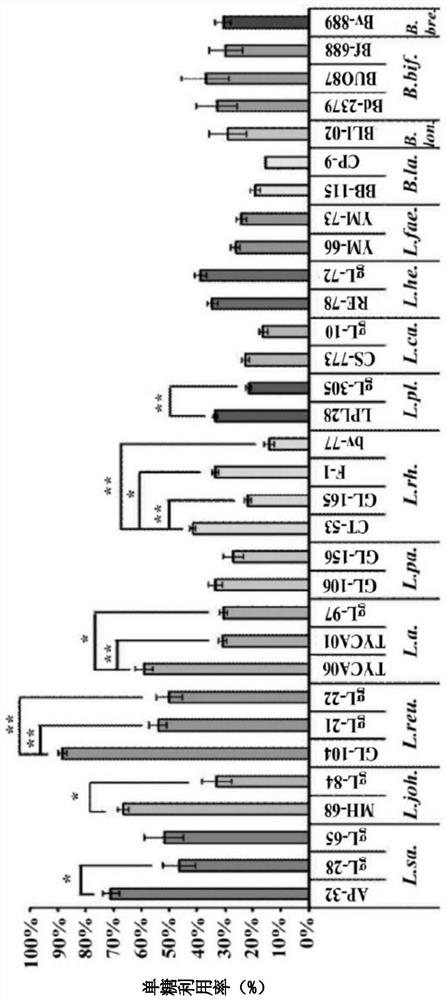
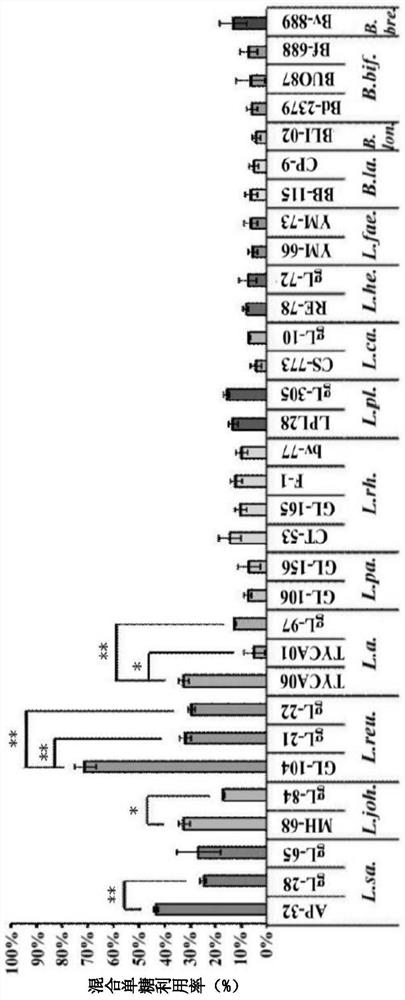
[0059] In the present embodiment, the lactic acid bacteria used include Lactobacillus salivarius (Lactobacillus salivarius) AP-32 strain, gL-28 strain and gL-65 strain, Lactobacillus johnsonii (Lactobacillus johnsonii) MH-68 strain and gL-84 strain, Lactobacillus reuteri GL-104 strain, gL-21 strain and gL-22 strain, Lactobacillus acidophilus TYCA06 strain, TYCA01 strain and gL-97 strain, Lactobacillus paracasei ) GL-106 strain and GL-156 strain, Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Lactobacillus rhamnosus) CT-53 strain, GL-165 strain, F-1 strain and bv-77 strain, plant Lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) LPL28 strain and gL-305 strain, Lactobacillus casei CS-773 strain and gL-10 strain, Lactobacillus helveticus RE-78 strain and gL-72 strain, Enterococcus faecium YM-66 strain and YM-73 strain, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp.lactis BB-115 strain and CP-9 strain, Bifido...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3: Screening of lactic acid bacteria strains capable of metabolizing mixed monosaccharides by in vitro tests
[0064] In this example, each of the above strains was inoculated with 1×10 8 The CFU is in the culture medium, wherein the culture medium is MFG culture medium (containing glucose 20mg / ml, fructose 20mg / ml, and galactose 20mg / ml). Then, after culturing in a 37°C incubator for 20 hours, the supernatant was collected, and the reducing sugar concentration was analyzed with DNS reagent (27.4mM 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid, 524mM Sodium hydroxide and 879mM Potassium sodium tartrate), and then the mixing of each strain was calculated. Monosaccharide utilization (%).
[0065] Please refer to figure 2 , the results show that Lactobacillus reuteri, Lactobacillus salivarius, Lactobacillus johnsonii, and Lactobacillus acidophilus have a better ability to metabolize mixed monosaccharides than other lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria in a mixed monosaccharide e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com