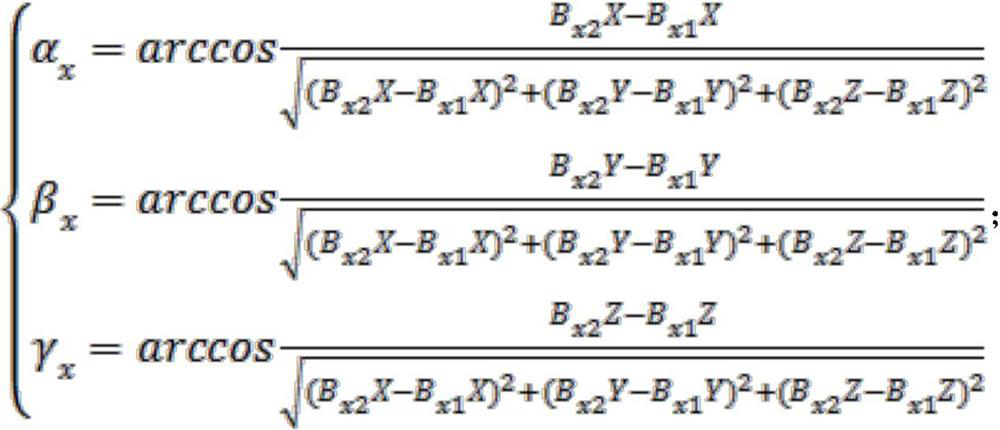Method for measuring and adjusting spatial position relationship of multiple positioners
A technology of spatial position and adjustment method, which is applied in the directions of measuring device, surveying and navigation, measuring inclination, etc. It can solve the problems of large external influence factors, influence of attitude adjustment accuracy, and large cumulative error.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
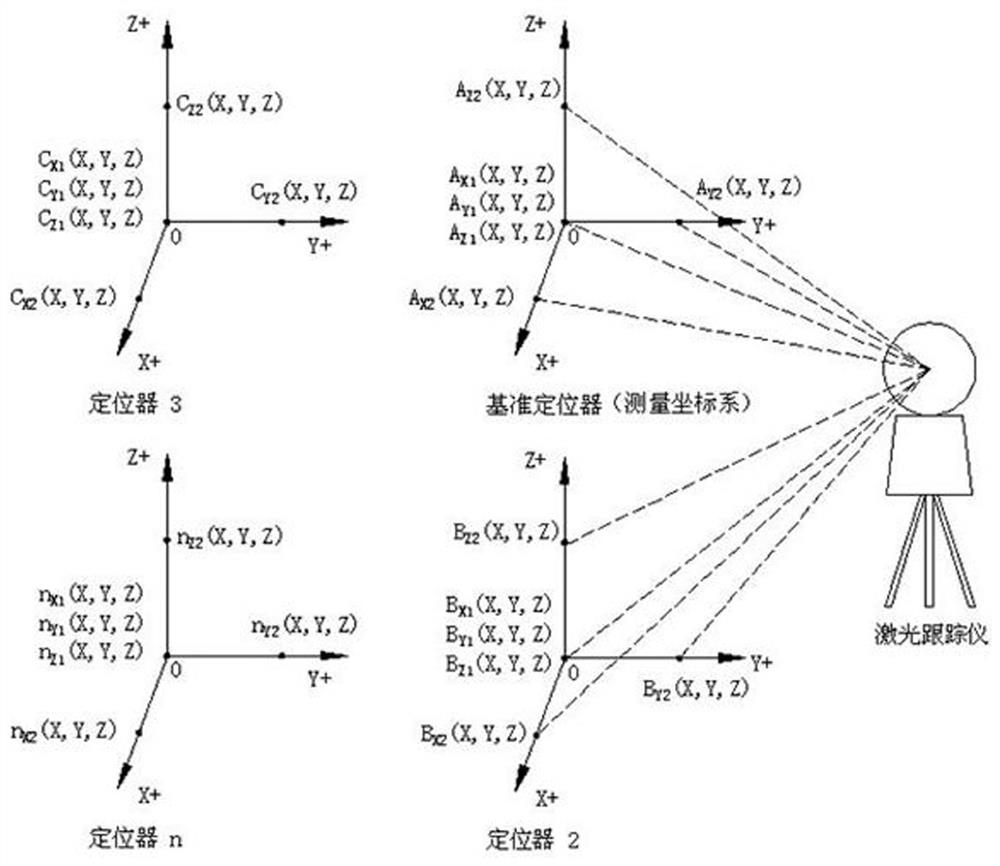
[0044] A method for measuring and adjusting the spatial position relationship of multiple locators in this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, step 1. Determine the reference X-axis and reference Y-axis that are perpendicular to each other, and use the reference positioner to level the reference X-axis and reference Y-axis, so that the reference X-Y plane remains horizontal, and establish a plane perpendicular to the reference X-Y plane. The reference Z axis forms the reference coordinate system;
[0045] Step 2. Use the adjusting positioner to measure the adjustment positioning coordinates of the positioner X-axis, positioner Y-axis, and positioner Z-axis respectively in the reference coordinate system, and calculate the positioner X-axis, positioner Y-axis, and positioning coordinates by adjusting the positioning coordinates. The spatial positional relationship between the Z-axis of the device and the reference X-axis, reference Y-axis, and reference Z-axis respectively; ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of Embodiment 1. In the step 2, two points are selected on the X-axis of the positioner, the Y-axis of the positioner, and the Z-axis of the positioner as the positive limit point and the negative limit point respectively. position, and then move the adjusting locator to the positive limit point and the negative limit point respectively to measure the coordinates of the positive limit point and the negative limit point, and obtain the locator through the positive limit coordinates and the negative limit coordinates The space position vector of the X-axis, the Y-axis of the locator, and the Z-axis of the locator.
[0052] Select the positive limit point and the negative limit point on the X-axis of the positioner respectively, and the coordinate of the negative limit measurement point on the X-axis of the positioner is B X1 (X, Y, Z), the positive limit measuring point coordinates of the X axis of the positioner is B X2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 or 2. The spatial position relationship refers to the X-axis of the locator, the Y-axis of the locator, the Z-axis of the locator and the reference X-axis, the reference Y-axis, and the reference Z. The angle relationship between two axes, the calculation formula of the angle relationship is as follows:
[0058] The included angles between the X-axis of the positioner and the reference X-axis, reference Y-axis, and reference Z-axis are:
[0059]
[0060] where: α x is the angle between the X-axis of the positioner and the reference X-axis; β x is the angle between the X-axis of the positioner and the reference Y-axis; γ x is the angle between the X-axis of the positioner and the reference Z-axis; B x1 X is the X coordinate value of the negative limit point of the X axis of the positioner; B x2 X is the X coordinate of the positive limit point of the X axis of the locator; B x1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com