Method for reducing algal toxin in water based on catalytic hydrogenation of supported noble metal catalyst
A precious metal catalyst, catalytic hydrogenation technology, applied in the direction of metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, chemical instruments and methods, reduced water/sewage treatment, etc. The technical energy consumption is high, the oxidation process is not selective, etc., to achieve the effect of fast speed, obvious toxicity removal, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
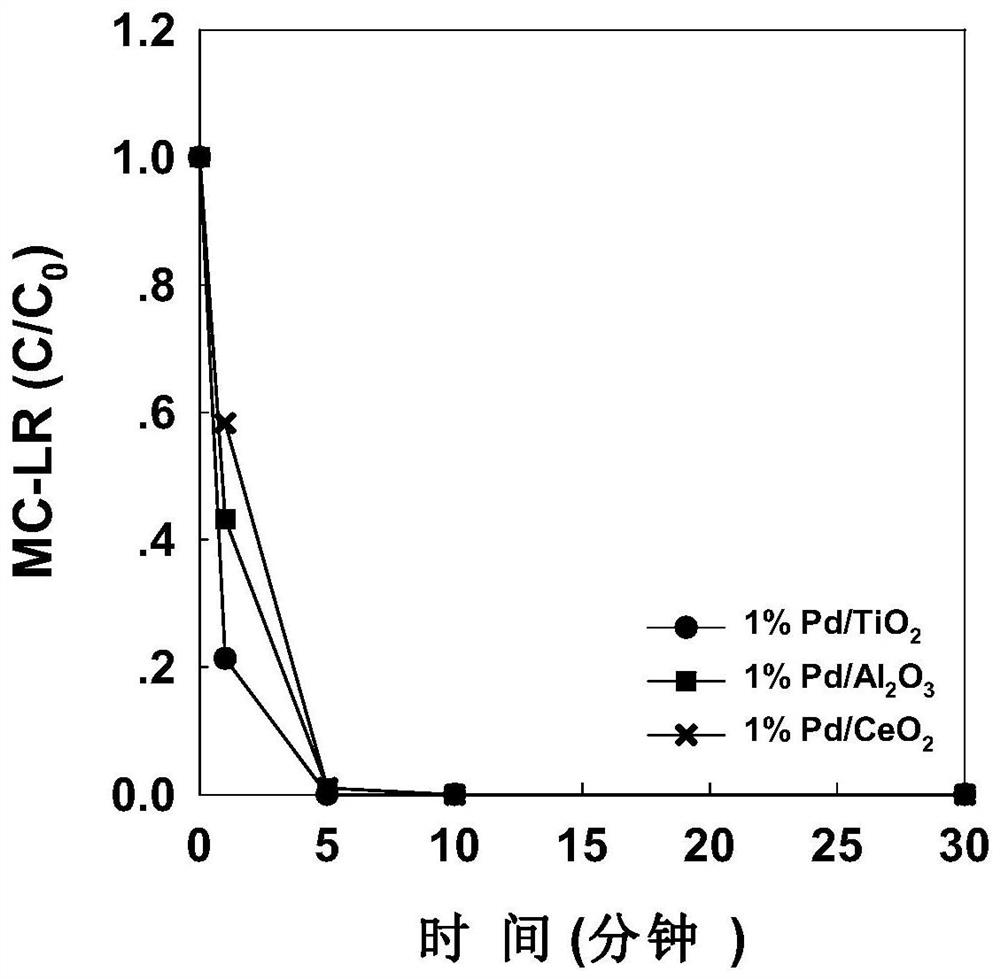
[0038] (1) Weigh 0.5g of titanium oxide, cerium oxide, and alumina carrier in a small beaker, calculate the volume of chloropalladium acid needed to load 1wt.%Pd according to the carrier mass, and use a pipette to add the volume according to the calculated volume Add chloropalladium acid solution to different supports to get 1%Pd / TiO 2 , 1%Pd / Al 2 o 3 , 1%Pd / CeO 2 Material.
[0039] (2) Magnetic stirring step (1) the solution in the beaker for 1h, and add 1M Na 2 CO 3 The solution was brought to pH=10.5, and stirring was continued for 1 h.
[0040] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) was washed with deionized water through a 0.45 micron filter membrane until neutral, dried in an oven at 105°C, and calcined in a muffle furnace at 300°C for 4 hours.
[0041] (4) The material after roasting in the step (3) is heated at 300° C. 2 (25mL min -1 ) in the atmosphere for 2h to obtain Pd materials with different supports.
[0042] (5) Weigh 5 mg of Pd material obtained in ste...
Embodiment 2
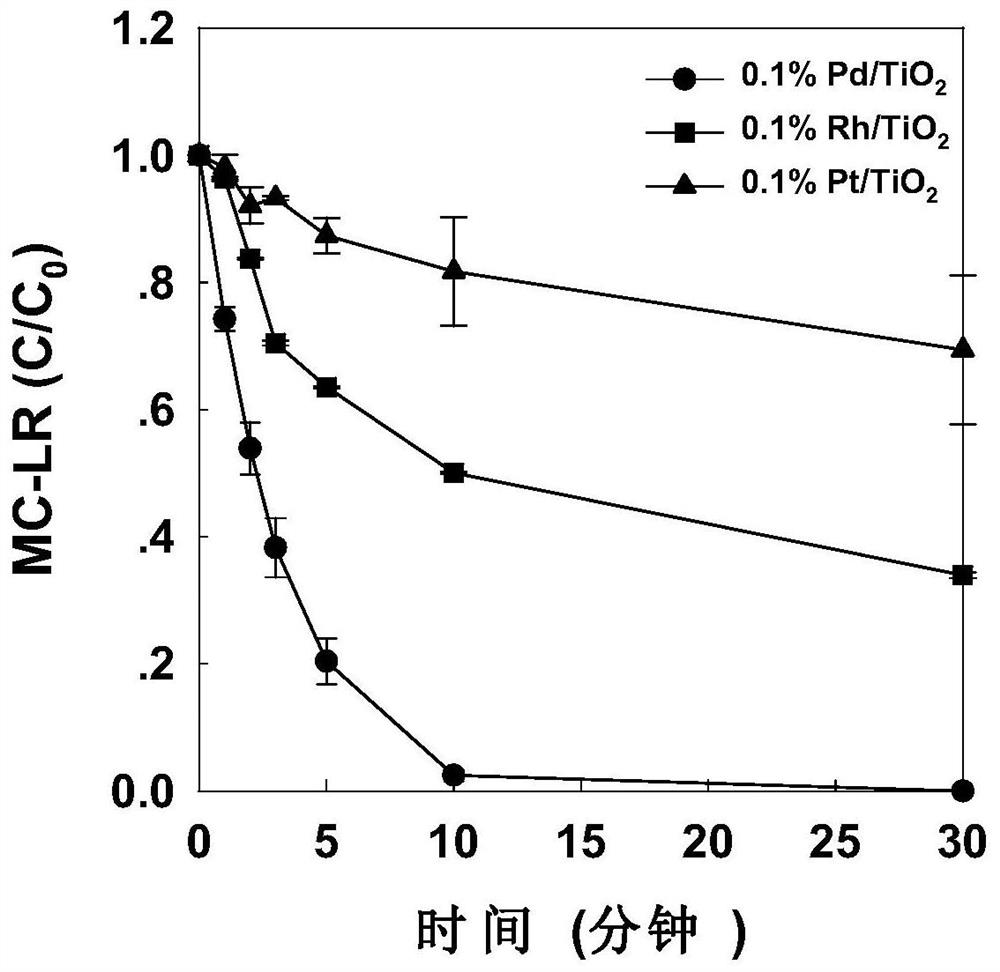
[0046] (1) Weigh 0.5g titanium oxide carrier in a small beaker, calculate the volume of chloropalladic acid, chloroplatinic acid, and rhodium chloride solution needed to load 0.1wt.% Pd, Pt, Rh according to the carrier mass, and obtain according to the calculation Add chloropalladic acid, chloroplatinic acid, rhodium chloride solution to titanium oxide with a pipette gun to get 0.1% Pd / TiO 2 , 0.1%Rh / TiO 2 , 0.1%Pt / TiO 2 Material.
[0047] (2) Magnetic stirring step (1) the solution in the beaker for 1h, and add 1M Na 2 CO 3 The solution was brought to pH=10.5, and stirring was continued for 1 h.
[0048] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) was washed with deionized water through a 0.45 micron filter membrane until neutral, dried in an oven at 105°C, and calcined in a muffle furnace at 300°C for 4 hours.
[0049] (4) The material after roasting in the step (3) is heated at 300° C. 2 (25mL min -1 ) in the atmosphere for 2h to obtain titanium oxide materials loaded with...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) Weigh 0.5g titanium oxide carrier in a small beaker, and calculate the volume of chloropalladium acid solution needed to load 0.1wt.% Pd, 0.2wt.% Pd and 0.3wt.% Pd according to the carrier mass, and obtain according to the calculation volume of chloropalladic acid solution was added to titania with a pipette to obtain different loadings of Pd / TiO 2 Material.
[0054] (2) Magnetic stirring step (1) the solution in the beaker for 1h, and add 1M Na 2 CO 3 The solution was brought to pH=10.5, and stirring was continued for 1 h.
[0055] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) was washed with deionized water through a 0.45 micron filter membrane until neutral, dried in an oven at 105°C, and calcined in a muffle furnace at 300°C for 4 hours.
[0056] (4) The material after roasting in the step (3) is heated at 300° C. 2 (25mL min -1 ) in the atmosphere for 2h to obtain catalysts Pd / TiO with different Pd loads 2 .
[0057] (5) Weigh the Pd / TiO of different Pd loadings...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap