Method for judging single-phase grounding fault of low-current grounding system
A single-phase grounding fault, small current grounding technology, applied in the fault location, detecting faults according to conductor types, measuring electricity and other directions, can solve the problems of high sampling rate requirements of equipment, error-prone fault determination, and difficult application, etc. Verify difficult effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
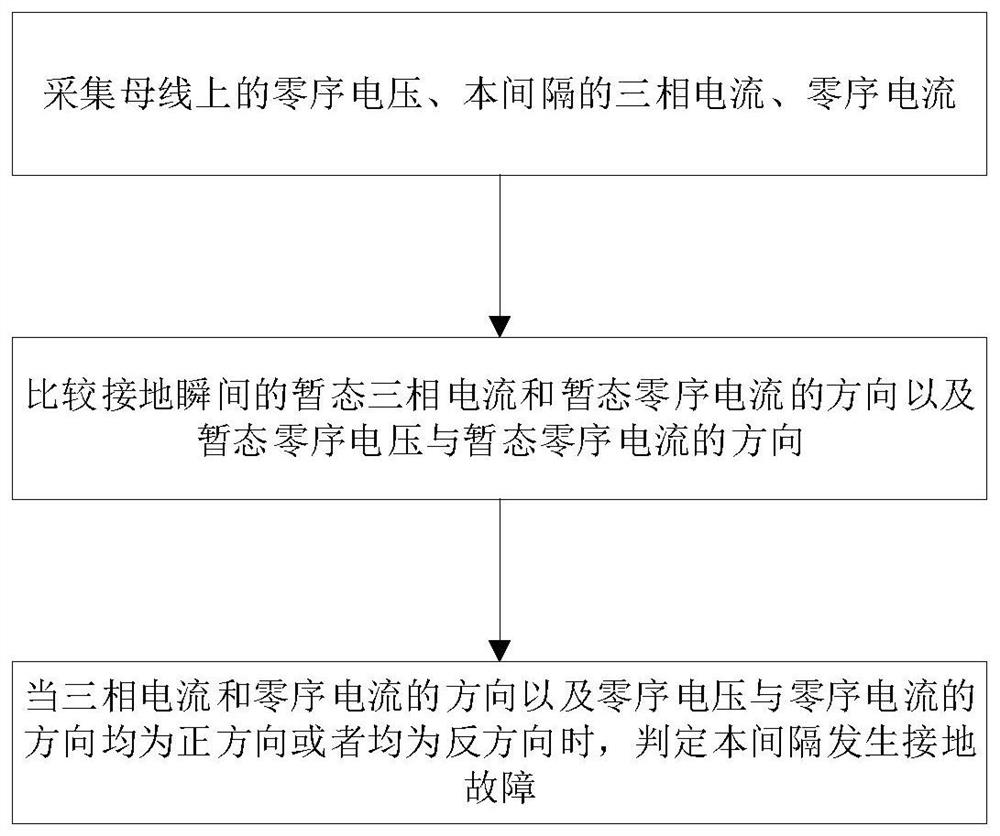
[0034] Embodiment 1 of a method for judging a single-phase ground fault in a small current grounding system, as shown in figure 1 shown, including:
[0035] Collect zero-sequence voltage on the bus, three-phase current and zero-sequence current in this interval;
[0036] Compare the direction of transient three-phase current and transient zero-sequence current at the moment of grounding, and the direction of transient zero-sequence voltage and transient zero-sequence current;
[0037] When the directions of the three-phase current and zero-sequence current and the directions of zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current are both positive or negative, it is determined that a ground fault occurs in this bay.
Embodiment 2
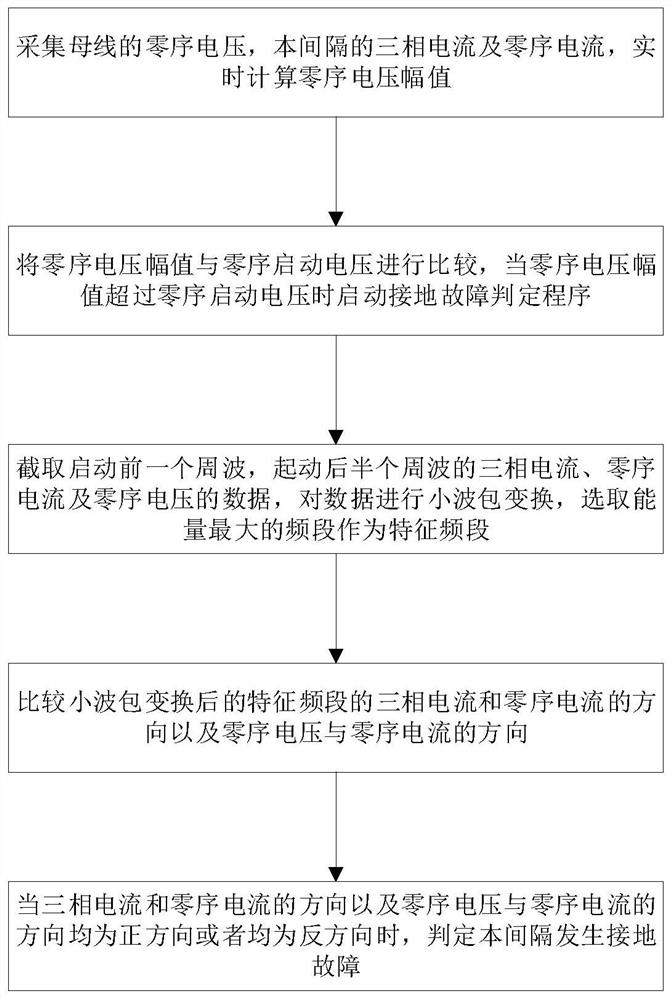
[0039] Embodiment 2 of a method for judging a single-phase ground fault in a small current grounding system, as shown in figure 2 Shown include the following steps:
[0040] Step (1): Collect the zero-sequence voltage of the bus, the three-phase current and zero-sequence current of this interval, and calculate the zero-sequence voltage amplitude in real time;
[0041] Step (2): Comparing the zero-sequence voltage amplitude with the zero-sequence starting voltage, when the zero-sequence voltage amplitude exceeds the zero-sequence starting voltage, start the ground fault judgment procedure and enter step (3), otherwise return to step (1);
[0042] Step (3): Intercept the data of the three-phase current, zero-sequence current and zero-sequence voltage of the first cycle before starting and the half cycle after starting, perform wavelet packet transformation on the data, select the frequency band with the largest energy as the characteristic frequency band, and obtain the charact...
Embodiment 3
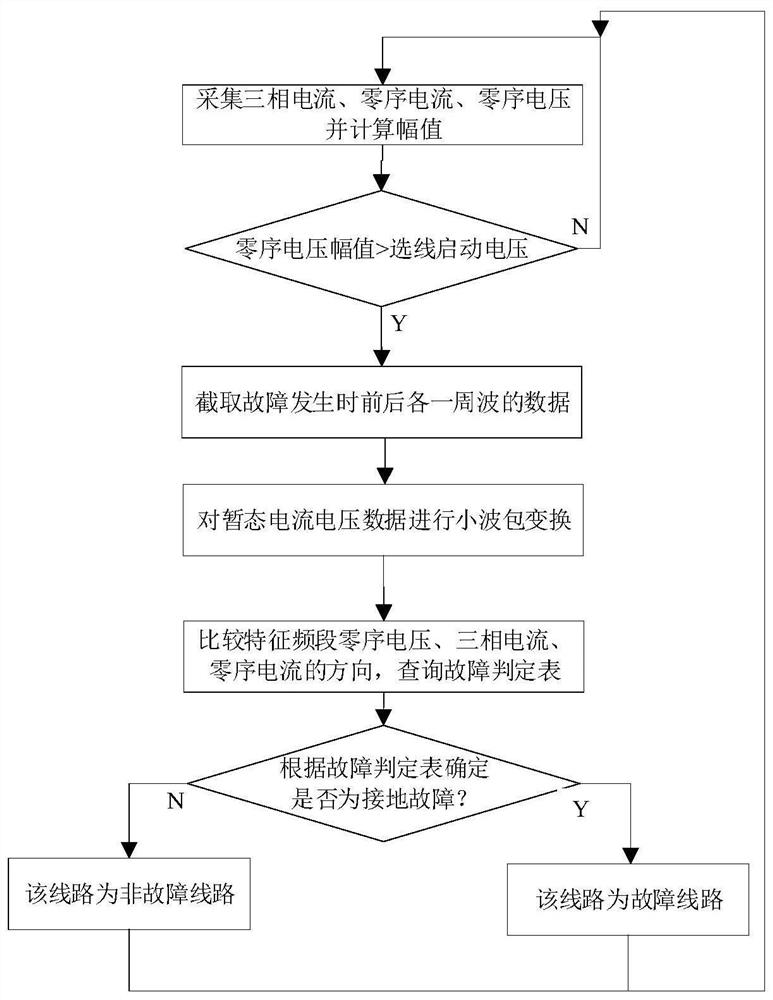
[0046] Embodiment 3 of a method for judging a single-phase ground fault in a small current grounding system includes the following steps:
[0047] Step (1): Collect the zero-sequence voltage of the bus, the three-phase current and zero-sequence current of this interval, and calculate the zero-sequence voltage amplitude in real time;
[0048] Step (2): Comparing the zero-sequence voltage amplitude with the zero-sequence starting voltage, when the zero-sequence voltage amplitude exceeds the zero-sequence starting voltage, start the ground fault judgment procedure and enter step (3), otherwise return to step (1);
[0049]Step (3): Intercept the data of the three-phase current, zero-sequence current and zero-sequence voltage of the first cycle before starting and the half cycle after starting, perform wavelet packet transformation on the data, select the frequency band with the largest energy as the characteristic frequency band, and obtain the characteristic frequency band The th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com