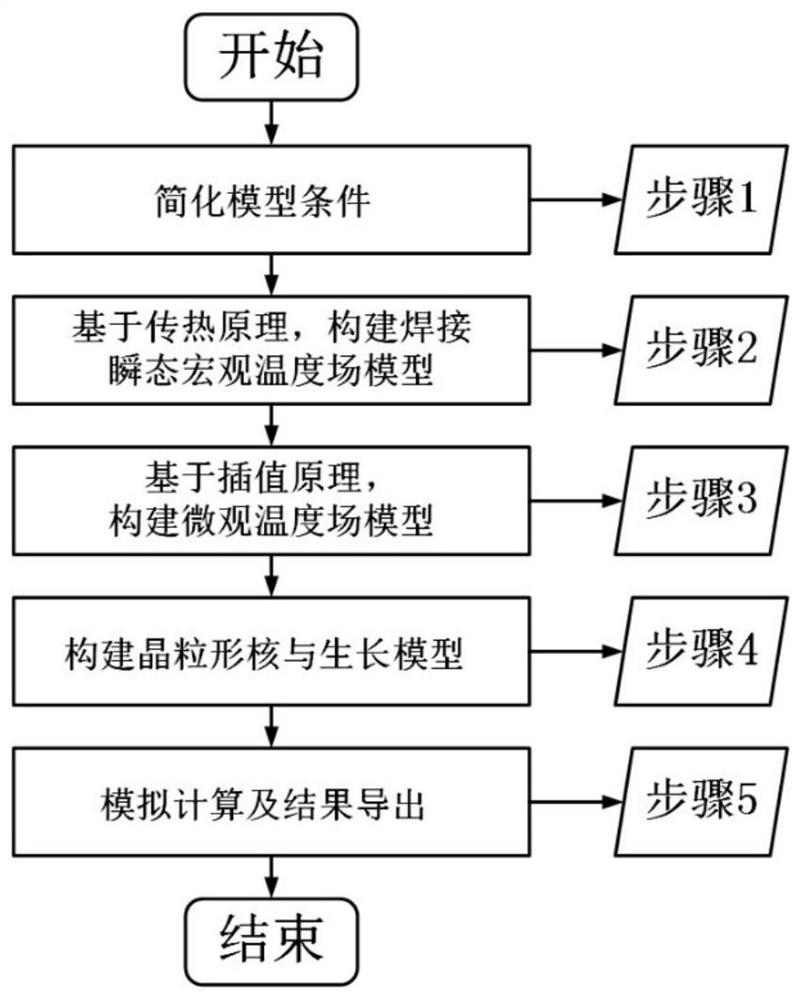
Three-dimensional numerical simulation method for grain growth of titanium alloy welding pool
A technology for grain growth and welding pool, applied in CAD numerical modeling, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problem of lack of three-dimensional numerical simulation method of grain growth and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
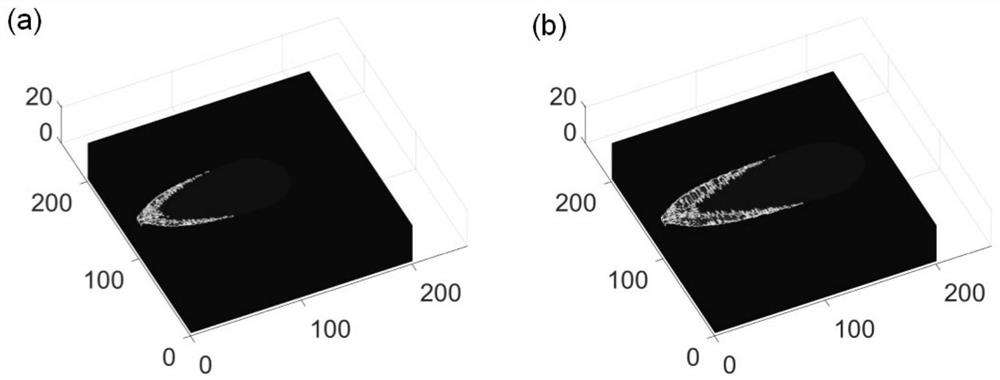
[0128] image 3 a and 3b are the three-dimensional simulation results of grain growth in the molten pool during the welding process of TC4 titanium alloy when the welding current is 60A. It can be seen that during the solidification process of the molten pool, grains nucleate at the edge of the molten pool and grow toward the center of the molten pool in the form of columnar crystals. Because the temperature in the molten pool is too high to meet the conditions for grain nucleation, the molten No crystal nuclei are produced in the center of the pool.
Embodiment 2
[0130] Figure 4 a and 4b are the three-dimensional simulation results of grain growth in the molten pool during the welding process of TC4 titanium alloy when the welding current is 70A. It can be seen that because the heat input is larger than that in Example 3, the weldment is completely penetrated, the cross-sectional shape of the weld pool is "trapezoidal", and the upper melting width of the molten pool is larger than the lower melting width. This is because the heat source directly acts on the weldment caused by the surface.
Embodiment 3
[0132] Figure 5 a and 5b are the three-dimensional simulation results of grain growth in the molten pool during the welding process of TA15 titanium alloy at a welding speed of 4 mm / s. It can be seen that with the movement of the welding heat source, the previously melted part gradually solidifies, and the molten pool is still composed of thick columnar crystals. The molten pool in the second half of the weldment is slightly larger than the first half, which is due to the accumulation of heat in the welding process. Caused.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com