Method of diagnosis of liver steatosis
A technology of hepatic steatosis and steatosis, which is applied in the field of diagnosis of hepatic steatosis, and can solve the problems of undisclosed and explicit denials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0208] Example 1. Overview
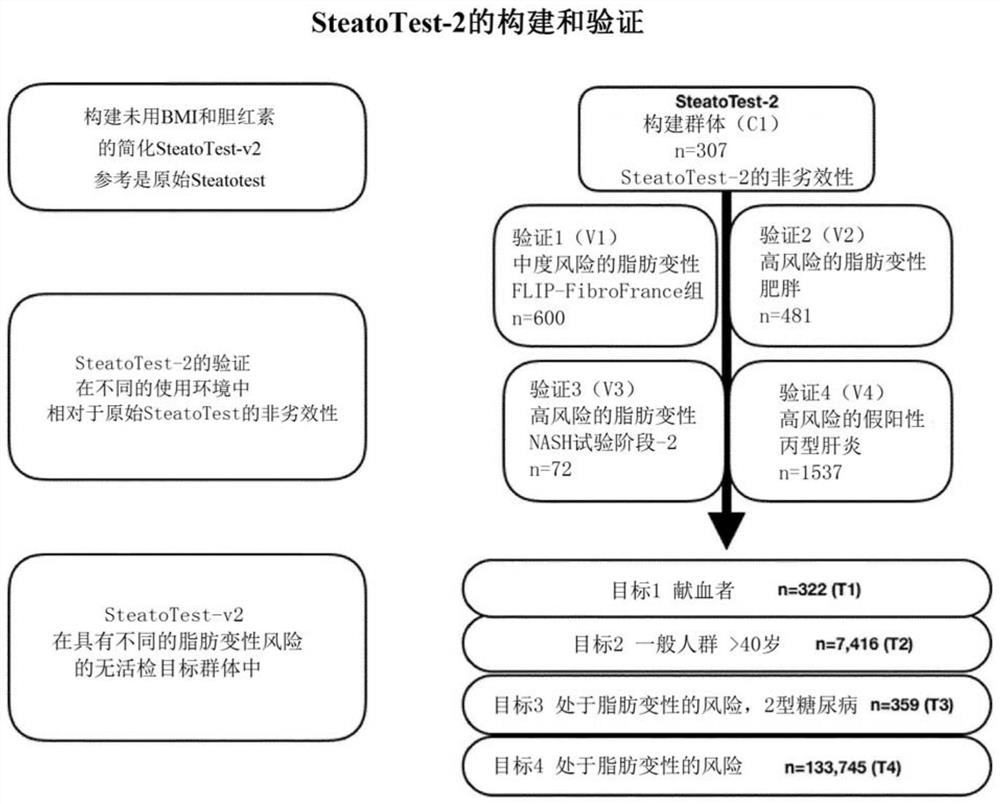
[0209] METHODS: Five different subgroups of 2997 biopsied patients were evaluated for test construction and validation, and four for the prevalence of steatosis in a target population at increased risk of steatosis. The performance of SteatoTest-2 was compared to the reference test using a non-inferiority test (0.10 cut-off) and the Lin coefficient of agreement.
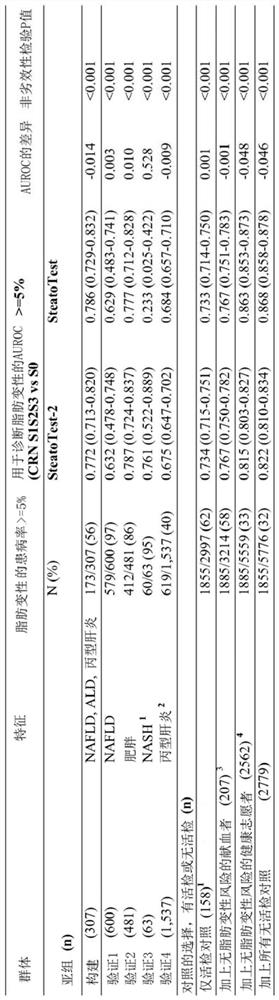
[0210] Results: The AUROC of SteatoTest-2 was not worse than the reference test (P<0.001). AUROC differed according to subgroup and prevalence of steatosis in SteatoTest-2 and reference test, which were 0.772 (95% CI 0.713-0.820) vs 0.786 (0.729-0.832) in 2997 biopsy cases, respectively, and 0.822 (0.810-0.834) vs 0.868 (0.858-0.878) among 5776 cases (including healthy subjects without steatosis risk factors as controls). Lin coefficients were highly consistent (P<0.001), ranging from 0.74 (0.74-0.74) in putative NAFLD to 0.91 (0.89-0.93) in constructed subgroups.
[0211] Conclusion...
Embodiment 2
[0212] Example 2. Patients and methods
[0213] Research design
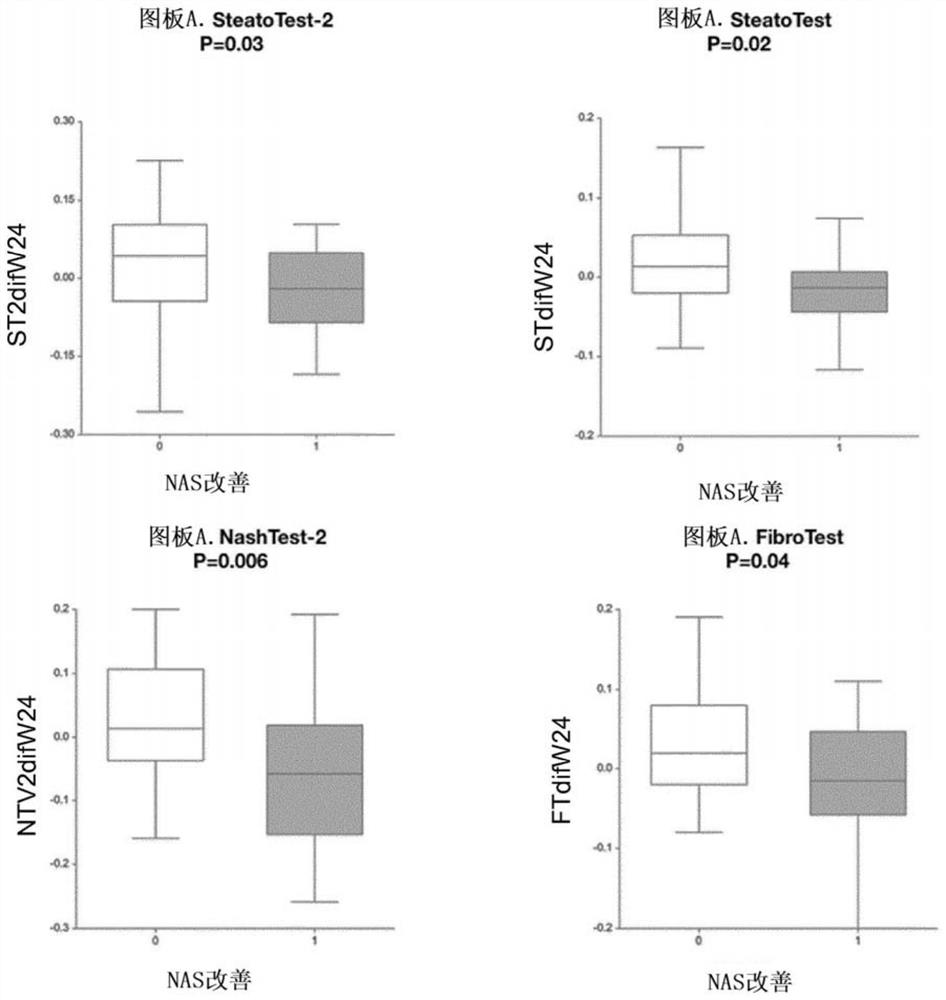
[0214] Prospective analysis of patient subgroups ( figure 1)'s research is to construct a simplified new SteatoTest-2 that is highly consistent with and not inferior to the first generation SteatoTest, with higher applicability in the general population and less risk of false positives lower. SteatoTest-2 was also evaluated based on paired biopsies before and after treatment in the prospective trial of slonertin for the treatment of NASH.
[0215] The second objective was to evaluate the performance of SteatoTest-2 when used in combination with NashTest-2 (as disclosed in WO2018050804) in non-invasive algorithms replicating histological NASH algorithms (CRN or FLIP) which require The presence of steatosis is used to diagnose NASH (Poynard et al., Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 30:384-391; Poynard et al., Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 30:569-577).
[0216] Variability in the SteatoTest-2 AUROC wa...
Embodiment 3
[0236] Example 3. Results
[0237] Characteristics of subjects included
[0238] A total of 2997 biopsied and histologically scored patients were evaluated by the SAF scoring system. Although the characteristics of the included subjects have been published in previous publications, the value of this integrated database lies in its broad characterization, which allows the robustness of blood tests to be assessed in terms of variability factors. The IQR for age ranged from 34 to 61 years. The prevalence of histologic steatosis ranged from 7.3% to 24.5%, NASH ranged from 13.7% to 100%, cirrhosis ranged from 0% to 42.6%, and the prevalence of T2 diabetes ranged from 7.5% to 70.8% The range of obesity (BMI ≥ 30) is 13.6% to 100%. The subgroup of obese subjects was younger, had a higher percentage of women, and had a lower prevalence of advanced fibrosis than other subgroups.
[0239] New SteatoTest-2
[0240] Unlike SteatoTest, SteatoTest-2 does not include BMI or total bili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com