AIS-based ship collision avoidance decision method
A decision-making method and collision avoidance technology, which can be used in ship traffic control, instruments, traffic control systems, etc., and can solve problems such as poor detection of small objects, false tracking, and clutter interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] In order to make the technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more clear, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention are clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention:
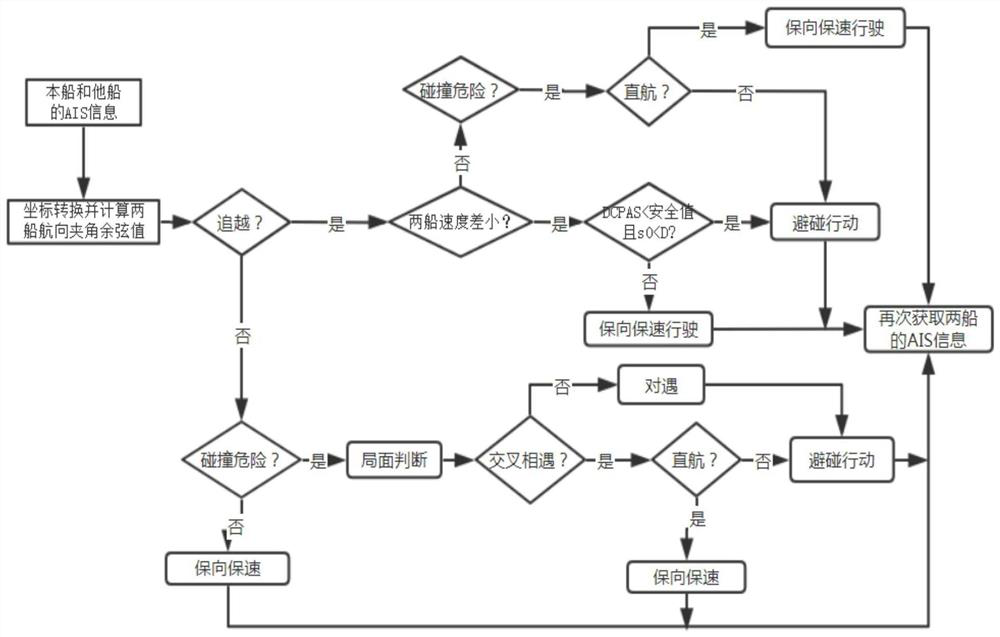
[0029] Such as figure 1 An AIS-based ship collision avoidance decision-making method shown specifically includes the following steps:
[0030] S1: Use the true motion mapping method to establish a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, calculate the velocity components of the own ship and other ships according to the principles of analytic geometry and AIS information, and calculate the closest encounter distance DCPA and the minimum encounter time TCPA size;
[0031] S2: Based on the calculation results obtained in S1, determine the risk of collision;
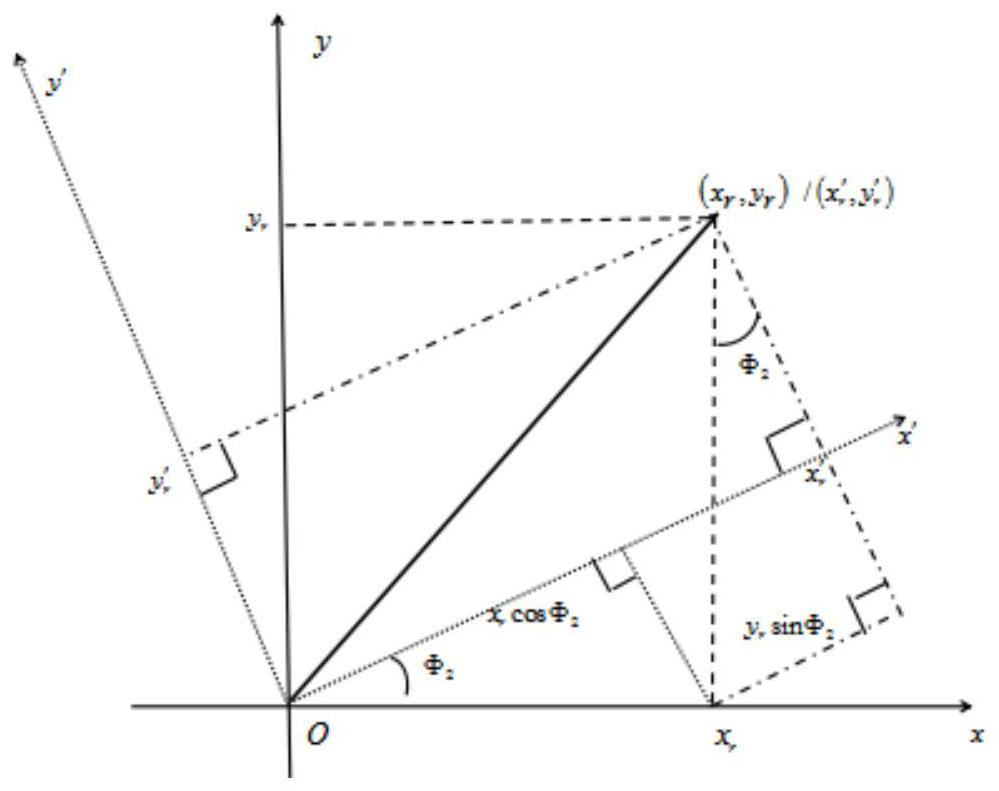
[0032] S3: Based on the calculation results obtained by S1 and S2, the coordinates of own ship and other ships are transformed into...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com