Bidirectional laminated slab dense splicing strong seam construction process and structure
A technology of laminated boards and dense joints, which is applied in the direction of building structures, floor slabs, building components, etc., can solve problems such as tear damage, weak laminated surfaces, disengagement, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing integrity and preventing tear damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
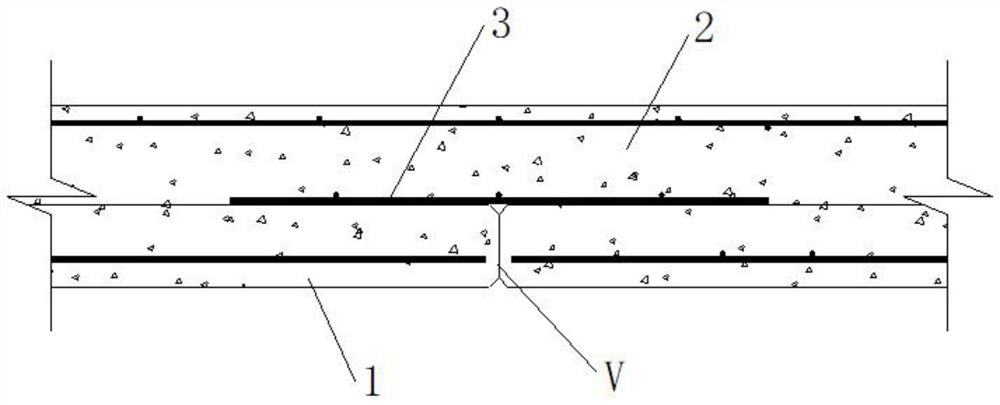
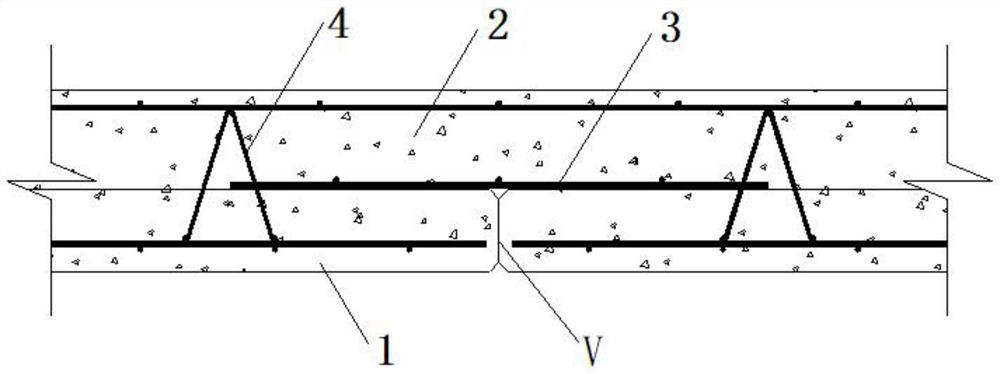
[0040] A construction technique for two-way laminated slab close-fitting strong joints, step (1) first laying the bottom plate connecting bars along the horizontal direction, laying the bottom plate reinforcing bars along the longitudinal direction, stacking the bottom plate reinforcing bars and the bottom plate connecting bars and binding them into the bottom plate reinforcement mesh, the bottom plate reinforcement mesh It is laid in the prefabricated slab template; the two ends of the bottom slab steel bars are bent upwards and protrude from the poured prefabricated slab surface, so that it can extend into the cast-in-place layer to enhance the integrity and safety of the structure and effectively prevent joints Larger cracks are generated along the superimposed surface, and then the tear damage occurs; finally, the truss reinforcement and suspension bars are placed on the bottom slab reinforcement mesh.
[0041] Step (2) Pouring the prefabricated slabs and performing wet mai...
no. 2 example
[0049] A construction technique for two-way laminated slab close-fitting strong joints, step (1) first laying the bottom plate connecting bars along the horizontal direction, laying the bottom plate reinforcing bars along the longitudinal direction, stacking the bottom plate reinforcing bars and the bottom plate connecting bars and binding them into the bottom plate reinforcement mesh, the bottom plate reinforcement mesh It is laid in the prefabricated slab template; the two ends of the bottom slab steel bars are bent upwards and protrude from the poured prefabricated slab surface, so that it can extend into the cast-in-place layer to enhance the integrity and safety of the structure and effectively prevent joints Larger cracks are generated along the superimposed surface, and then the tear damage occurs; finally, the truss reinforcement and suspension bars are placed on the bottom slab reinforcement mesh.
[0050] Step (2) Pouring the prefabricated slabs and performing wet mai...
no. 3 example
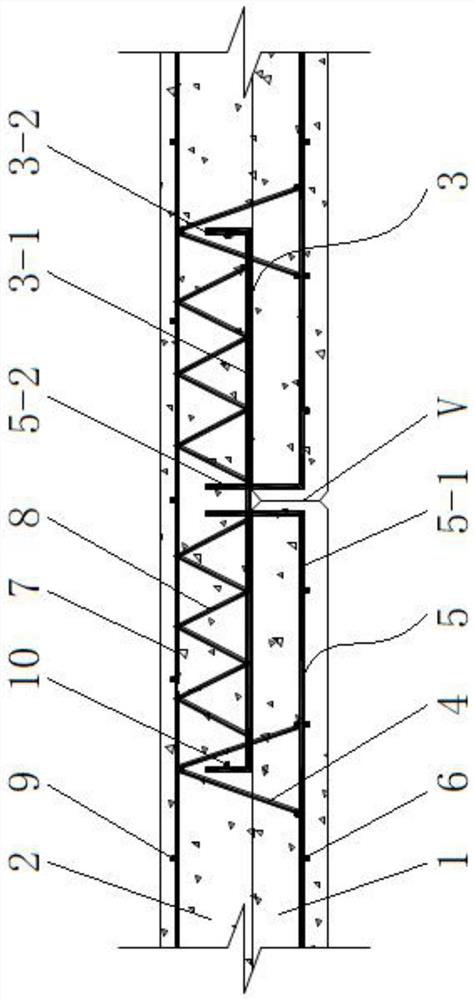
[0057] Such as image 3 As shown, a two-way laminated slab dense joint strong joint structure includes a prefabricated slab 1 and a cast-in-place layer 2. After the prefabricated slab 1 is mirror-symmetrically spliced, the cast-in-place layer 2 is poured on the prefabricated slab 1 . The prefabricated slab 1 is provided with bottom plate steel bars 5 laid longitudinally and bottom plate connecting bars 6 laid horizontally, and the bottom plate steel bars 5 and the bottom plate connecting bars 6 are fixed into a bottom plate reinforcement mesh by binding. The truss reinforcement 4 is laid horizontally on the reinforcement mesh of the bottom slab. The end of the base plate reinforcement 5 near the joint V of the prefabricated panel 1 is bent upwards by 90°, the horizontal section is the base plate stress reinforcement 5-1, and the vertical section is the base plate fixing reinforcement 5-2. The bottom plate fixing steel bar 5-2 passes through the prefabricated slab 1 and extend...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com