Method for performing continuous over write of file in nonvolatile memory
A non-volatile storage, non-volatile technology, used in memory systems, memory address/allocation/relocation, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the size and cost of solid-state drives, data loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
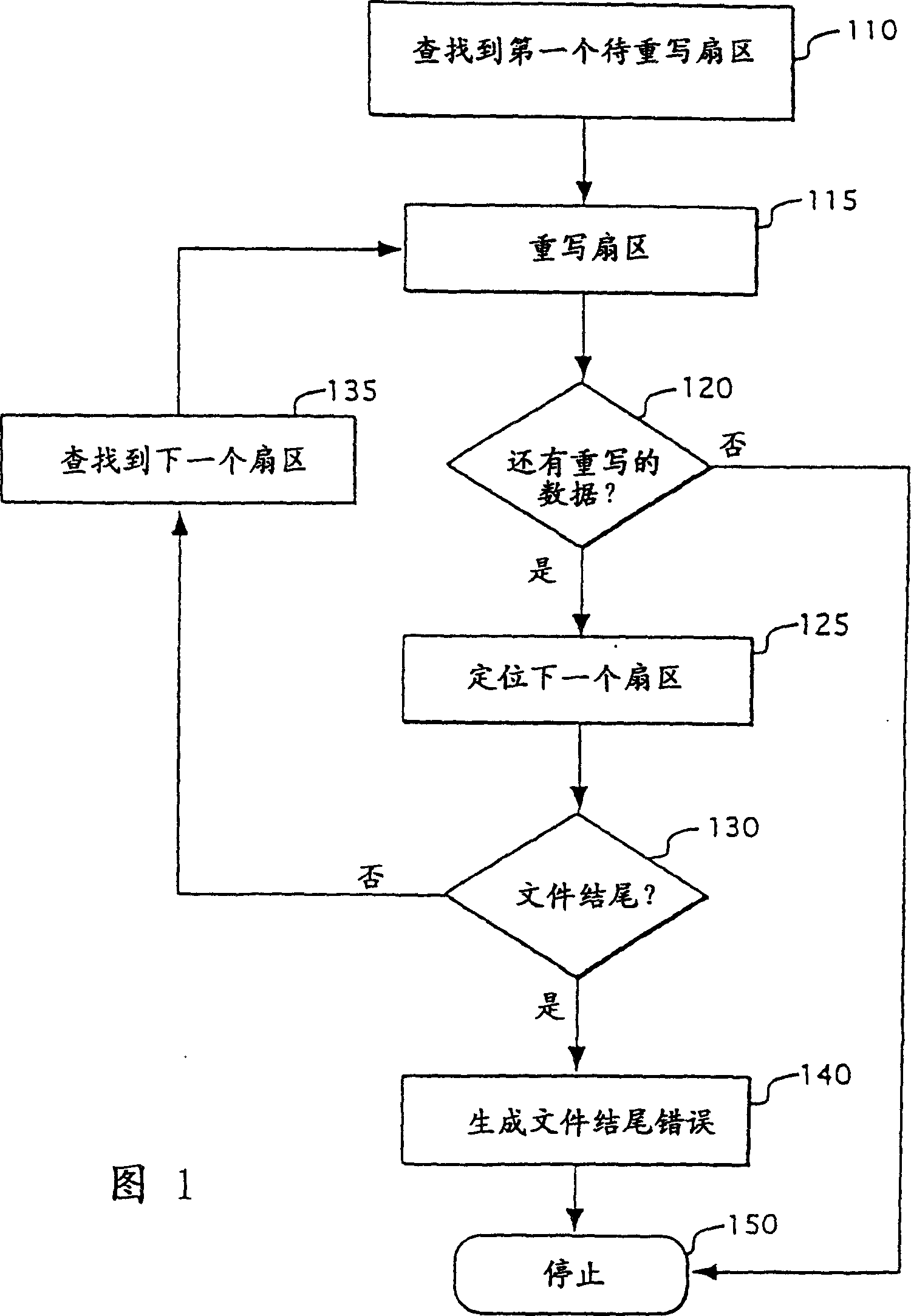
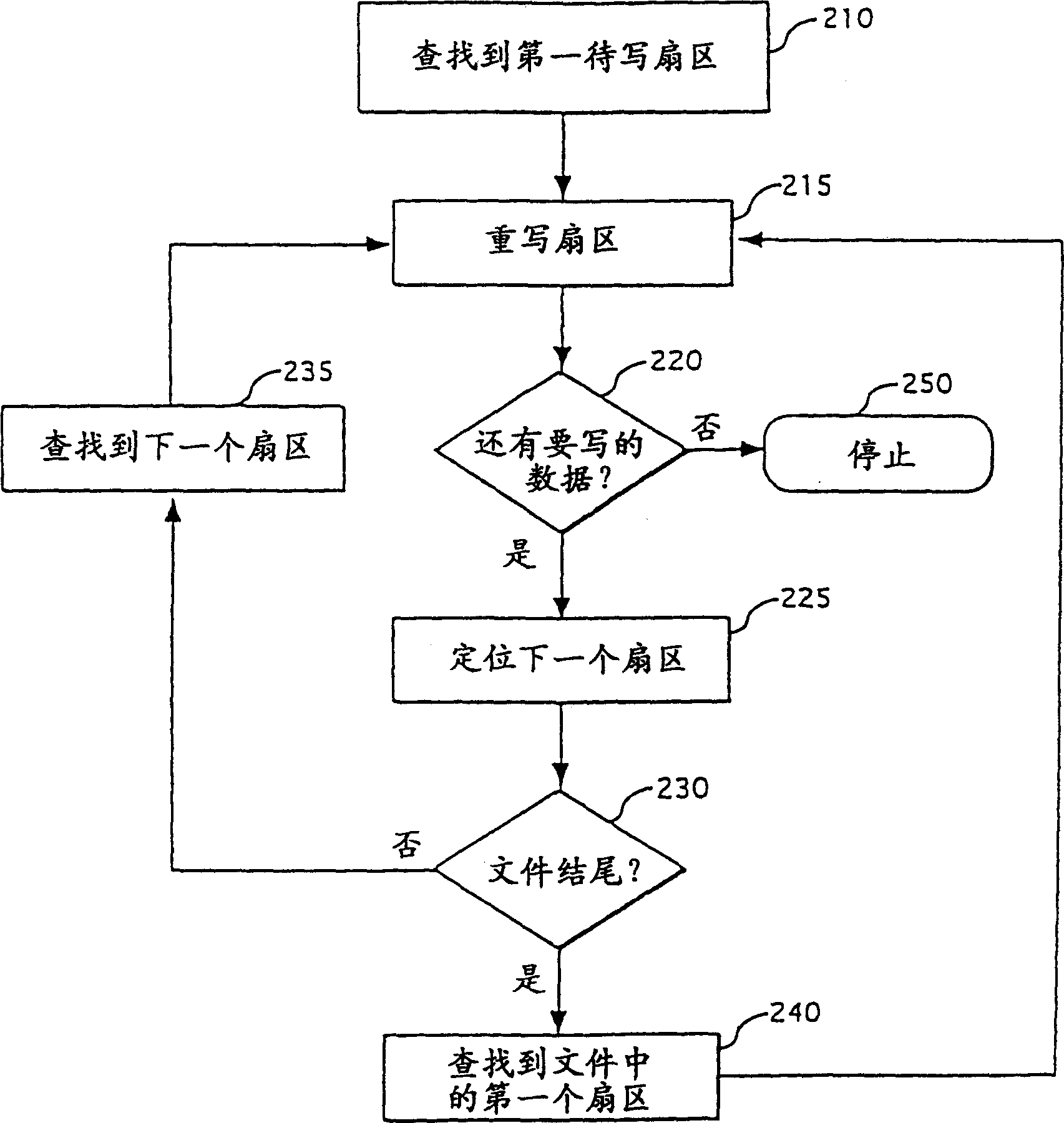
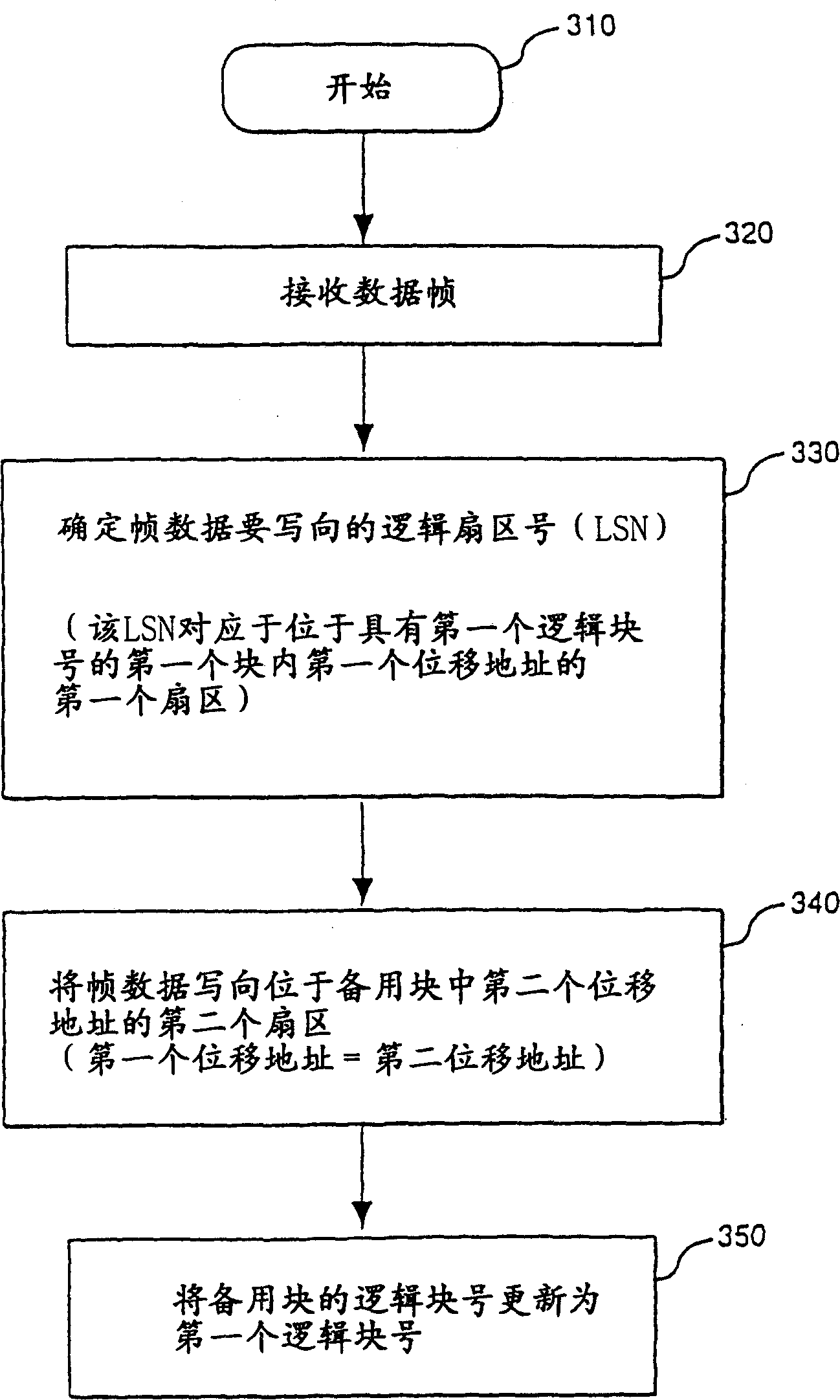
[0025] Operating systems that support electromechanical hard drives typically use a sector-based scheme for managing files. Sector numbers are usually not directly involved when a user or an individual application reads or writes data on an electromechanical hard drive. Typically, operating systems support the use of file pointers to locate or identify specific sectors of a file. So the operating system is responsible for passing the sector number to the electromechanical hard drive to store or retrieve the data sector associated with the file.
[0026] Operating systems typically use some type of allocation map to locate all the sectors associated with a given file. One class of sector-based file systems uses a file allocation table (FAT) to keep track of the sectors associated with a particular file. FAT is a table made up of allocation units, usually stored in a predetermined location in an electromechanical hard drive. The allocation unit is the smallest amount that can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com