Method for detecting influence of transcranial magnetic stimulation on working memory based on Granger causality
A technology of transcranial magnetic stimulation and working memory, applied in magnetic therapy, electrotherapy, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties and achieve the effect of improving the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
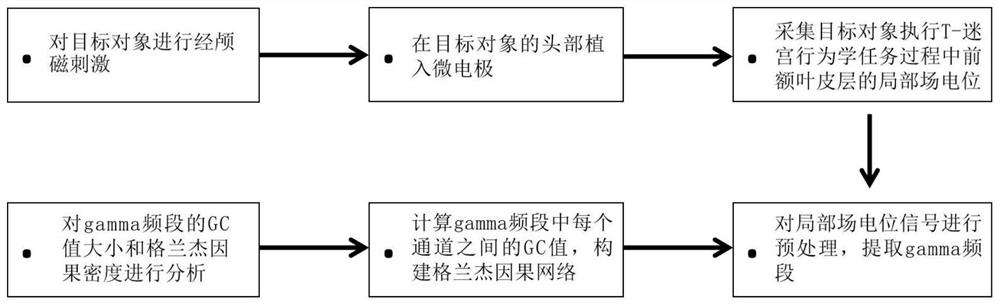
[0038] In this example, rats are used as the target object to illustrate the method for detecting the influence of transcranial magnetic stimulation on working memory based on Granger causality, including the following steps:
[0039] The first step is to apply transcranial magnetic stimulation to rats, and implant microelectrodes in the prefrontal brain area of rats;
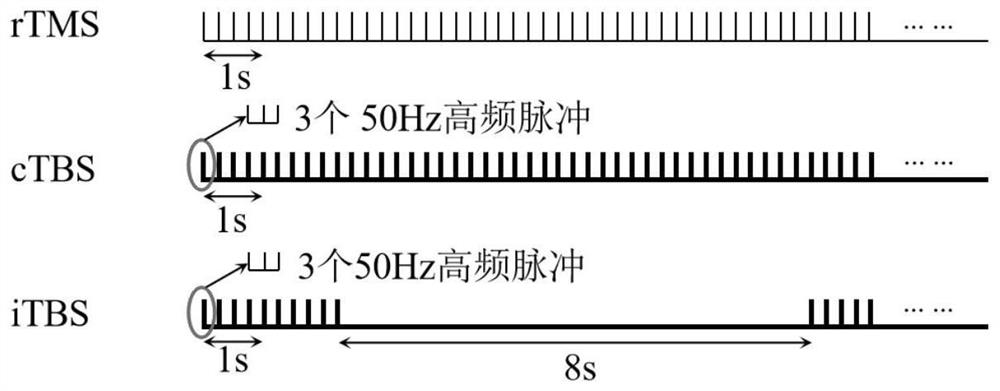
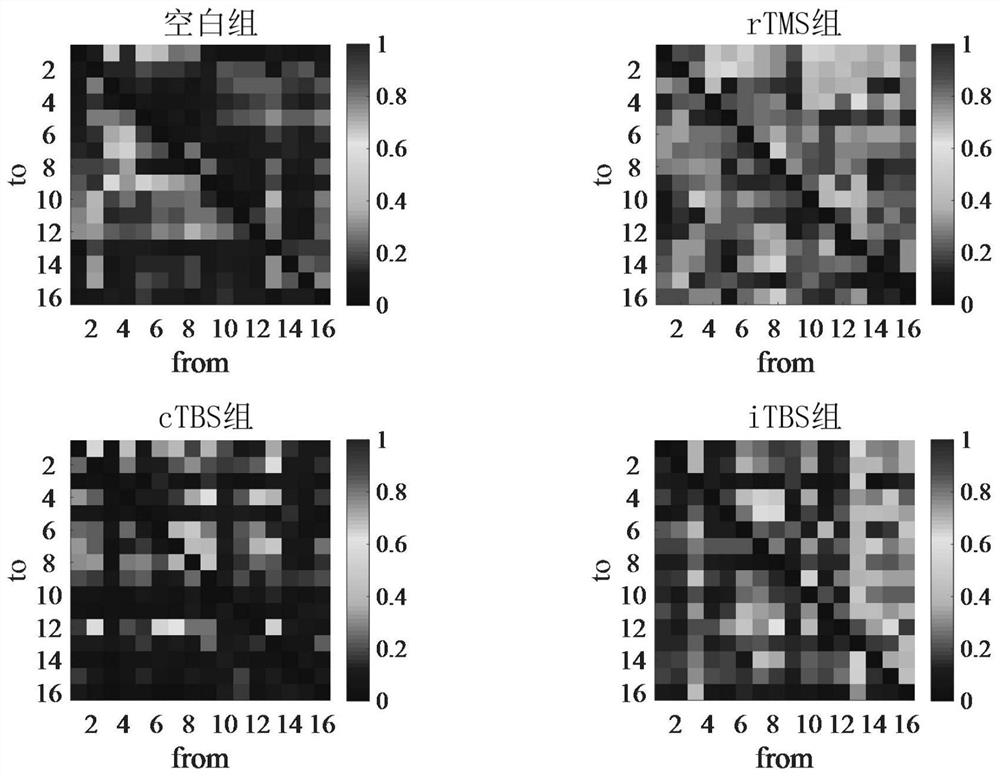
[0040] A number of rats were divided into four groups, namely blank group, rTMS group, cTBS group and iTBS group; the rTMS group was given high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS for short) with a frequency of 5 Hz; the cTBS group was given continuous theta rhythm Stimulation (cTBS for short), the iTBS group was given intermittent theta rhythmic stimulation (iTBS for short), the pulses of cTBS and iTBS were released in the form of clusters, the inter-cluster frequency was 5 Hz, and the intra-cluster frequency was 50 Hz, cTBS continuously delivered cluster stimulation , iTBS stimulati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com