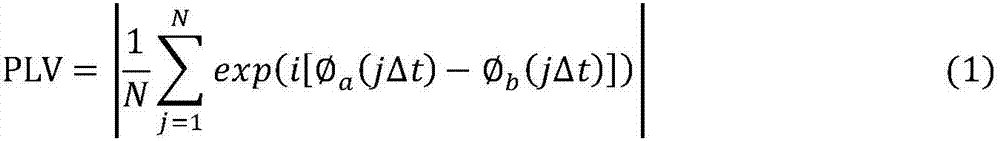Patents
Literature
56 results about "Local field potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
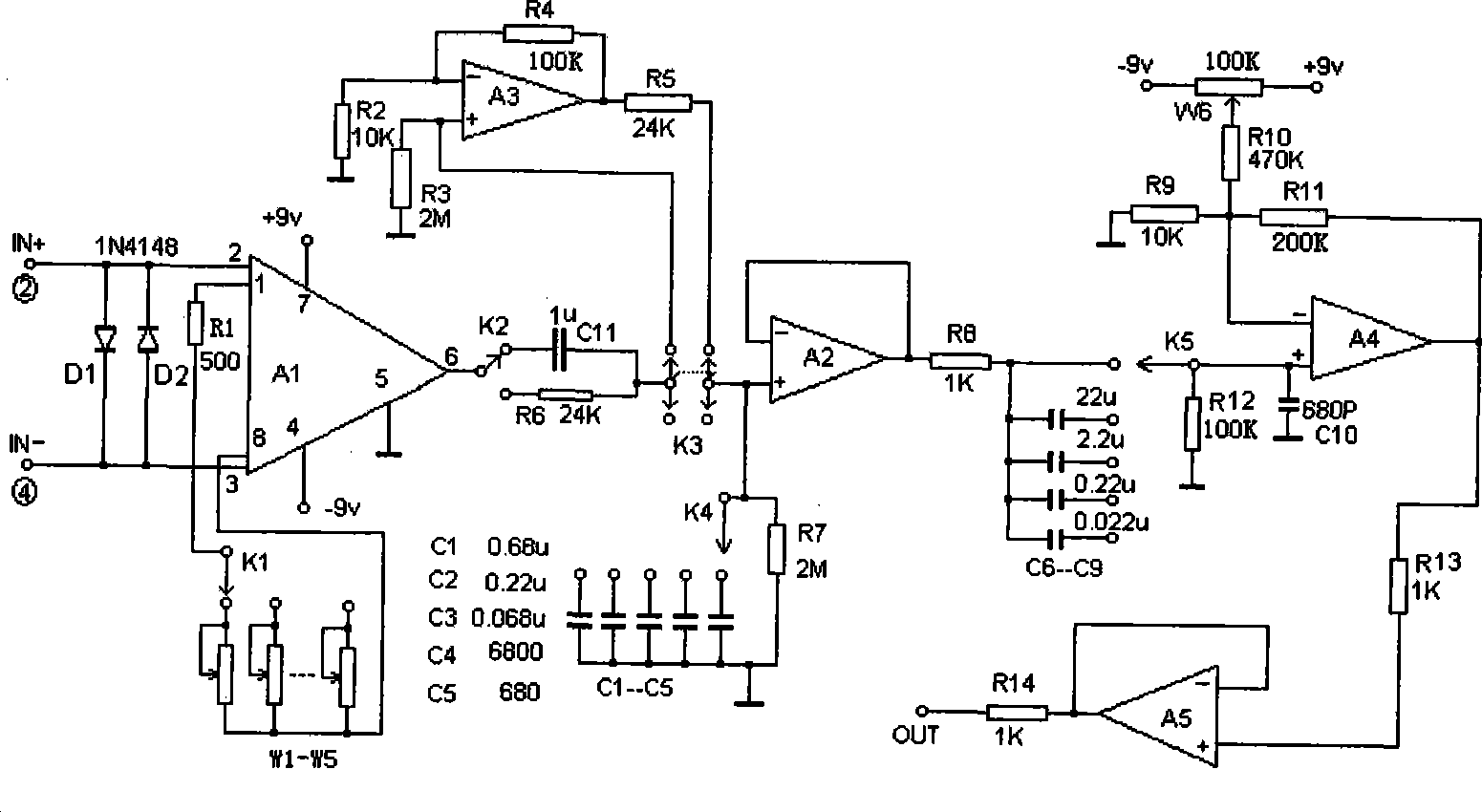
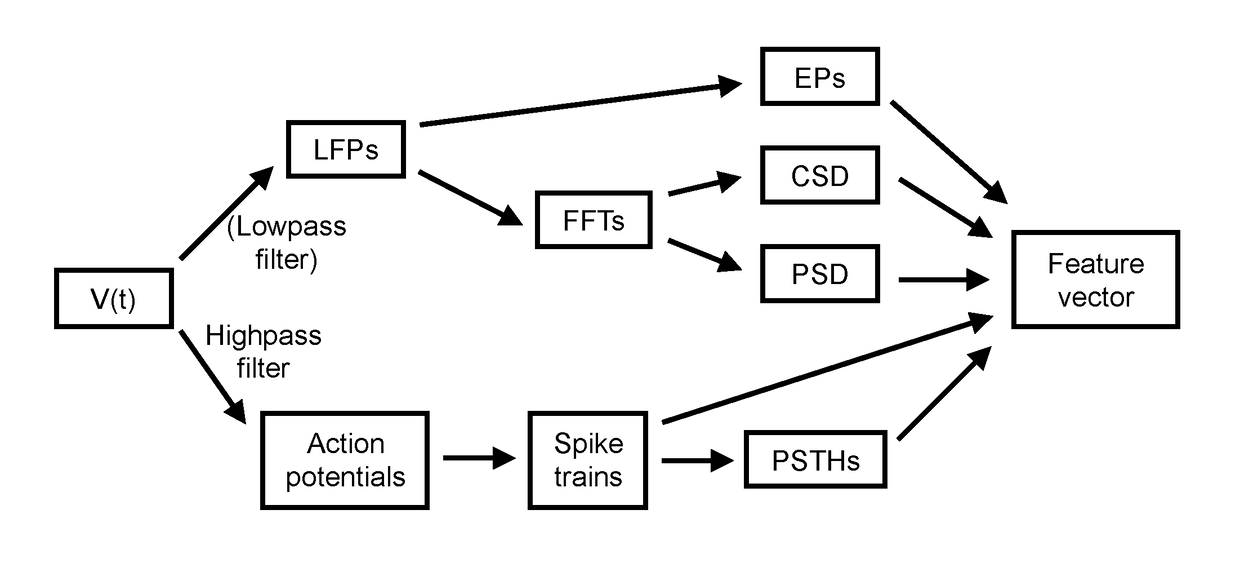
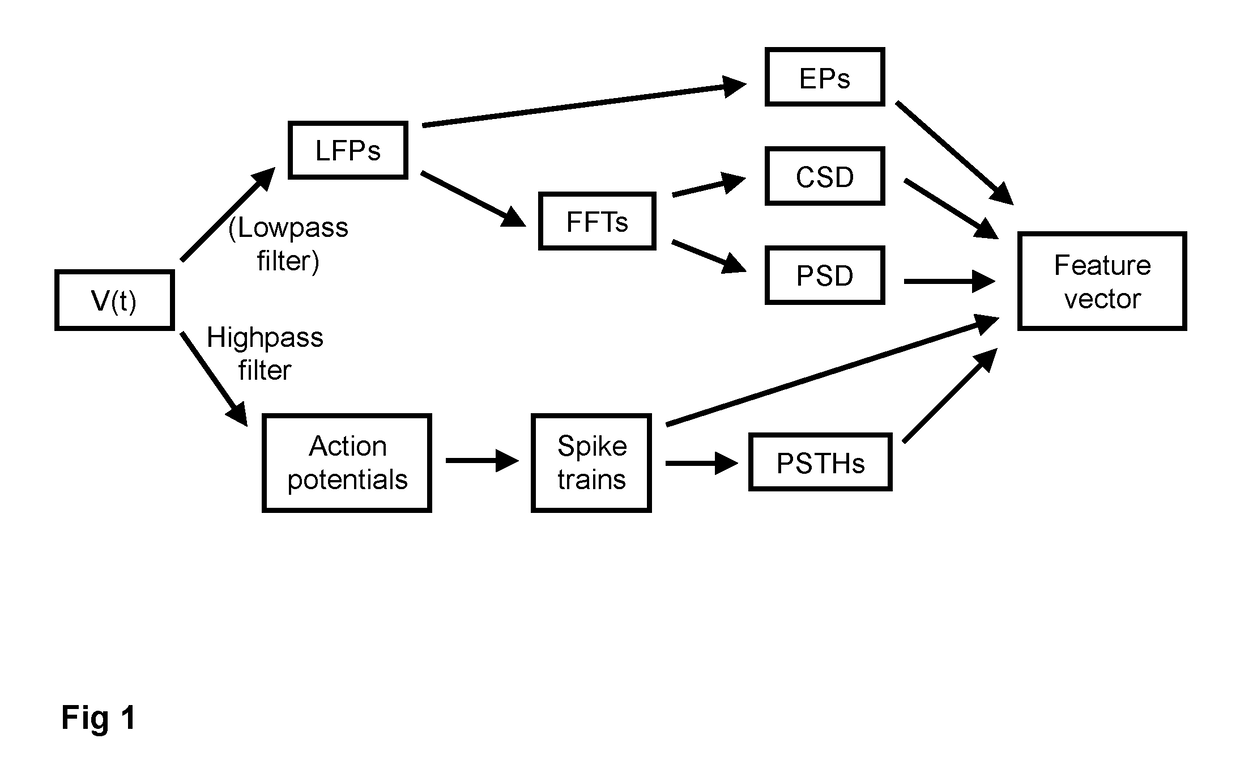
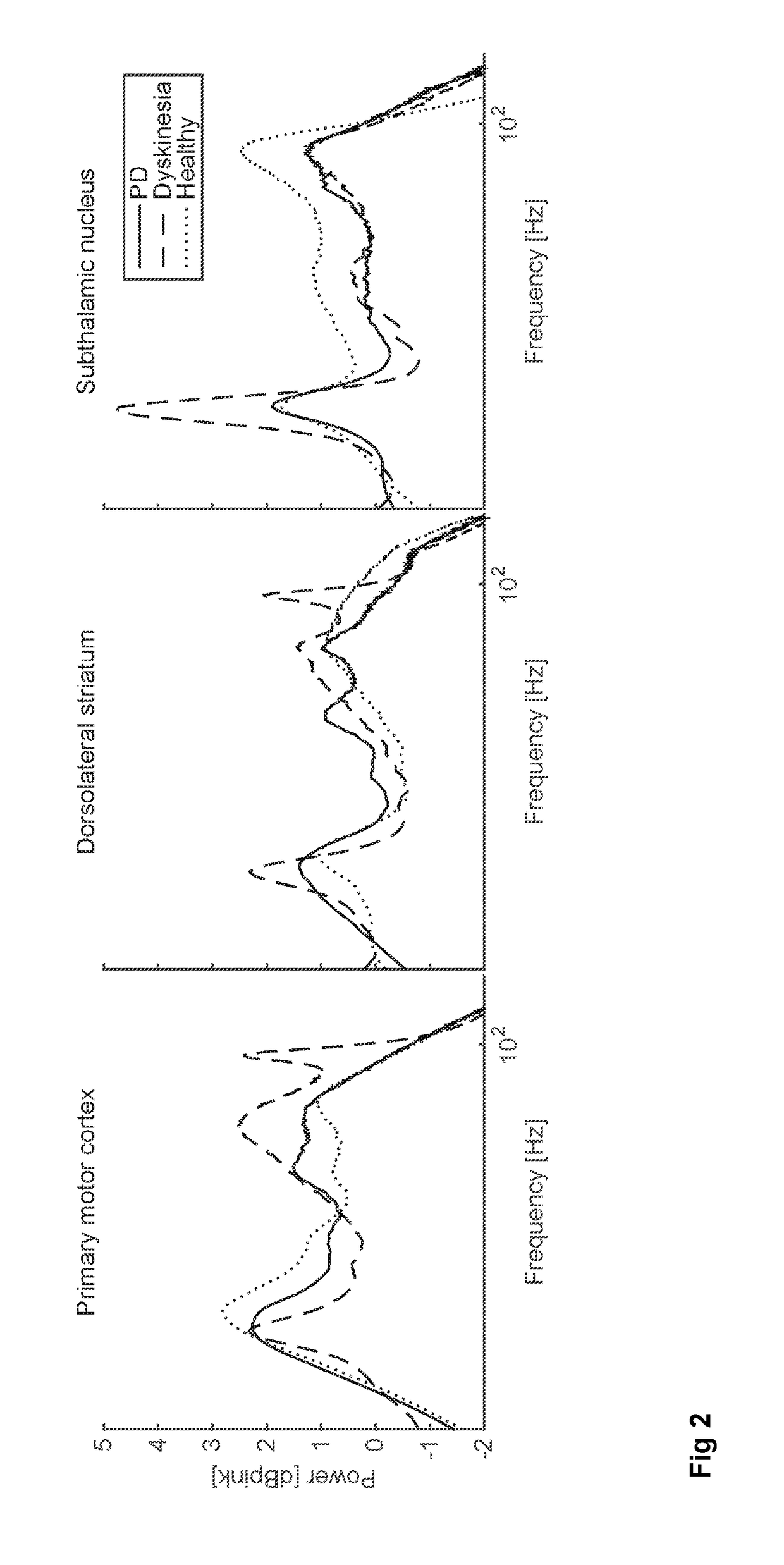
Local field potentials (LFP) are transient electrical signals generated in nervous and other tissues by the summed and synchronous electrical activity of the individual cells (e.g. neurons) in that tissue. LFP are "extracellular" signals, meaning that they are generated by transient imbalances in ion concentrations in the spaces outside the cells, that result from cellular electrical activity. LFP are 'local' because they are recorded by an electrode placed nearby the generating cells. As a result of the Inverse-square law, such electrodes can only 'see' potentials in spatially limited radius. They are 'potentials' because they are generated by the voltage that results from charge separation in the extracellular space. They are 'field' because those extracellular charge separations essentially create a local electric field. LFP are typically recorded with a high-impedance microelectrode placed in the midst of the population of cells generating it. They can be recorded, for example, via a microelectrode placed in the brain of an anesthetized animal, or in an in vitro brain thin slice.
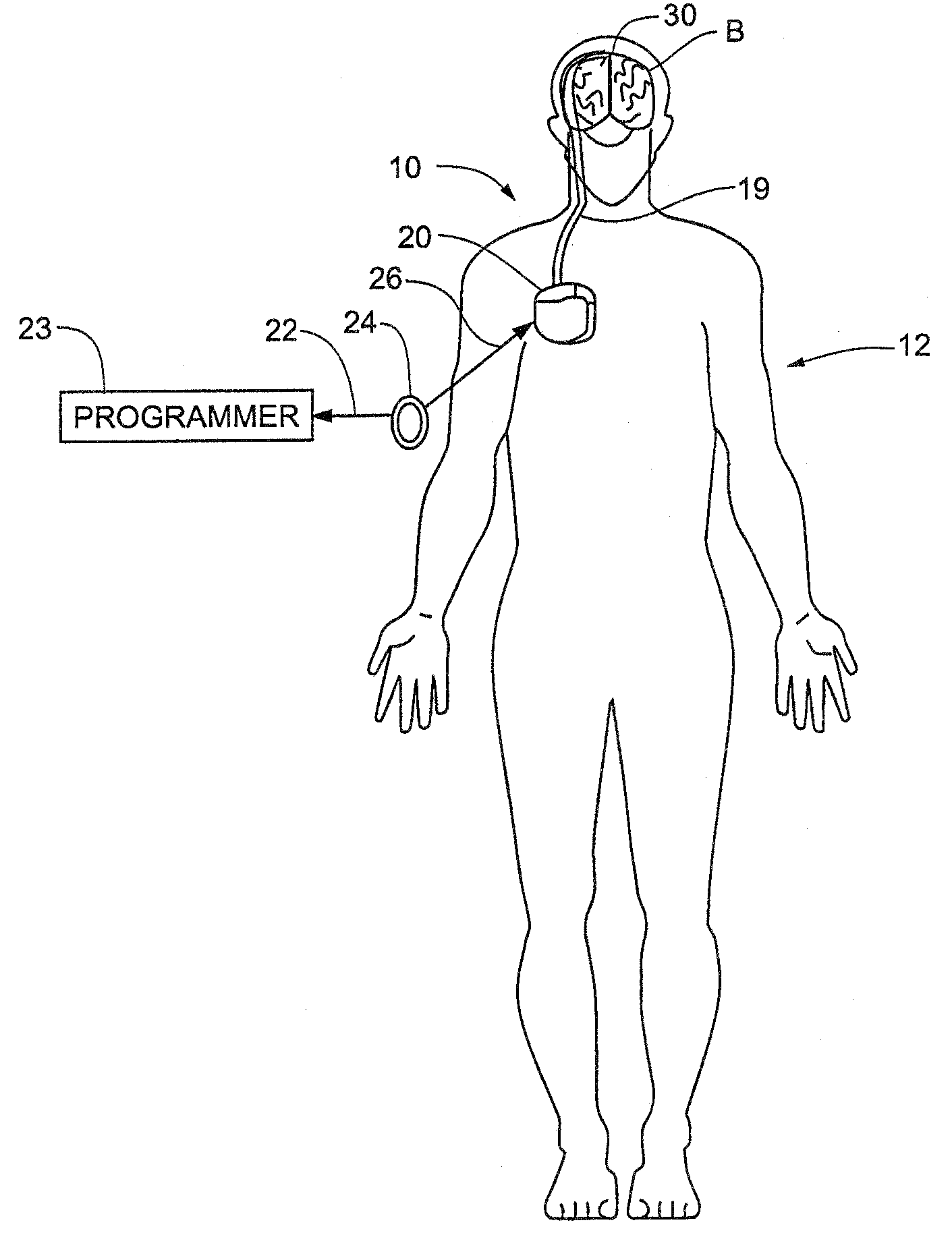
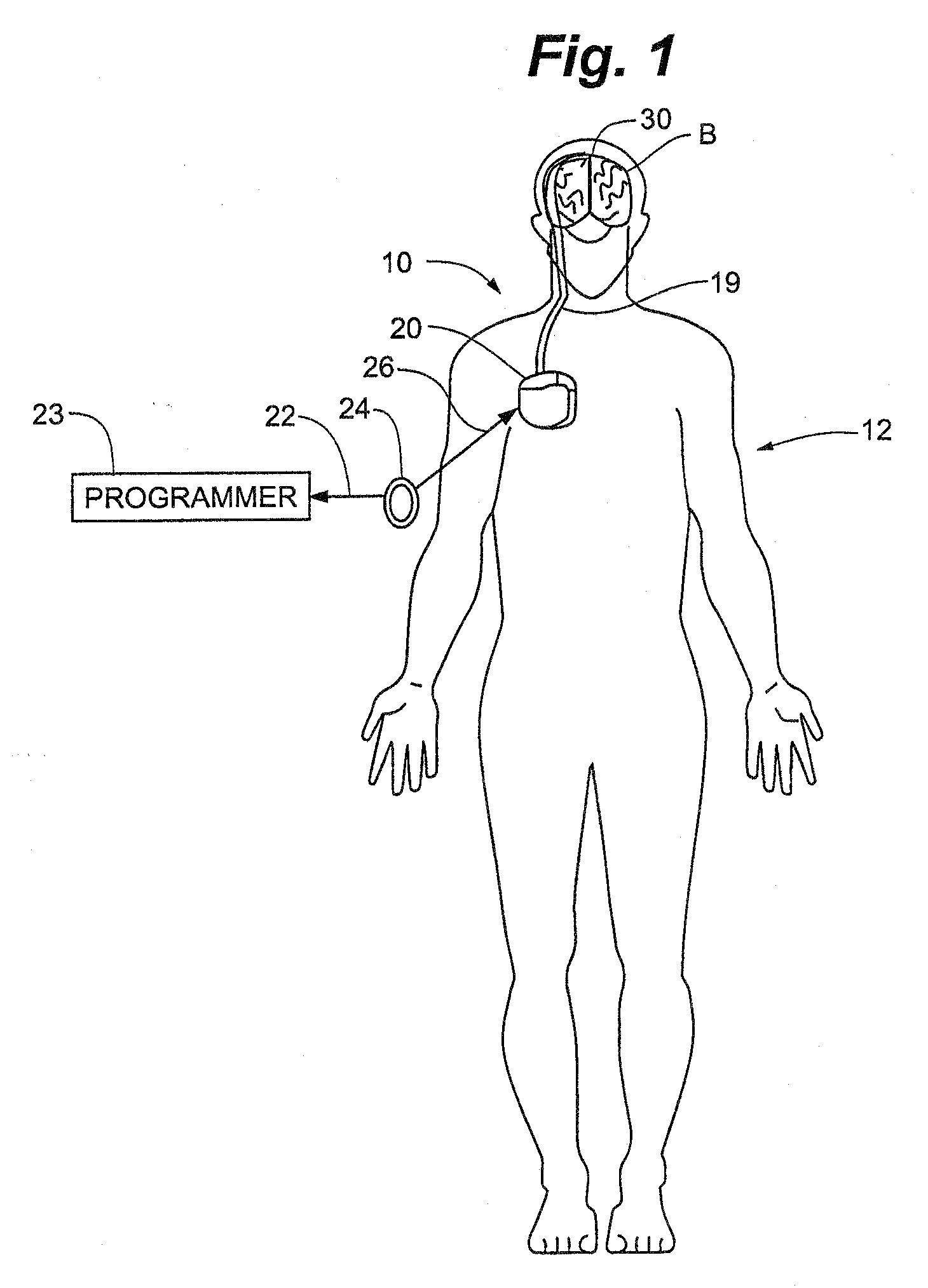
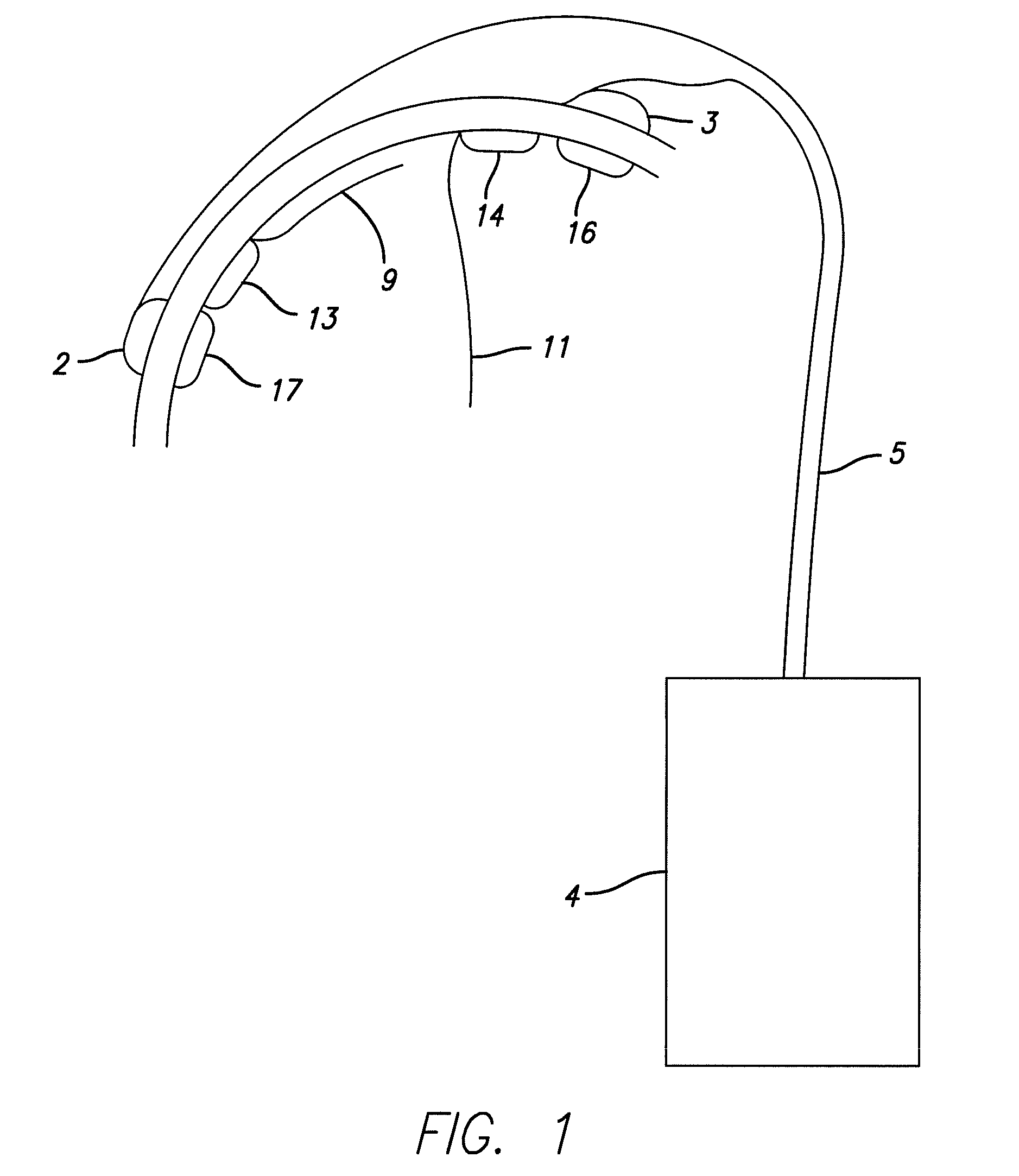
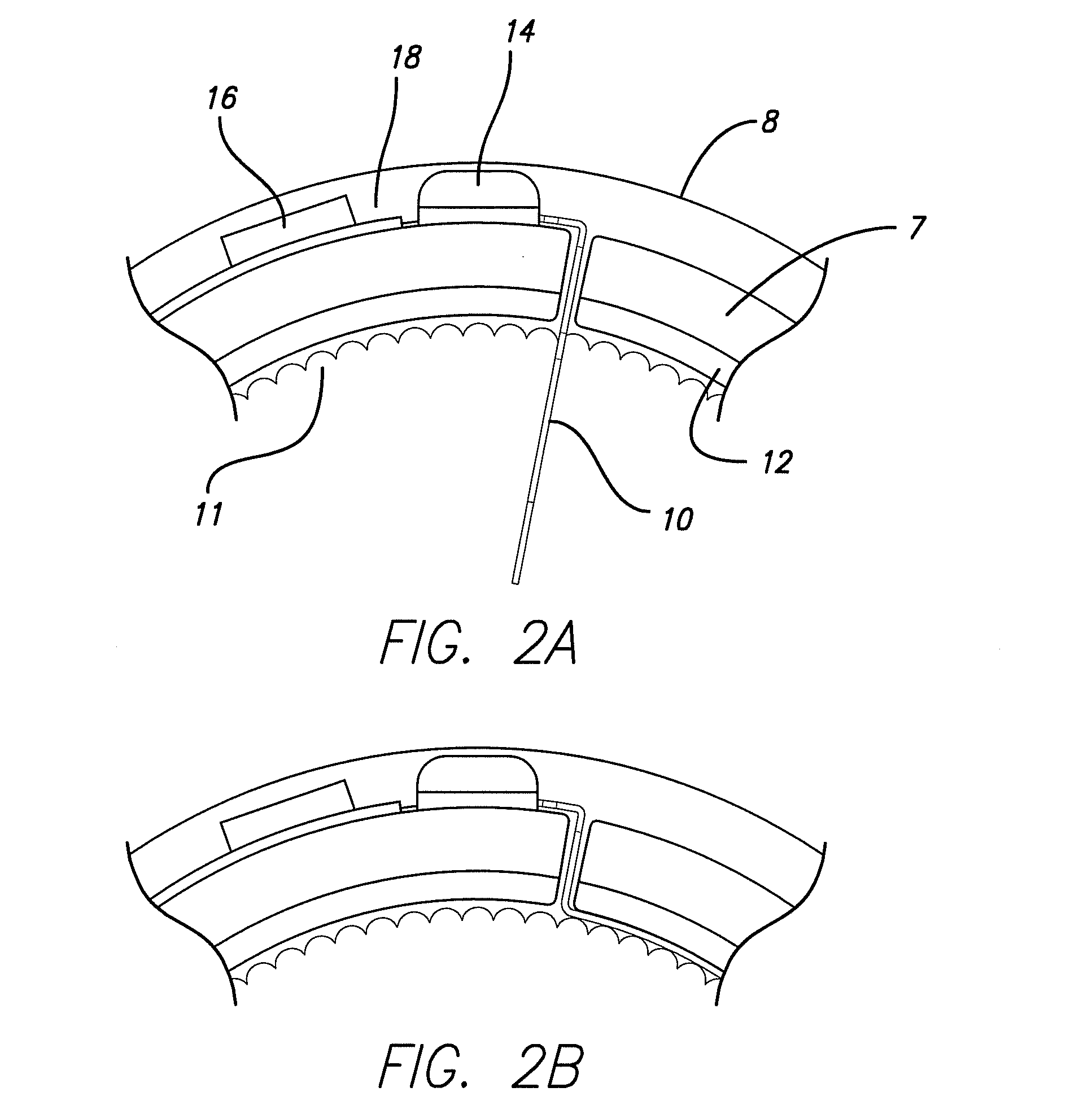
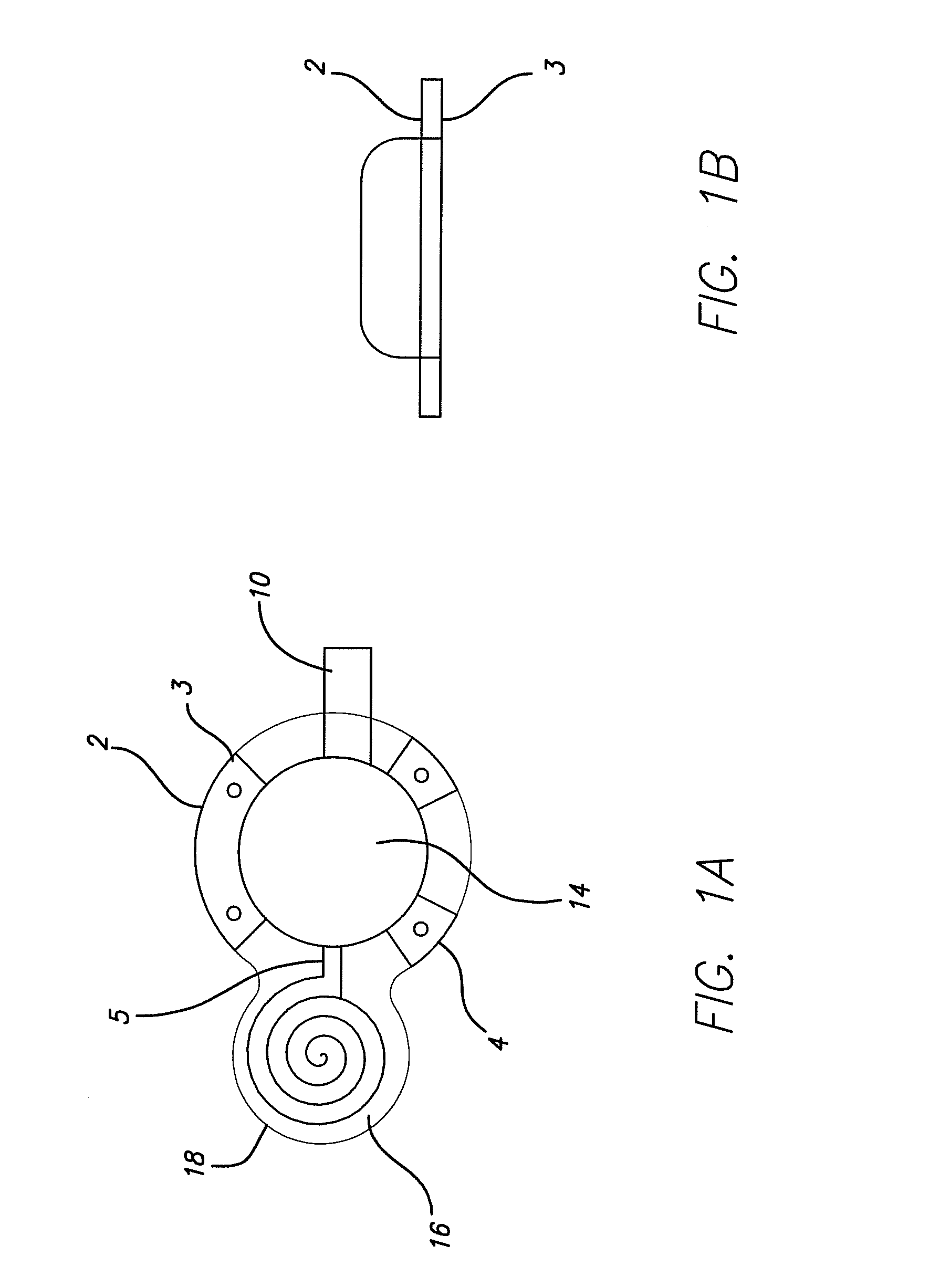
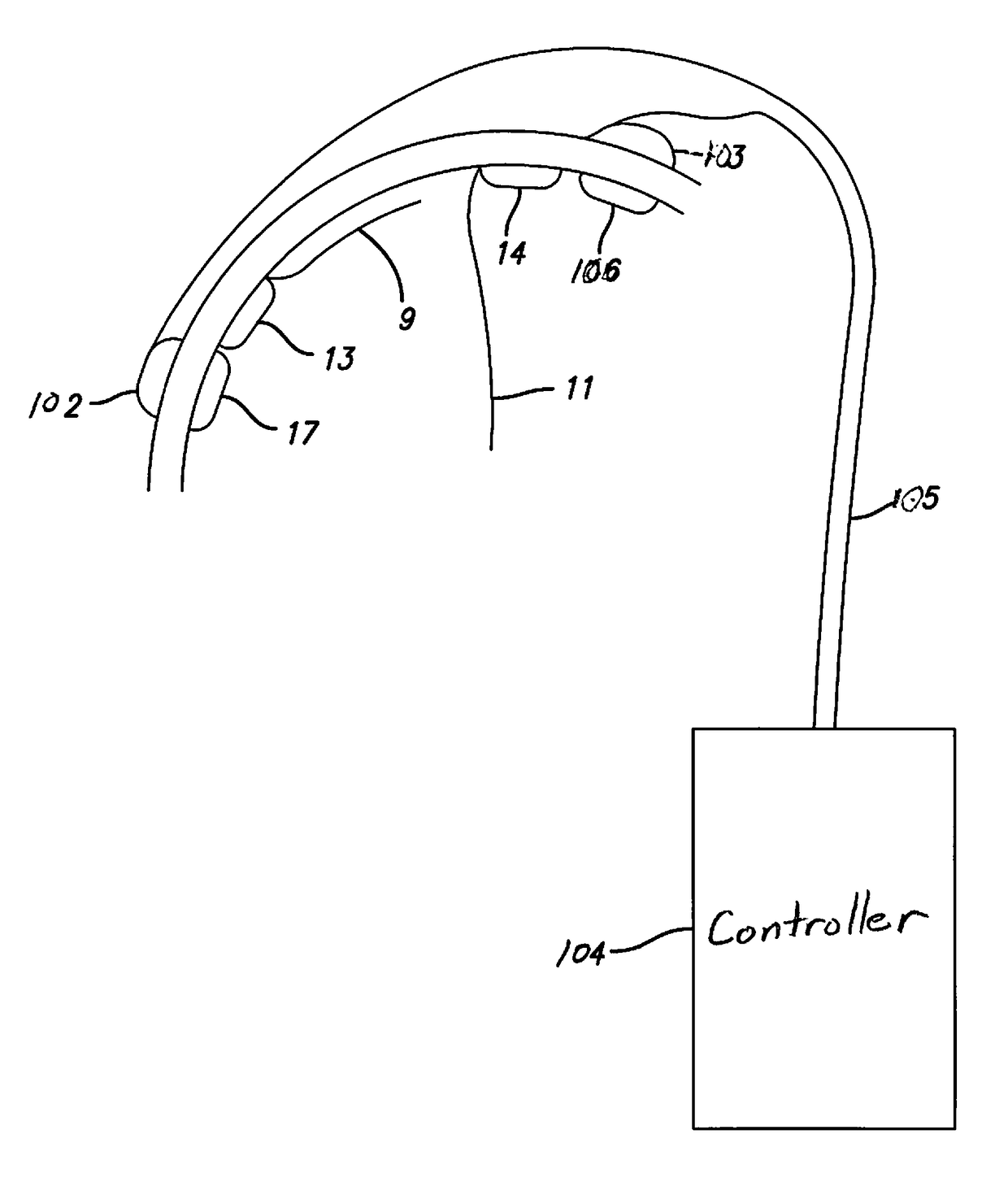
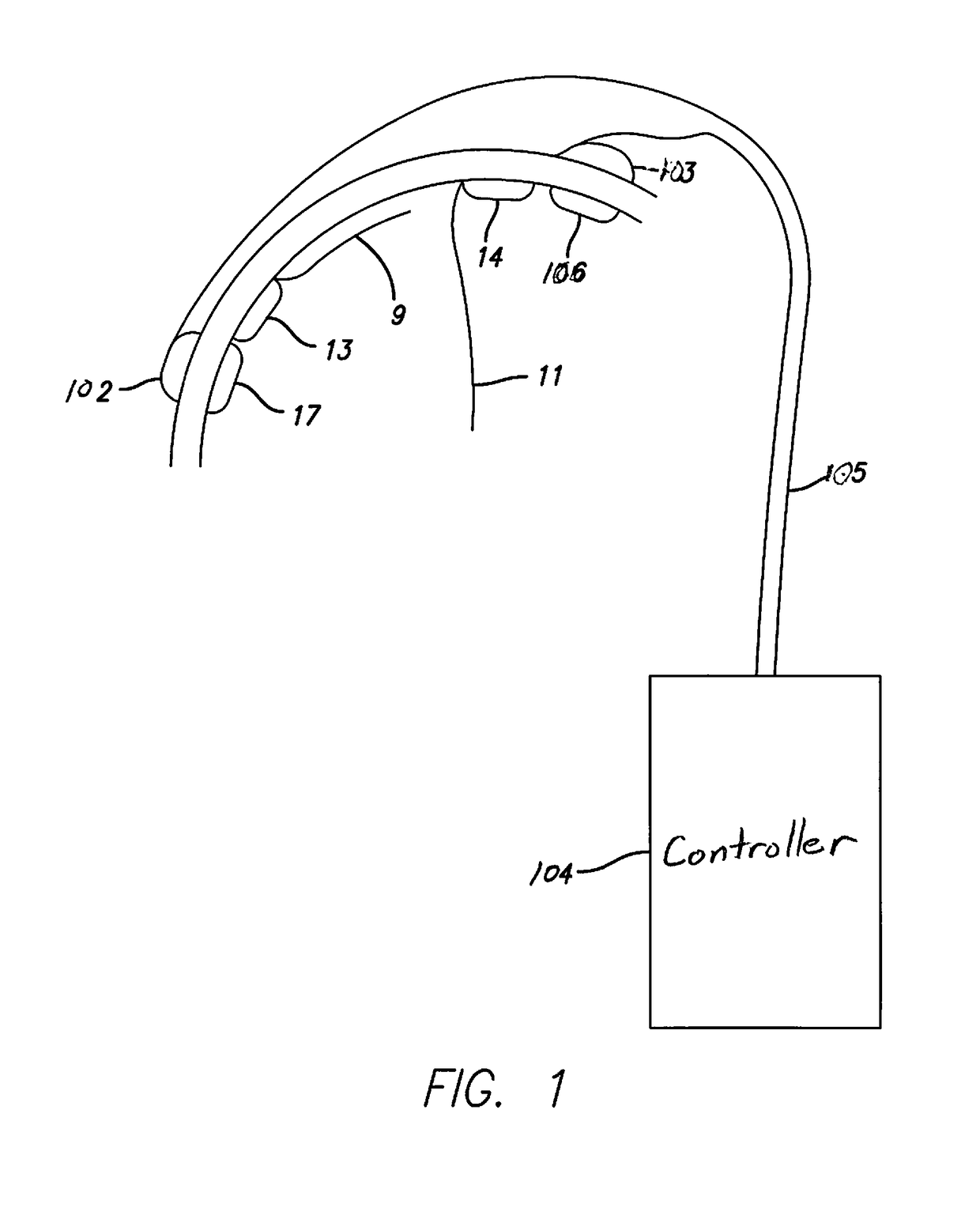
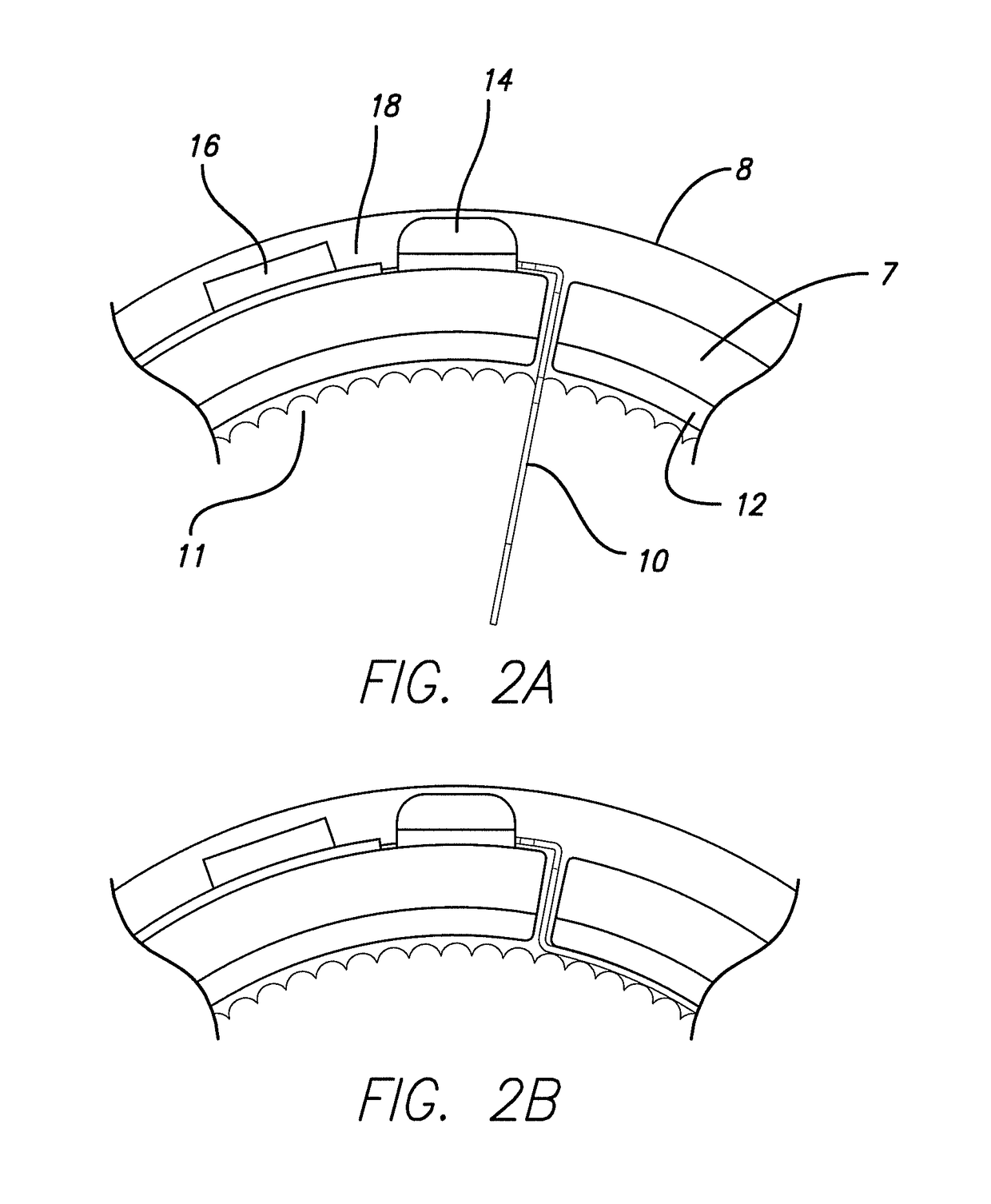
Method and Apparatus for the Treatment of Movement Disorders
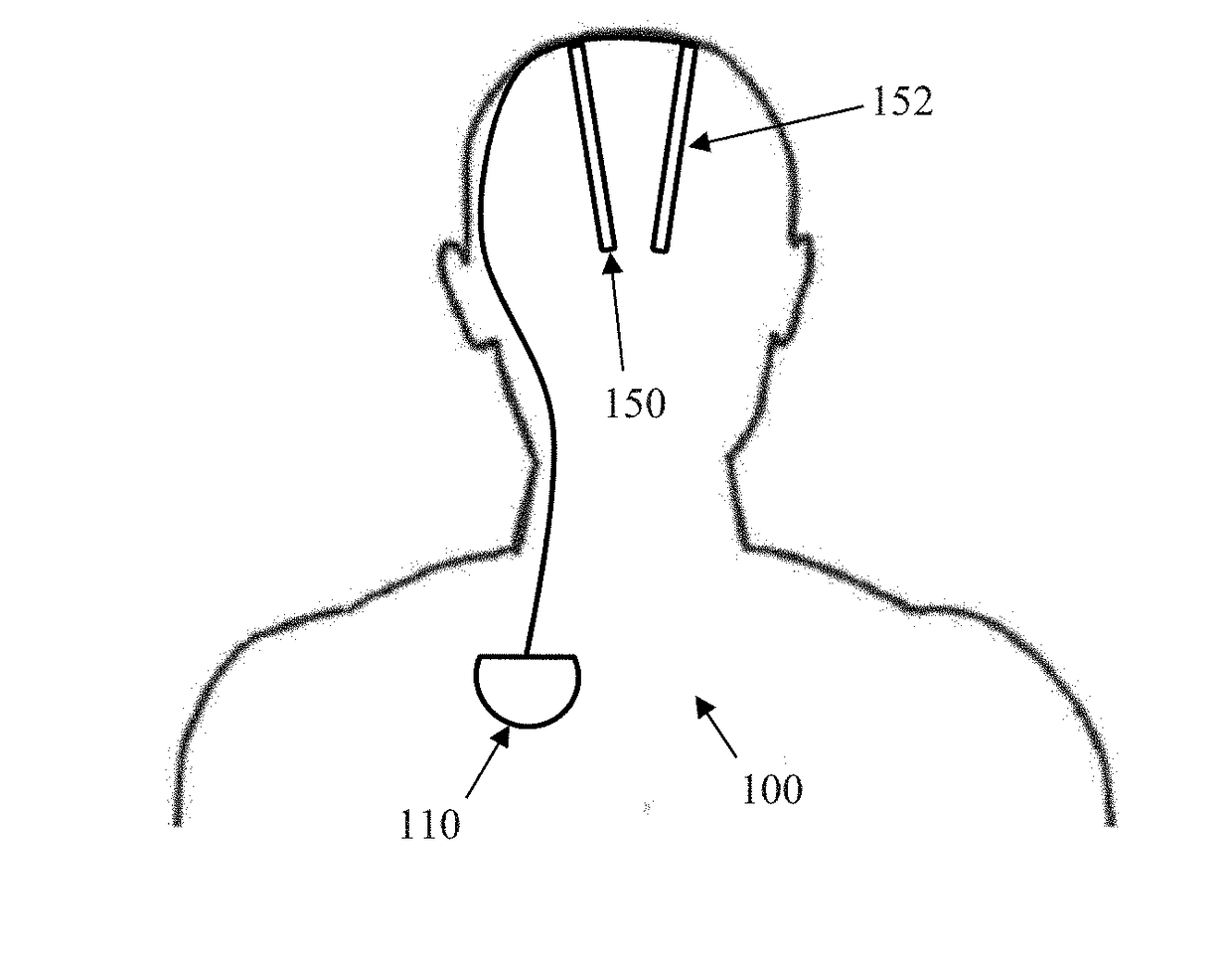
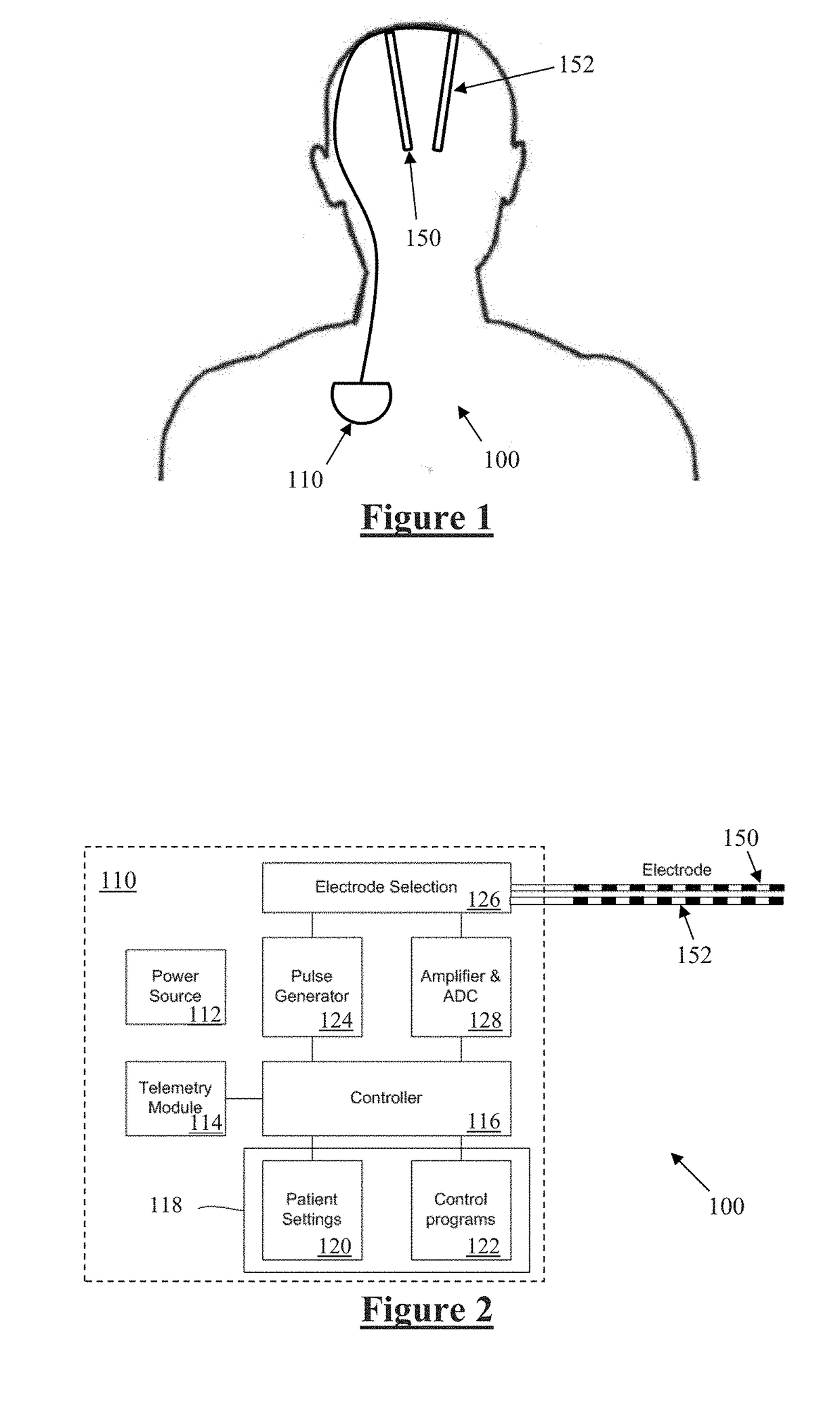
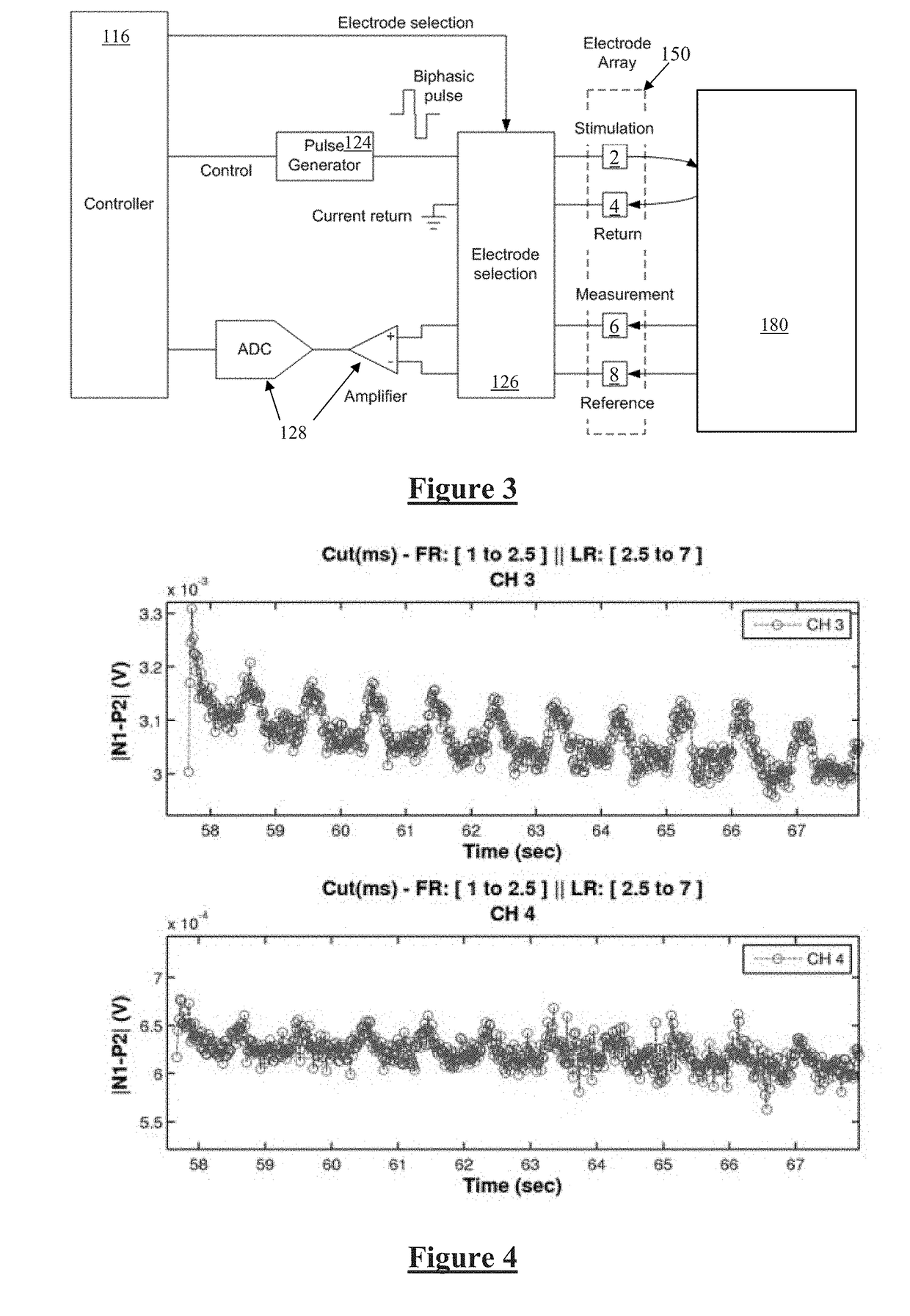
A method, apparatus, and system for treating patients suffering from movement disorders having the ability to determine one or more biomarkers indicative of a disease state. In some embodiments, the biomarker may be used as a closed-loop feedback signal to control the delivery of therapy (such as electrical stimulation or drug therapy), and which may also be used as an indication of therapy effectiveness. One embodiment uses electrodes placed in the brain to measure EEG or local field potential (LFP) signals, from which the one or more biomarkers may be determined.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
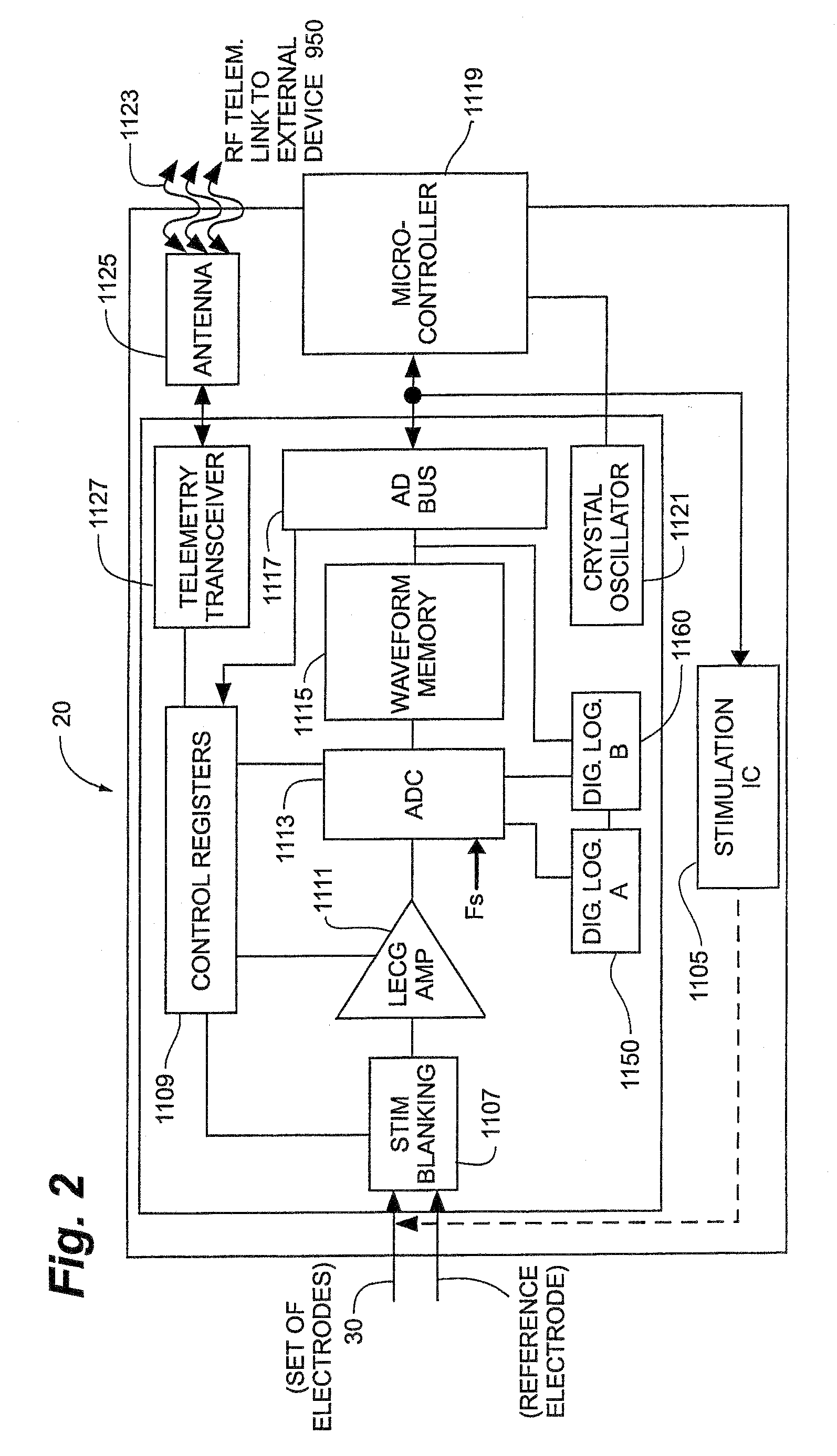
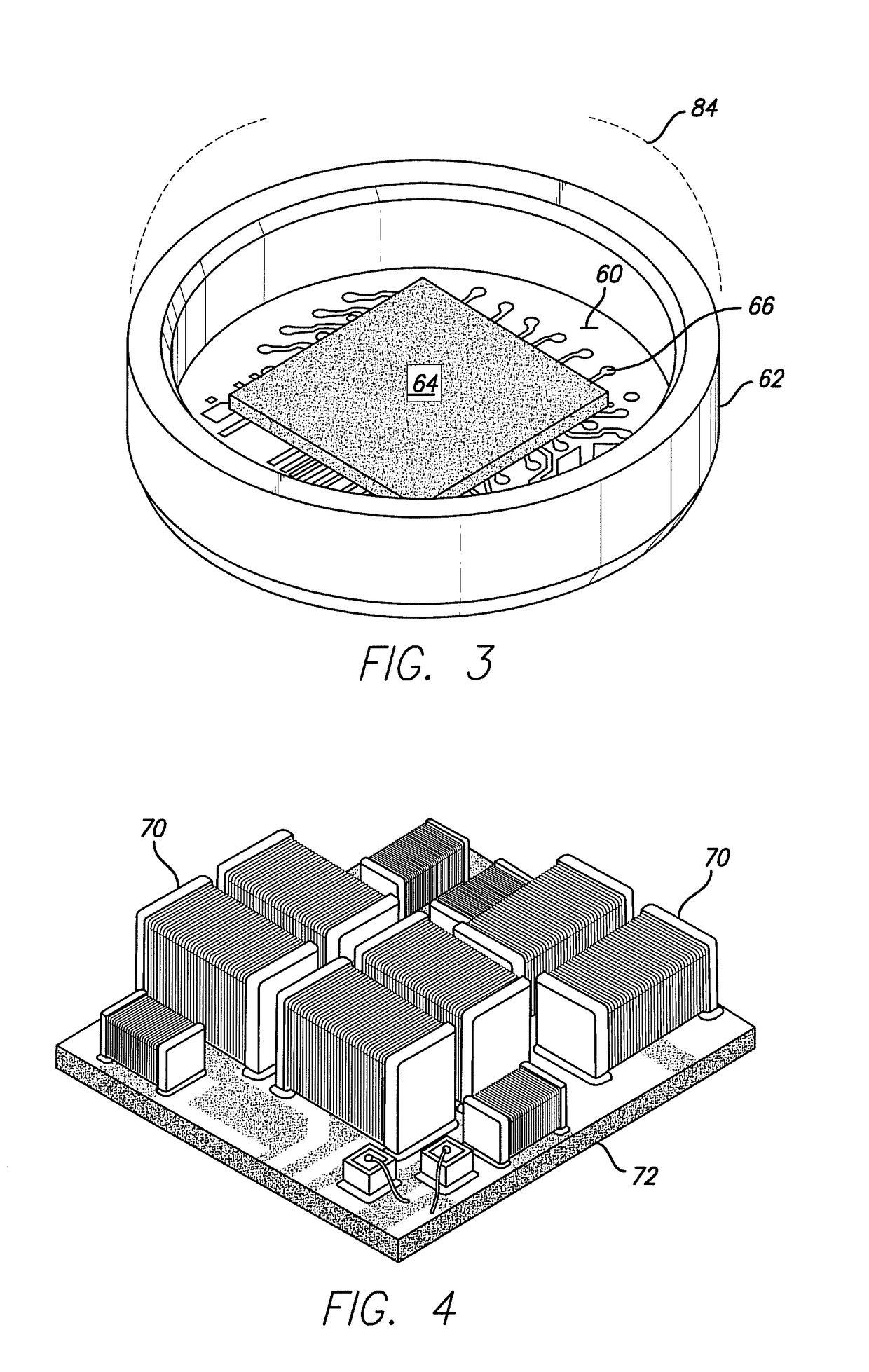
Cortical Implant System for Brain Stimulation and Recording
ActiveUS20150157862A1Shorter electrode arraysLess distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLaminating printed circuit boardsDiseaseEngineering
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. A brain stimulator, preferably a deep brain stimulator, stimulates the brain in response to neural recordings in a closed feedback loop. The device is advantageous in providing neuromodulation therapies for neurological disorders such as chronic pain, post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), major depression, or similar disorders. The invention and components thereof are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Cortical Interface for Motor Signal Recording and Sensory Signal Stimulation
ActiveUS20120296444A1Small sizeIncrease the number ofHead electrodesPrinted circuit aspectsSensory FeedbacksProsthesis
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to the at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that is / are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. The output signals provide control for a motor prosthesis and the inputs signals provide sensory feedback for the motor prosthesis. The invention, or components thereof, is / are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Method and apparatus for the treatment of movement disorders
A method, apparatus, and system for treating patients suffering from movement disorders having the ability to determine one or more biomarkers indicative of a disease state. In some embodiments, the biomarker may be used as a closed-loop feedback signal to control the delivery of therapy (such as electrical stimulation or drug therapy), and which may also be used as an indication of therapy effectiveness. One embodiment uses electrodes placed in the brain to measure EEG or local field potential (LFP) signals, from which the one or more biomarkers may be determined.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Monitoring Brain Neural Activity
Monitoring brain neural activity comprises repeatedly applying electrical stimuli to evoke neural responses in the brain. Neural responses evoked by the stimuli are recorded. The recorded neural responses are assessed for changed characteristics over time, to monitor a time-varying effect on the recorded neural responses of local field potentials arising from a source other than the electrical stimuli.
Owner:CLOSED LOOP MEDICAL PTY LTD
Brain signal telemetry and seizure prediction
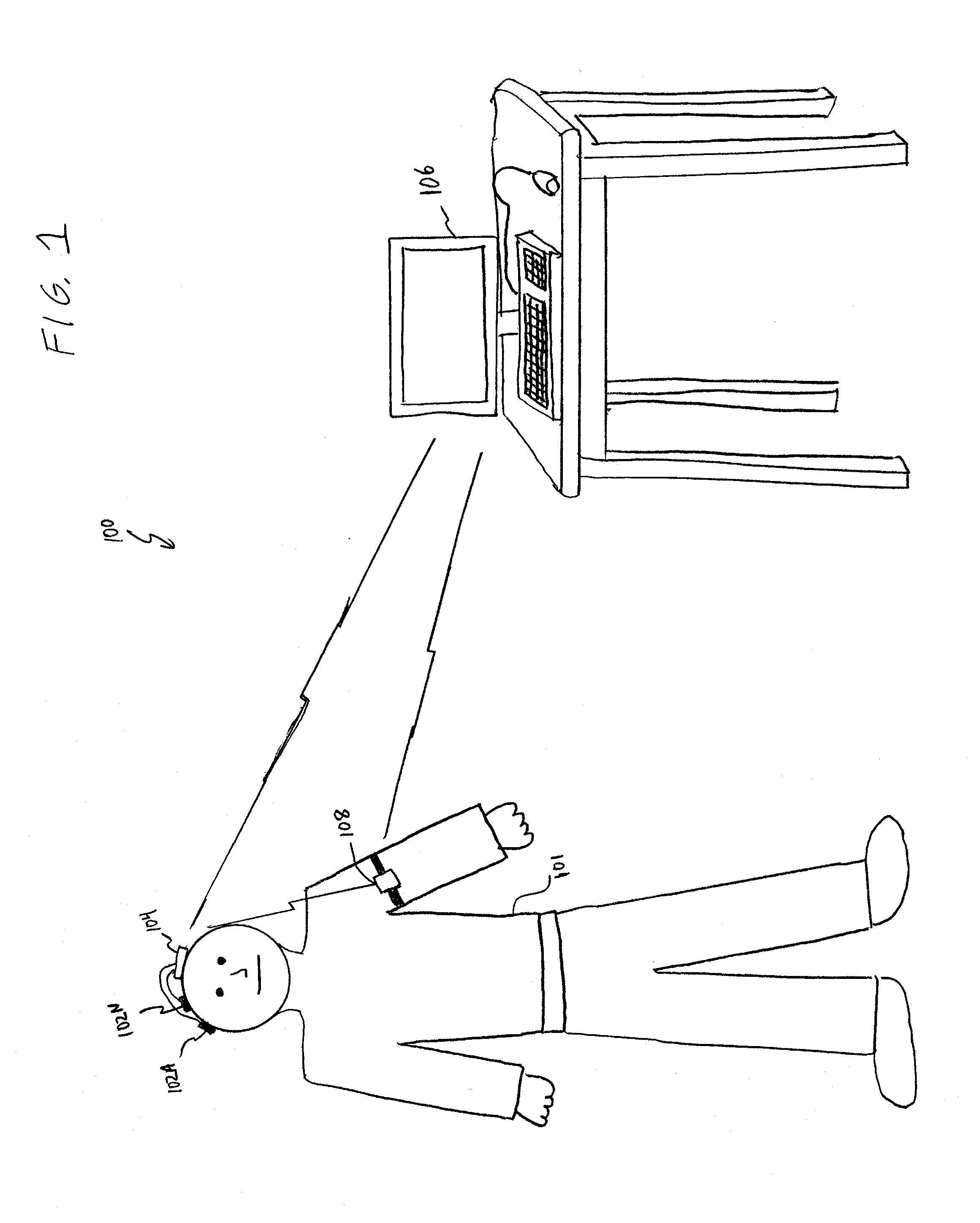
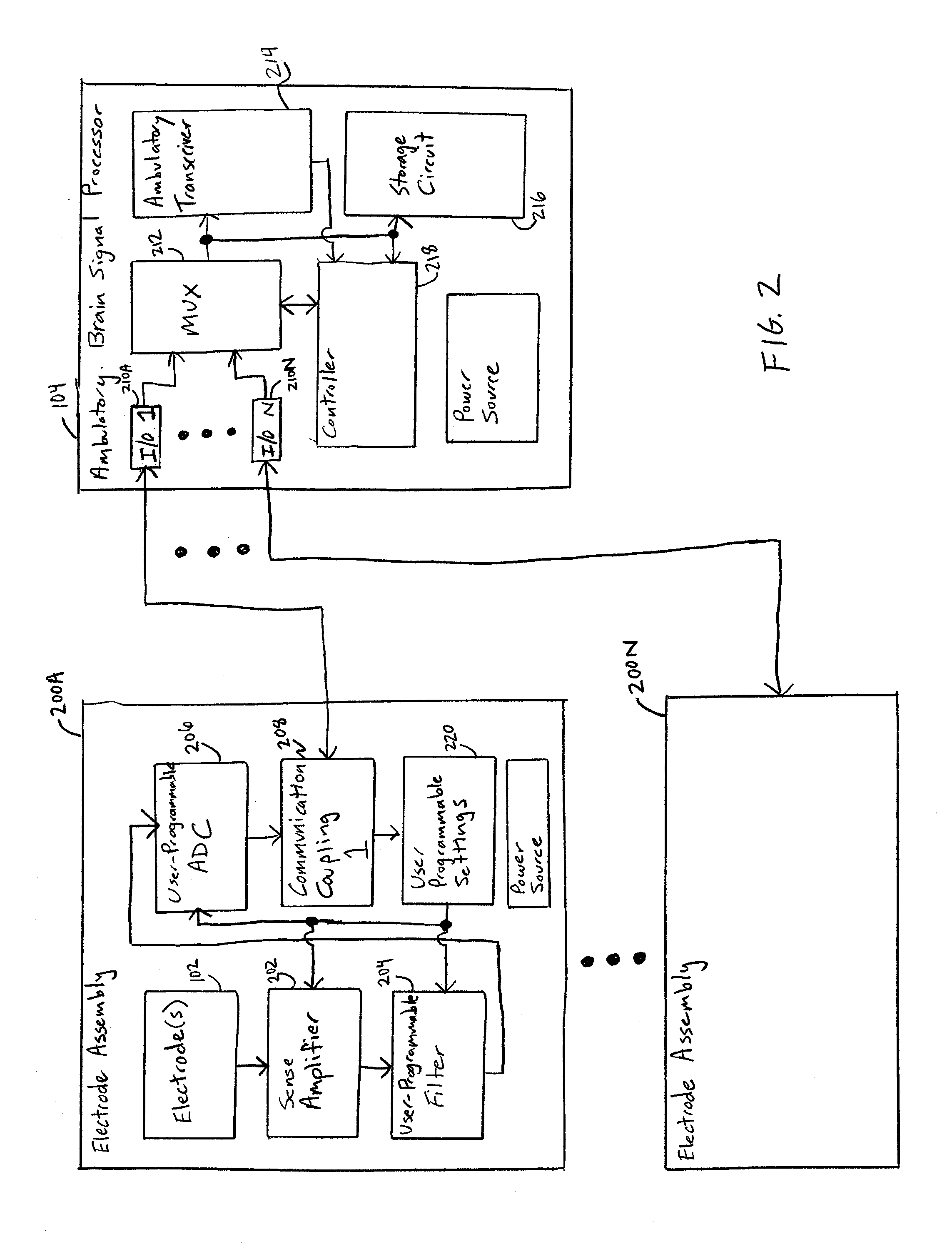
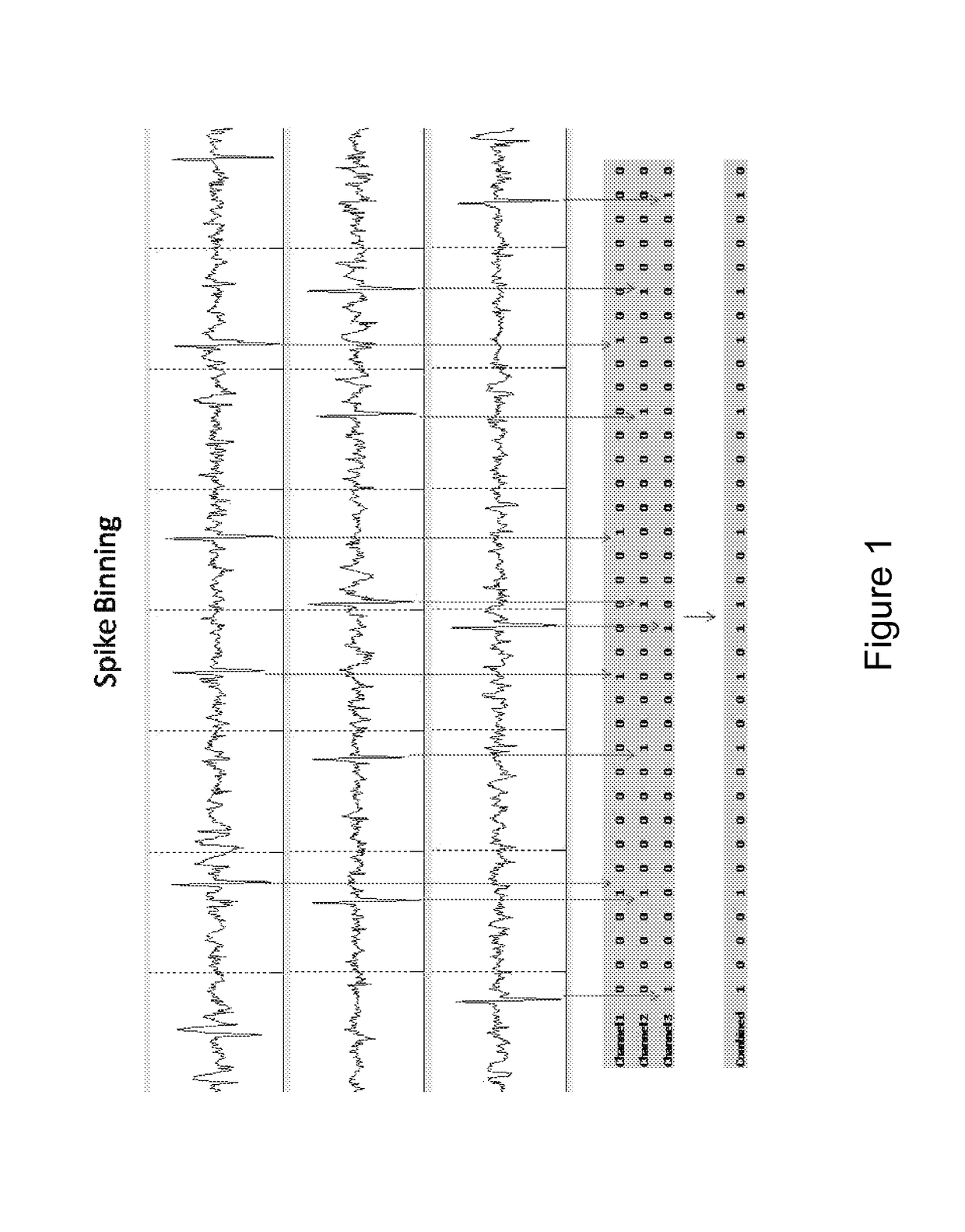
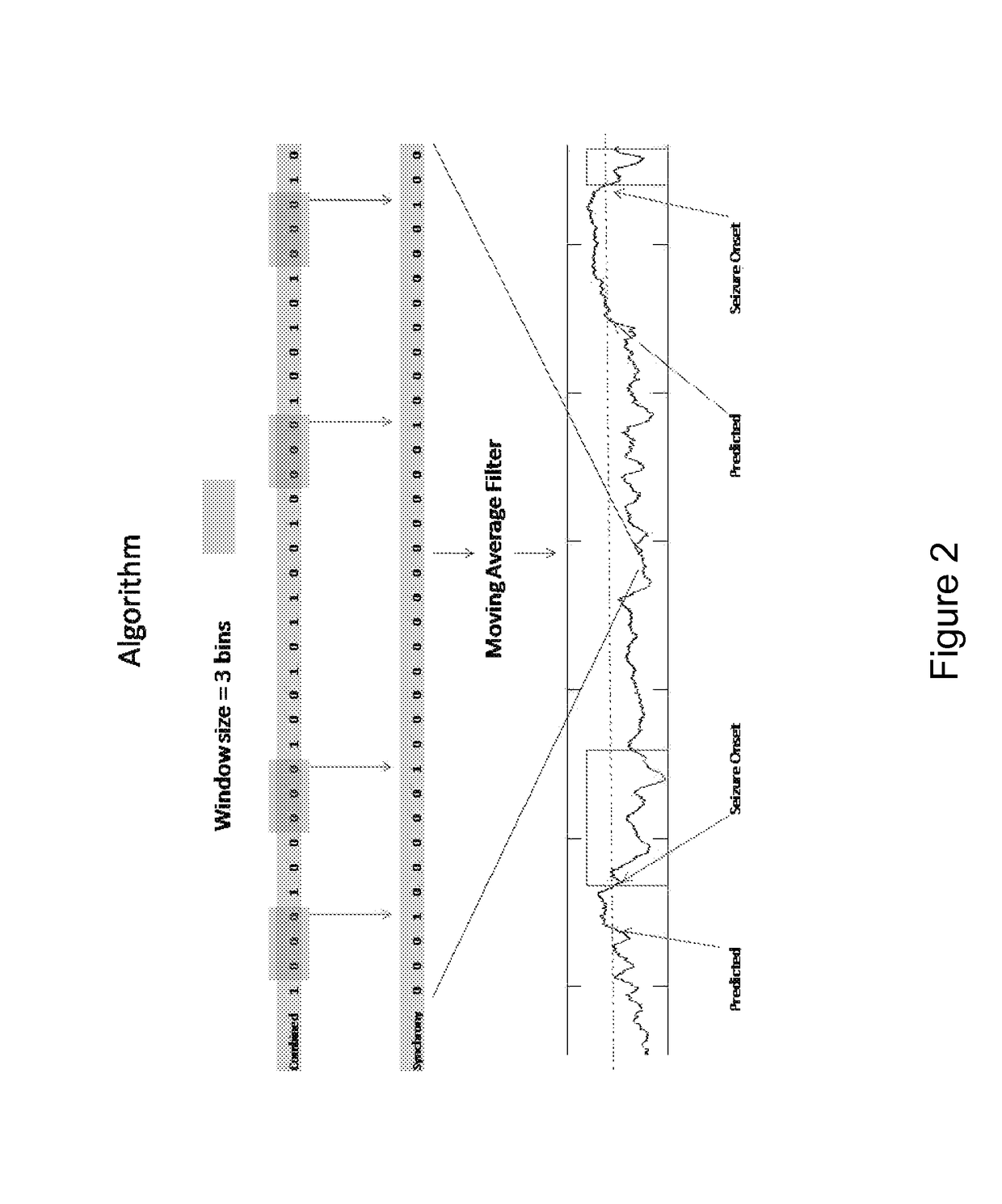
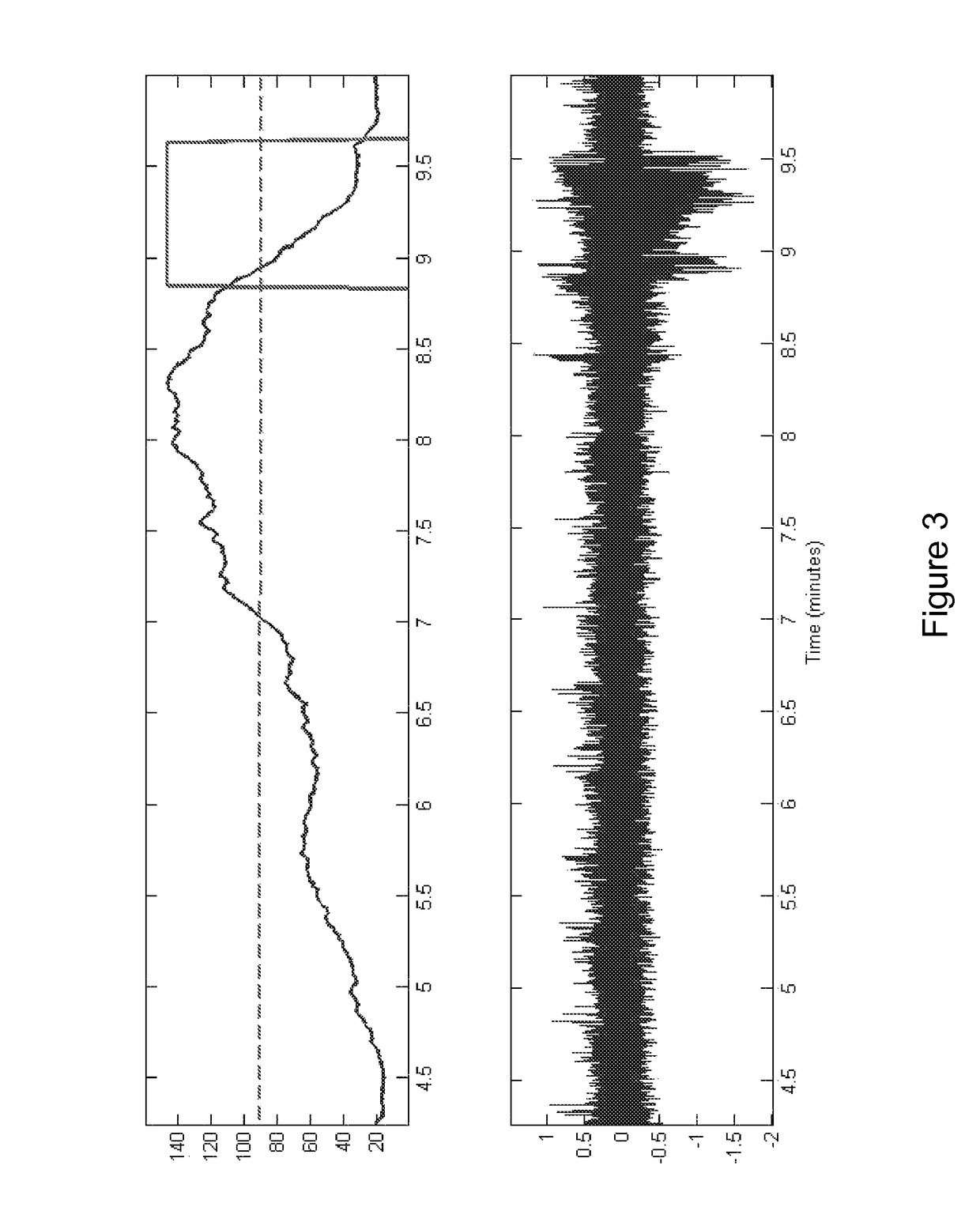
An ambulatory intrinsic brain signal processor circuit is coupled to a plurality of electrodes. The signal processor circuit can include a digital multiplexer circuit coupled to the electrodes to multiplex brain signal data from different electrodes together into a multiplexed data stream. An ambulatory transceiver circuit wirelessly communicates information to and from a remote transceiver. A controller circuit permits a user to control which of the electrodes contribute data, a data resolution, and whether the data includes one or both of neural action or local field potential data. Seizure prediction components and methods are also described.
Owner:BIO SIGNAL GROUP CORP
Electroencephalograph (EEG)-based epilepsy detection and intervention device
ActiveCN102613971AReduce the risk of side effectsImprove the quality of lifeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityMedicine
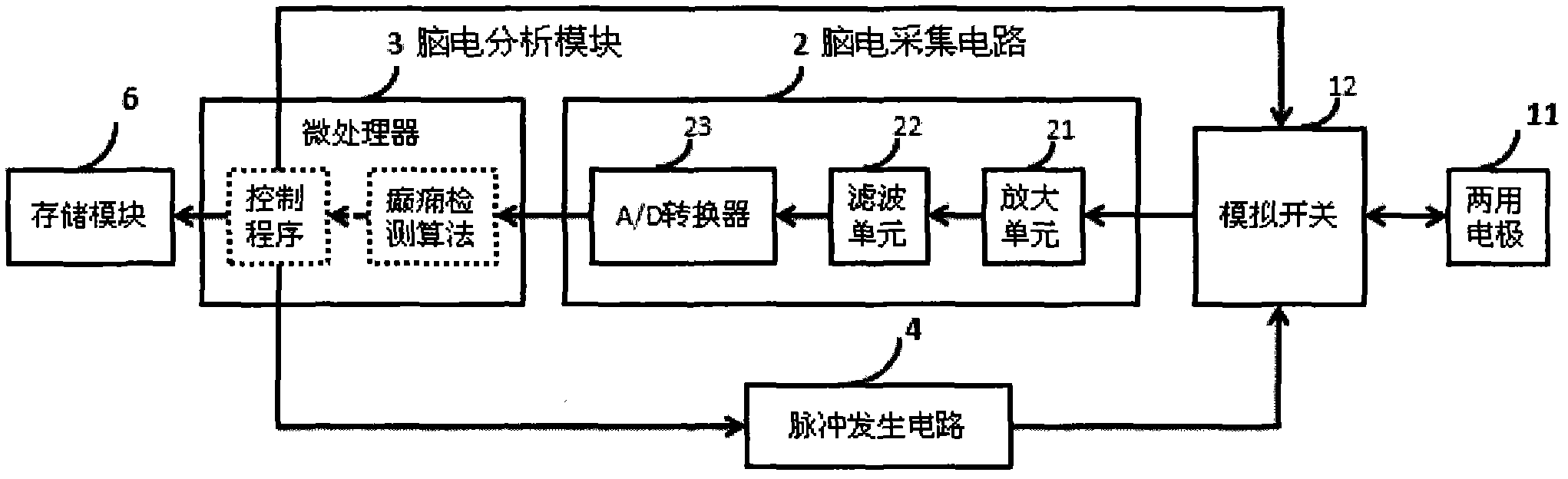
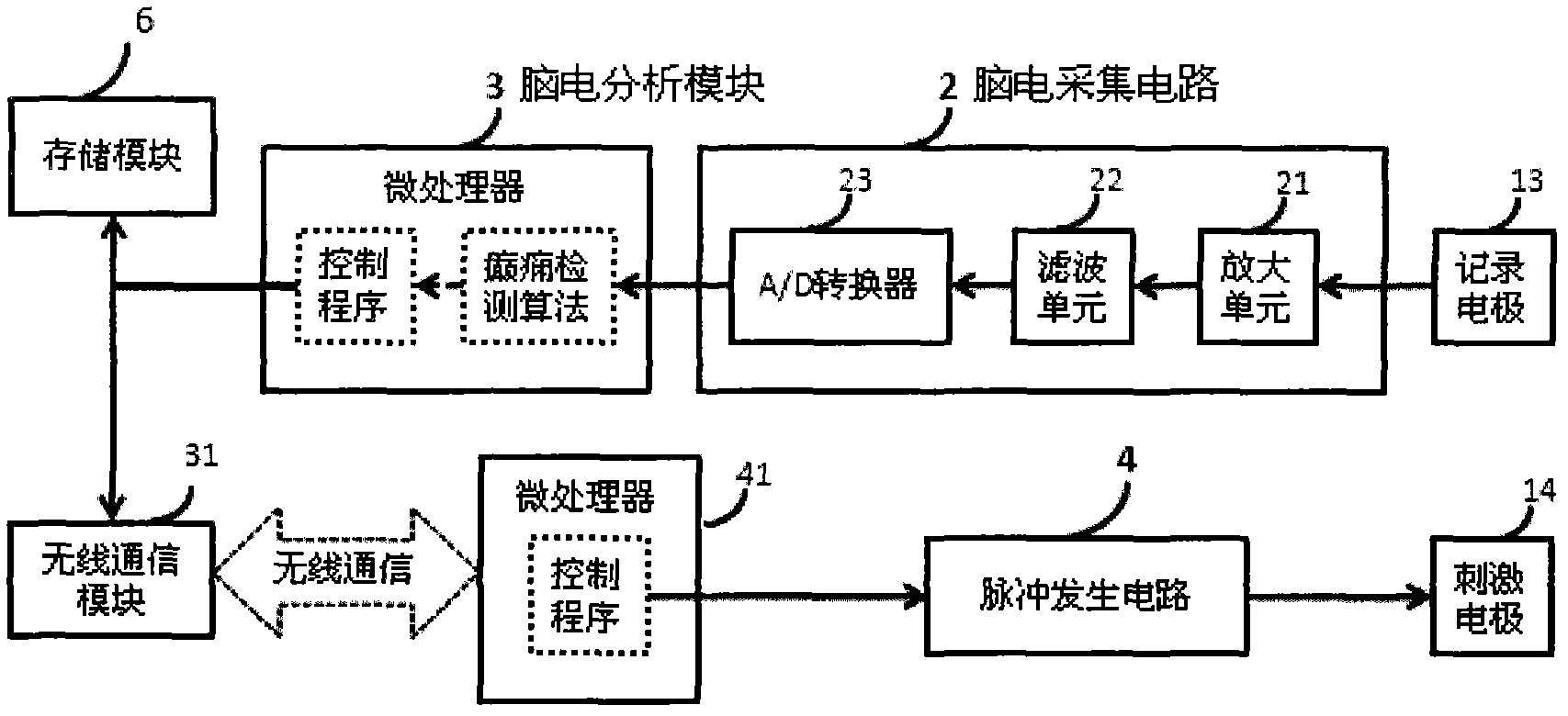
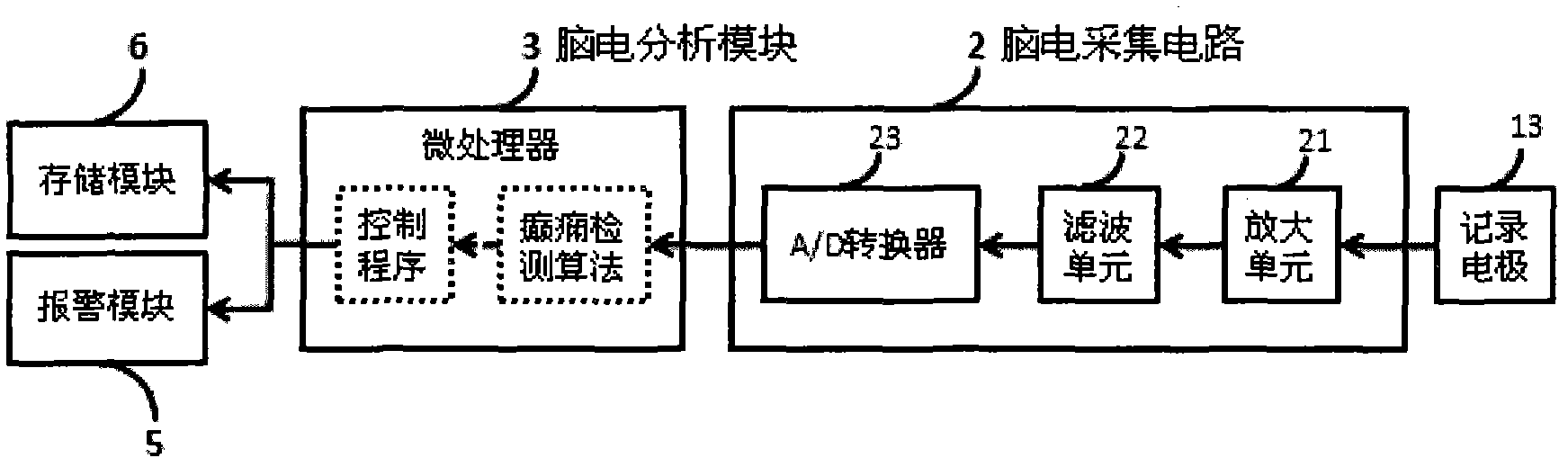
The invention provides an electroencephalograph (EEG)-based epilepsy detection and intervention device, which has the functions of recording EEG (scalp EEG, electrocorticogram (ECoG) and deep local field potential (LFP) EEG), analyzing the recorded EEG, detecting epilepsy electrograph onset (EO), forecasting epilepsy behavior onset and giving an alarm about the forecast epilepsy onset or implementing intervention means such as electrical stimulation. The device can also be used for research of corresponding animal experiments.
Owner:BEIJING PINS MEDICAL +1
Chronically implantable hybrid cannula-microelectrode system for continuous monitoring electrophysiological signals during infusion of a chemical or pharmaceutical agent
InactiveUS20090187159A1Increasing its useful lifespanEfficiently sensedMedical devicesSensorsMultivariate statisticalPharmaceutical care
A device for assessing the effects of diffusible molecules on electrophysiological recordings from multiple neurons allows for the infusion of reagents through a cannula located among an array of microelectrodes. The device can easily be customized to target specific neural structures. It is designed to be chronically implanted so that isolated neural units and local field potentials are recorded over the course of several weeks or months. Multivariate statistical and spectral analysis of electrophysiological signals acquired using this system could quantitatively identify electrical “signatures” of therapeutically useful drugs.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and System For Physiological Target Localization From Macroelectrode Recordings and Monitoring Spinal Cord Function
ActiveUS20160051812A1Improve detection rateReduce excitabilityHead electrodesElectromyographyAnatomical structuresNervous system
Provided herein are a method and system are provided for the localization of clinically relevant electrophysiological signals necessary for the proper placement of the electrodes for nervous system stimulation. The system provides electrical and mechanical means to stimulate or excite neural structures in order to elicit specific neural responses. The method can include mechanical vibratory stimulation, cutaneous electrical stimulation, electrical stimulation of the peripheral nerves, or photic stimulation, and recording of local field potentials and extracting evoked potentials in response to stimulation. The method also includes extracting components of the evoked potentials that relate the signal in the evoked potentials to specific anatomical structures and localization of the source of the evoked potentials recorded so as to identify the location of the source relative to the recording electrode with high resolution by sampling the evoked potentials with a relative large (macro) electrode that is moved in small incremental steps.
Owner:GREENVILLE NEUROMODULATION CENT
Methods, Computer-Readable Media, and Systems for Predicting, Detecting the Onset of, and Preventing a Seizure
InactiveUS20150351701A1Raise the possibilityImplantable neurostimulatorsMedical automated diagnosisMedicinePartial field
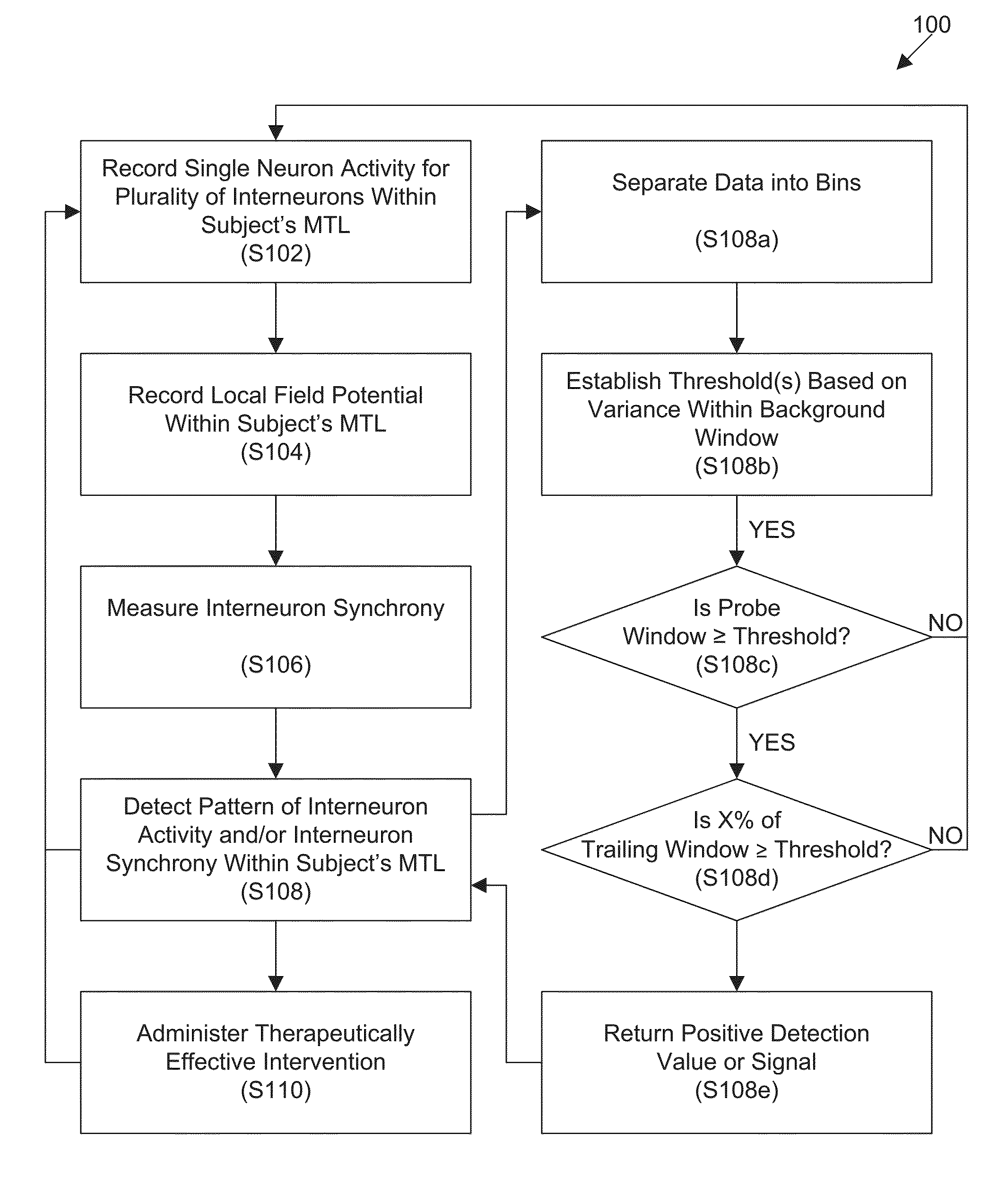
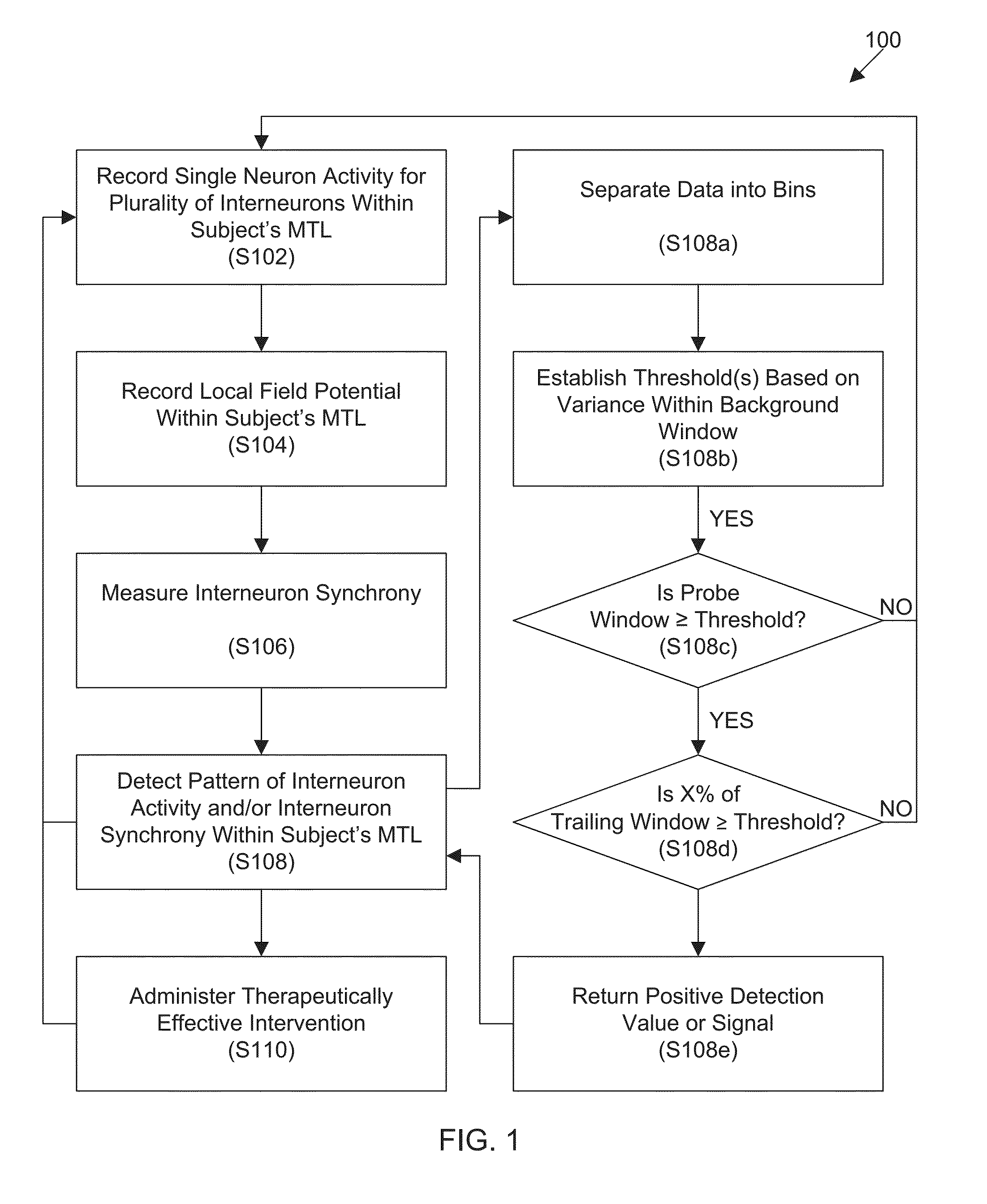
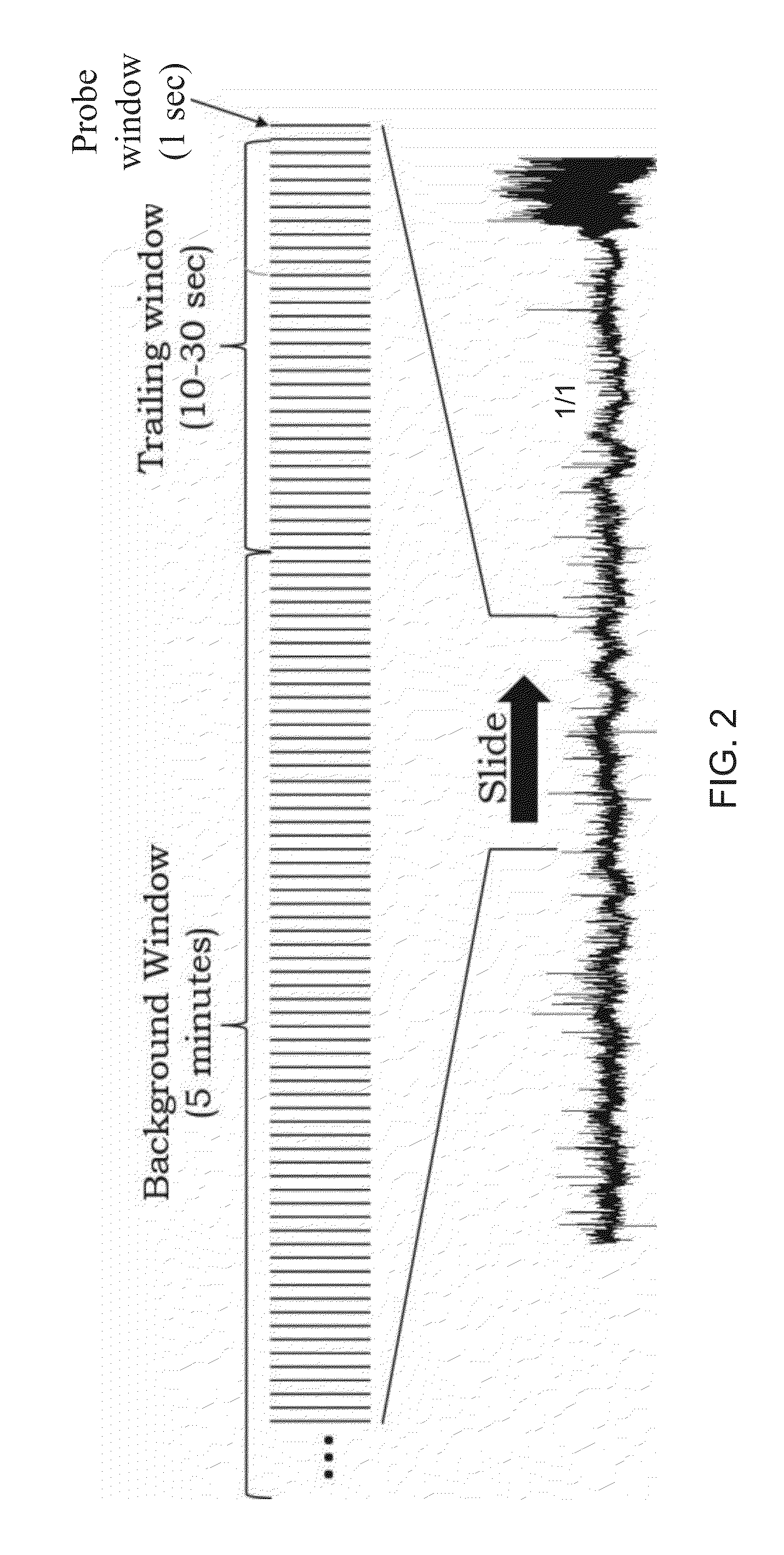
One aspect of the invention provides a method of predicting a seizure in a subject comprising: (a) recording single neuron activity for a plurality of interneurons within the subject's mesial temporal lobe; (b) recording local field potential (LFP) within the subject's mesial temporal lobe; (c) measuring interneuron synchrony within the subject's mesial temporal lobe; and (d) detecting a pattern of interneuron activity and interneuron synchrony within the subject's mesial temporal lobe associated with an increased likelihood of a seizure. Another aspect of the invention provides a method for preventing a seizure in a subject comprising: (a) performing any one of the methods described herein; and (b) upon detection of the pattern, administering a therapeutically effective intervention to the subject to prevent onset of a seizure. Another aspect of the invention provides a non-transitory computer readable medium containing computer-readable program code including instructions for performing any of the methods described herein.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Method for detecting learning, memory and cognitive function of rat based on neuronal oscillatory activity
InactiveCN106963371AReflect memory functionReflect cognitive functionMedical automated diagnosisSensorsTime domainTheta rhythm
The invention discloses a method for detecting learning, memory and cognitive function of a rat based on a neuronal oscillatory activity. The method comprises the following steps: collecting the LFPs signal, filtering and denoising the LFPs signal, and extracting the theta rhythm and the gamma rhythm from the LFPs signal; calculating the coupling relationship of the neural rhythm, including calculating the neural rhythm of the rhythm in the same brain region and different brain regions; taking the calculated neural rhythm as a characteristic parameter; statistically analyzing the extracted characteristic parameter so as to achieve the detection of the learning, memory and cognitive function of the rat. According to the method, a device for collecting local field potential of the rat is constructed; the LFPs of the hippocampal CA1 and CA3 brain regions of the rat are collected; the signal is analyzed in time domain and frequency domain and the like; and then the learning, memory and cognitive function of the rat are reflected by analyzing the cross coupling between the theta rhythm and the gamma rhythm.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Stimulation, recording and administration combined device for research on use of hippocampal field potentials of mouse and rat
InactiveCN101804240AFacilitate experimental researchCompact structureVeterinary instrumentsArtificial respirationMedicineCatheter
The invention relates to a stimulation, recording and administration combined device for the research on the use of ippocampal field potentials of mouse and rat, belonging to a device used in medical electrophysiologic experiment of animals and mainly solving the difficult technical problem that the current device has low successful rate in field potation guidance owing to complex operations and plenty of consumed time and used drugs. The technical proposal of the invention is that: a stimulation, recording and administration combined device for the research on the use of ippocampal field potentials of mouse and rat comprises an eccentric circle dual-pole stimulating electrode, a hollow single-pole recording electrode, an electrode fixation device and a recording electrode core, wherein the eccentric circle dual-pole stimulating electrode and the hollow single-pole recording electrode are arranged inside the electrode fixation device in parallel, and the recording electrode core is arranged in an administration hole in the center of the hollow single-pole recording electrode. The device further comprises an administration device consisting of a hollow administration catheter, a hose and a microinjector, wherein the upper end of the hollow administration catheter is connected with one end of the hose the other end of which is connected with the microinjector.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
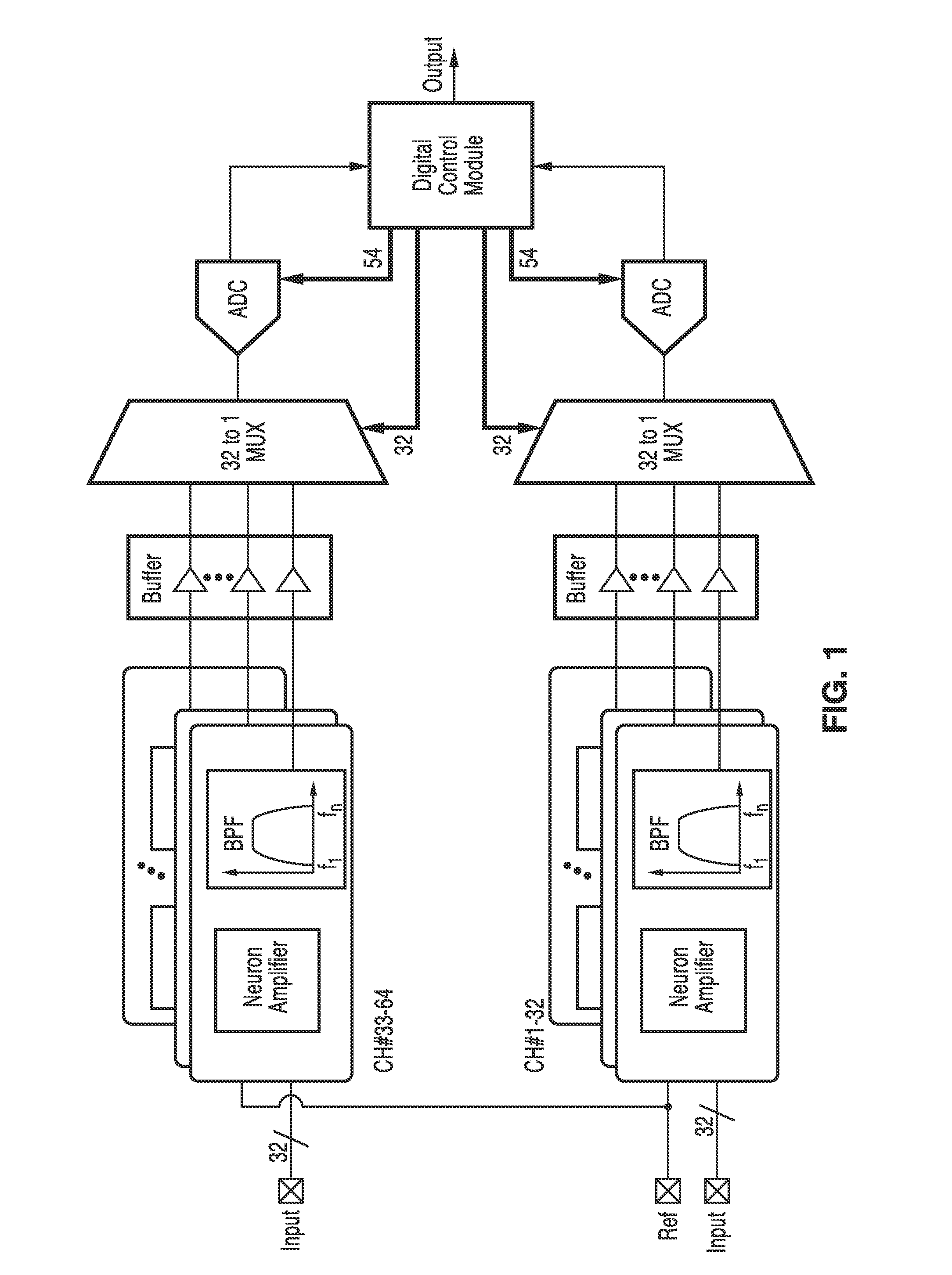
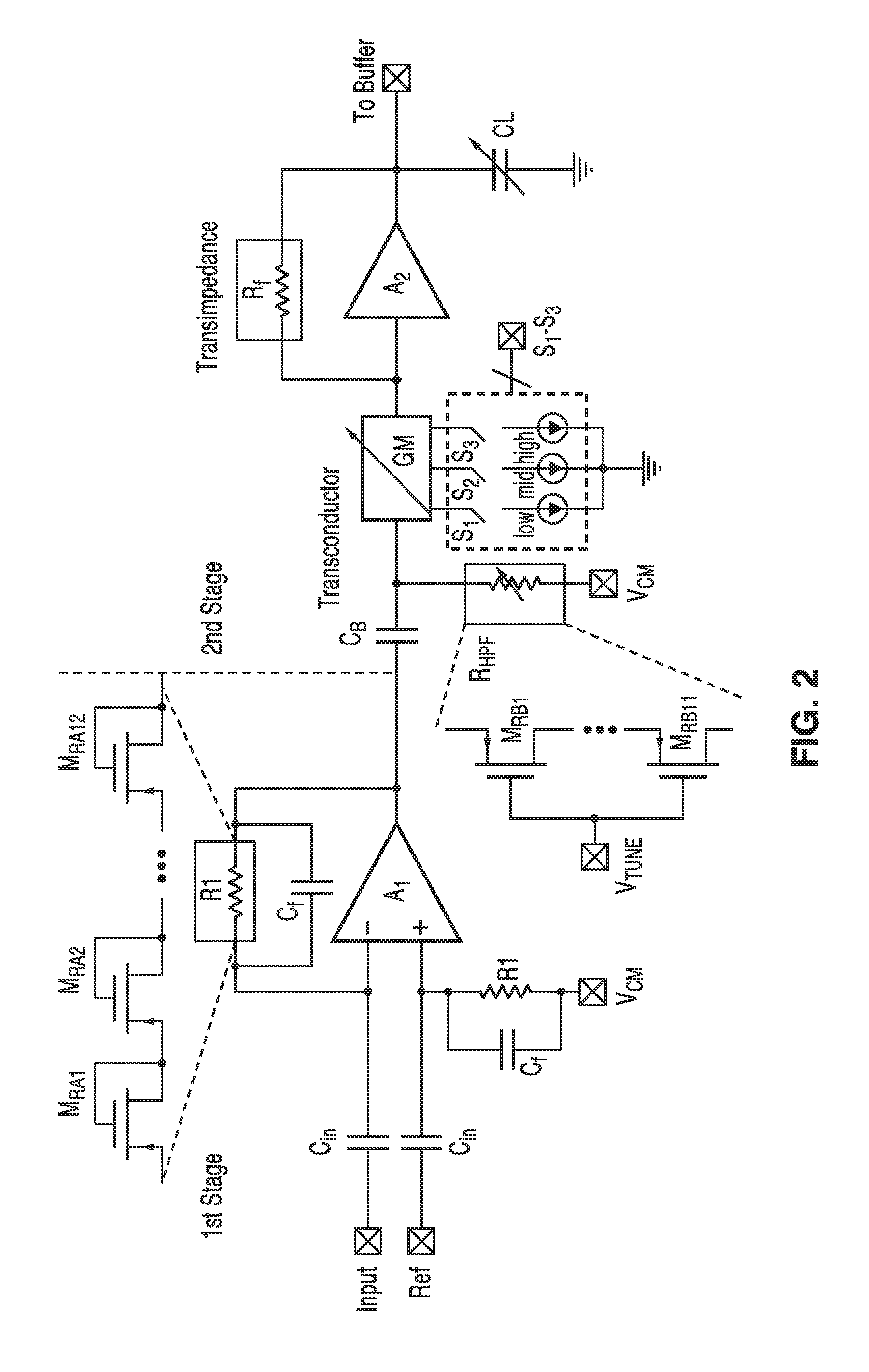
Neural recording system
ActiveUS20140180052A1Reduce power supply voltageSmall output resistanceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesDiagnostic recording/measuringAudio power amplifierPartial field
A neuron recording system was provided. By using the gain-boosted topology, the amplifier input impedance can be increased while simultaneously reducing the noise. The system can be configured to record local field potentials (LFPs) and neuron spikes, respectively, with low-power consumption. With the flexible digital controller module (DCM), any subset of the recording channels can be activated for recording with independent sampling rate at each channel. A wireless interface to transmit recorded neuron data and an on-chip neuron processor to perform real-time signal processing can be incorporated in the system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Integral multi-point synchronous recording and multi-brain zone function relation monitoring system and method
InactiveCN101496719AFriendly interfaceReasonable structureDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMulti siteRandom combination
The invention belongs to the field of neuroscience experiment, technology and research, and particularly relates to a method and a system for overall multi-site simultaneous recording and multiple brain area functional linkage monitoring. The system comprises a signal acquisition unit and a signal analysis unit which are connected through parallel interfaces, wherein the signal acquisition unit comprises an amplifier, an analog-digital converter, a microprocessor and a data signal transmission interface and simultaneously records the bioelectrical signals at different sites in the brain, the bioelectrical signals are amplified by the amplifier and converted into digital signals by the analog-digital converter, and the digital signals are transmitted to the signal analysis unit; and the signal analysis unit comprises a computer and analysis software, wherein the analysis software analyzes the digital signal from the signal acquisition unit. At the same time, the recorded bioelectrical signals are random combinations of local field potentials at different sites and central nucleus unit discharge activities. The system provides scientific research with a proactive tool for multi-site simultaneous recording and multiple brain area functional linkage monitoring of a nervous system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
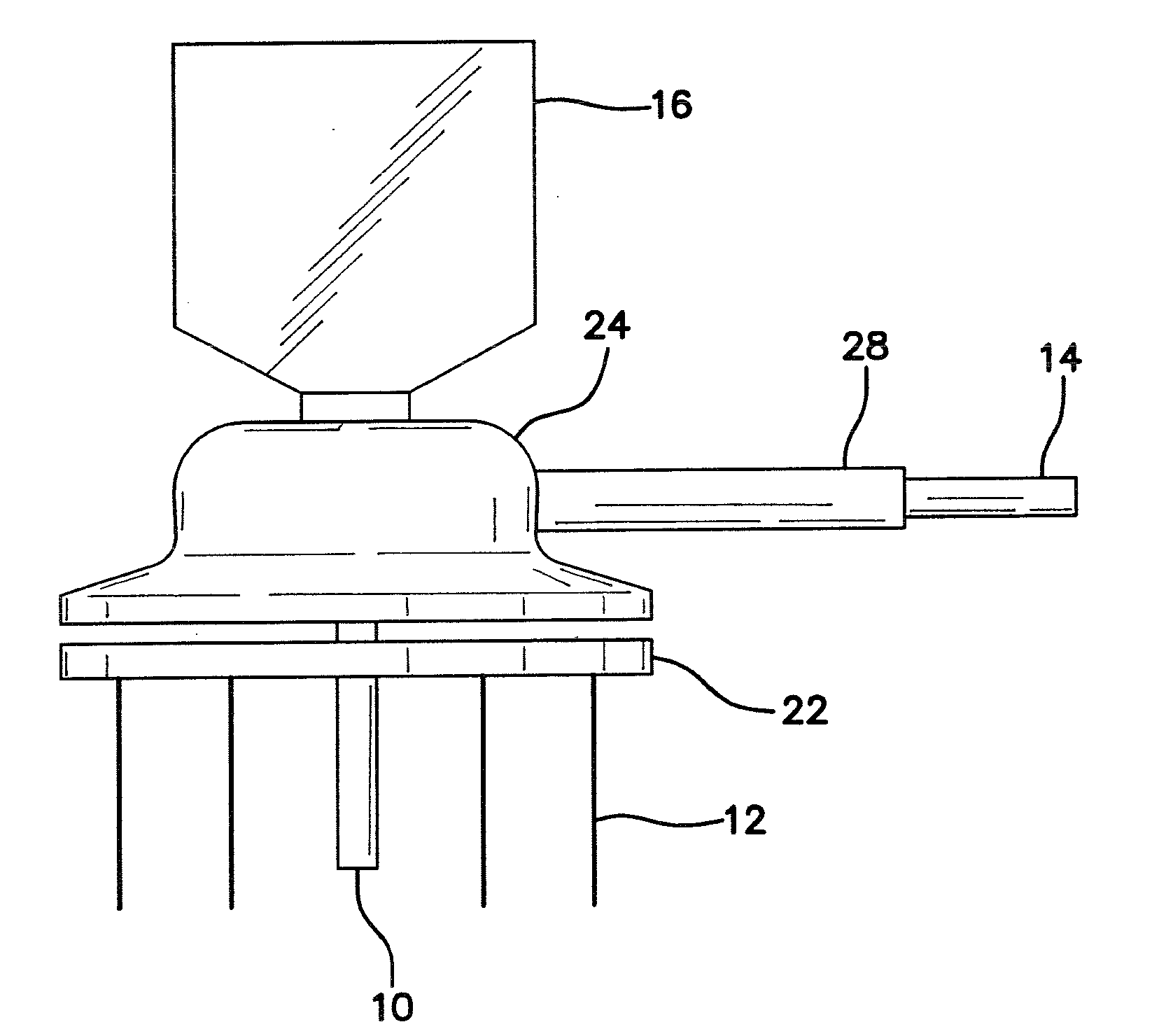
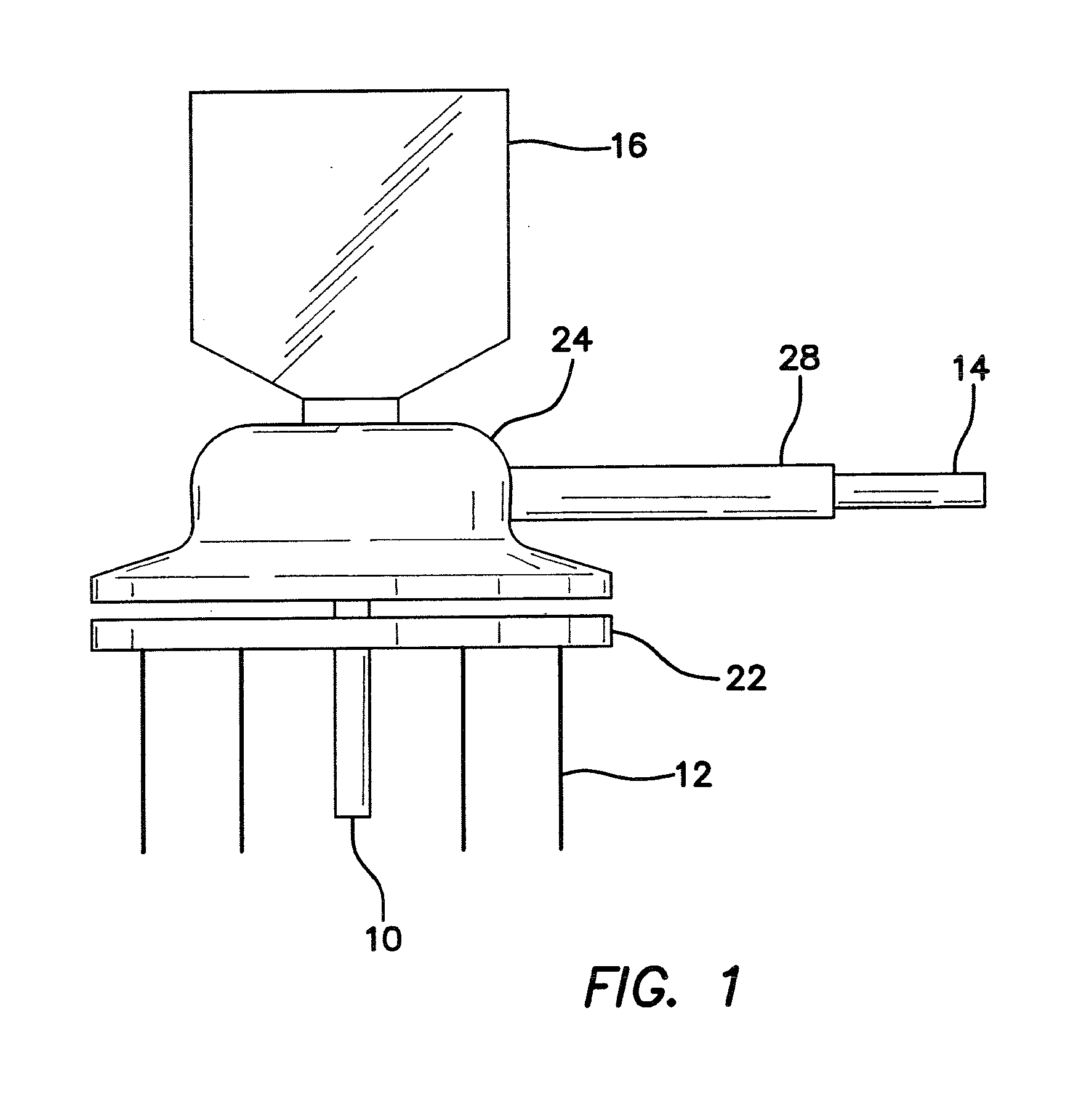
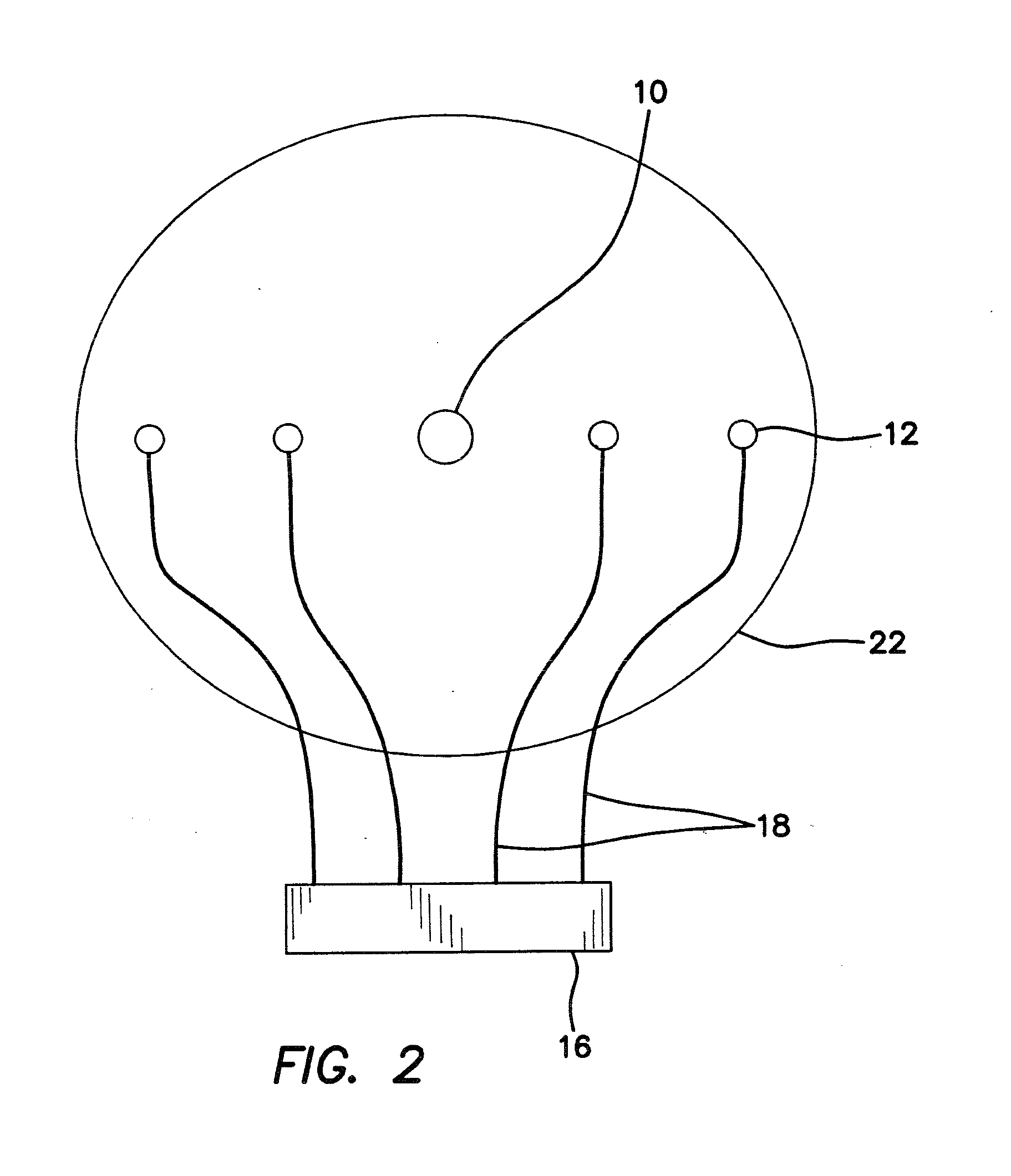
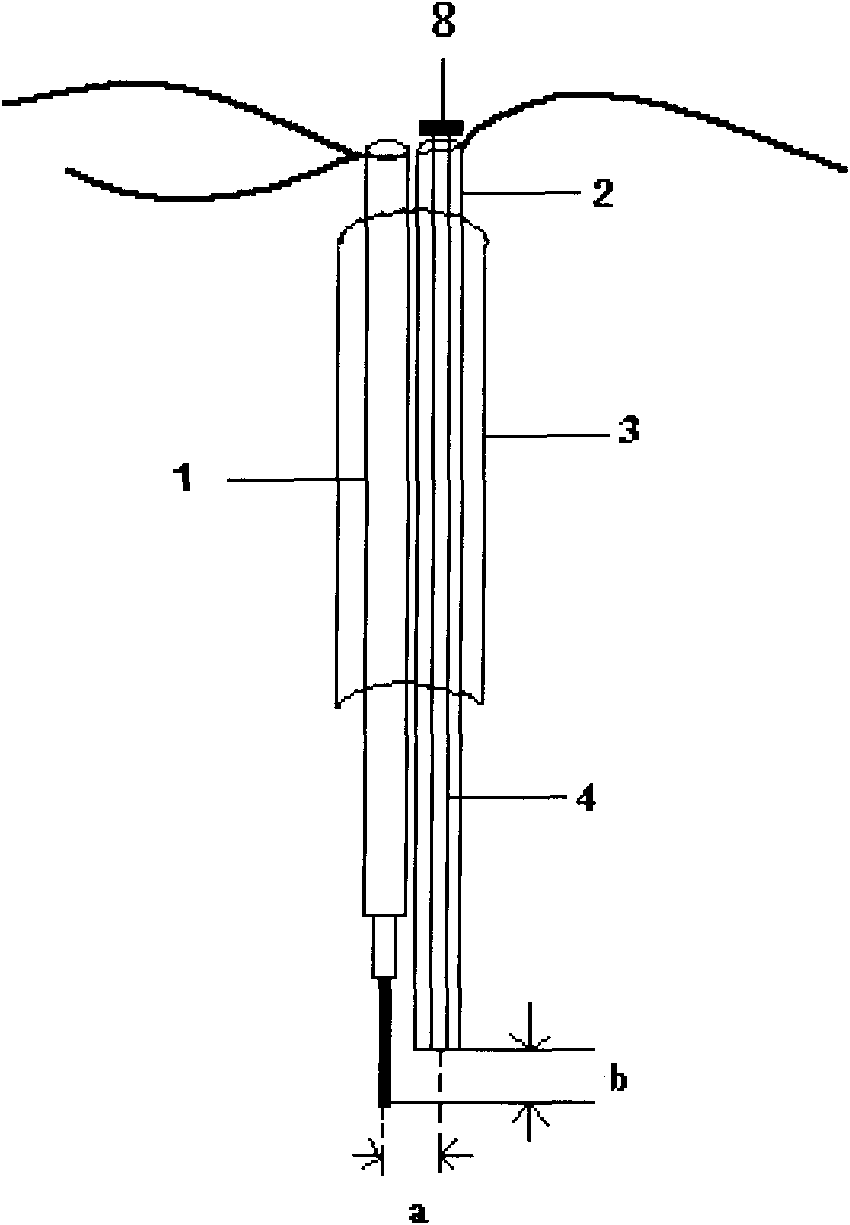
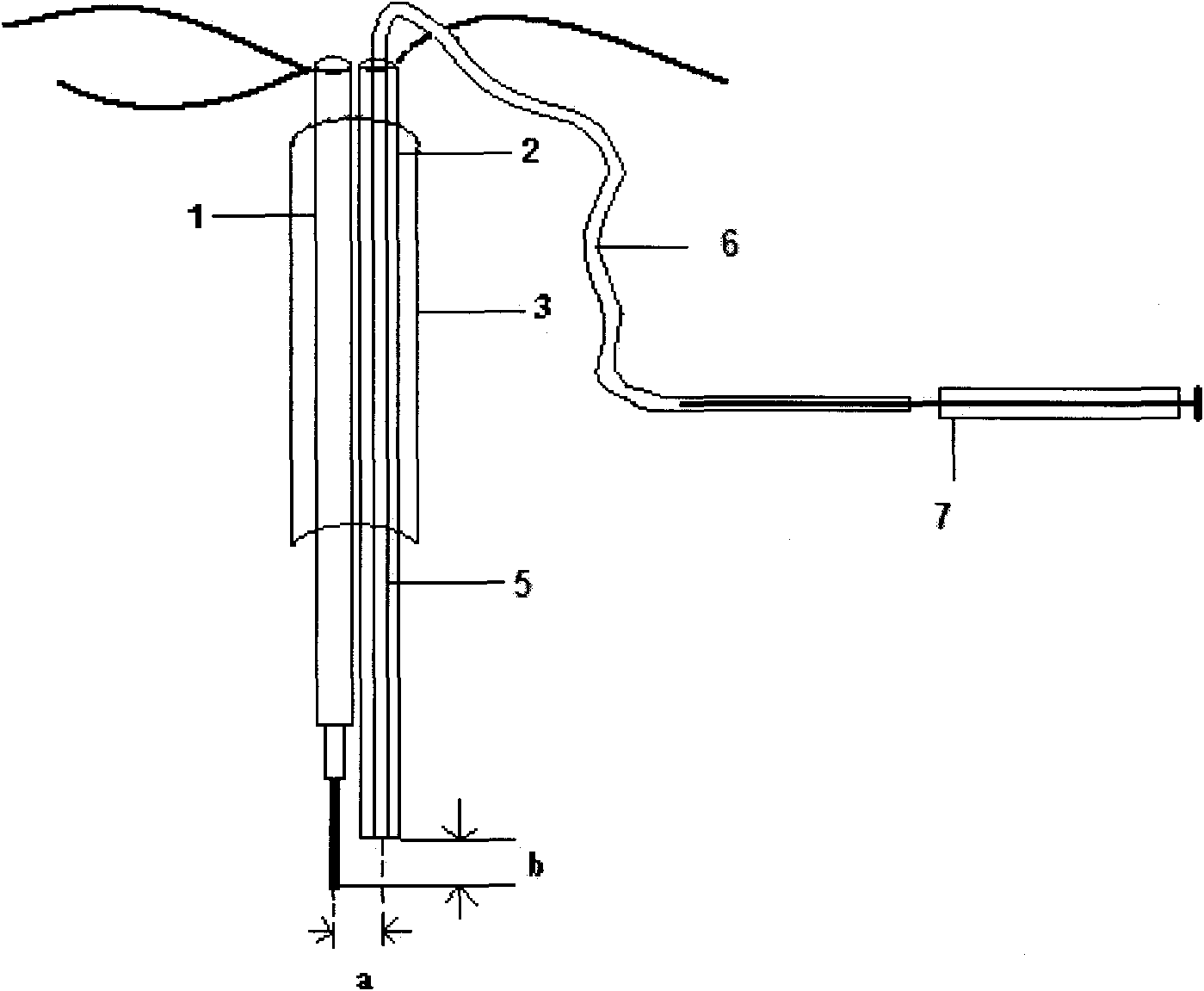
Multi-encephalic region field potential recording electrode and implantation method
InactiveCN106562786ASimple styleSimplified implantation methodDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPartial fieldLocal field
The embodiment of the invention discloses a multi-encephalic region field potential recording electrode which comprises multiple single-encephalic region electrodes and single-encephalic region electrode needle holders, wherein the single-encephalic region electrodes are implanted into target encephalic regions; and the single-encephalic region electrode needle holders are used to clamp the single-encephalic region electrodes, move the multiple single-encephalic region electrodes under guidance of a stereoscopic positioning instruction respectively and implant the multiple single-encephalic region electrodes into the multiple target encephalic regions. The embodiment of the invention also discloses an implantation method for the multi-encephalic region field potential recording electrode. Through application of the electrode and the method disclosed by the invention, only local field potentials of multiple encephalic regions need to be recorded; electrode formats of multi-encephalic region field potential recording as well as corresponding electrode implantation methods can be simplified; and loads of implanted electrodes can be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
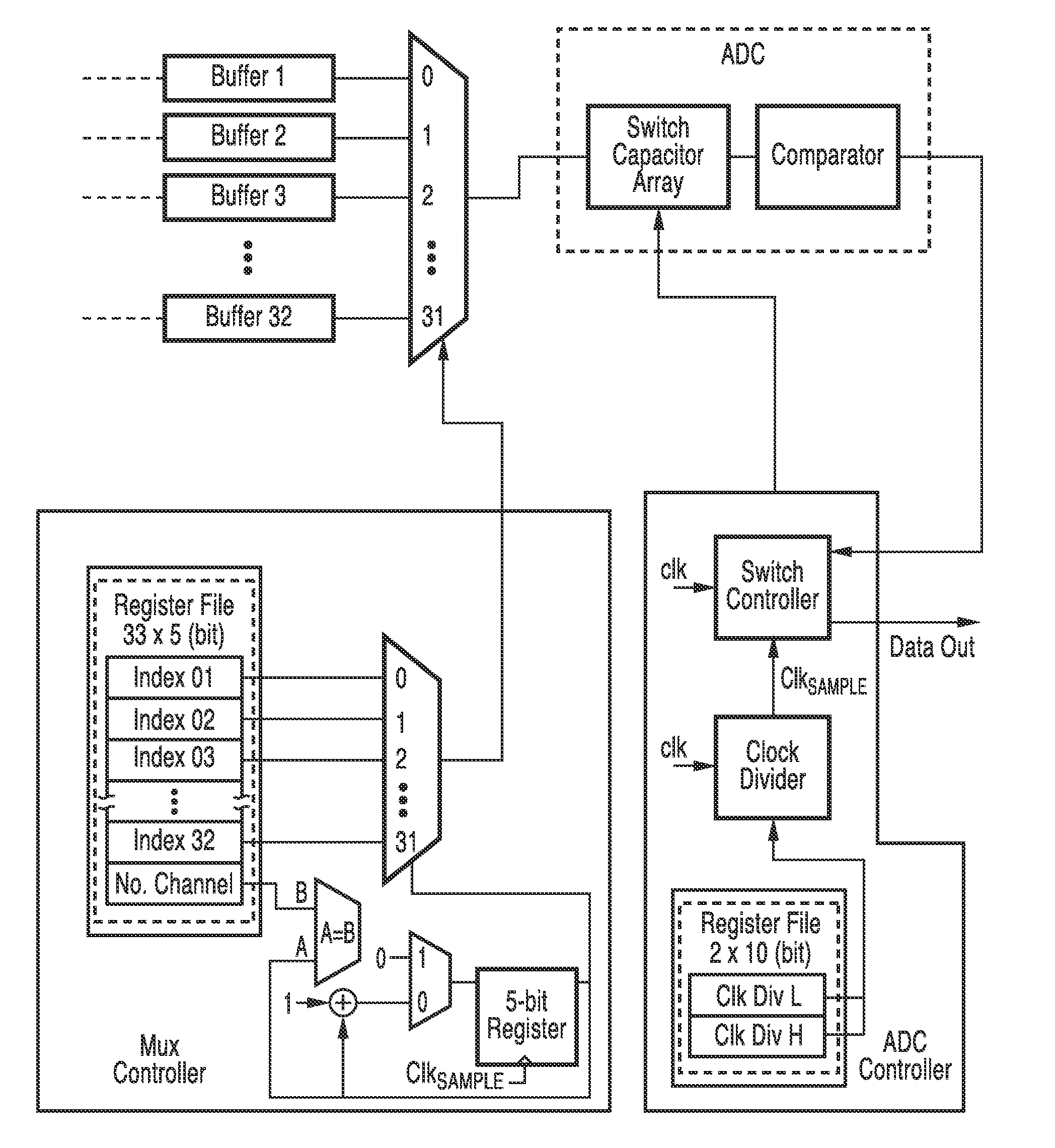
Integrated system and method for multichannel neuronal recording with spike/lfp separation, integrated a/d conversion and threshold detection
ActiveUS20090091377A1Reduced dynamic range requirementsBig ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionOscillations generatorsProgrammable logic deviceOffset calibration
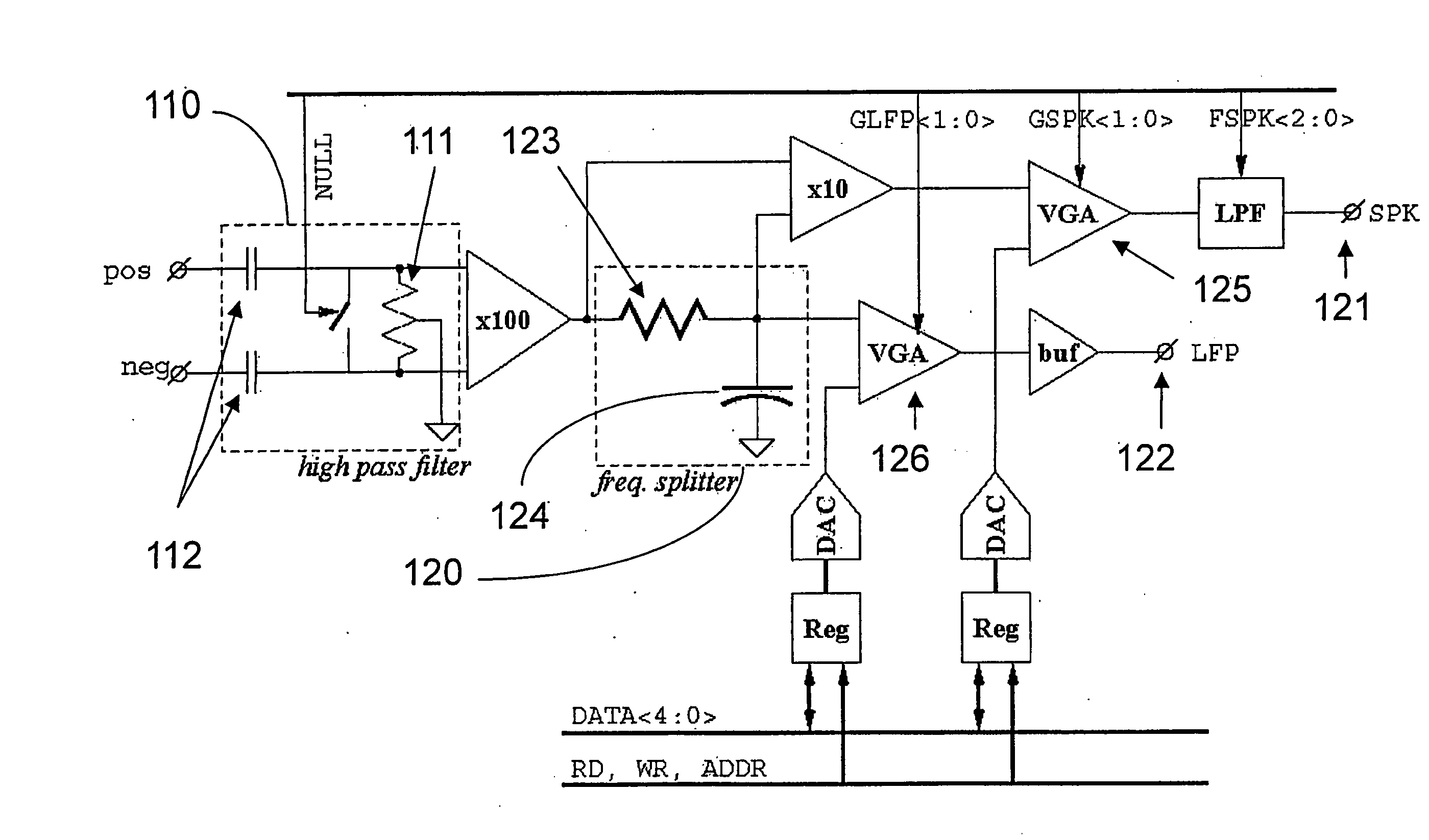
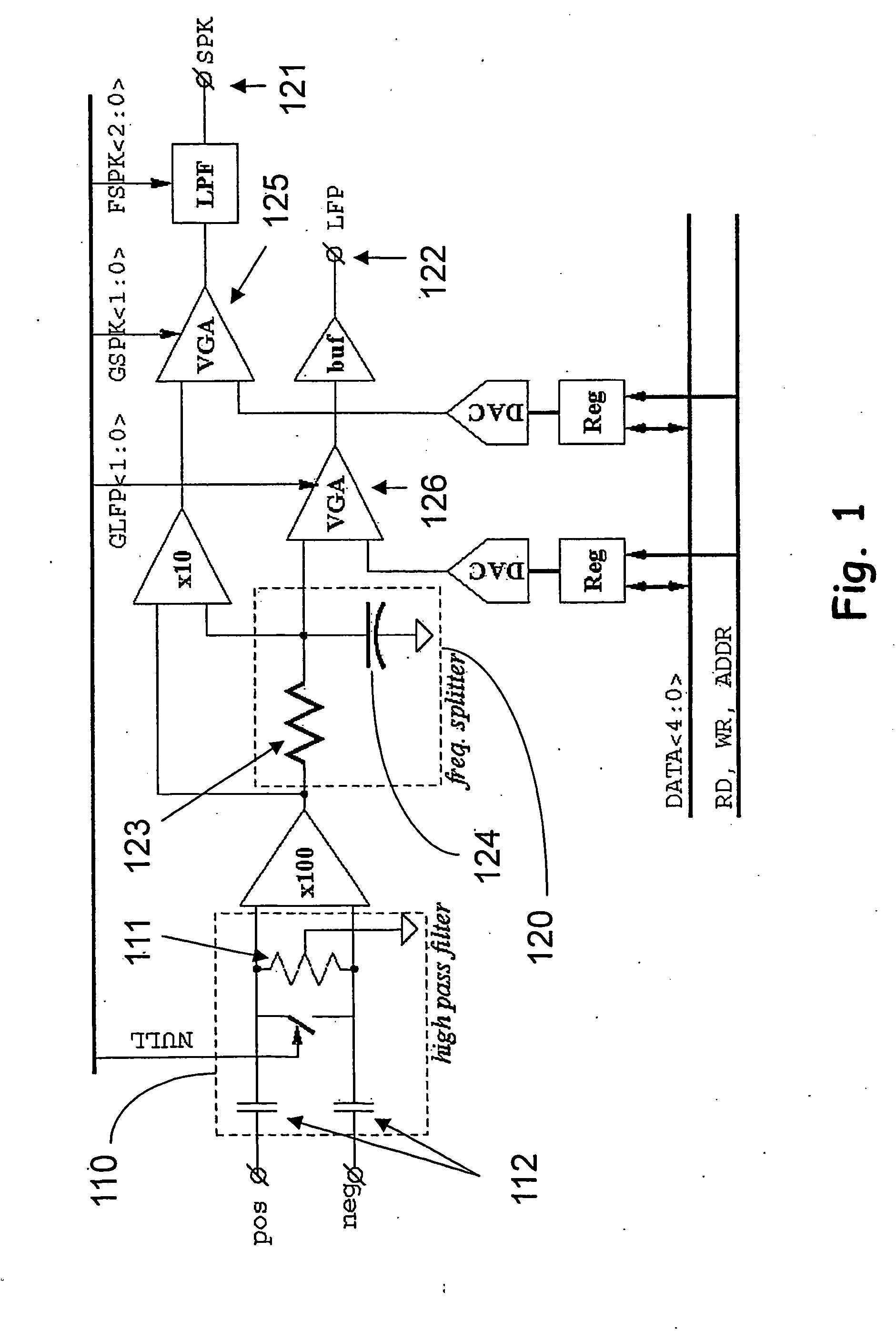
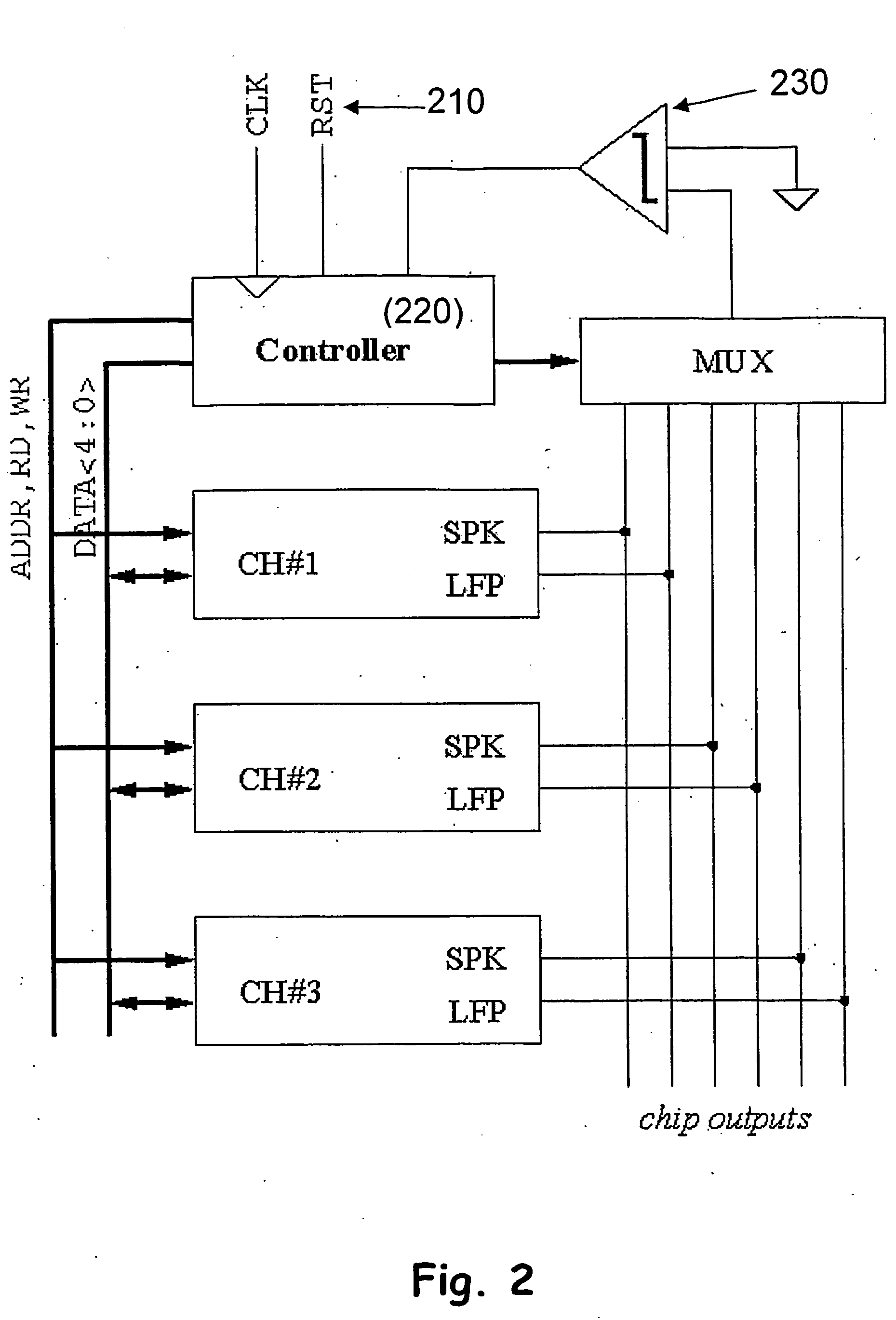
A CMOS integrated circuit for multi-channel neuronal recording with twelve true-differential channels, band separation and digital offset calibration. The recorded signal is separated into 2 bands: a low-frequency, local field potential (LFP); and high-frequency spike data. Digitally programmable gains for the LFP and spike bands are provided. A mixed-signal front-end processor for multi-channel neuronal recording is also described. It receives twelve differential-input channels of implanted recording electrodes. A programmable cutoff HPF blocks DC and low frequency input drift at about 1 Hz. The signals are band-split at about 200 Hz to low-frequency local field potential (LFP) and high-frequency spike data (SPK), which is band limited by a programmable-cutoff LPF. The analog signals are converted into digital form, and streamed out over a serial digital bus at up to 8 Mbps. A special interface system incorporating an embedded CPU core in a programmable logic device accompanied by real-time software allows connectivity to a computer host.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Chemical heredity epilepsy persistent state disease animal model and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN111839800AInhibitory activityClearly reusableImplantable neurostimulatorsVeterinary instrumentsHippocampal regionMetabolite
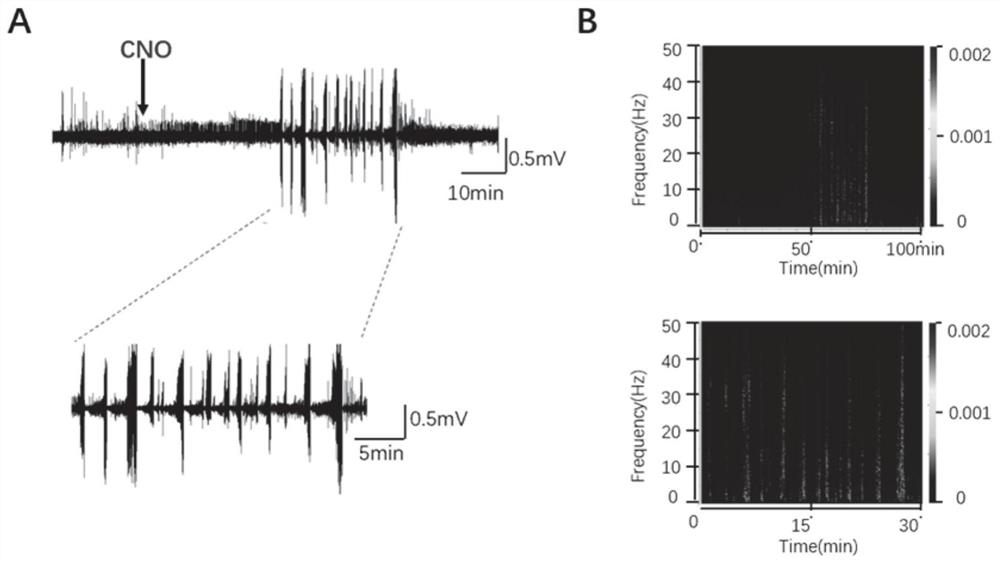
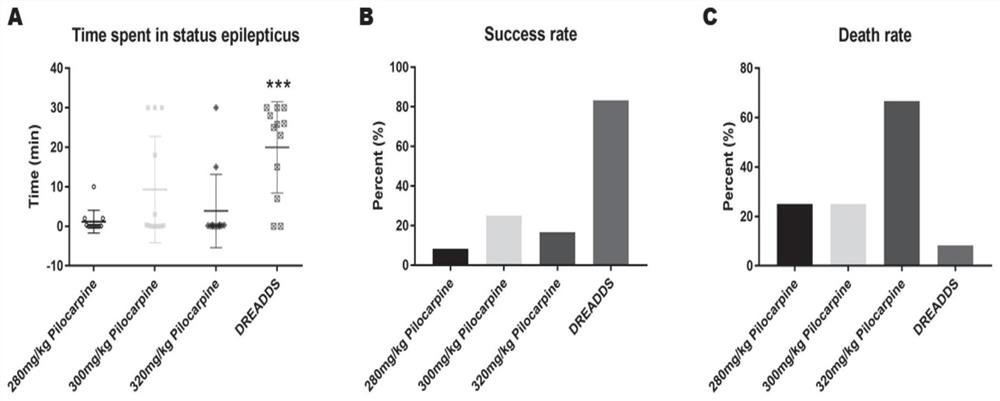
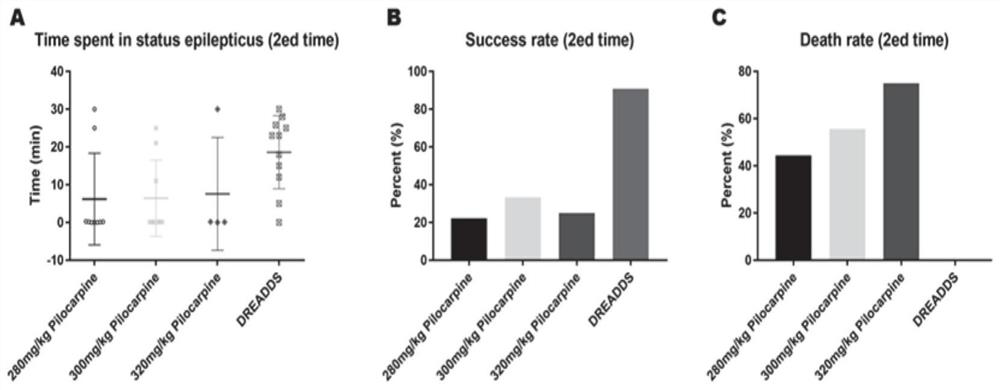
The invention provides a chemical heredity epilepsy persistent state disease animal model and a construction method and application thereof. The epilepsy persistent state disease animal model is a mouse brain kernel group (a hippocampus CA1 region and a thalamus anterior nucleus VA region of a model I); injecting a brain stereotaxic virus (a chemical genetic virus rAAV-CaMKIIa-hM3D (Gq)-mCherry-WPREs-pA) in an apricot kernel BLA region and a thalamus anterior nucleus VA region on the outer side of a substrate of the model II, and embedding an electrode array in a mouse hippocampus CA3 region;after the mouse is recovered for one week, a metabolite CNO of clozapine is injected into the abdominal cavity so that the CNO is combined with a virus expression receptor, neurons are activated to induce epileptic persistent state attack, and the epilepsy persistent state disease animal model is obtained through behavioral observation and in-vivo multichannel local field potential recording judgment. The epilepsy persistent state disease animal model constructed by the method is stable in seizure duration, high in success rate, low in death rate and good in repeatability, and has important significance in researching the origin and formation mechanism of epilepsy persistent state, and screening and mechanism of drug-resistant epilepsy persistent state drugs.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Systems Level State Characteristics in Experimental Treatment of Disease
Methods and system for assessment of a state of the central nervous system (CNS) of a subject and / or differentiation between states of the CNS at a specific time point based on electrophysiological recordings of signals from at least two anatomical structures, wherein the signals are recorded from recording sites located in the anatomical structures, wherein the electrophysiological recordings comprise spatiotemporal fluctuations in the recorded extracellular potential, wherein the electrophysiological recordings are action potentials and / or local field potentials (LFPs) in the anatomical structures and represent the state of the CNS, a s well as the use of the method for assessment of a state of the CNS and / or differentiation of at least two states of the CNS, as well as to the use of the method for evaluating the effect of a treatment of a condition or disease, wherein the condition or disease is neurological and / or psychiatric.
Owner:PETERSSON PER FREDRIK
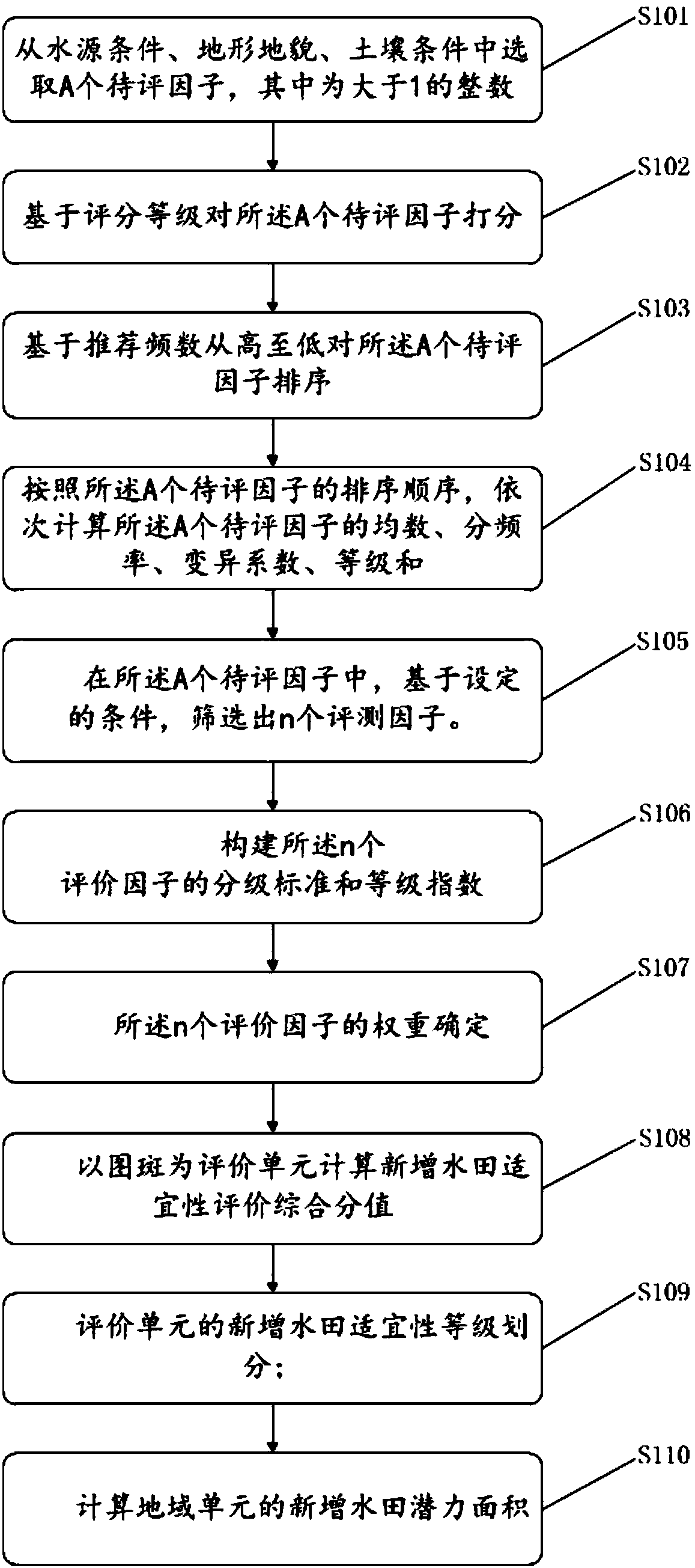
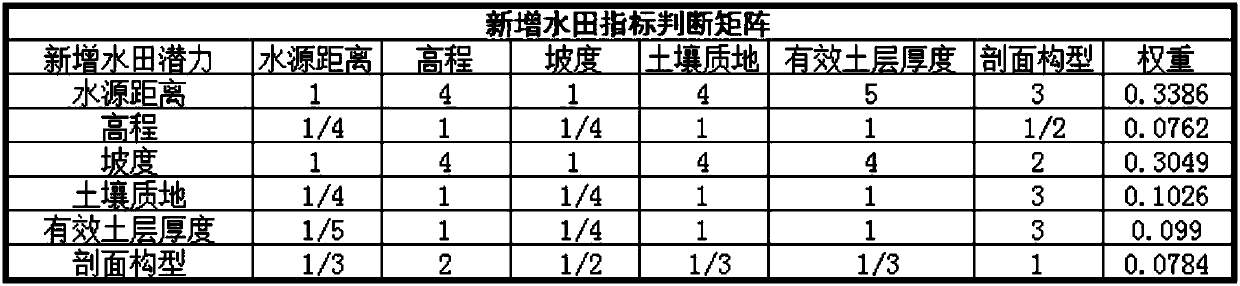
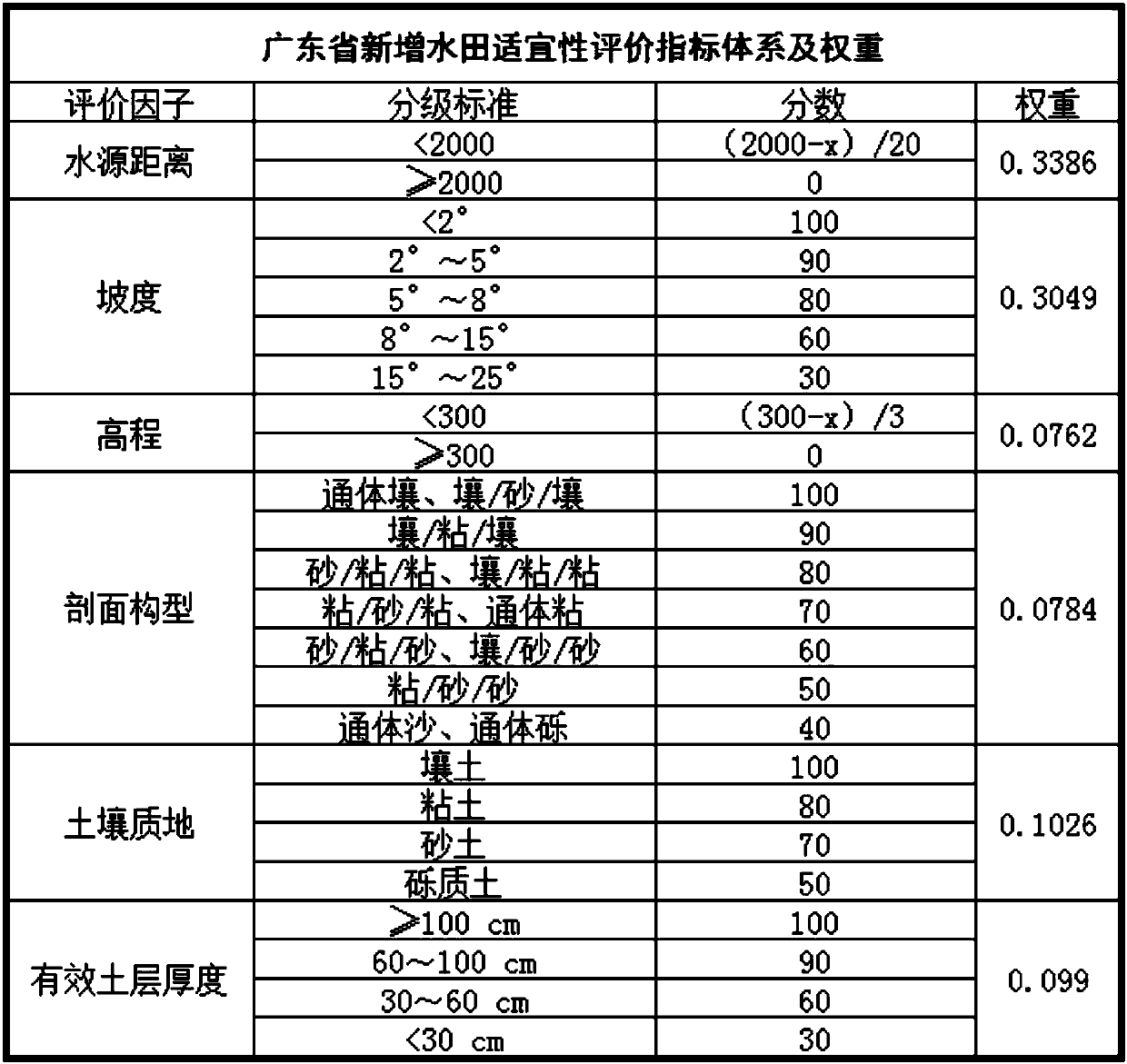
Estimation method and system of newly increased paddy field potential
The present invention provides a new paddy field potential evaluation method and system. The evaluation method uses the Delphi method to construct an evaluation factor system, builds a new paddy field suitability scoring model, and classifies the new paddy field suitability of the evaluation unit. Quantifying the potential area of newly-increased paddy fields in regional units can provide a data-based reference for policy implementation of newly-increased paddy fields, and has good practicability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Cortical implant system for brain stimulation and recording
ActiveUS9949376B2Shorter electrode arraysLess distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLaminating printed circuit boardsDiseaseEngineering
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. A brain stimulator, preferably a deep brain stimulator, stimulates the brain in response to neural recordings in a closed feedback loop. The device is advantageous in providing neuromodulation therapies for neurological disorders such as chronic pain, post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), major depression, or similar disorders. The invention and components thereof are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
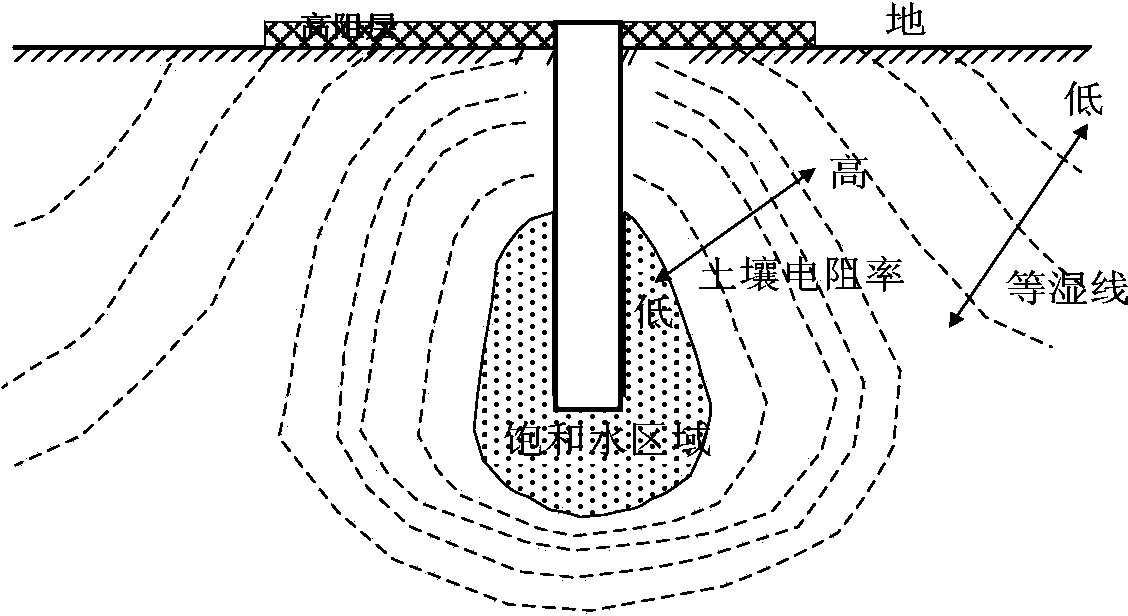
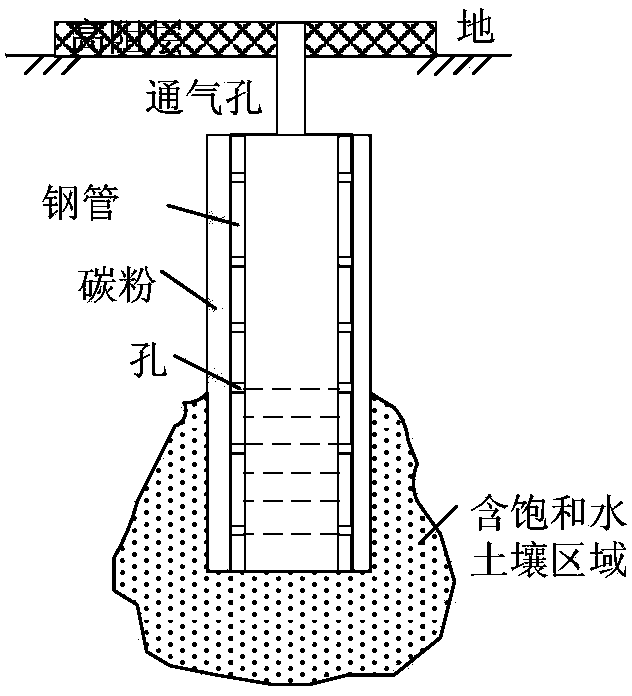
Method for improving local step potentials of transformer substation
ActiveCN103928846AIncrease humidityIncrease tolerance limitEarthing arrangementsTolerance limitTransformer
The invention relates to a method for improving local step potentials of a transformer substation, and belongs to the technical field of transformer substation operation and high voltage, wherein the method is used for improving the local step potentials of a standard-exceeding area of the transformer substation and protecting the safety of personnel in the transformer substation. The method comprises the steps of analyzing the performance of a grounding network, determining the area with the step potentials exceeding the standard, surveying the water lever of the transformer substation, determining the length of a grounding pipe, manufacturing the grounding pipe, arranging the grounding pipe in a buried mode and welding the grounding pipe and the horizontal grounding network. The method increases the human body tolerance limiting value, lowers the step potentials and effectively protects the personal safety.
Owner:广东电网有限责任公司惠州供电局 +3
Cortical interface for motor signal recording and sensory signal stimulation
ActiveUS10137303B2Small sizeIncrease the number ofHead electrodesPrinted circuit aspectsSensory FeedbacksProsthesis
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to the at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that is / are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. The output signals provide control for a motor prosthesis and the inputs signals provide sensory feedback for the motor prosthesis. The invention, or components thereof, is / are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Composite electrode for recording deep brain signals
PendingCN107198522AImprove recording effectEasy to collectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityComposite electrode
The invention relates to a composite electrode for recording deep brain signals. The composite electrode comprises at least one large electrode contact capable of recording local field potential and at least one microelectrode contact capable of recording single cells in brain tissue and is characterized in that a large electrode wire and a microelectrode wire are arranged in the composite electrode, the large electrode wire is electrically connected with the large electrode contact, and the microelectrode wire is electrically connected with the microelectrode contact. The composite electrode has the advantages that single cell potential and local field potential in the brain tissue can be recorded at the same time, a good recording effect is achieved, electric signals can be well collected and clearly displayed even when the electric signals are weak, and the composite electrode is of great significance and value to the diagnosis, treatment and researches of various neurologic diseases such as epilepsy.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
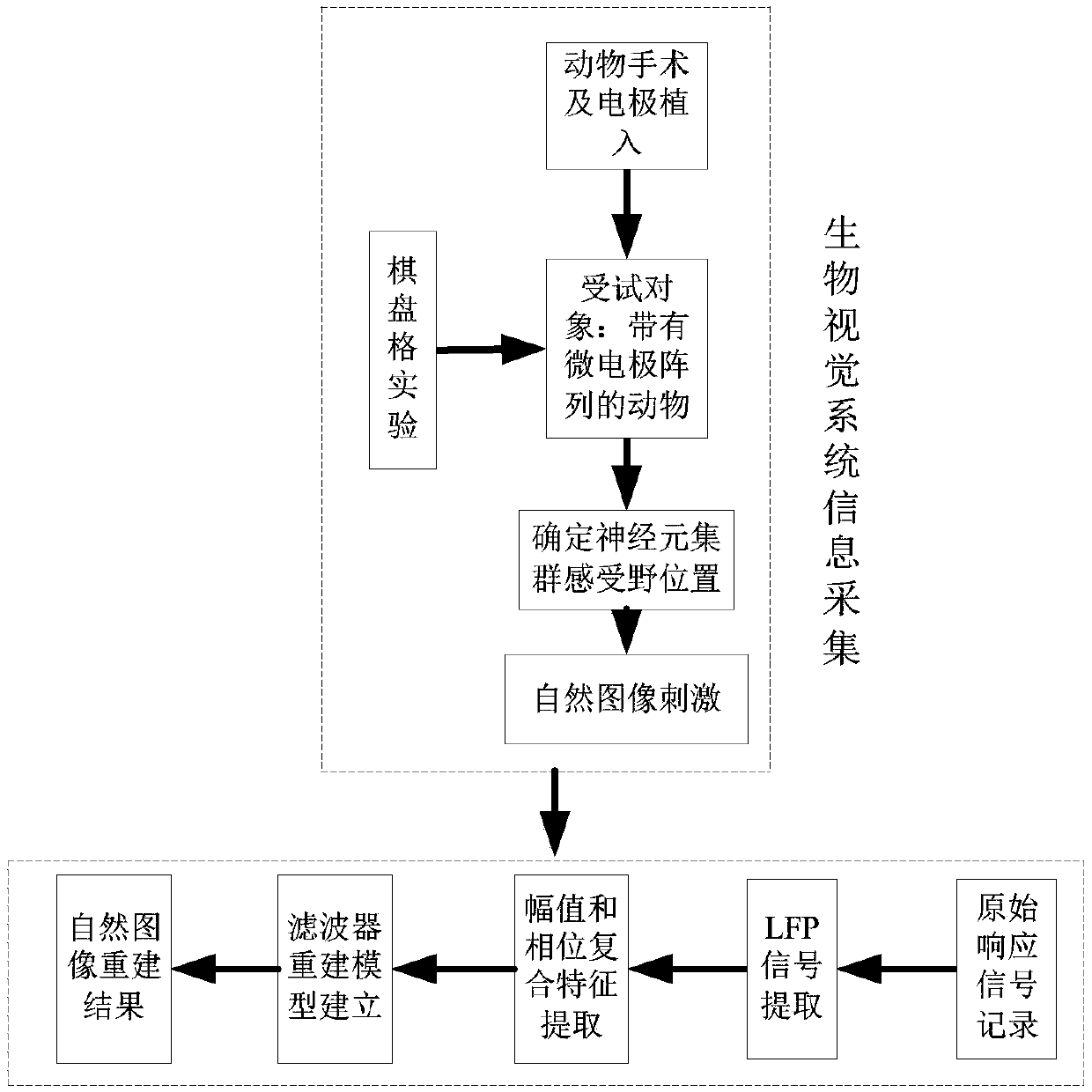
Natural image reconstruction method based on local field potential amplitude-phase composite features
InactiveCN108961219AHigh degree of reductionImprove reconstruction resultsImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingVisual cortex
The invention discloses a natural image reconstruction method based on local potential amplitude-phase composite features, and relates to the technical field of information processing. The natural image reconstruction method comprises the steps of collecting a local field potential signal of the visual cortex of the brain under image stimulation, and respectively processing the image stimulation and the local field potential signal to obtain sample stimulation data, target simulation data, sample response data and target response data; obtaining a sample amplitude-phase composite feature and atarget amplitude-phase composite feature according to training response data and the target response data, and constructing a sample response matrix and a target response matrix; building a reconstruction filter model according to the sample stimulation data and the sample response matrix; substituting the target response matrix into the reconstruction filter model, and obtaining a natural imageafter acquiring target reconstruction stimulation data. The natural image reconstruction method solves problems that the existing image stimulated reconstruction implemented based on biological visionis complex in image reconstruction experiment process and that the reconstruction image is poor in effect and unclear.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Implantable brain-computer interface neuron spike potential classification method
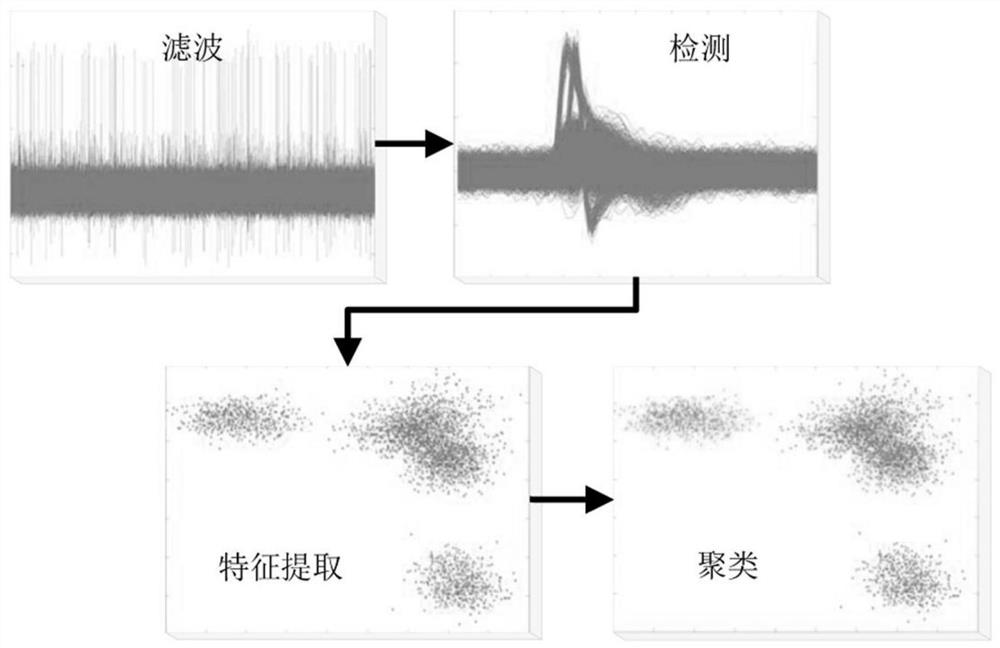
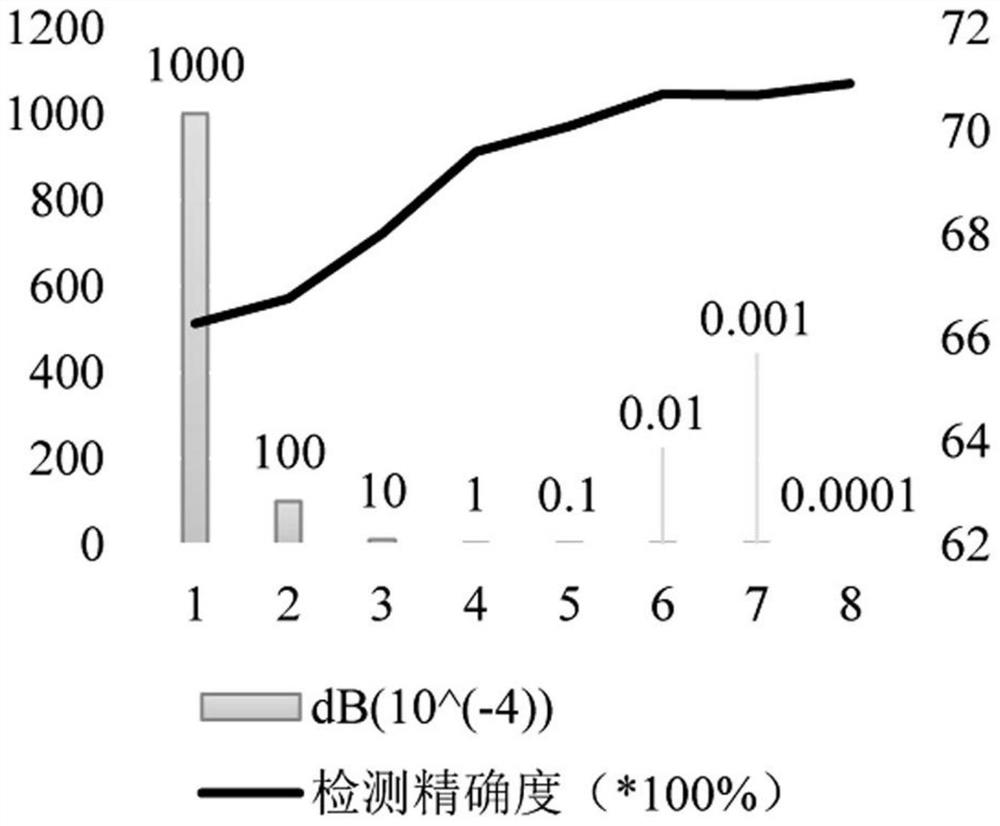
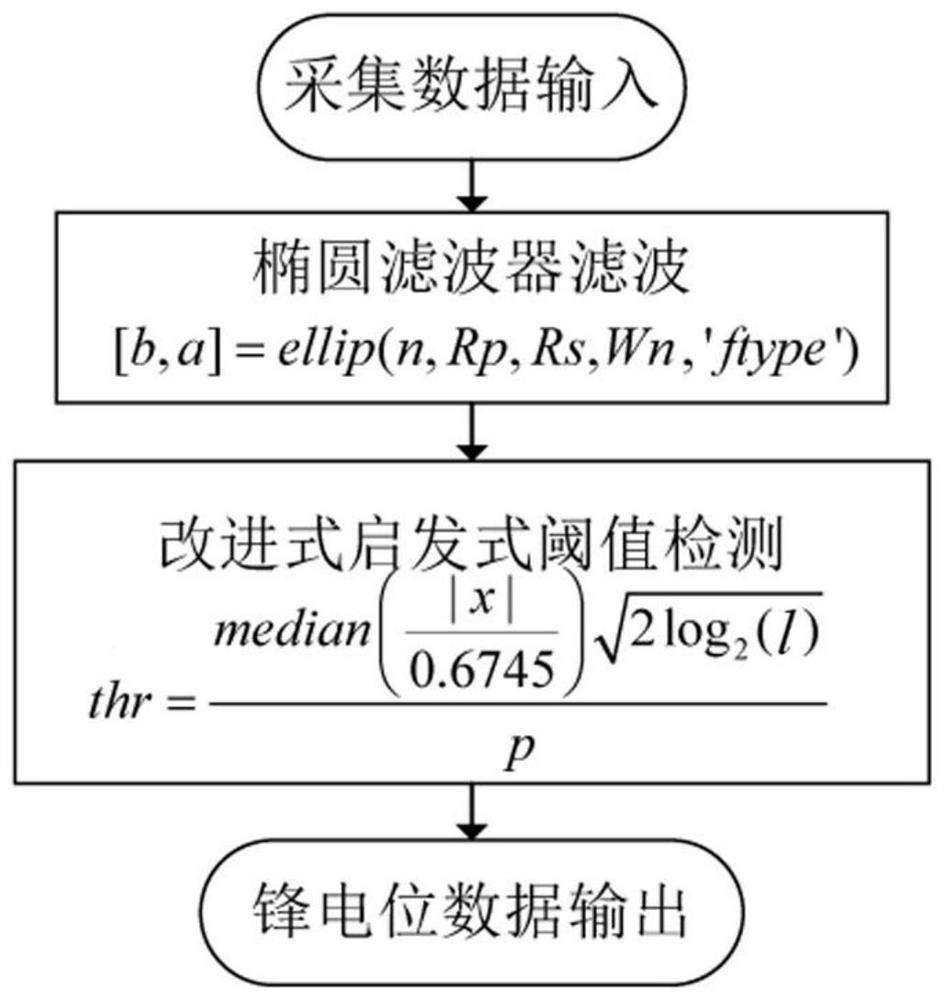
PendingCN113378737ASolve low signal-to-noise ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringCluster algorithmFeature extraction
The invention provides an implantable brain-computer interface neuron spike potential classification method. The method comprises the following steps of: a, filtering an original signal by using a band-pass elliptical filter, and filtering out local field potential of a low-frequency band and background noise of a part of a high-frequency band in the signal; b, using an improved heuristic threshold detection algorithm to extract and retain spike potential data in the filtered signal; c, performing feature extraction on the spike potential data by using principal component analysis; and d, aggregating the data which represents the spike potential and is mapped in the feature space into different clusters by using a K multi-mean clustering algorithm based on improved dynamic time warping. Through the processing of the method provided by the invention, the low-amplitude spike potential is fully reserved from the original signal, and the effective classification of the high-precision spike potential is realized.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
System and method of detecting and predicting seizures
InactiveUS10172567B2Raise the possibilityIncrease firing rateElectroencephalographyImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicinePartial field
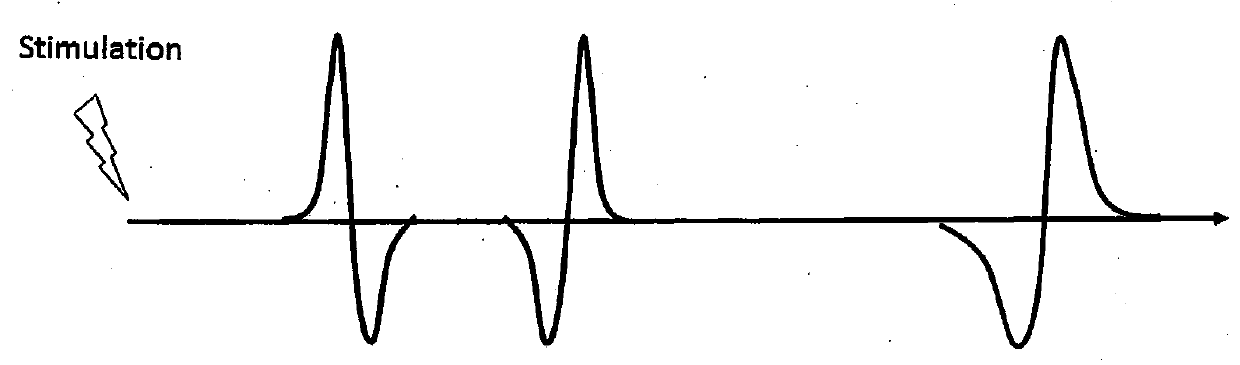
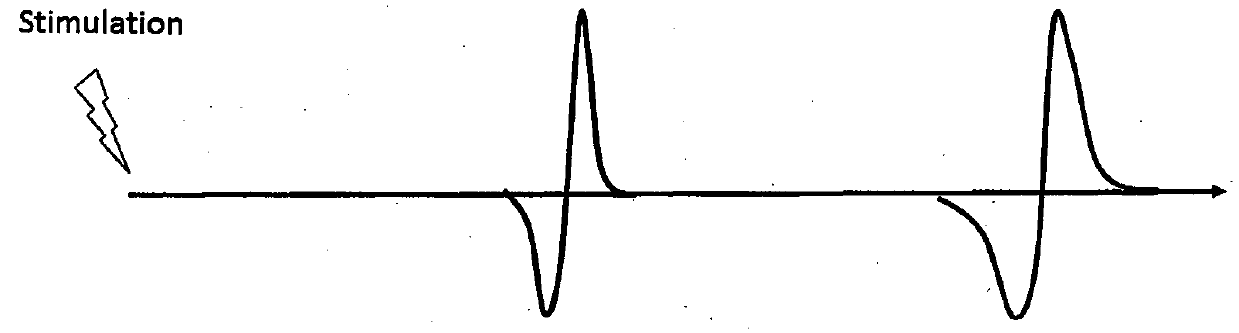
The present invention describes systems and methods for predicting and detecting a seizure in a subject. The methods of the invention comprise measuring interneuron synchrony in terms of the coherence between interneuron action potentials and local field potential oscillations. In one embodiment, the detection of specific patterns of coherence, correlation and firing rate of interneurons predicts an upcoming seizures.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Noise deep-brain-stimulation system based on delayed feedback control
ActiveCN110681050ADischarge conditions are good for regulationFlexible adjustment of electrode functionHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerThalamus
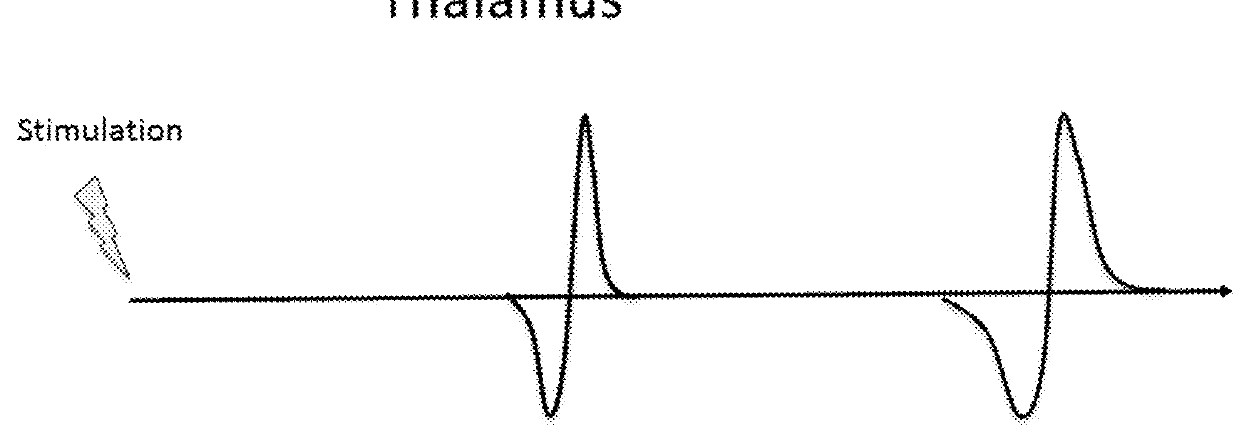
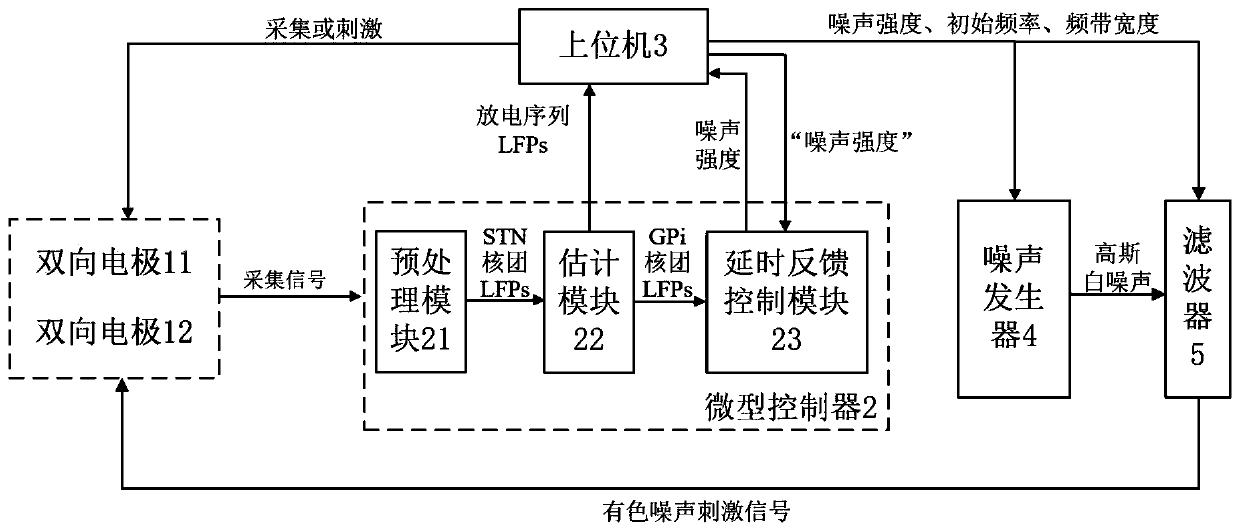
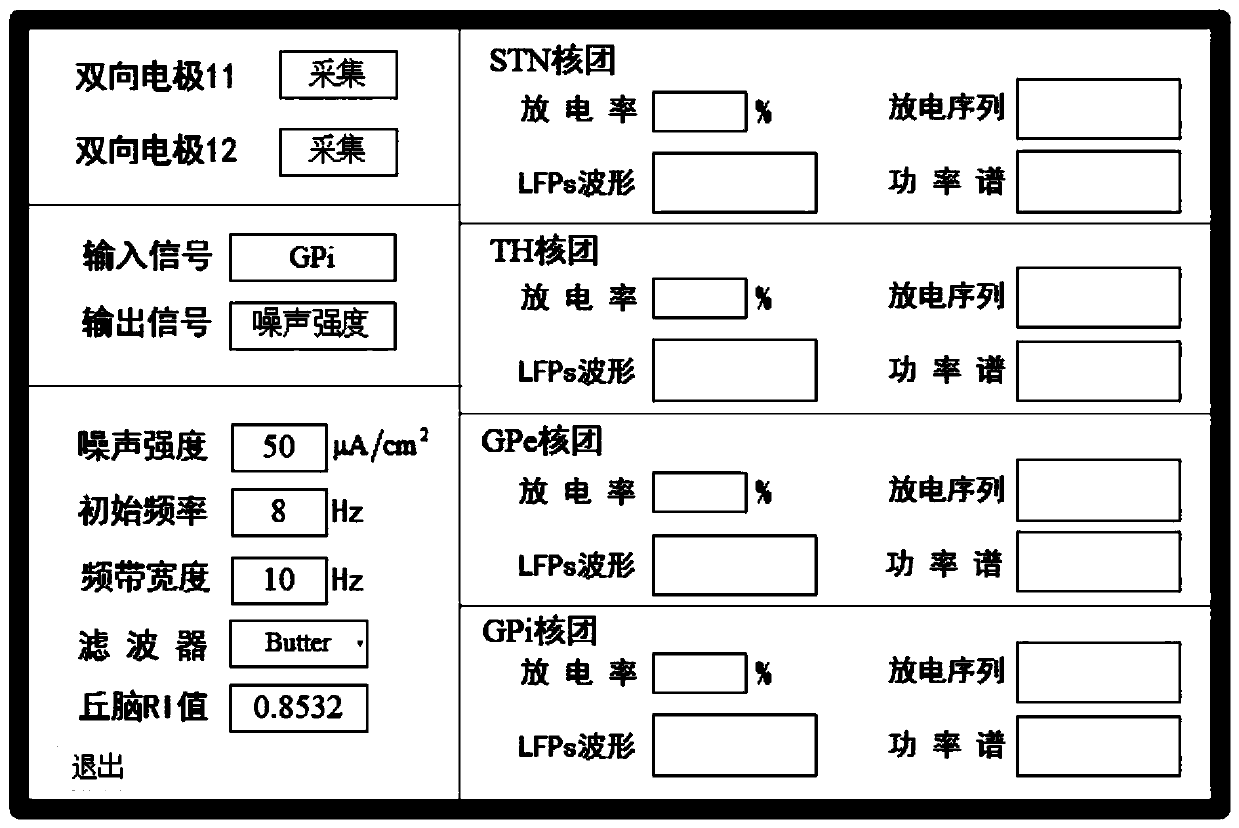
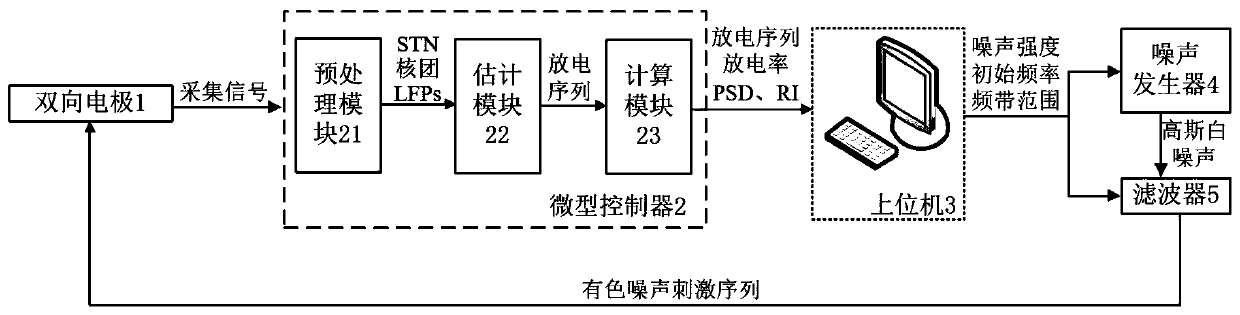
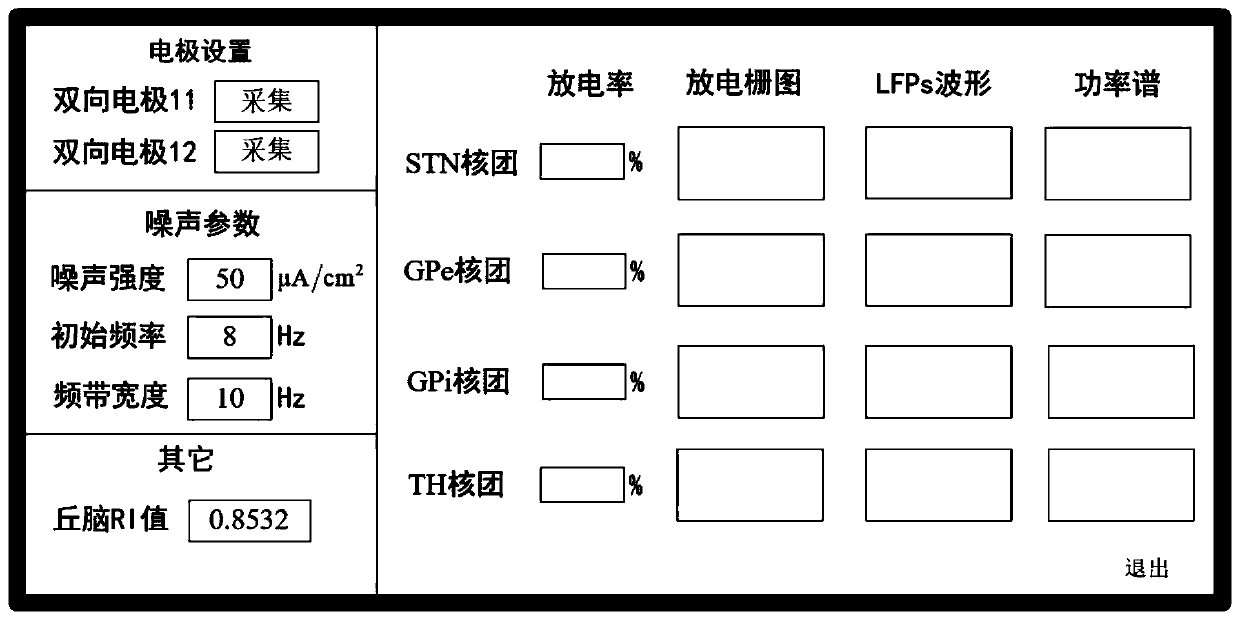
The invention relates to a noise deep-brain-stimulation system based on delayed feedback control. The noise deep-brain-stimulation system based on delayed feedback control is characterized by comprising two bidirectional electrodes, a microcontroller, a host computer, a noise generator and a filter, wherein the two bidirectional electrodes are separately inserted into STN in a left basal nucleus and a right basal nucleus of the brain, the bidirectional electrodes have two properties of acquisition and stimulation, acquisition of local field potentials (LFPs) of the STN of a subthalamic nucleusand application of noise stimulation are achieved, and an acquisition signal is transmitted to the microcontroller; the microcontroller comprises a pre-processing module, an estimation module and a delayed feedback control module; the host computer is used for calculating and displaying a discharge sequence, the LFPs, a discharge rate and power spectral density (PSD) of the nucleuses in the basalnucleuses, a discharge sequence and a reliability index (RI) of a thalamus nucleus and all noise parameters, and transmitting the noise parameters to the noise generator and the filter.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
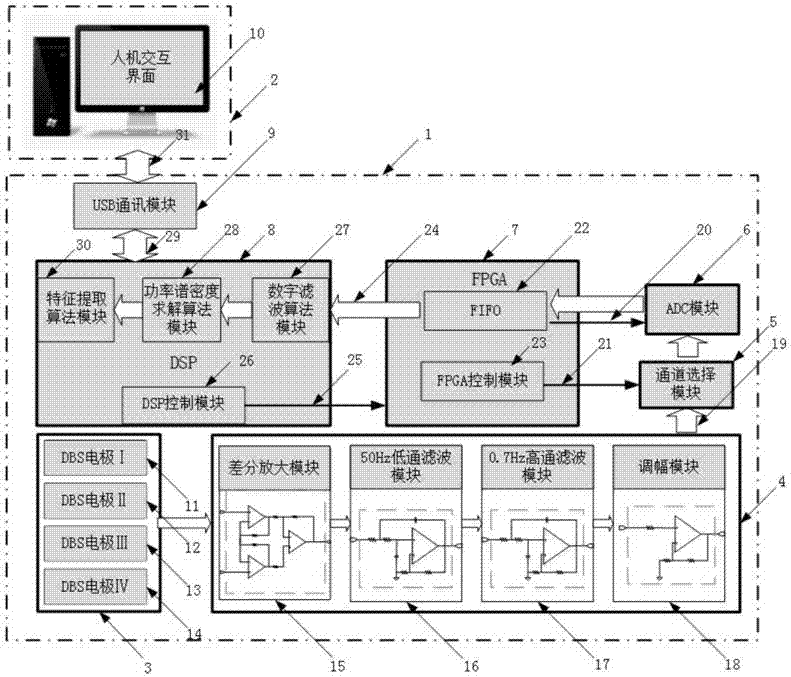
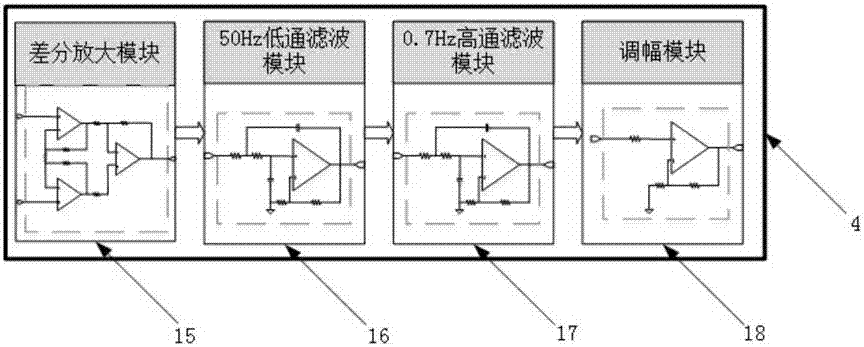
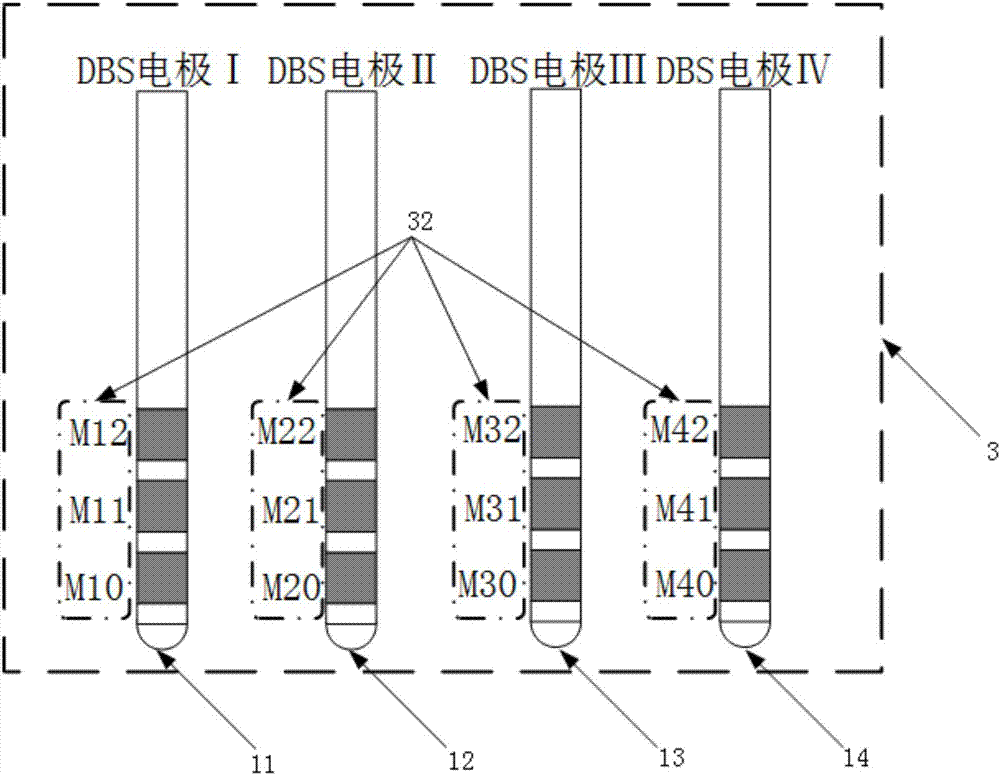
DSP+FPGA based local field potential real time detection analysis platform eliminating DBS artifacts
InactiveCN107510888ARealize monitoringRealize analysisHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringData operationsPartial field
The invention provides a DSP+FPGA based local field potential real time detection analysis platform eliminating DBS artifacts. According to the invention, advantages of efficient data operation and processing and high time sequence logic control of DSP and FPGA are taken in combination, a DSP and FPGA combined system is adopted as a lower computer for performing collection, amplification, filtering, characteristic extraction and analysis on local field potential signals and uploading local field potential information subjected to analysis and processing to an upper computer through a USB communication module for display. The upper computer can realize setting of a collection channel of the local field potential signals and switching between channel setting and a display function through interface writing. The invention has an effect that by adding the signal collection and pre-processing functions in a DBS electrode, direct collection and pre-processing of the local field potential signals are enabled in DBS implementation process and closed-loop DBS is made possible.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Noise depth brain stimulation system for Parkinson's disease
InactiveCN110664401ASuppress synchronous discharge phenomenonState reliefElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
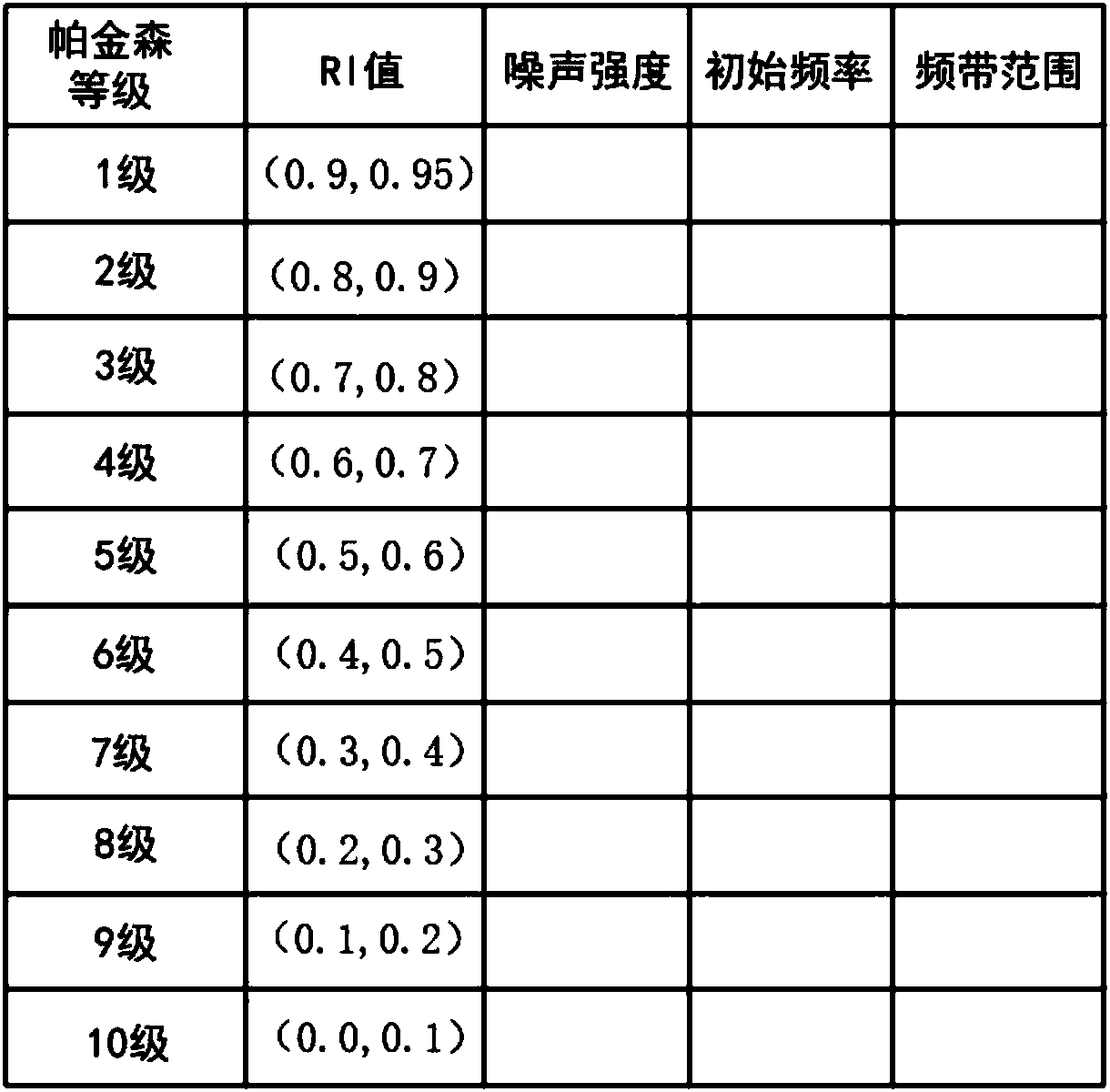
The invention relates to a noise depth brain stimulation system for Parkinson's disease. The noise depth brain stimulation system is characterized by consisting of a bidirectional electrode, a microcontroller, an upper computer, a noise generator and a filter, wherein the bidirectional electrode has two attributes of collection and stimulation, collection of a subthalamic nucleus (STN) nucleus local field potential (LFPs) and application of noise stimulation are respectively realized by setting the attributes of the electrode on the upper computer, and the bidirectional electrode can transmita discharge signal to a microcontroller; a Parkinson's disease state grade distribution table is stored in the upper computer, the table is divided into ten grades according to RI values, if a RI value is smaller, the Parkinson's disease state is more serious, grade classification is conducted on the current Parkinson's disease state according to the table, the parameters corresponding to noise stimulation are extracted, and the parameters are transmitted to the noise generator and the filter.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
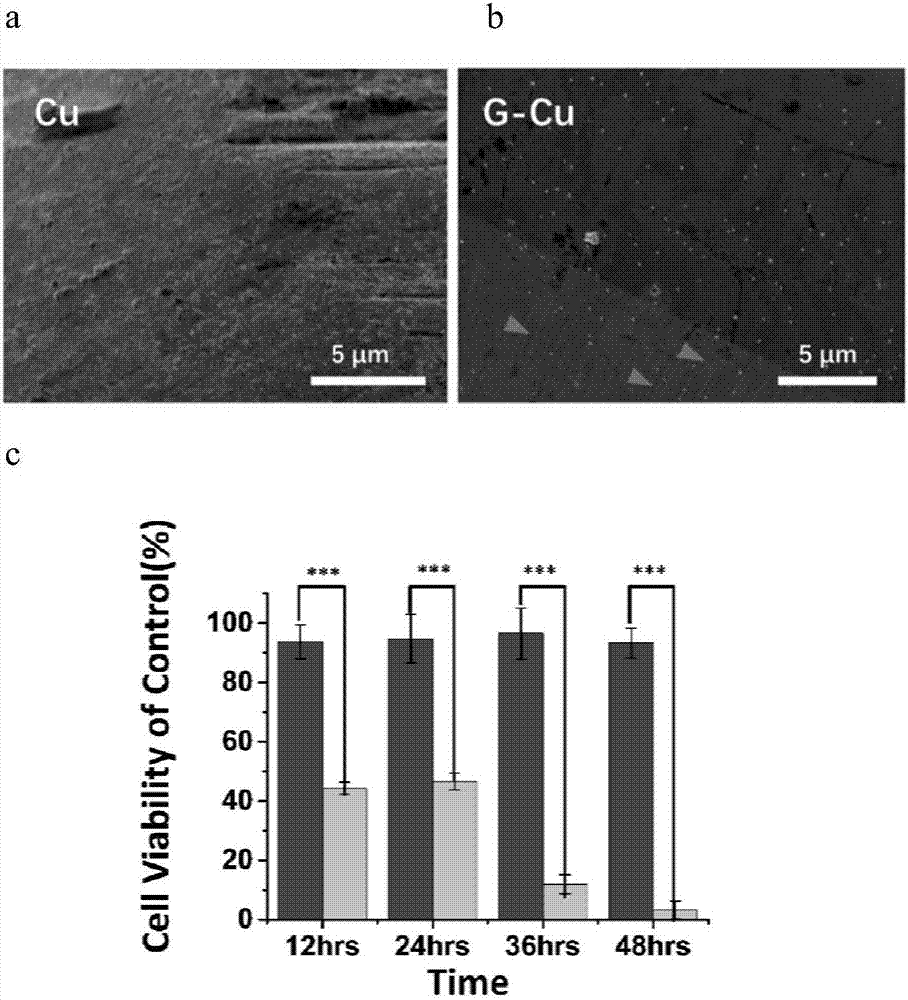
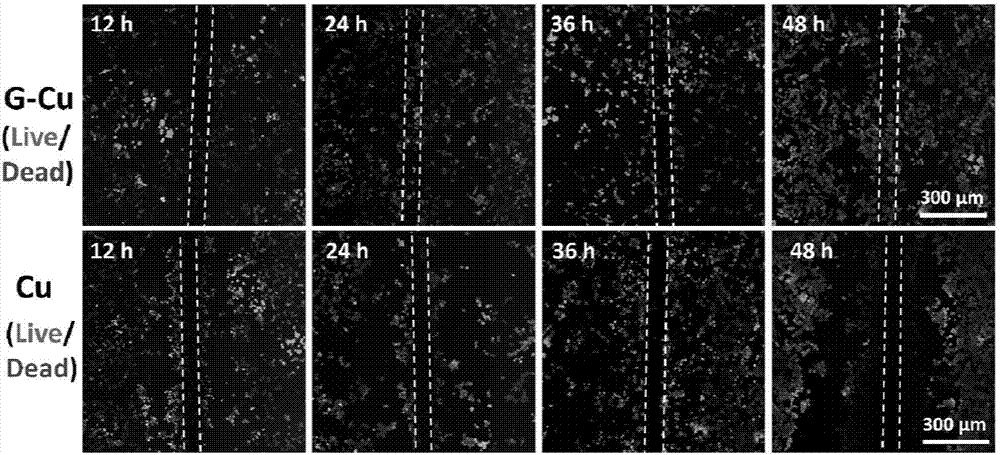
Graphene cladded copper-base biological material as well as preparation method and application thereof
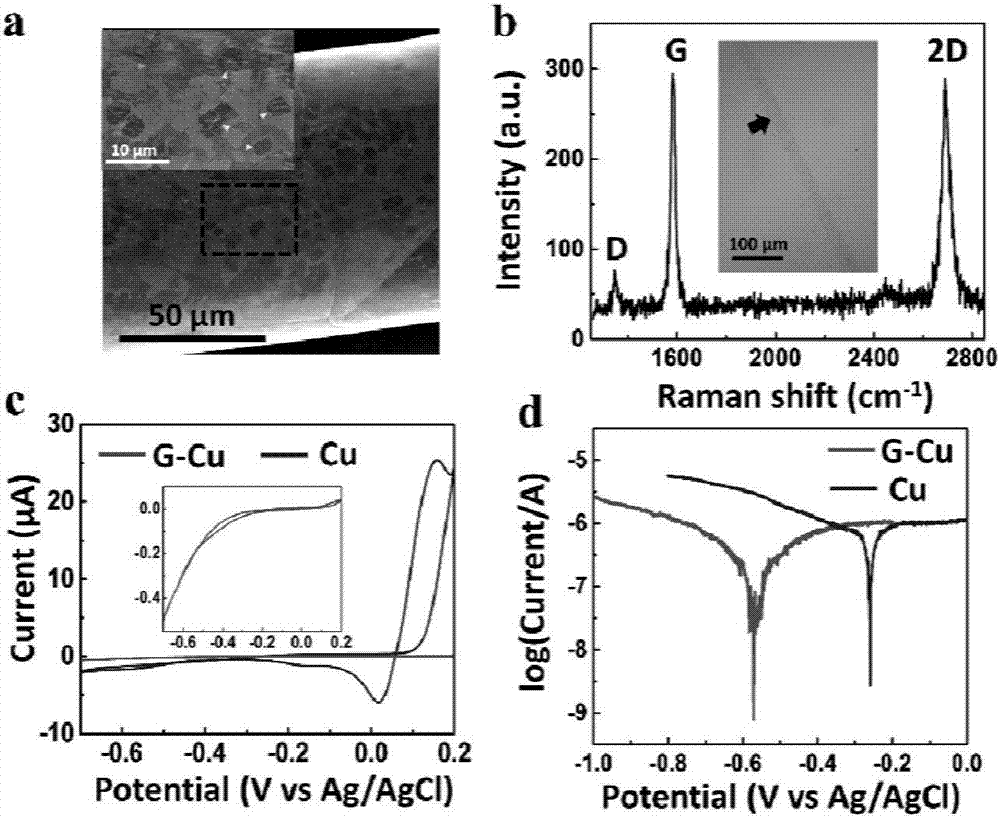
ActiveCN107875456APrevent spontaneous corrosionInhibition releaseSurgeryChemical vapor deposition coatingIn vivoBiological materials
The invention discloses a graphene cladded copper-base biological material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The graphene-packaged composite material contains copper and graphene, wherein the surface of copper is totally packaged with graphene. The material has a good cladding effect, the toxin introduced by copper can be eliminated, and the death of cells and the necrosis and edema of tissues are avoided. The material can be taken as an electrode, particularly a neural electrode and can be applied to an in vivo or in vitro signal recording such as the signal recording of neuronal discharging and / or local field potential change. The material and a commercial platinum-iridium alloy electrode do not generate an artifact in a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging technique, and the observation of the quality and an implementation position of a nuclear magnetic resonance is greatly assisted.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com