Continuous flipping elimination decoding method based on absolute value change of log-likelihood ratio
A technology of log-likelihood ratio and absolute value, which is applied in the field of continuous elimination of flip decoding based on the change of the absolute value of log-likelihood ratio, which can solve the problems of large delay and high decoding complexity, and reduce the decoding complexity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
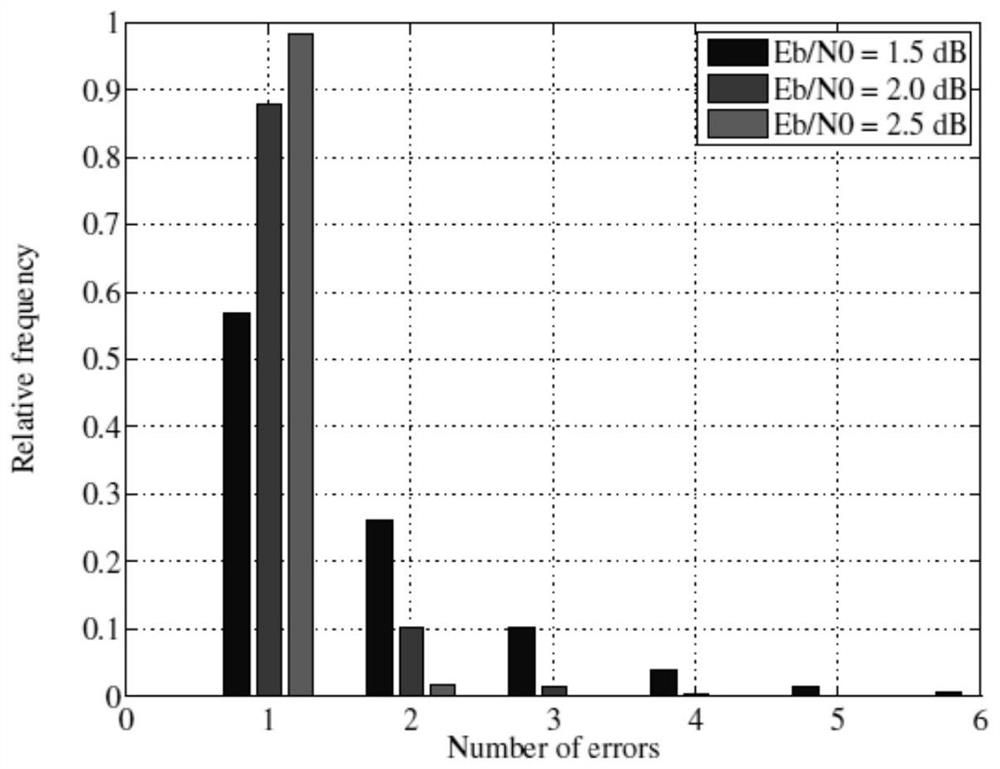
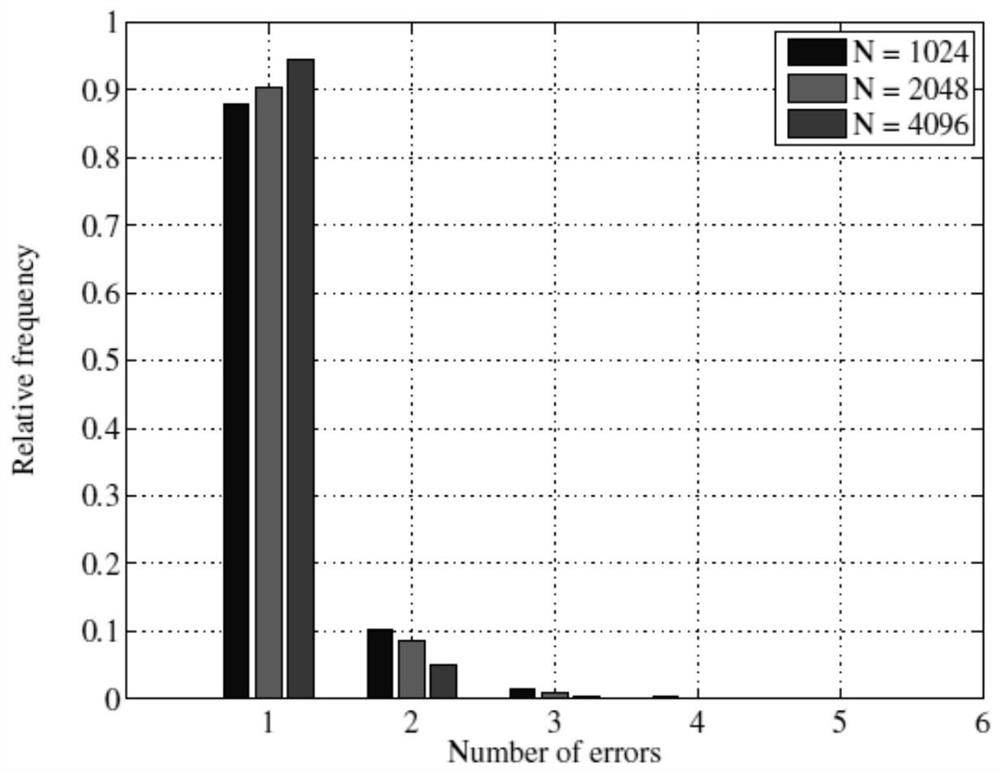
[0040] This embodiment considers the advantages of the SCL algorithm, because the SC decoding algorithm is a local optimal algorithm, and it chooses a direction that is more likely to become the correct bit in each step and advances. The SCL algorithm is a globally optimal algorithm, and it will finally choose a path with the largest metric value, which is often the one with the largest sum of LLR absolute values. In other words, the accumulation of the absolute value of the LLR of the path that can be decoded correctly by the SCL algorithm but cannot be decoded by the SC algorithm is often larger than the accumulation of the absolute value of the LLR of the wrong path obtained by the SC algorithm .
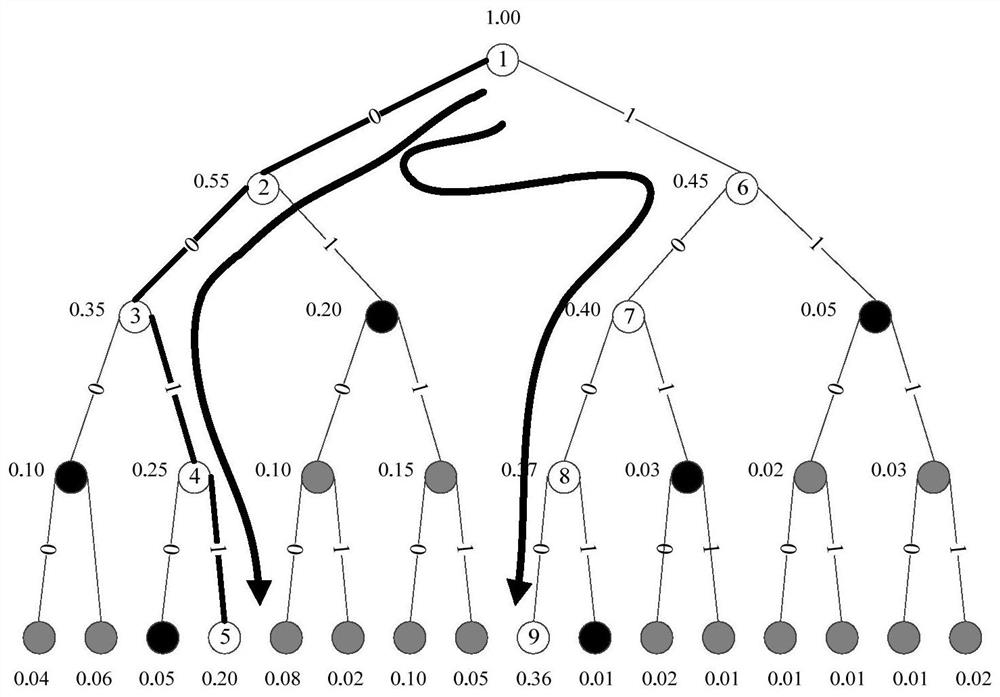
[0041] like Figure 4 Shown, a kind of continuous elimination flip decoding method based on logarithmic likelihood ratio absolute value change, described method comprises steps as follows:
[0042] S1: After a frame is decoded by the SC decoding algorithm, perform a CRC check o...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A computer system includes a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and operable on the processor. When the processor executes the computer program, the steps of the method are as follows:
[0063] S1: After a frame is decoded by the SC decoding algorithm, perform a CRC check on the obtained decoding result;
[0064] S2: When the CRC check is not passed, a flip list is obtained by sorting the LLR absolute value of the decoded bits from small to large;
[0065] S3: Select a bit in sequence from the inversion list, and invert its decoding result. After being inverted by the SCF decoding algorithm, calculate the accumulated value of the LLR absolute value change of a certain part of the bit after the bit; A part of bits is represented by a set S, and the set S includes the number S of bits N, select several kinds of information on the position of the bit;
[0066] S4: Judging whether the accumulated value is greater than the set threshold V, the...
Embodiment 3
[0068] A computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps of the method implemented are as follows:
[0069] S1: After a frame is decoded by the SC decoding algorithm, perform a CRC check on the obtained decoding result;
[0070] S2: When the CRC check is not passed, a flip list is obtained by sorting the LLR absolute value of the decoded bits from small to large;
[0071] S3: Select a bit in sequence from the flipping list, and flip its decoding result. After being flipped by the SCF decoding algorithm, calculate the cumulative value of the LLR absolute value change of a certain part of the bit after the bit; A part of bits is represented by a set S, and the set S includes the number S of bits N , select several kinds of information on the position of the bit;
[0072] S4: Judging whether the accumulated value is greater than the set threshold V, then consider the inverted bit to be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com