Collaborative learning-based visual malicious software detection method
A malware and detection method technology, applied in the field of cyberspace security, can solve the problems of high analysis cost, left idle, a large number of manual decoding, etc., and achieve the effect of solving collection difficulties and reducing dependence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
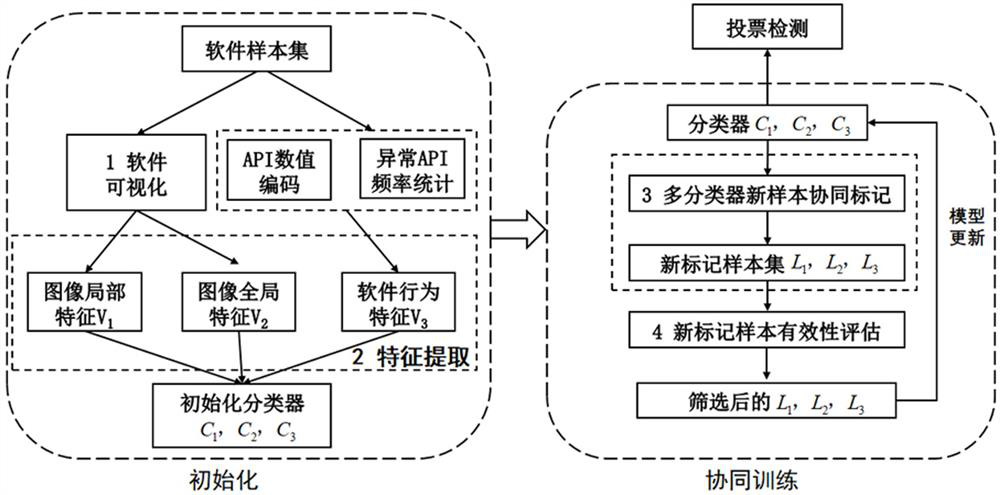
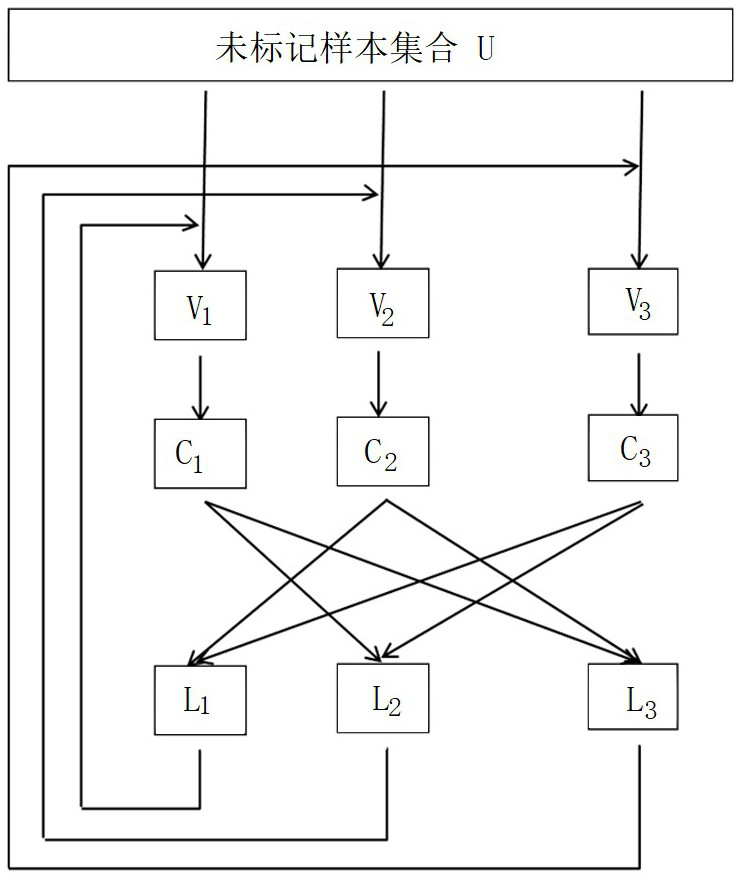
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, a visual malware detection method based on collaborative learning includes two processes of initialization and collaborative training. The initialization process includes: 1. Software visualization, 2. Feature extraction; the collaborative training process includes: 3. Multi-classifier Collaborative labeling of new samples, 4. Effectiveness evaluation of new labeled samples.
[0064] Next, this embodiment is described in detail:
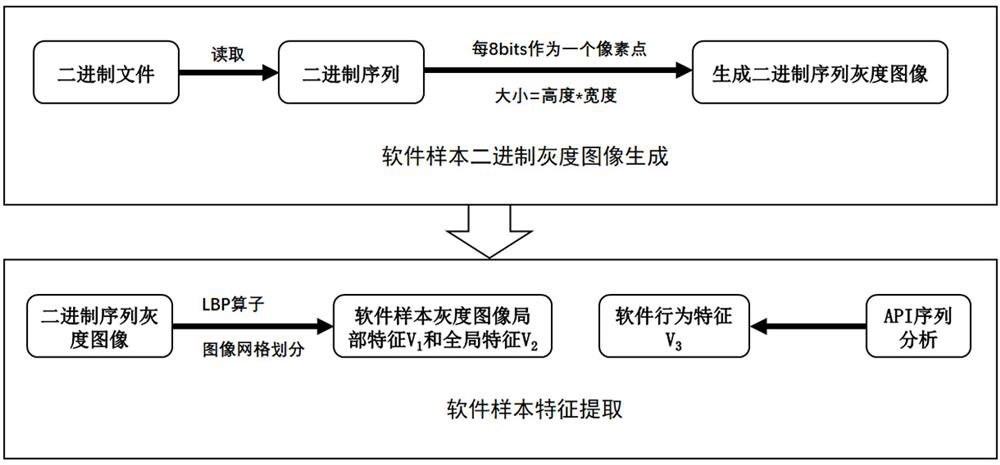
[0065] (1) Software visualization: After obtaining the binary file of the software, first read each binary file to obtain the binary string corresponding to each file, where each character read in the binary file is expressed as 8 bits unsigned variable. Then the obtained binary strings are formed into a two-dimensional matrix; the values in the two-dimensional matrix are converted into pixel values, and each pixel value is spliced into a grayscale image according to the color transition from black to white. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com