Quasi-coaxial crack feed cavity-backed antenna
A coaxial, cavity-backed technology, used in the field of quasi-coaxial slit-fed cavity-backed antennas, can solve the problems of limited bandwidth, high-frequency end pattern distortion, and easy damage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
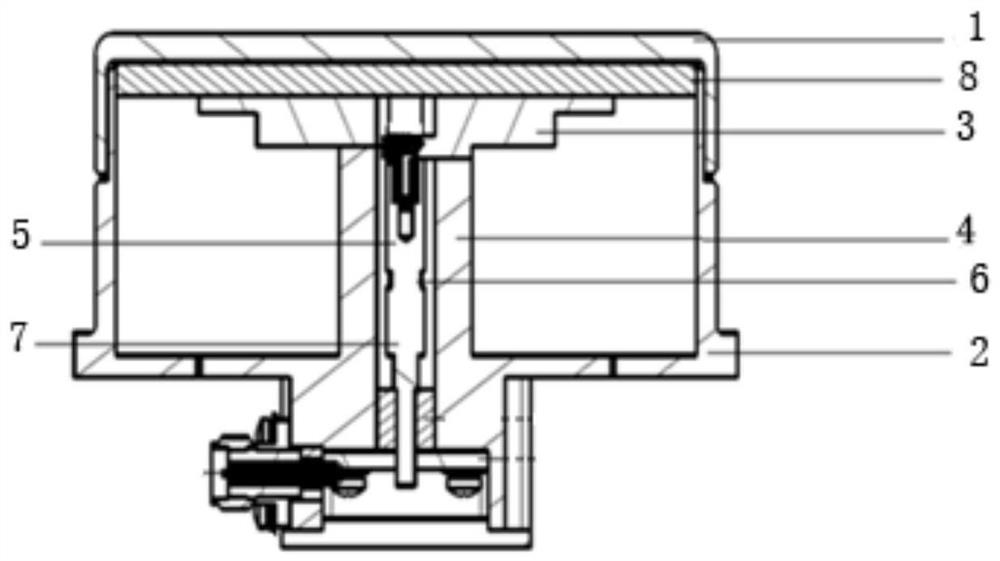
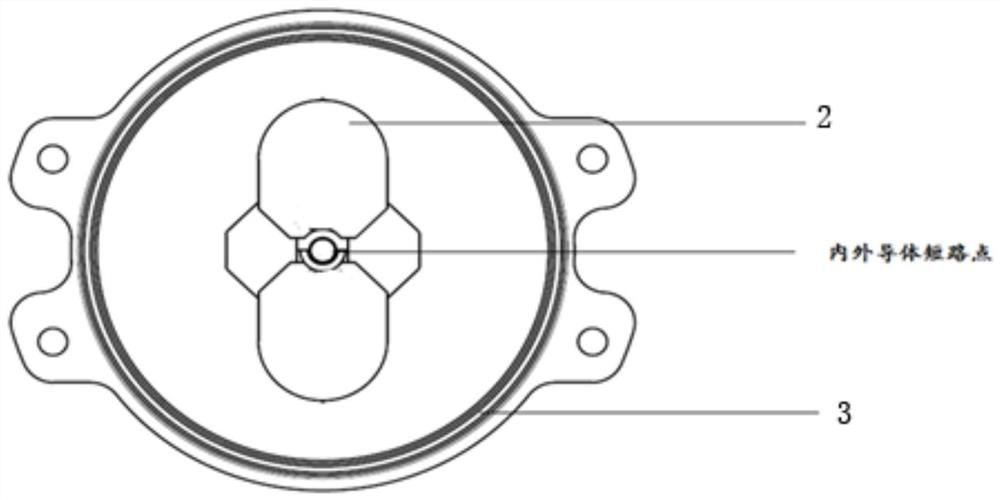
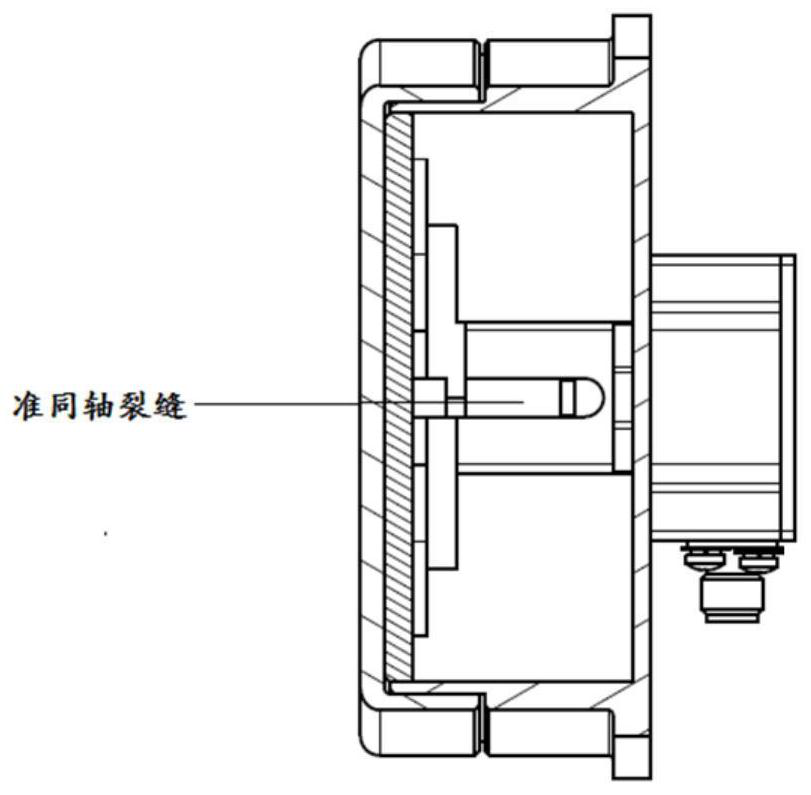
[0038] This embodiment specifically provides a quasi-coaxial slot-fed cavity-backed antenna. Compared with the existing cavity-backed antenna, its improvement lies in expanding The operating bandwidth of the cavity antenna. Its overall structure is as figure 1 As shown, the antenna includes a symmetrical vibrator, an impedance transformer, a dielectric radome, a quasi-coaxial crack balancer, a foam layer, and a reflective back cavity; the dielectric radome is assembled on the reflective back cavity, and the symmetrical vibrator is installed On the quasi-coaxial crack balancer, the impedance transformer is assembled in the crack of the quasi-coaxial crack balancer, and the impedance transformer is also connected to the symmetrical vibrator, and the foam layer is arranged on a symmetrical Between the vibrator and the dielectric radome, it is used to fix the relative distance between the symmetrical vibrator and the dielectric radome.
[0039] In this example, if figure 1As sh...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A quasi-coaxial slot-fed cavity-backed antenna provided in this embodiment has the same design idea and working principle as that of Embodiment 1, and the only difference is that the specific parameters are different. The antenna includes a symmetrical vibrator, an impedance transformer, a dielectric radome, A quasi-coaxial crack balancer, a foam layer and a reflective back cavity; the dielectric radome is assembled on the reflective back cavity, the symmetrical vibrator is mounted on the quasi-coaxial crack balancer, and the impedance converter is assembled on the In the crack of the quasi-coaxial crack balancer, and the impedance transformer is also connected to the symmetrical vibrator, the foam layer shown is arranged between the symmetrical vibrator and the dielectric radome, for fixing the symmetrical vibrator and the dielectric radome the relative distance between them.
[0051] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the symmetrical vibrator is a stepped structu...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A quasi-coaxial slot-fed cavity-backed antenna provided in this embodiment has the same design idea and working principle as that of Embodiment 1, and the only difference is that the specific parameters are different. The antenna includes a symmetrical vibrator, an impedance transformer, a dielectric radome, A quasi-coaxial crack balancer, a foam layer and a reflective back cavity; the dielectric radome is assembled on the reflective back cavity, the symmetrical vibrator is mounted on the quasi-coaxial crack balancer, and the impedance converter is assembled on the In the crack of the quasi-coaxial crack balancer, and the impedance transformer is also connected to the symmetrical vibrator, the foam layer shown is arranged between the symmetrical vibrator and the dielectric radome, for fixing the symmetrical vibrator and the dielectric radome the relative distance between them.
[0060] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the symmetrical vibrator is a stepped structu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com