Method for migrating generative adversarial network with adversarial learning and discriminative learning
A discriminative and adversarial technology, applied in the field of deep learning neural networks, which can solve problems such as difficult image datasets, training, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
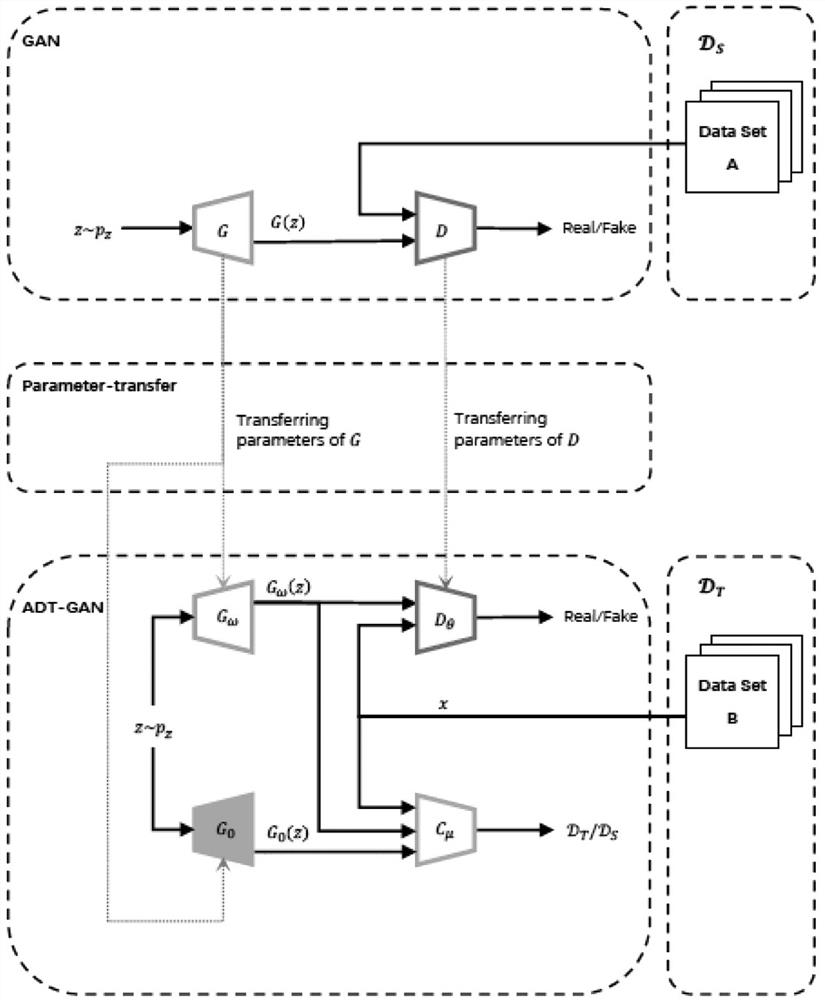
[0064] An adversarial neural network model ADT-GAN and a training method based on the combination of adversarial learning and discriminative row learning, which includes:
[0065] S1. Prepare image dataset
[0066] Prepare a source domain image dataset with a larger amount of data and a target domain image dataset with a smaller amount of data, and perform the following processing on the source domain dataset and the target domain dataset respectively:
[0067] 1) Split the image data set into source domain data set and target domain data set;
[0068] 2) Standardize the pictures in the dataset to the same resolution;
[0069] MNIST is a dataset of handwritten digits, consisting of 60,000 training data and 10,000 test data of images, and the present invention only uses training data. For the MNIST handwritten data set, each handwritten digit image is normalized to a grayscale image of 28×28 pixels and placed in the center of the image. In order to test the effect of ADT-GAN...
Embodiment 2
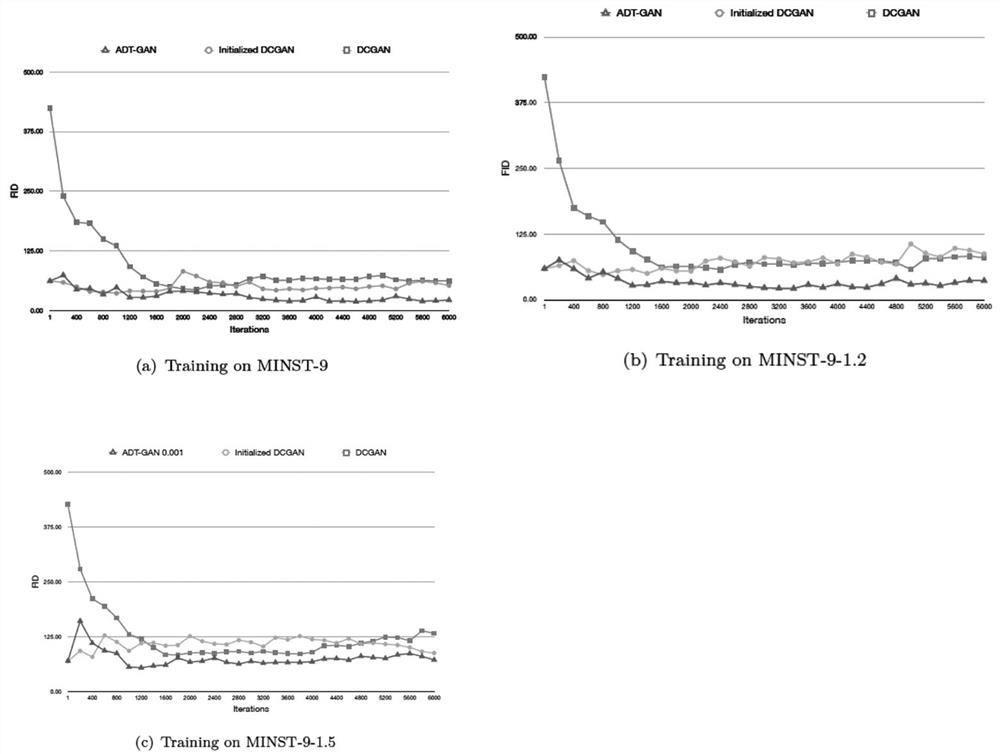
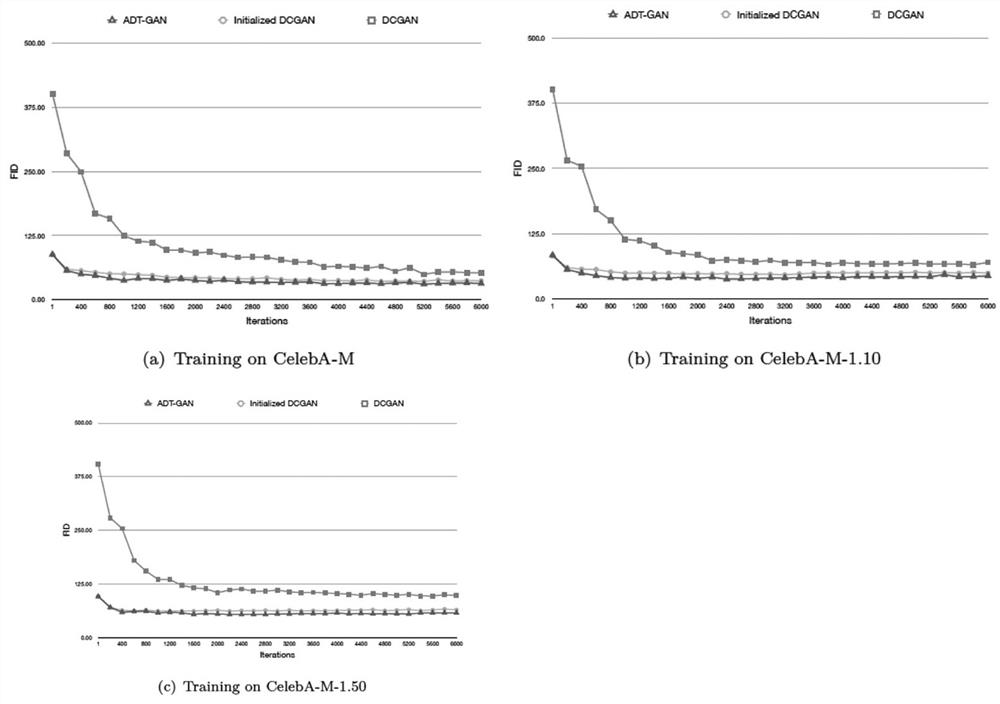
[0118] Example 2 Evaluation of the model after training
[0119] The evaluation of GAN (including ADT-GAN) can measure the similarity between the generated image and the real image by the Fréchet initial distance (FID) of the intermediate features of the network obtained from the generated image and the real image in the Inception v3 image classification model. The generated image and the real image are obtained in the Inception v3 image classification model. The intermediate features of the network can be modeled as a Gaussian distribution, and the mean values are m r and m g , the covariance matrix is Σ r and Σ g . The FID describing the statistical similarity of two intermediate features is defined as
[0120]
[0121] The smaller the FID, the more similar the two groups of images are; the larger the FID, the greater the difference between the two groups of images.
[0122] The FID values of DCGAN, initialized DCGAN and ADTGAN in the same iteration are used ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com