Direct cell conversion-based method for differentiation of neural stem cells into astrocytes
A technology of astrocytes and neural stem cells, applied in nervous system cells, biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, etc. Problems such as low differentiation time efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Example 1: Astrocyte Differentiation Medium
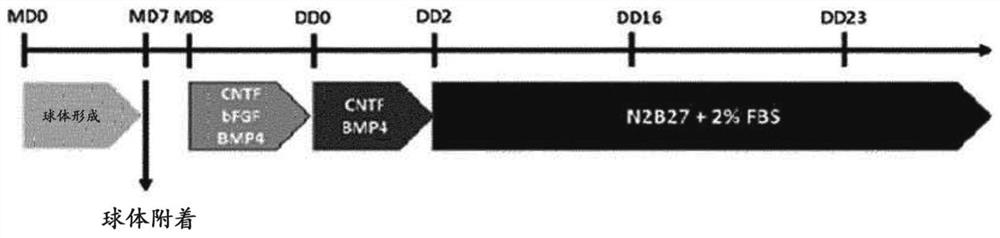
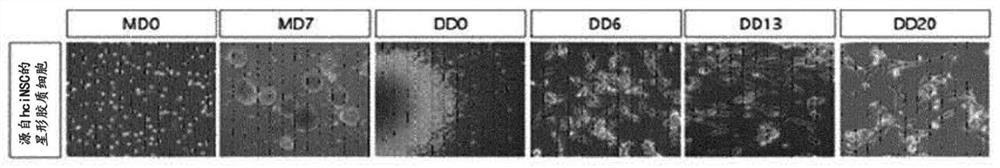
[0093] Prepare 1x10 in a 60mm Petri dish 5 Personal neural stem cells (see Korean Patent No. 1816103) were cultured the next day in neurobasal medium containing DMEM / F12, N2, B27, bFGF, and EGF. Then, the culture solution was changed every 2 to 3 days. On day 5, cells were removed using Accutase and seeded on Petri dishes 1x10 6 cells were cultured in suspension. At this point, the seeded NSCs aggregated together rather than attaching to the bottom of the plate, forming pellets. The medium was replaced with fresh medium every 2 days, and after about 7 days, the spheres had reached a size visible to the naked eye. The plate was first coated with PLO / FN and then the spheres were placed on it.
[0094] The next day, the medium was replaced with a medium for differentiation into astrocytes. A medium containing CNTF (5 ng / ml), bFGF (8 ng / ml) and BMP4 (10 ng / ml) in a basal medium containing DMEM / F12, N2 and B27 was used for ...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2: Validation of Characterization of Differentiated Astrocytes
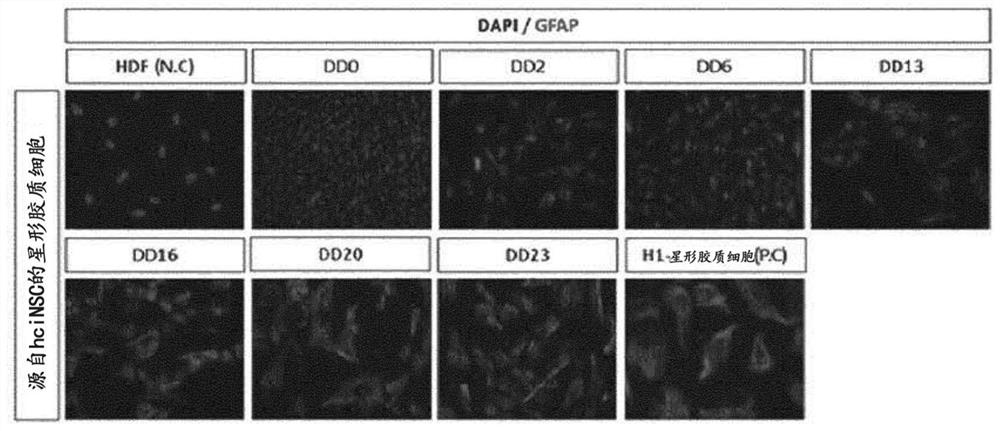
[0097] Neural stem cells were differentiated into astrocytes by the method using the differentiation medium of Example 1, and it was determined whether the differentiated astrocytes exhibited general characteristics.
[0098] First, immunocytochemistry (ICC) was performed to determine whether astrocytes expressed astrocyte markers. Differentiated cells were fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in the refrigerator. Cells were washed twice with PBS buffer and then treated with 0.1% triton X-100 for 10 minutes to create an environment for efficient staining (permeabilization step). After blocking with 10% NDS (normal donkey serum) for one hour, the primary anti-GFAP antibody was diluted 1:400 in 2% NDS to stain the cells, and the cells were treated with the resulting antibody at 4°C for one day. The next day, the cells were reacted with the secondary antibody for one hour at room temperature...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Example 3: Validation of Maturation of Differentiated Astrocytes
[0104] Astrocytes must mature to be able to perform their primary functions, such as supporting the maintenance of neuronal function. To verify this maturation, it was determined whether ion channels were localized in the astrocyte membrane, or whether glutamate uptake was being performed appropriately.
[0105] 3-1: Detection of ion channel markers
[0106] The presence of ion channels in astrocytes was used as a criterion for determining whether astrocytes were mature enough to perform various functions. Therefore, aquaporin 4 (AQP4), Kir4.1, and Twik-1, which are ion channel markers present in astrocytes, were detected by PCR. The results showed that channels that could exchange ions were formed in differentiated astrocytes (Fig. 2A). AQP4, Kir4.1 and Twik-1 were not detected in negative control HDFs (human dermal fibroblasts), but the expression of AQP4, Kir4.1 and Twik-1 was detected in differe...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap