A Human-Robot Collaborative Path Planning Method for Mobile Robots in Unstructured Environments
A mobile robot and unstructured technology, applied in the direction of instruments, non-electric variable control, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of performance decline, operator difficulty, and inability to operate autonomously, so as to improve work efficiency , reduce the burden of manipulation, and overcome the effect of being unable to independently complete complex field planning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
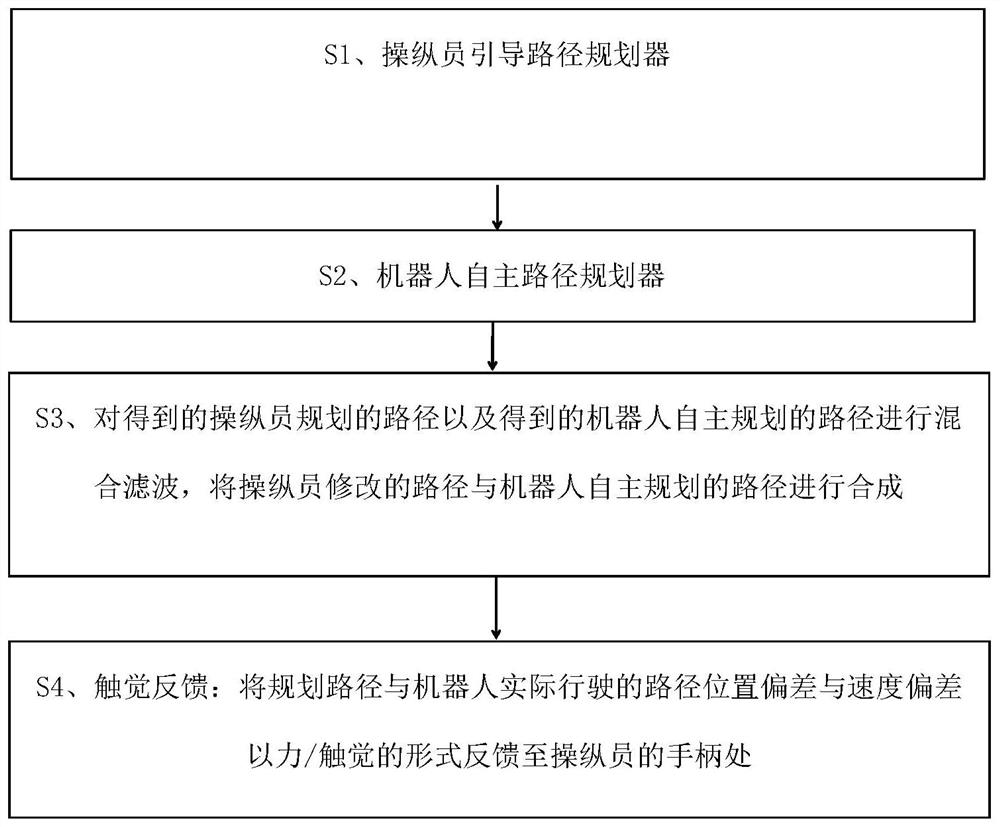
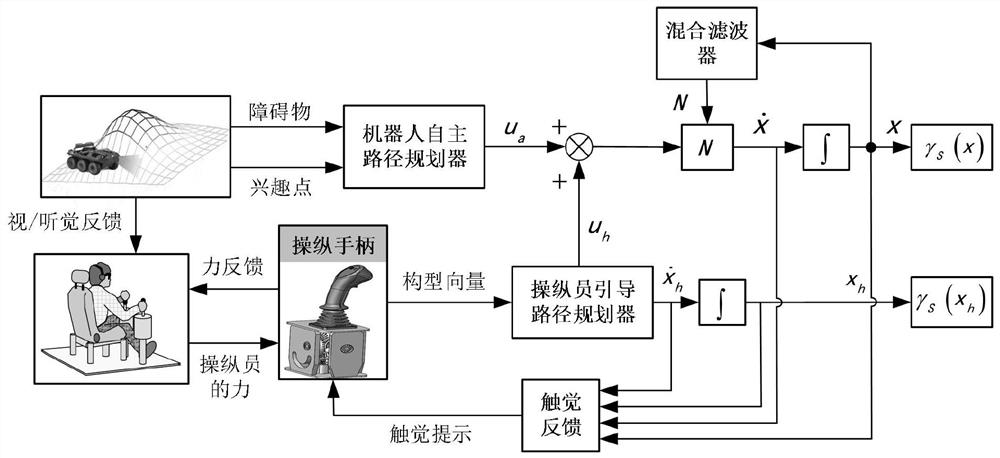
[0108] see figure 2 , which shows a flow chart of a human-machine collaborative path planning method for a mobile robot in an unstructured environment in an embodiment of the present invention, the method includes:
[0109] Operator-guided path planner:
[0110] The operator-guided path planning of the present invention is realized based on the B-spline curve, which is a linear combination of B-spline basis functions, which is improved from the Bezier curve, which makes up for the inability of the Bezier curve to be locally modified defect, the curve expression is:
[0111] gamma S (x)={γ(x,s)∈R 2 |s∈S} (1)
[0112] in, Represents the control point vector, s represents the node of the B-spline curve, and the set S represents the node vector.
[0113] Modifications to the path by the manipulator are done through the joysticks:
[0114]
[0115] Among them, q represents the configuration vector of the joystick, M(q) represents the inertia matrix, denote the Corioli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com