Apparatus and method for evaluating sediment wettability based on imbibition NMR
A technology of nuclear magnetic resonance and sedimentation, which is applied in the direction of analysis by nuclear magnetic resonance, measuring devices, material analysis through resonance, etc., can solve problems such as unavailability, evaluation of wettability, and easy dispersion of the skeleton
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
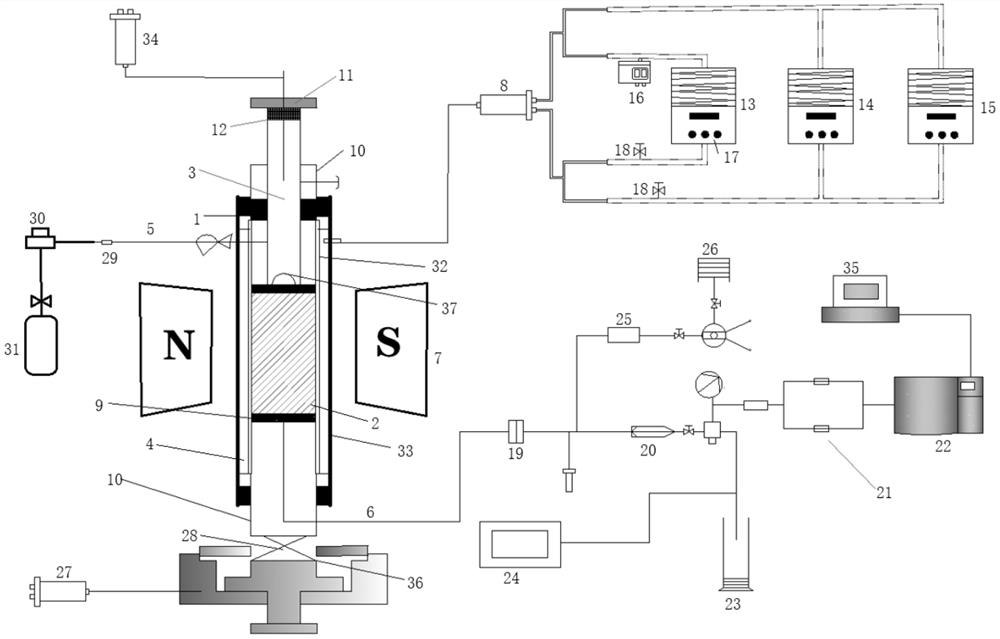
[0051] like figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a device for evaluating sediment wettability based on imbibition nuclear magnetic resonance, including: axial pressure loading equipment, holder 1 , temperature control equipment for confining pressure fluid, and nuclear magnetic resonance instrument 7 .
[0052] Wherein, the holder includes a sample part 2, a drip part 3 and a confining pressure part 4, the drip part 3 is located above the sample part 2, and the confining pressure part 4 is located around the sample part 2, The sample part 2 is used for placing samples, the drip part 3 is used for dropping liquid, and the confining pressure part 4 is used for injecting confining pressure liquid. The axial pressure loading device is located below the sample part 2 and is used to apply axial pressure to the sample part 2 . The dripping part 3 is connected with a gas inlet 5 , and the bottom end of the sample part 2 is connected with a gas outlet 6...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for evaluating sediment wettability based on imbibition nuclear magnetic resonance, including:
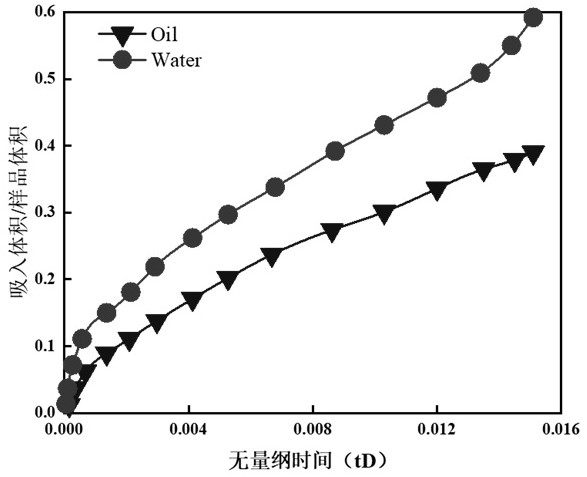
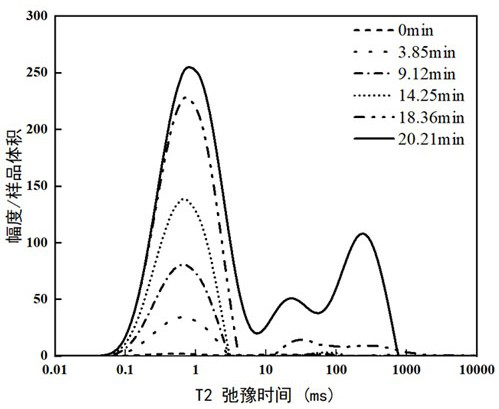
[0078] Carry out water droplet and oil droplet imbibition tests on two seabed sediment samples in the same formation, and measure the NMR T2 spectrum of the sample after each imbibition, and calculate the NMR T2 spectrum area;
[0079] Calculate the water volume or oil volume inhaled into the sample at the corresponding time according to the NMR T2 spectrum area at different times;
[0080] The macroscopic wetting index of the sample was calculated using the following formula:
[0081]
[0082]
[0083] In the formula, I w is the maximum water absorption volume per unit pore volume, I o is the maximum oil absorption volume per unit pore volume, WI w is the water wettability index, WI o is the oil wettability index;
[0084]
[0085]
[0086] In the formula, V wmax and V omax are the maximum wa...
specific example
[0101] In a specific example of the present invention, the device provided in Embodiment 1 is used to evaluate the wettability of seabed sediments, and the following steps are adopted:
[0102] Step 1. From the same hydrate formation, take two seabed sediment samples and process them into cylinders, and measure the mass and diameter of the two samples. d w and length l w , for dripping water and oil dripping tests, respectively.
[0103] In step 2, one of the samples is placed in the holder to ensure that the sample is within the range of the nuclear magnetic resonance. Apply confining pressure and axial pressure to the sample, and raise the temperature of the confining pressure fluid injected into the confining pressure part to 60-80°C through the confining pressure fluid temperature control equipment. Use a gas cylinder and a gas booster to continuously feed dry methane gas into the dripping part, and air-dry the sample until the nuclear magnetic resonance signal no long...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com