Brain CT medical image processing method based on unsupervised feature matching
A feature matching and medical image technology, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems of poor brain CT image accuracy, high computing power cost training loss, learning efficiency and low quality, etc., to improve accuracy, save training costs, Guaranteed efficiency and robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
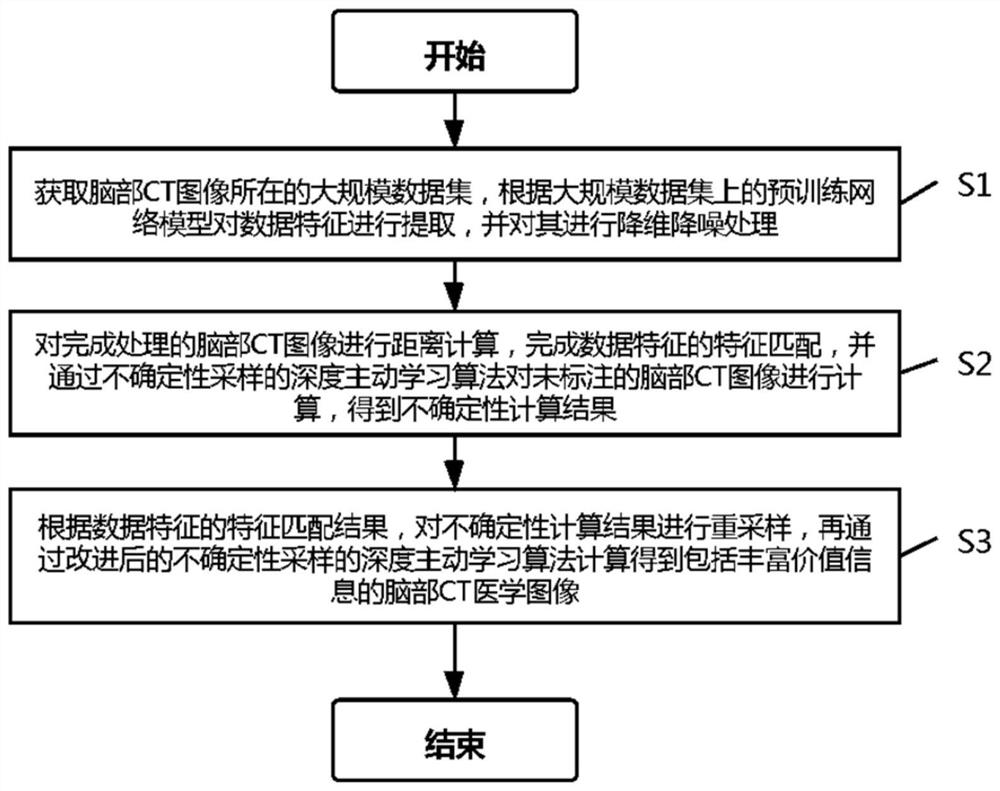
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, a brain CT medical image processing method based on unsupervised feature matching specifically includes the following steps:
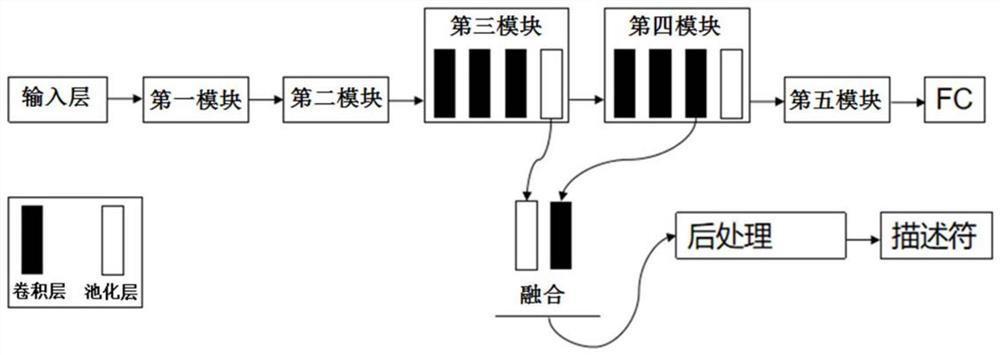
[0030] S1. Acquire the large-scale data set where the brain CT images are located, extract the data features according to the pre-trained network model on the large-scale data set, and perform dimensionality reduction and noise reduction processing on it;
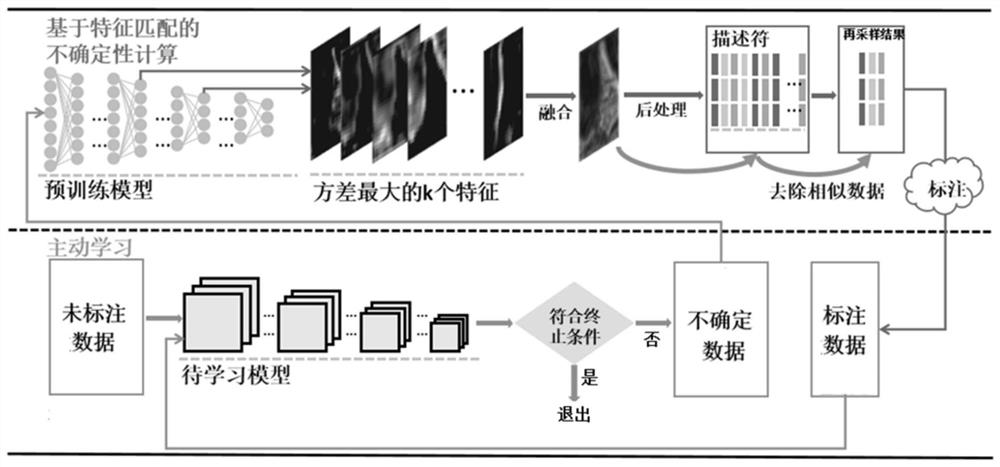
[0031] S2. Perform distance calculation on the processed brain CT image, complete feature matching of data features, and calculate the unlabeled brain CT image through the deep active learning algorithm of uncertainty sampling to obtain the uncertainty calculation result;
[0032] S3. According to the feature matching results of the data features, the uncertainty calculation results are re-sampled, and then the brain CT medical images containing rich value information are calculated through the improved uncertainty sampling deep active learning algorithm, such as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com