Method for detecting comprehensive toxicity of water sample
A detection method and toxicity technology, which is applied in the field of comprehensive toxicity detection of water samples, can solve problems such as failure to meet regulatory needs, false positives, etc., and achieve reliable detection results, comprehensive functions, and improved reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
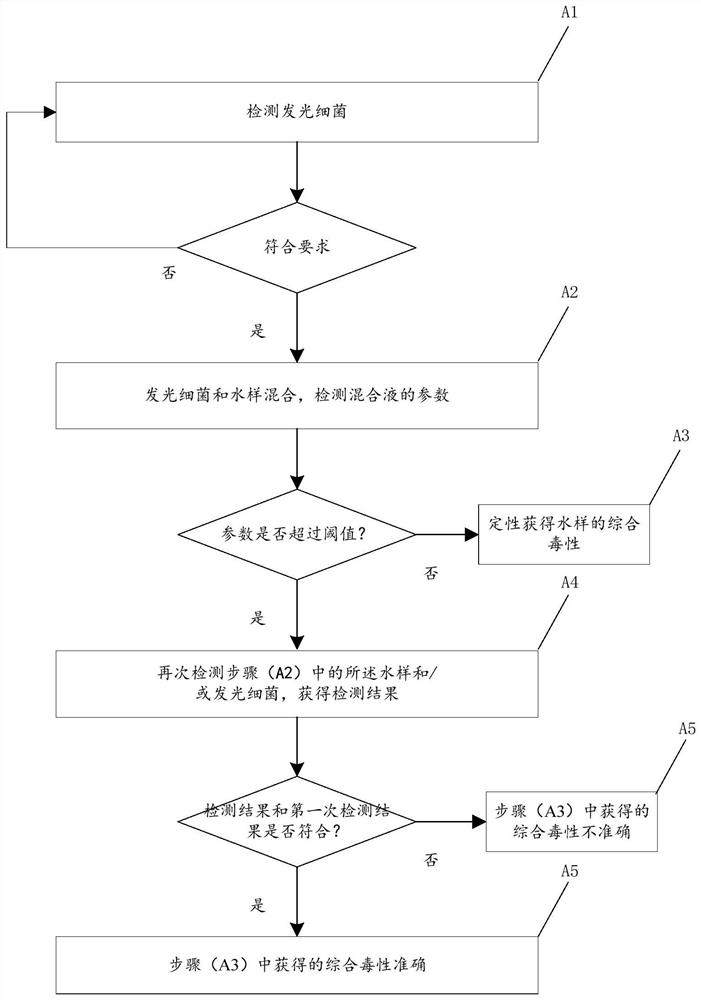
[0031] figure 1 Schematically provides the flow chart of the detection method of water sample comprehensive toxicity of the embodiment of the present invention, as figure 1 As shown, the detection method of described water sample comprehensive toxicity comprises the following steps:
[0032] (A1) Detect luminescent bacteria and judge whether the luminescent bacteria meet the requirements;
[0033] If the requirements are met, proceed to step (A2);
[0034] If the requirements are not met, replace the luminescent bacteria until the requirements are met;
[0035] (A2) Mix the luminescent bacteria and the water sample, and detect the parameters of the mixture, such as luminescence inhibition rate and / or correction factor;
[0036] (A3) judging whether the parameter exceeds a threshold;
[0037] If exceeding the threshold, enter step (A4);
[0038] If the threshold is not exceeded, qualitatively obtain the comprehensive toxicity of the water sample;
[0039] (A4) re-detectin...
Embodiment 2
[0059] An application example of the detection method for comprehensive toxicity of water samples according to Example 1 of the present invention.
[0060] (A1) Mix the luminescent bacteria-Vibrio fischeri with the standard poison to obtain the comprehensive toxicity of the standard poison, such as inhibition rate, correction factor or half-maximal effect concentration;
[0061] Judging whether the comprehensive toxicity of the standard poison (prepared with zinc sulfate heptahydrate) exceeds the threshold, the threshold of the inhibition rate is 50%, the threshold of the correction factor is 0.6-1.8, and the threshold of the half-maximal effect concentration is 1.4-2.9mg / L;
[0062] If the threshold value is exceeded (parameters representing comprehensive toxicity all exceed the threshold value, if the parameters use inhibition rate and correction factor, the inhibition rate and correction factor both exceed the threshold value), and the number of times exceeding the threshold...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com