Implementation method for persistent super-hydrophilicity of sapphire surface
A realization method, sapphire technology, applied in the field of laser processing to prepare super-hydrophilic materials, to achieve the effect of wide application range and long-lasting super-hydrophilic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The realization method of the sapphire surface durable superhydrophilicity provided by the embodiment of the present invention 1 comprises the following steps:
[0048] S0, putting the sapphire into an ethanol solution for ultrasonic cleaning.
[0049] S1. A femtosecond laser is used to ablate the surface of sapphire to form a periodic micron-scale groove structure on the surface of sapphire and simultaneously generate hydrophilic γ-phase alumina.
[0050] After cleaning the sapphire, use an optical lens with a focal length of 100mm to focus and irradiate the femtosecond laser on the sapphire surface, and ablate at equal intervals with a space period of 35 μm to form a micron-scale groove structure.
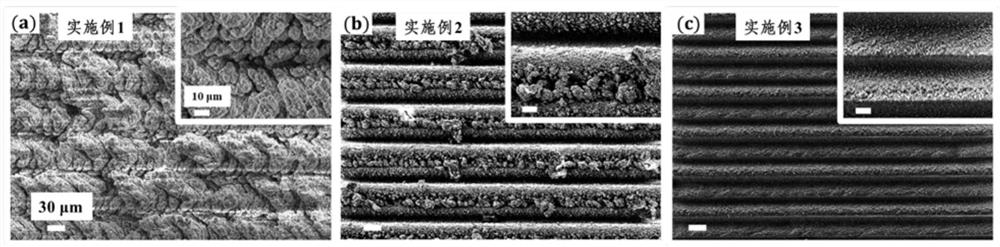
[0051] When the laser power of the femtosecond laser is 200mW and the scanning speed is 0.1mm / s, the depth of the micron-scale groove structure is 92.31μm, and the opening width is 32.44μm. The surface morphology is as follows: figure 2 In (a) shown.
[0052] S2. Spin-c...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that the scanning speed of the femtosecond laser is 0.3 mm / s, the depth of the formed micron-scale groove structure is 30.77 μm, and the opening width is 34.15 μm, such as figure 2 Shown in (b) among, other steps are identical with embodiment 1.
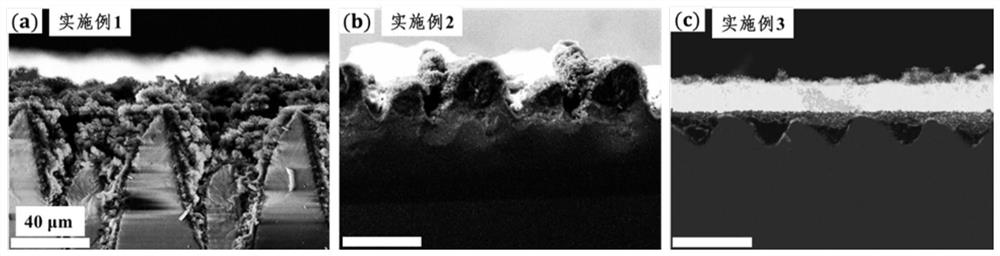
[0062] After high-temperature annealing, the anatase titanium dioxide crystal coating partially fills the micron-scale groove structure, such as image 3 As shown in (b), the surface morphology of the anatase titanium dioxide crystal coating formed in Example 1 is different.
[0063] At this time, the contact angle of the sapphire surface was measured to be 0°, and the super-hydrophilic state could be maintained for 60 days. After 60 days, the contact angle began to increase gradually. The results are as follows Figure 4 In (b) shown.
Embodiment 3
[0065] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is that the scanning speed of the femtosecond laser is 0.5 mm / s, the depth of the formed micron-scale groove structure is 28.26 μm, and the opening width is 34.49 μm, such as figure 2 Shown in (c), other steps are identical with embodiment 2.
[0066] After high-temperature annealing, the anatase titanium dioxide crystal coating is basically filled into the micron-scale groove structure, such as image 3 As shown in (c), the anatase-type titanium dioxide crystal coating formed in Example 2 is partially filled in the micron-scale groove structure, so it can be seen that the anatase-type titanium dioxide formed in Example 3 and Example 2 The surface morphology of the crystal coating is different.
[0067] At this time, the contact angle of the sapphire surface was measured to be 0°, and the superhydrophilic state could be maintained for 27 days. After 27 days, the contact angle began to increase gradually. The results...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com