High speed data bus driver
A data bus, bus technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that the form of the bus driver does not meet the needs of the application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
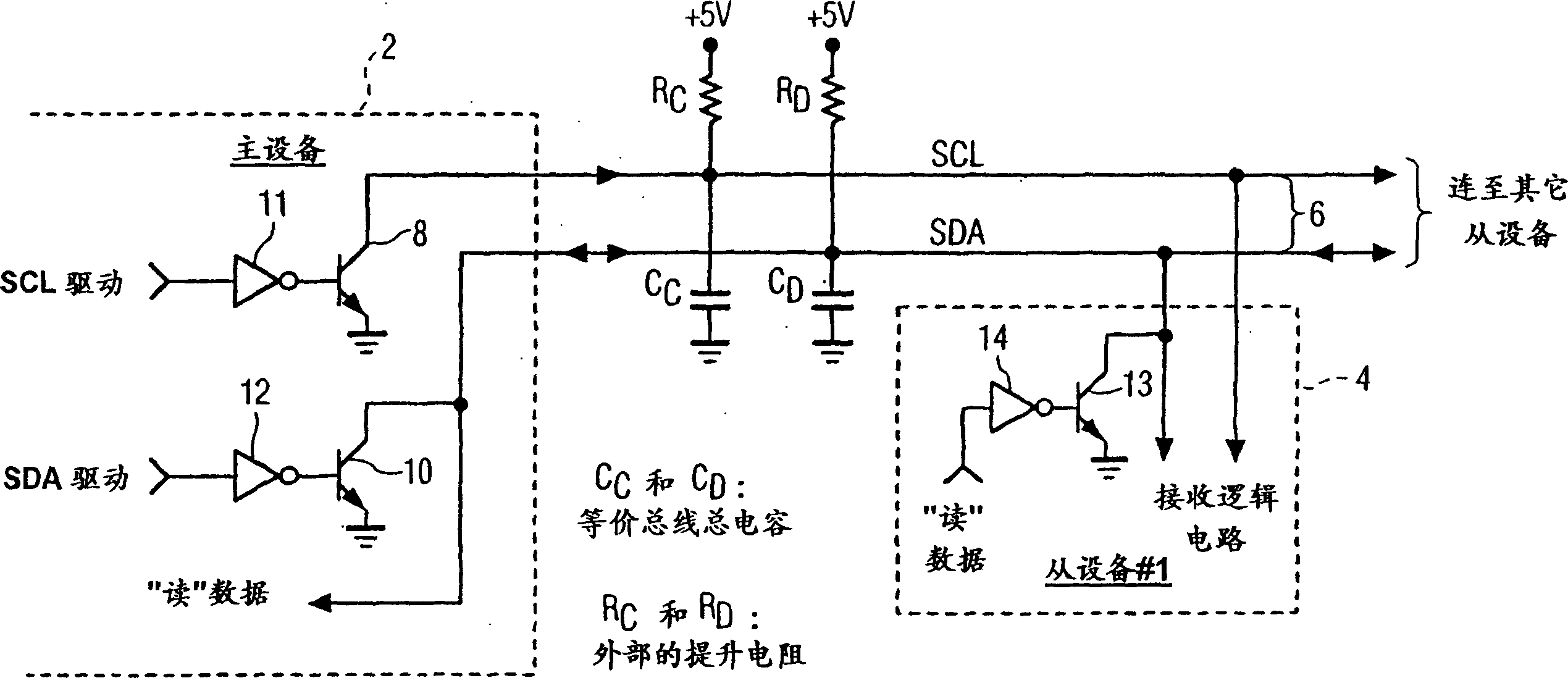
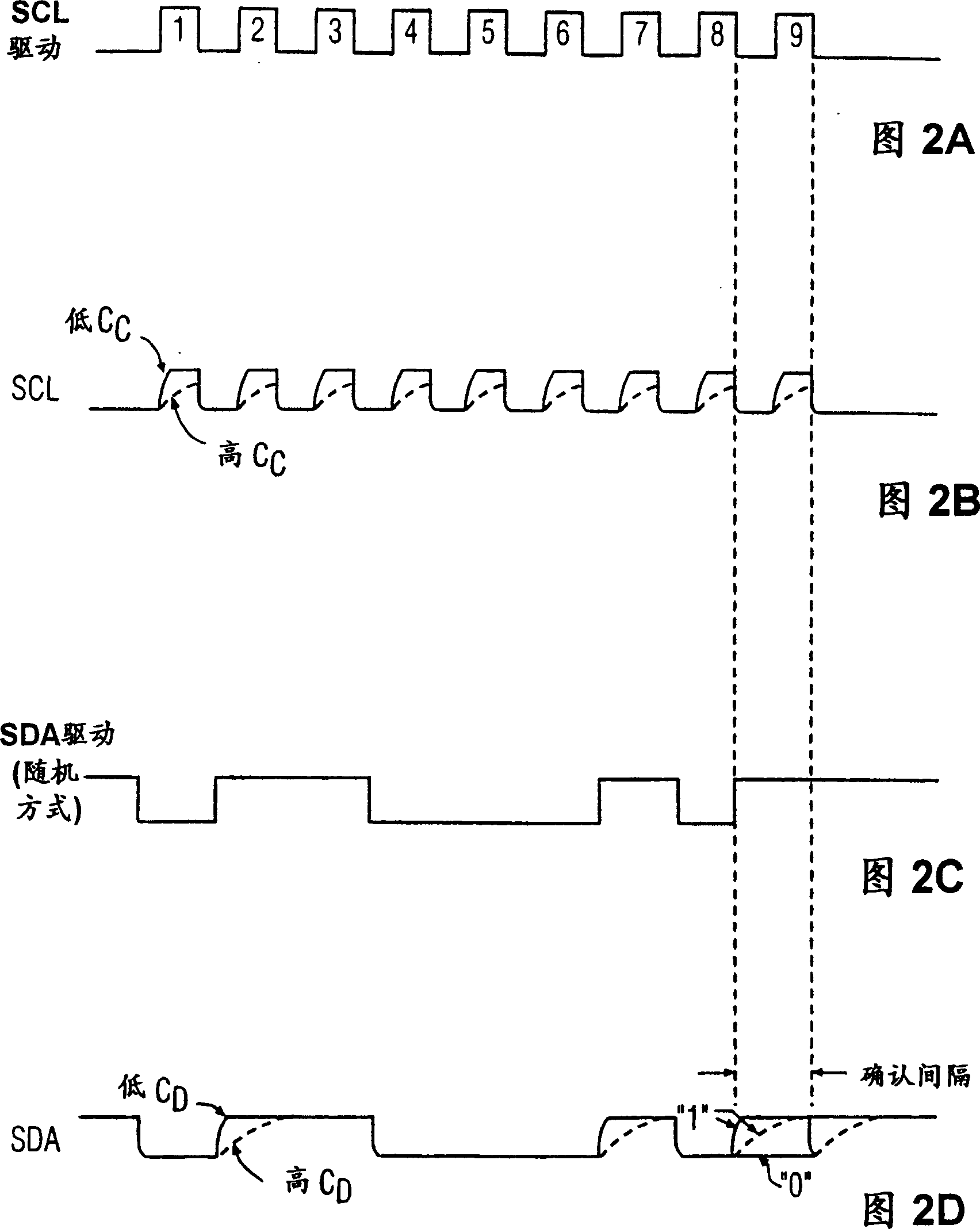
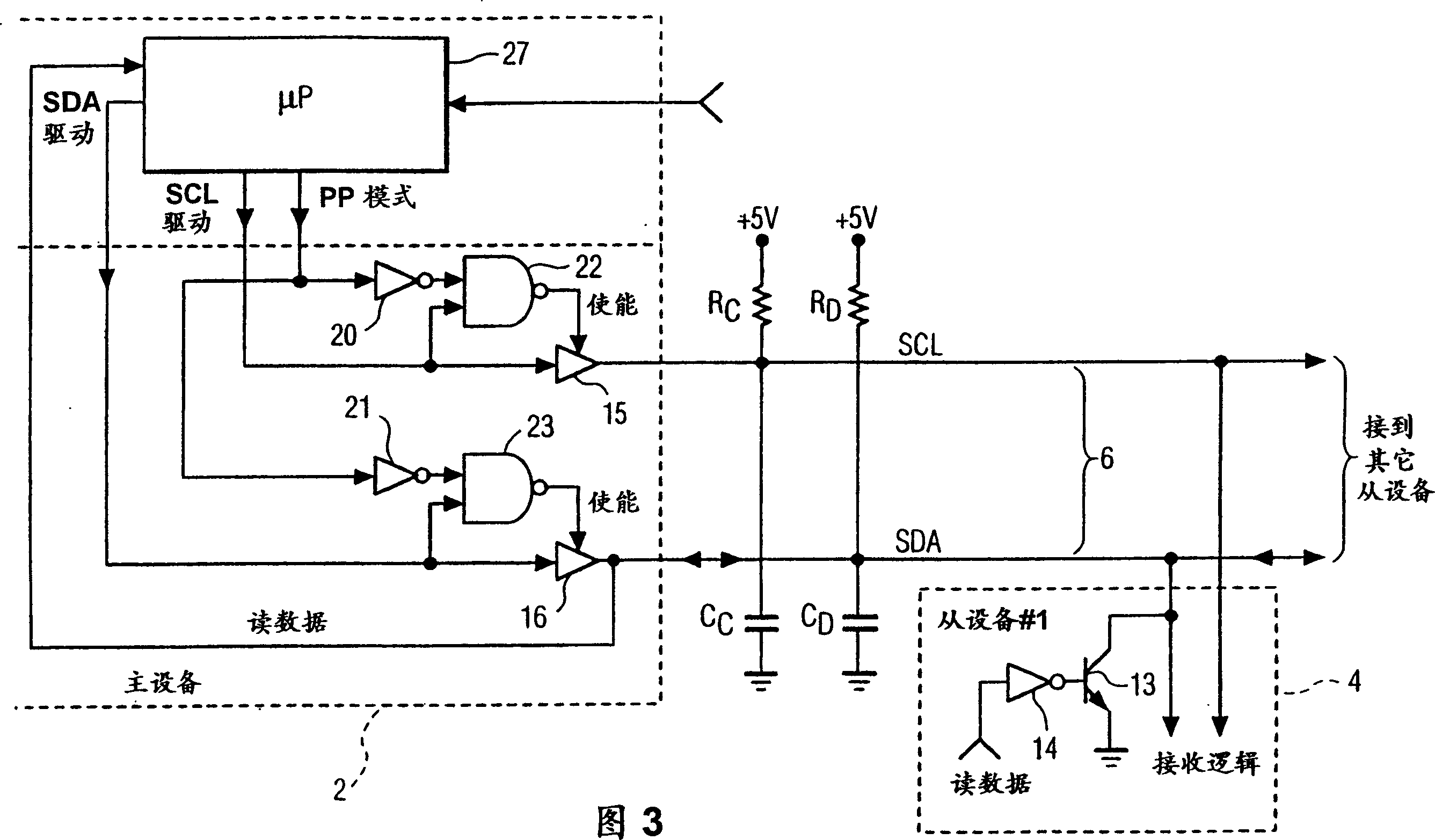
[0025] in such as figure 1 shown as I 2 In the traditional bus system of the C bus, the master device 2 passes through the I 2 C bus 6 is connected to slave device 4 (labeled as slave device #1). According to I 2 C bus rules, the labels SDA and SCL are used to identify the serial data line and the clock line respectively. The master device 2 has a driver respectively to drive each line. more specifically, figure 1 The middle lines SCL and SDA are respectively driven by NPN bipolar transistors 8 and 10 connected thereto.
[0026]The base of each transistor 8 and 10 is connected to the output of an inverter 11, 12 respectively. The independent drive signals SCL drive and SDA drive are respectively connected to the input terminals of the corresponding inverters 11 and 12 . When the SCL drive and SDA drive signals are logic high, the respective NPN transistors 8 and 10 are not turned on, and the lines SCL and SDA are raised to a high level through the boost resistors RC and...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap