LuMyb gene for regulating and controlling flax cellulose synthesis and application of LuMyb gene
A cellulose and flax technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of not being able to determine the direct regulator of secondary wall cellulose synthase, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 flax LuCesA8 Identification of key regulatory regions in gene promoters
[0026] Download from the Phytozome website (https: / / phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov / ) LuCesA8 (Lus10029245) The 2000bp promoter sequence upstream of the ORF of the gene, the cis-acting elements in the promoter were analyzed through the PLACE database, and the -426~-52bp upstream of the promoter was predicted to be the key regulatory region of the promoter (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) . Use the software Primer Premier 5.0 to design specific primers LuCesA8F and LuCesA8R (see Table 1), and use PCR technology to clone in the flax variety "Dazihua" LuCesA8 The sequence between the gene promoter -426~-52bp (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) obtained the promoter pLuCesA8B (-426~-52bp), and inserted the promoter sequence into the multiple cloning site EcoRI of the pCAMBIA1300-GUS vector Between -XbaI and GUS reporter gene ORF, construct the plant expression recombinant vector p1300LuCesA8 (-426~-52bp)::G...
Embodiment 2
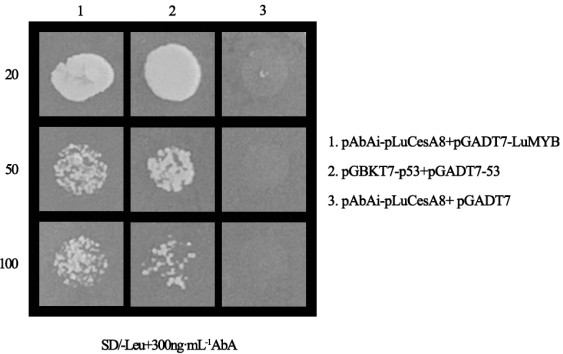
[0028] Example 2 Yeast one-hybrid screening of transcription factor TF upstream of LuCesA8 promoter
[0029] In the early stage, 1 gene was screened by weighted co-expression analysis with LuCesA8 A candidate transcriptional regulator of gene coexpression, LuMyb (Lus10039610). Primers LuMybF and LuMybR were designed to clone the cDNA sequence of LuMyb gene (1158bp, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2), and connected to the pGADT7 vector to construct the prey vector pGADT7-Lus10039610. The primer sequences are shown in Table 1. Will LuCesA8 The gene promoter -426~-52bp sequence (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) was connected to the pAbAi vector to construct the bait vector pLuCesA8-AbAi. The prey vector pGADT7-Lus10039610 and the bait vector pLuCesA8-AbAi, the two vectors were simultaneously transformed into yeast, and the transformation products were diluted at the ratio of 1:20, 1:50 and 1:100 respectively, and the dilution was prepared in SD / -Leu+ 300ng·mL -1 Cultured on AbA medium, pLuCe...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3 LuMyb Functional verification of genes
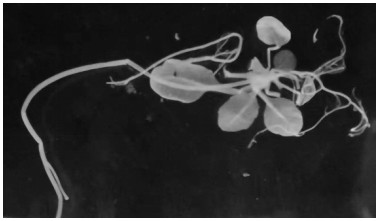
[0032] According to the gene sequence of flax LuMyb (Lus10039610) in Phytozome public database, upstream and downstream primers LuVIGSF / LuVIGSR were designed to clone flax LuMyb The target sequence of the gene (441bp, as shown in SEQ ID NO.3), the target sequence fragment was inserted into the pTRV2 vector to construct the VIGS silencing vector pTRV2-LuMyb. flax phytoene dehydrogenase LuPDS (Lus10021967) Gene sequence design upstream and downstream primers LuPDSF / LuPDSR clone flax LuPDS The target sequence of the gene (437bp, as shown in SEQ ID NO.4), the target sequence fragment was inserted into the pTRV2 vector to construct the VIGS silencing vector pTRV2-PDS. The "Dazihua" flax seeds were evenly planted in the nutrient soil, placed in a light incubator, 23°C, 16h light, 18°C, 8h dark cultivation. After normal culture for about 10 days, the seedlings grow 2 cotyledons, and the VIGS test is carried out when the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com