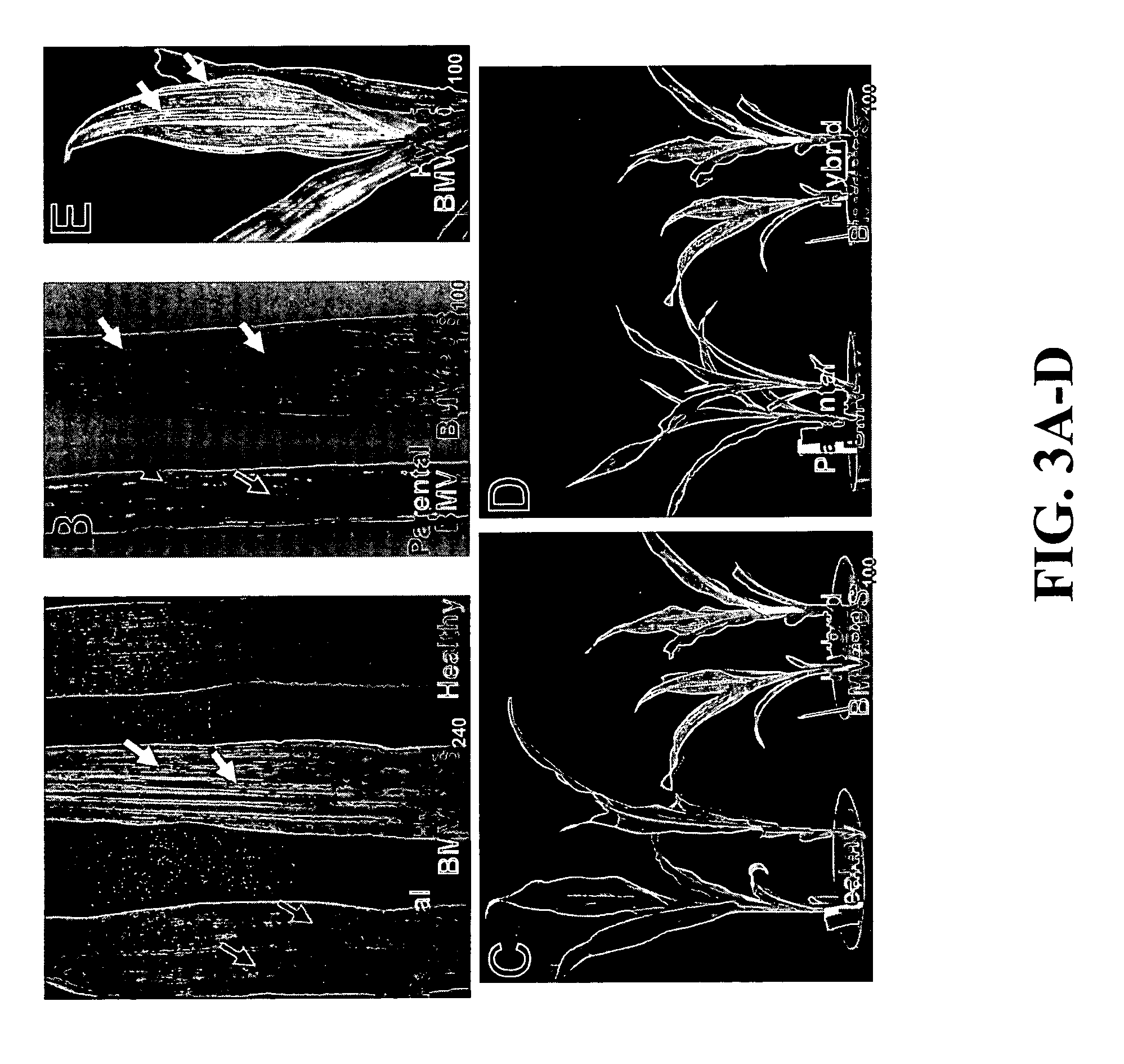
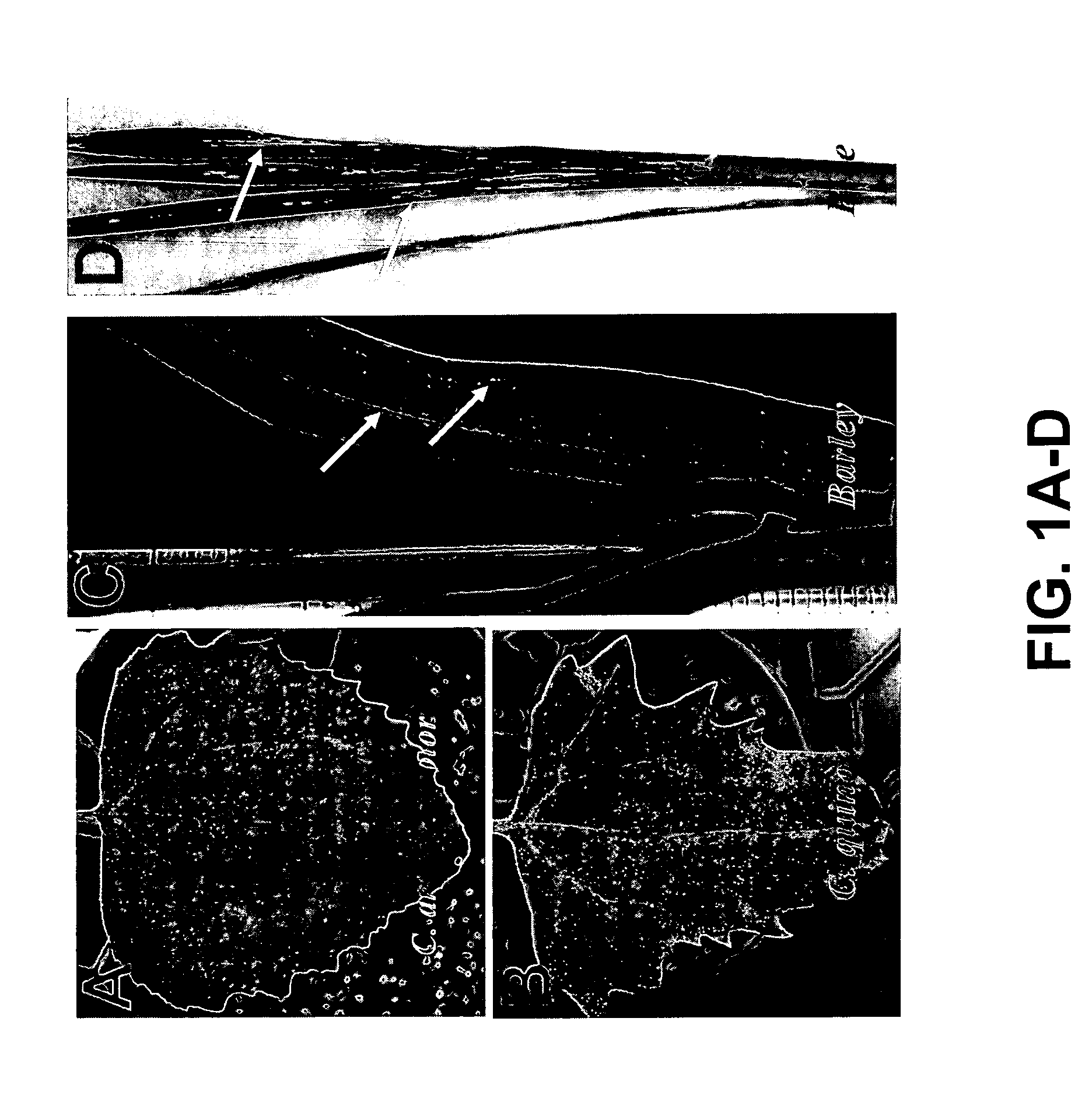
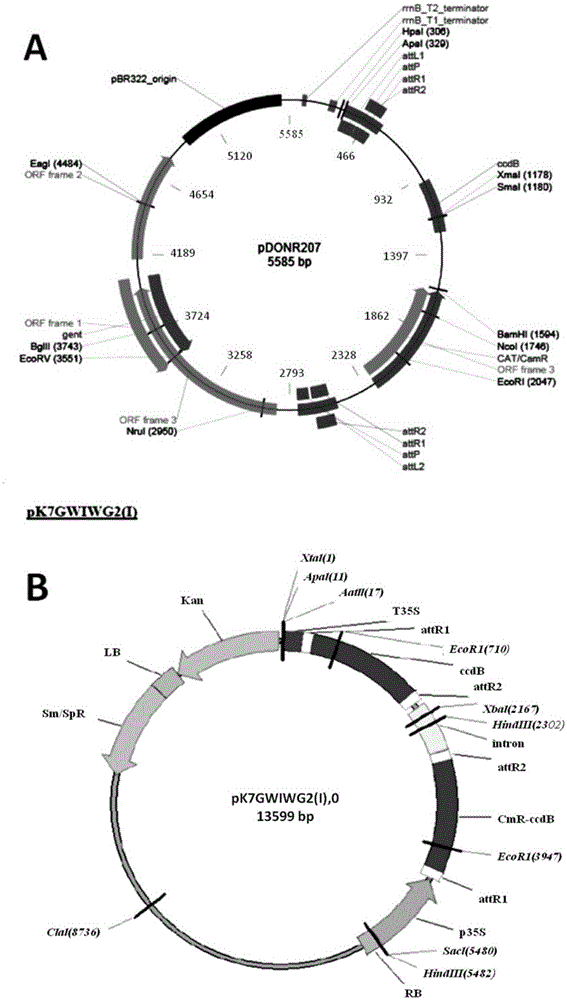
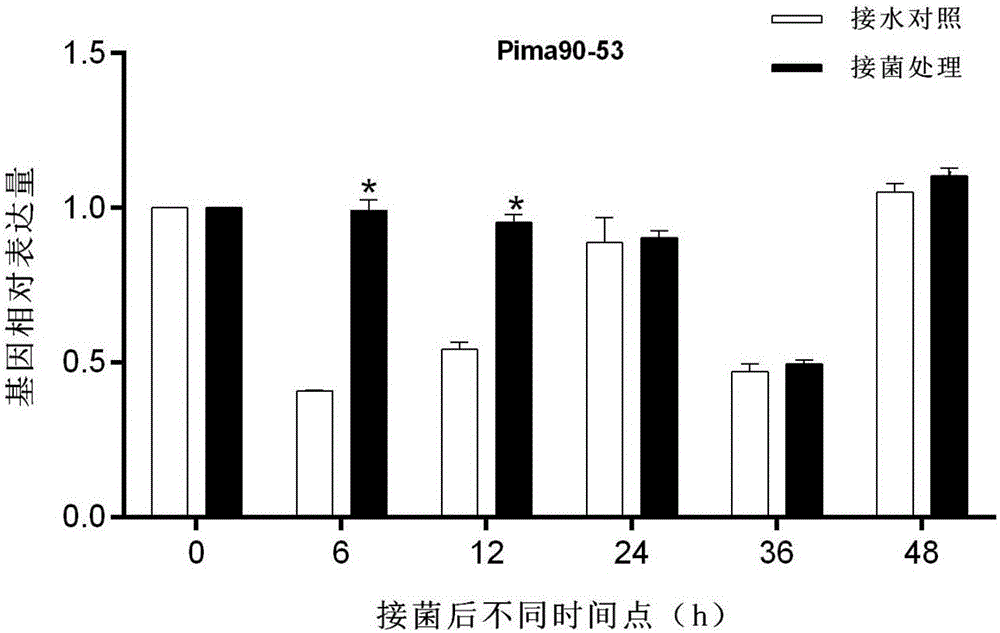
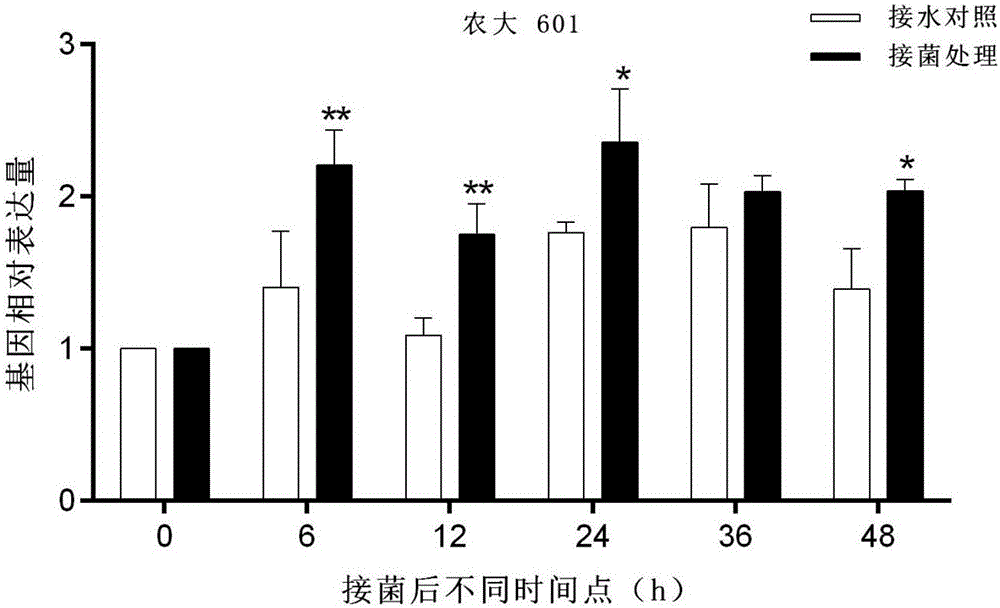
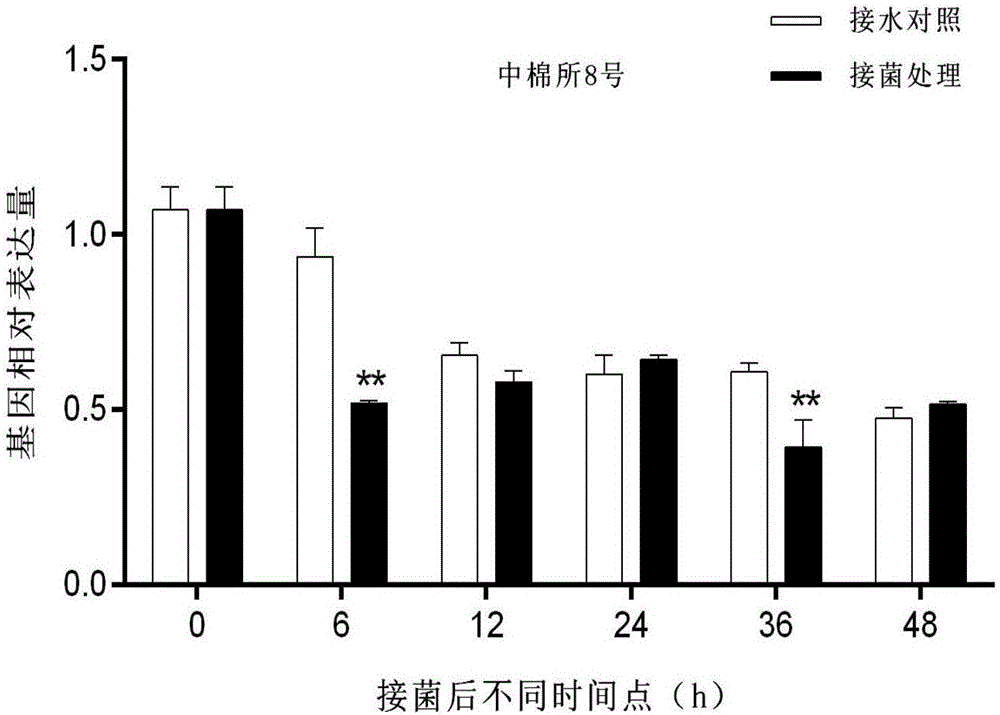
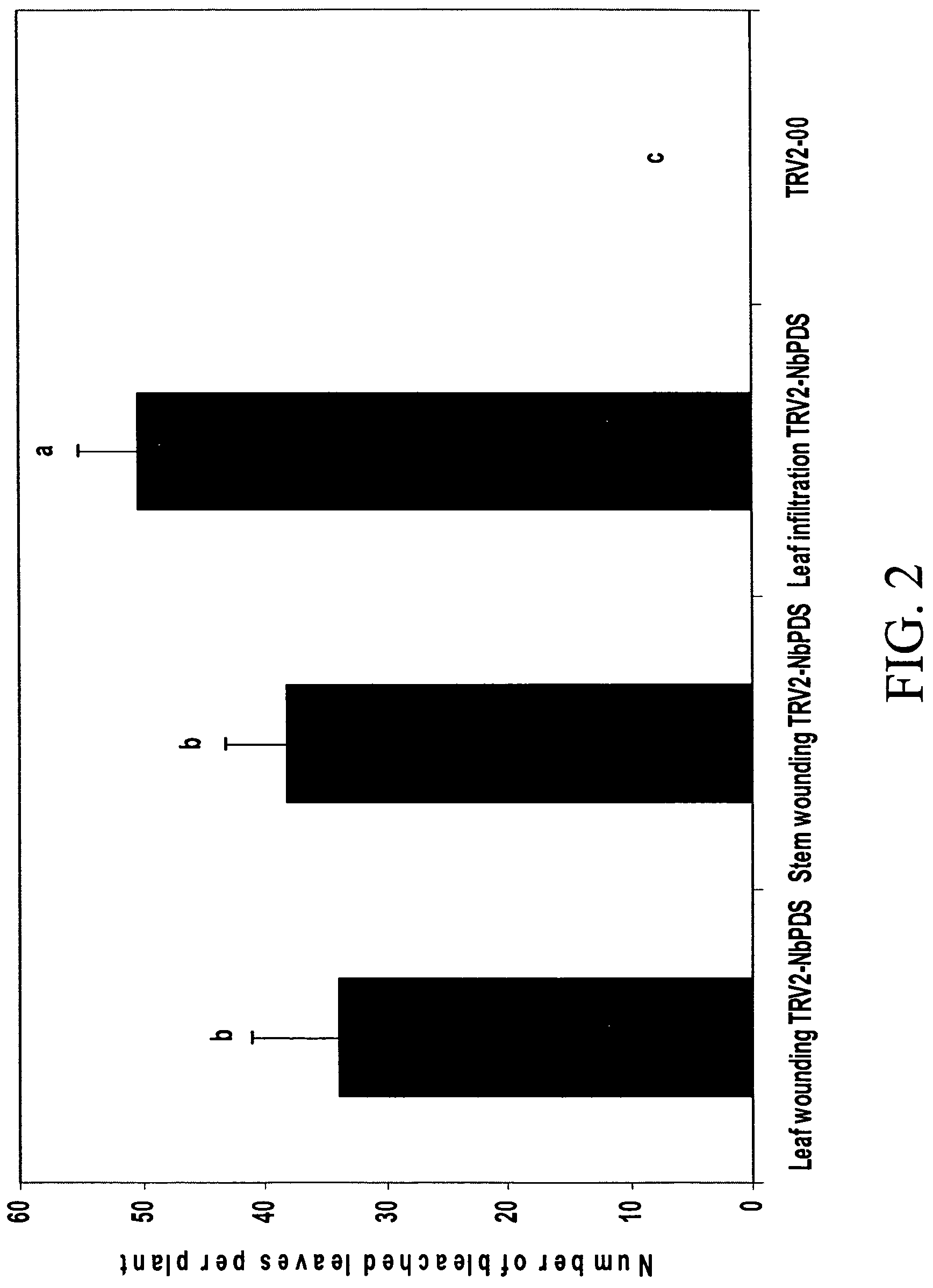
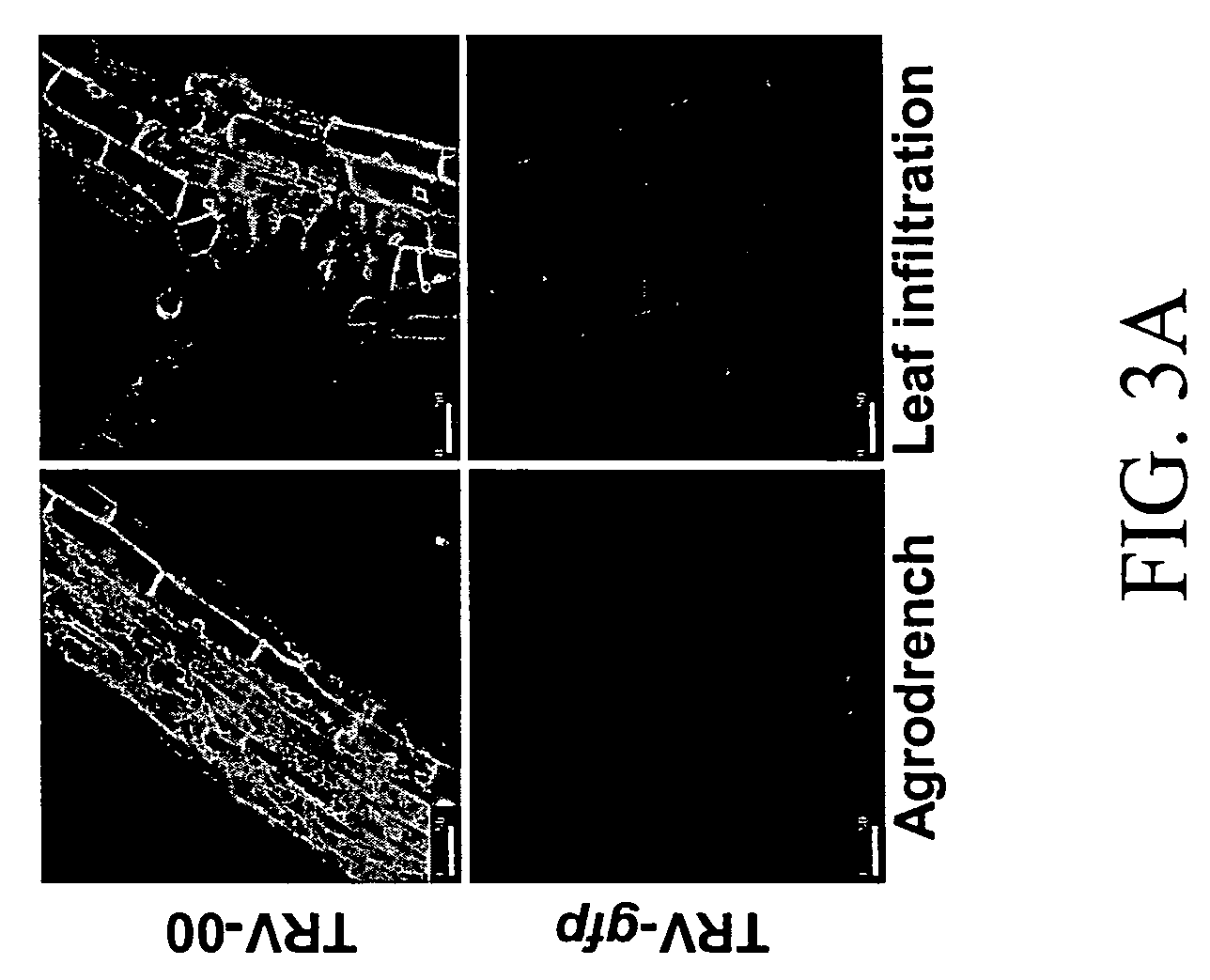
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Virus-induced gene silencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
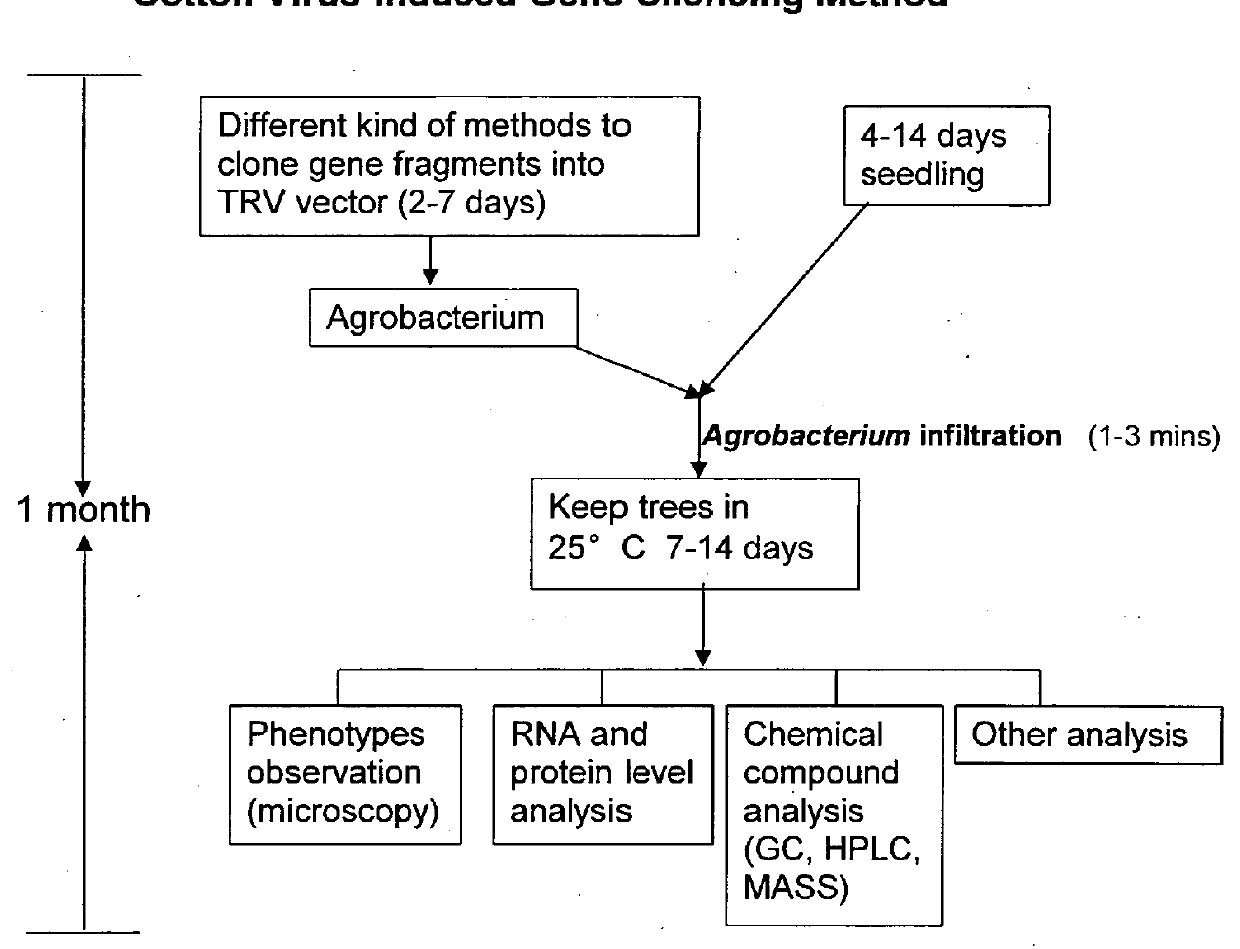
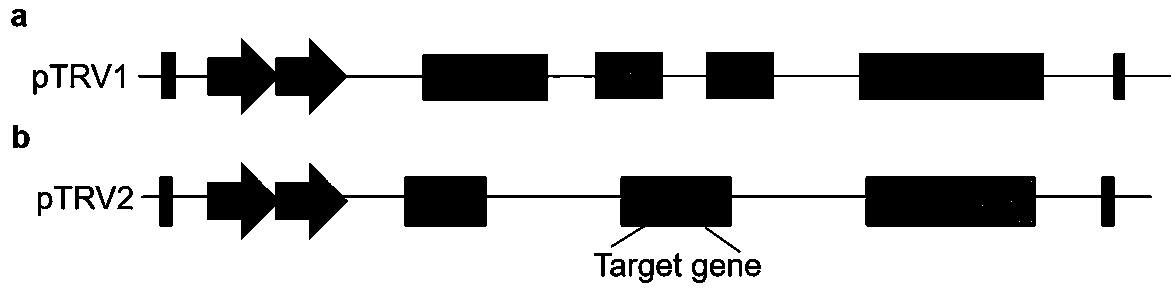
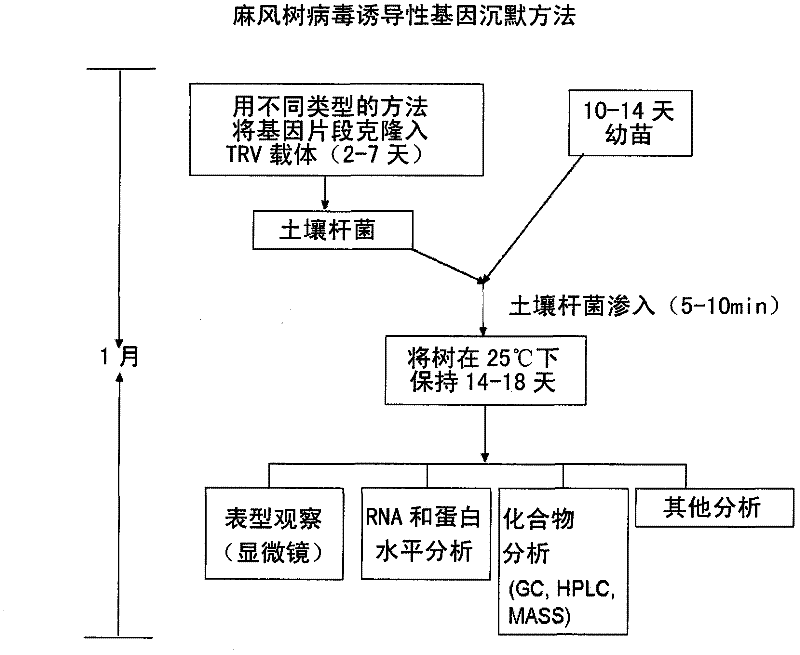
Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) is one of the reverse genetics tools for analysis of gene function that uses viral vectors carrying a target gene fragment to produce dsRNA which trigger RNA-mediated gene silencing.
Methods and compositions for analysis of plant gene function
The invention provides novel methods and compositions for modulating gene function in plants. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions that allow, for the first time, virus-induced gene silencing in rice. The invention is significant in that prior techniques were not available for rice and because of the major importance of rice to agriculture. The invention therefore provides techniques for the analysis of gene function in rice, as well as in other monocotyledonous species and dicotyledonous plant species.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
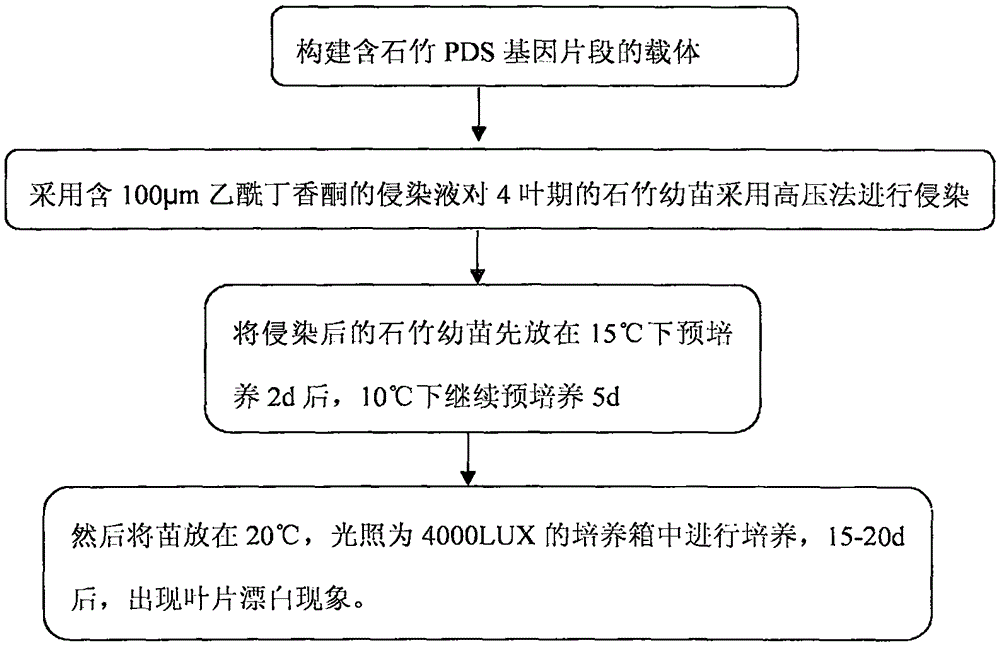
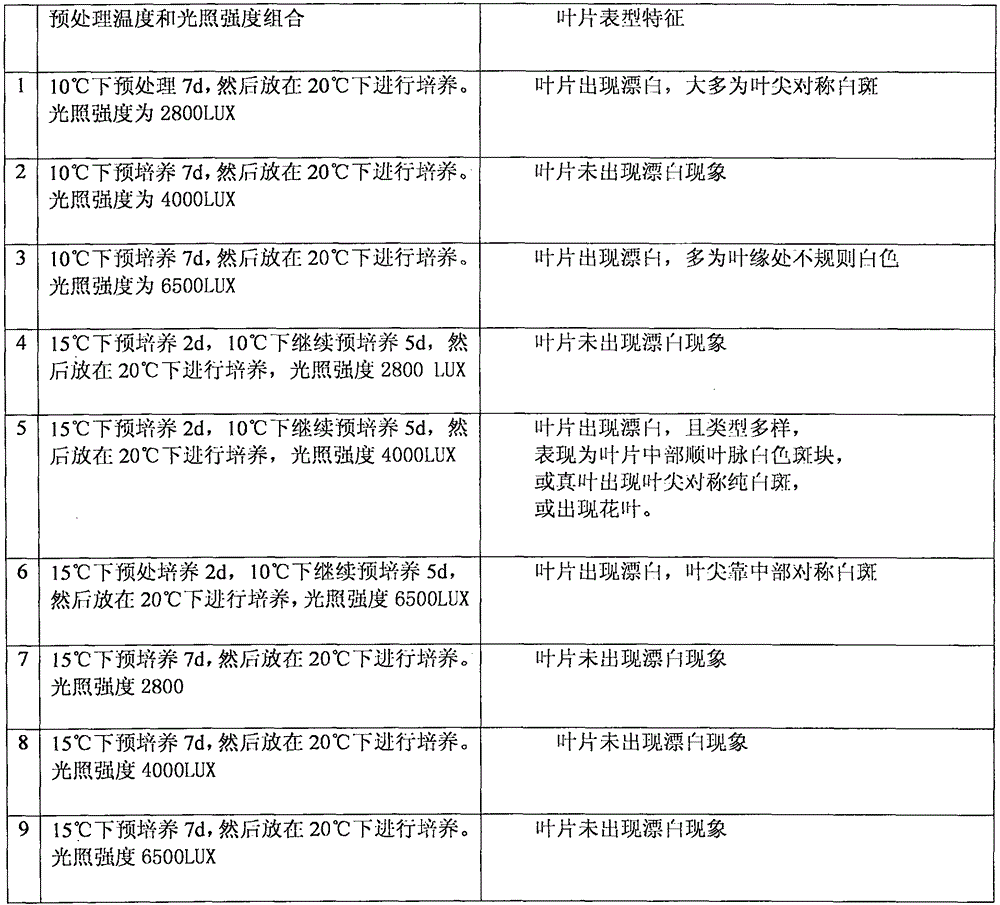
Efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink
InactiveCN105296535ASolving questions about gene functionGenetic engineeringFermentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
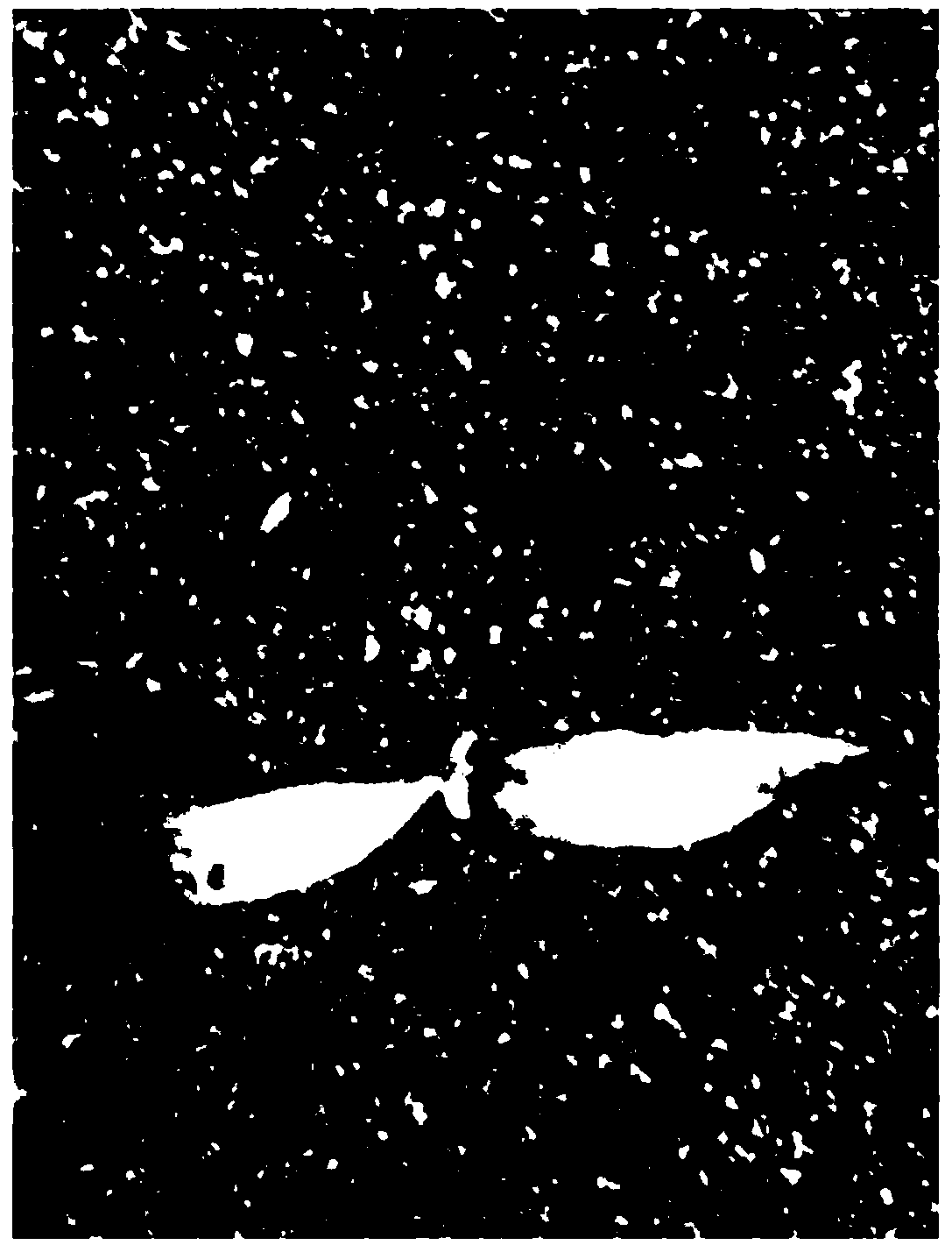
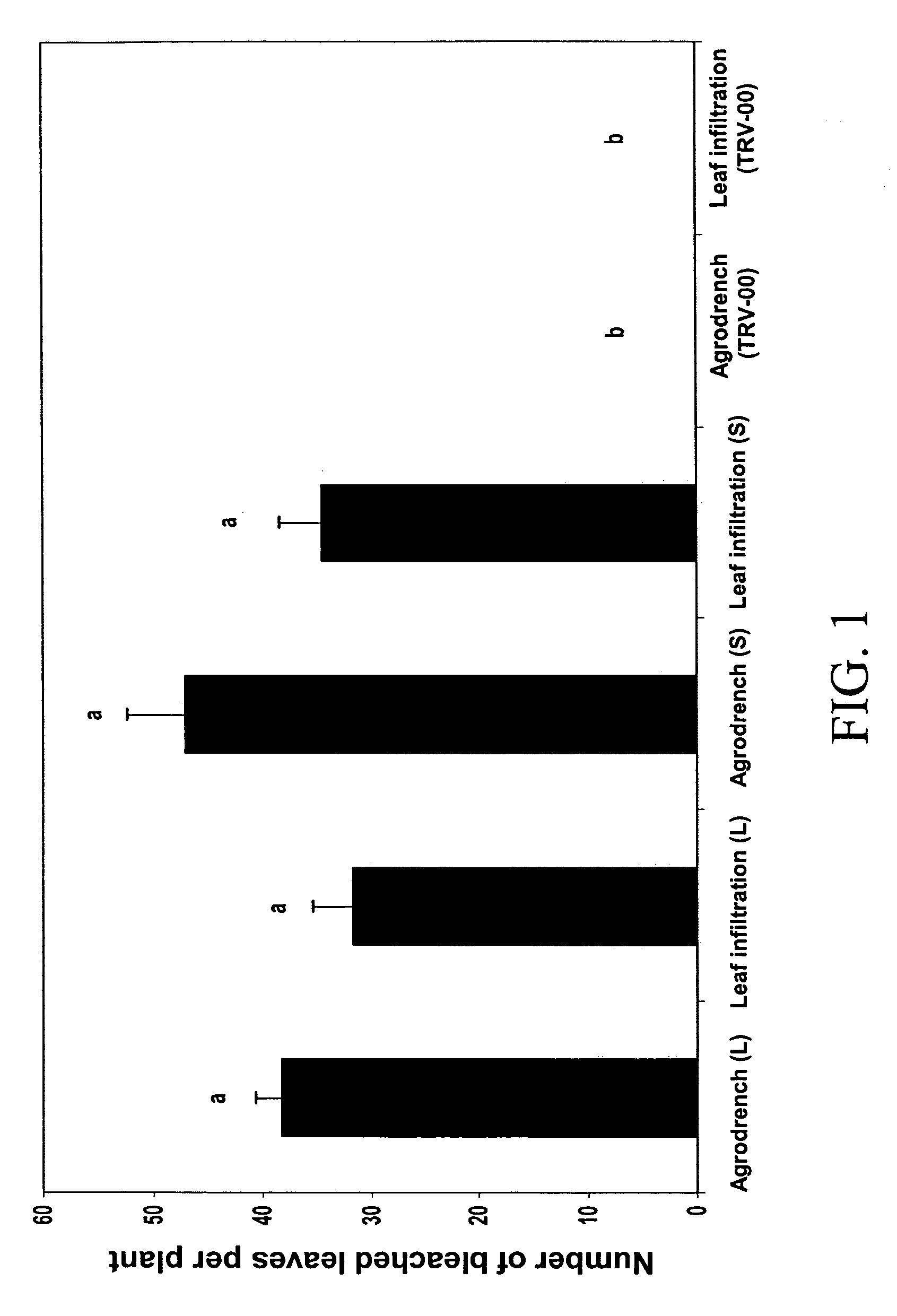
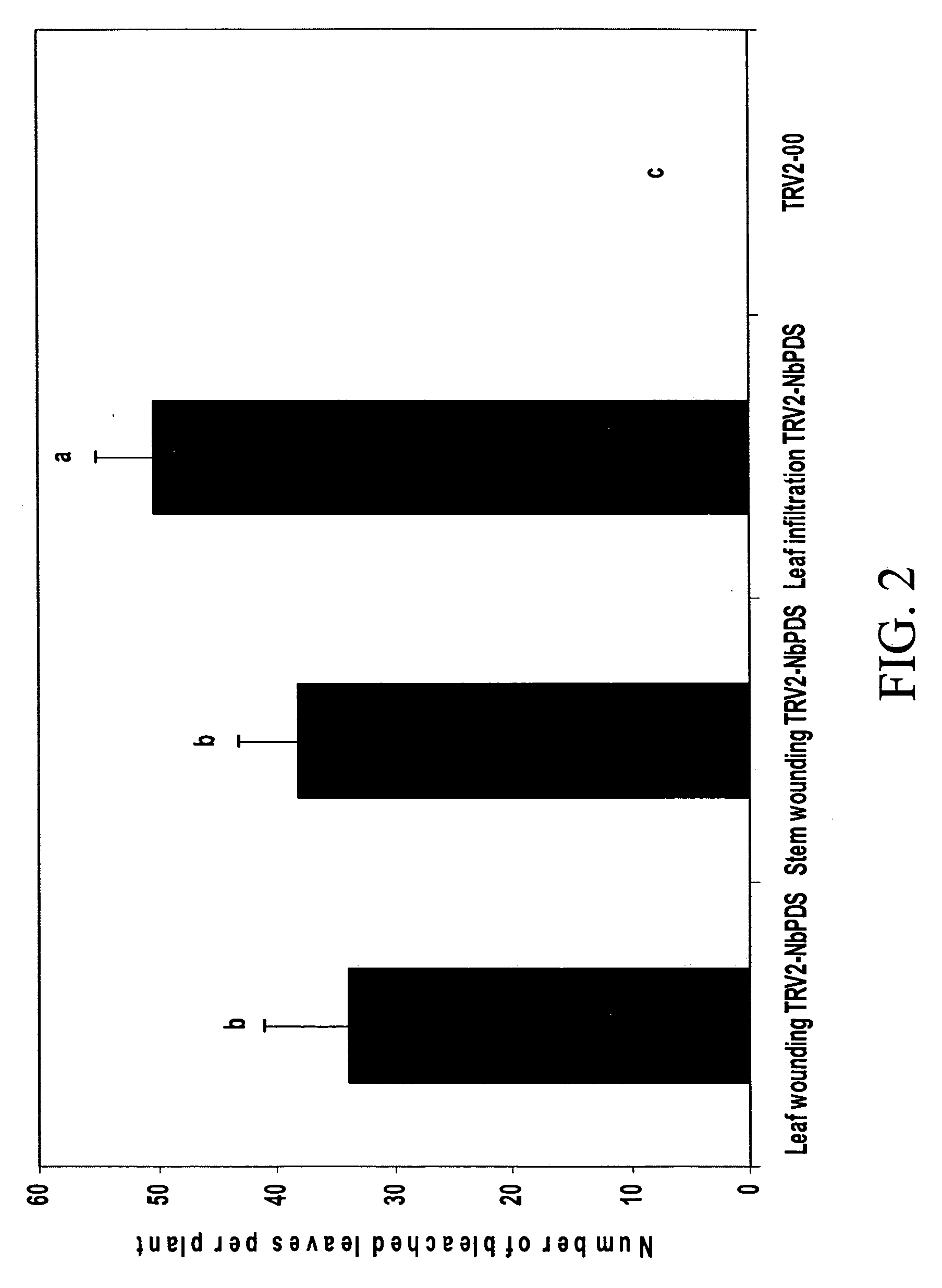
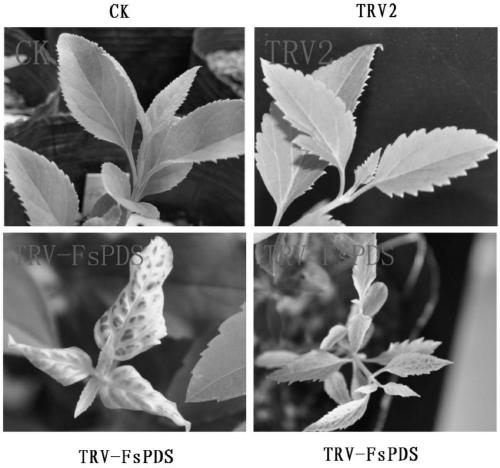
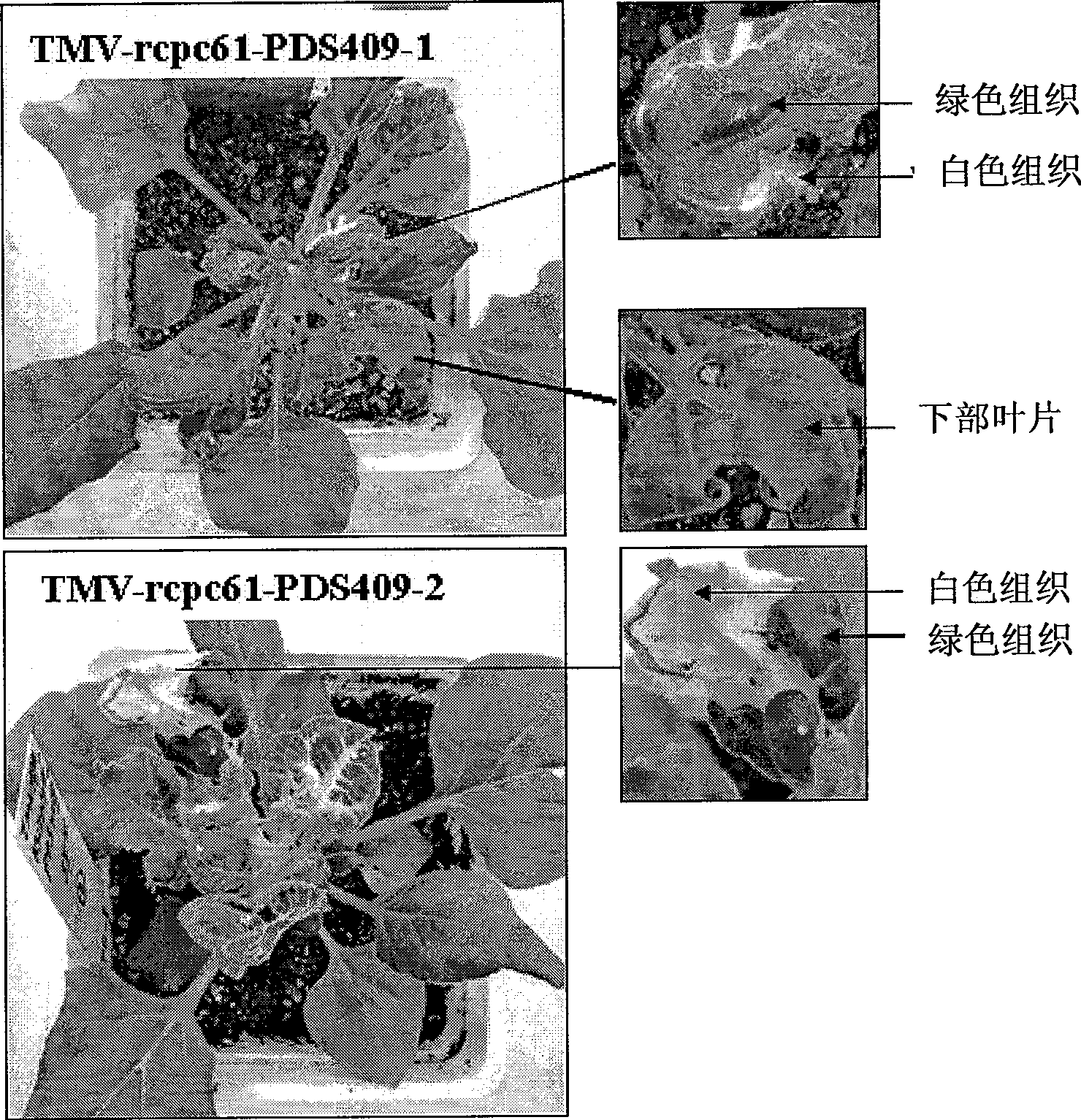
The invention discloses an efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink. A specific primer is designed according to a coding gene sequence of PDS (phytoene desaturase), and about 500bp cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments are amplified in the Chinese pink through RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction). Obtained PDS cDNA fragments are connected to TRV2, and acetosyringone concentration, seedling age and preculture temperature after infection as well as light conditions for plants after preculture are integrated in an assorted manner by optimizing an agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silence system according to photobleaching frequency, bleached leaf area and bleached conditions of the plants, so that the rapid efficient virus-induced silence system is established, virus-induced gene silence character can be obtained, and further, the problem that Chinese pink gene functions are verified effectively is solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Indicator gene used in TRV-mediated gene silencing system as well as construction method and application of carrier thereof
InactiveCN104480124AEasy to buildSignificant silent phenotypeFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumGene carrier
The invention discloses an indicator gene used in a TRV-mediated gene silencing system, and the base sequence of the indicator gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Virus induced gene silencing in the invention is a good tool for studying plant gene functions by using reverse genetics; according to the invention, an extremely good indicator gene carrier is provided for a tobacco rattle virus induced gene silencing technology; and the indicator gene carrier is simple in construction, significant in silencing phenotype and lasting in trait expression, and achieves a good indication effect on quick gene function researches.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
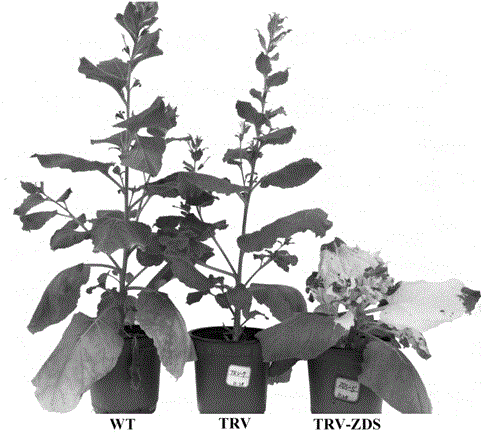
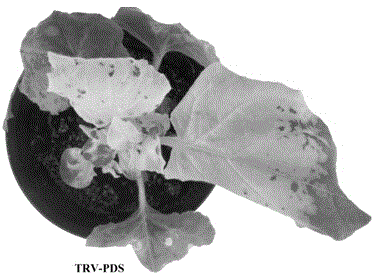
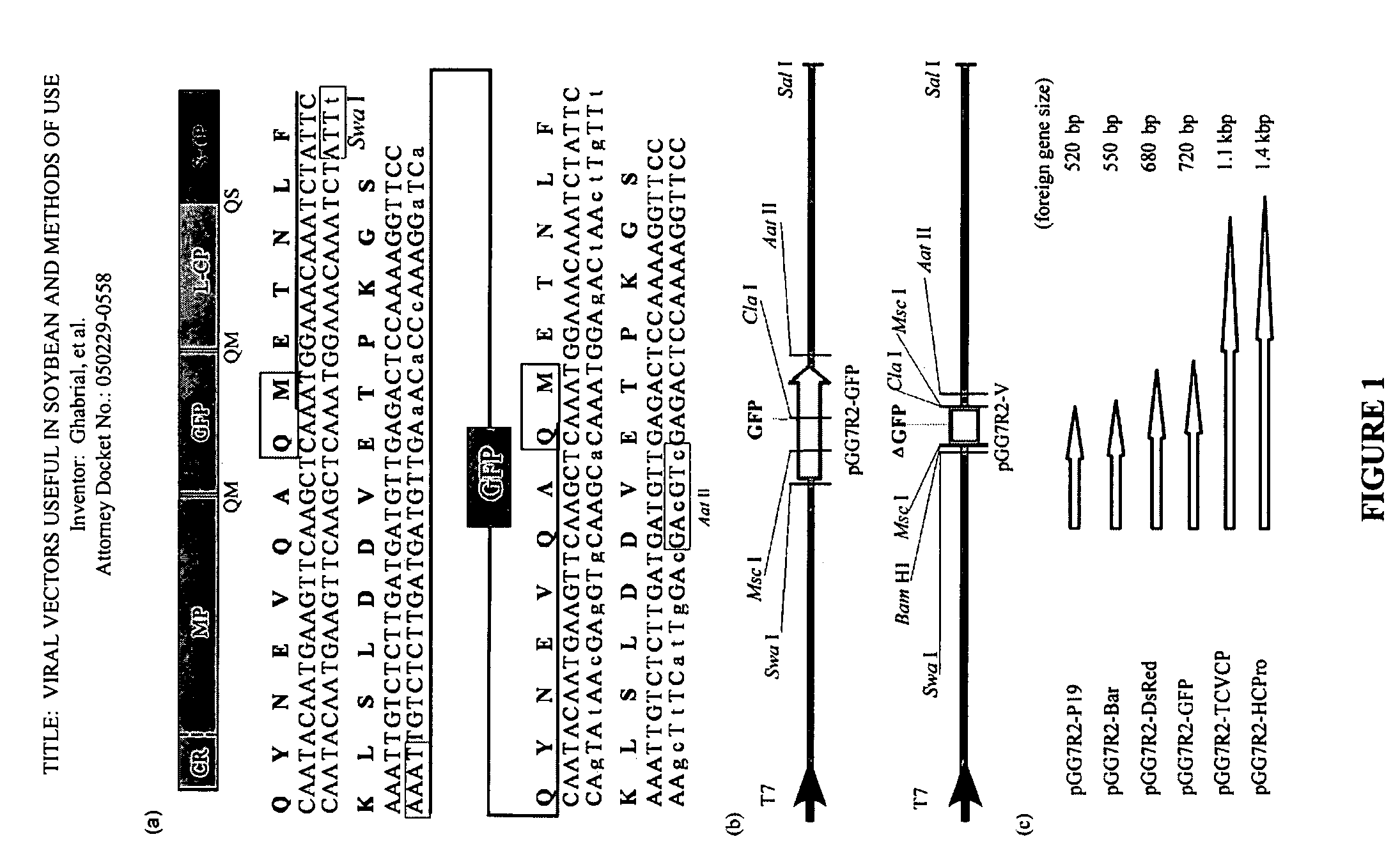
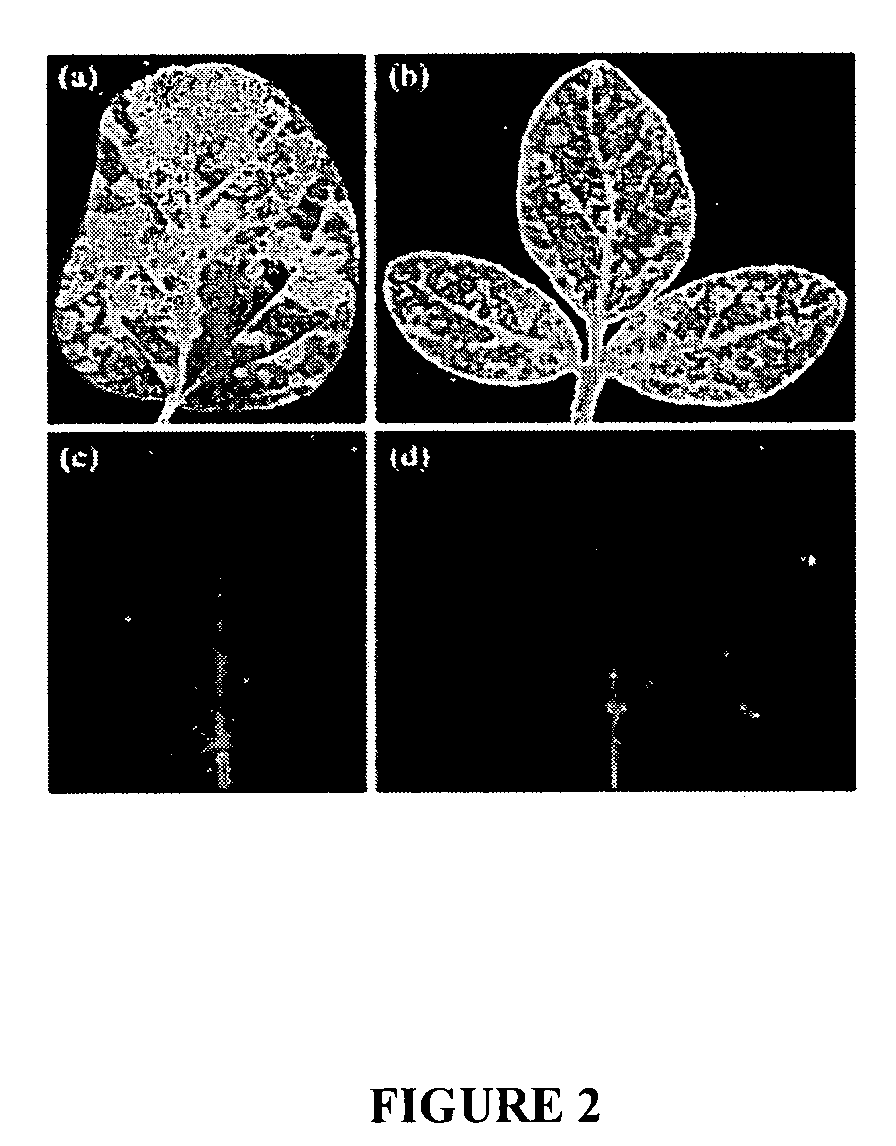
Viral vectors useful in soybean and methods of use
ActiveUS7618815B2Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousBean pod mottle virus
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Biological agent and method for preventing and controlling banana wilt
ActiveCN105557510AFusarium wilt control is goodInhibition of developmentBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention discloses a biological agent and a method for preventing and controlling banana wilt. The method comprises the following step: performing gene silencing regulation and control on genes or similar genes of relevant proteins of a banana wilt bacterium tropical No.4 physiological race ergosterol biosynthesis process. The active ingredients of the biological agent for preventing and controlling banana wilt include a double-stranded RNA interfere vector, an anti-sense RNA interfere vector or a microRNA interfere vector constructed by aiming at the genes or similar genes of relevant proteins of the banana wilt bacterium tropical No.4 physiological race ergosterol biosynthesis process, wherein the double-stranded RNA interfere vector, the anti-sense RNA interfere vector or the microRNA interfere vector is capable of causing target coding gene silencing. According to the invention, key protein and important metabolic pathways for the early development of banana wilt bacterium physiological race are identified and verified, and the research result can serve as a target site for development of new bactericides and disease-resistant new germplasm culture based on host plant virus-induced gene silencing.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying salt resisting function of gene
InactiveCN102154362AThe identification result is accurateWith anti-salt functionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionSalt resistanceVirus
The invention discloses a method for identifying the salt resisting function of a gene. The method for detecting whether the target gene in a plant has the salt resisting function provided by the invention comprises the following steps: losing the functions of the target gene in the target plant by use of a virus-induced gene silencing method, and marking the obtained plant as a gene silencing plant; performing salt stress processing on the gene silencing plant; detecting the salt-stress-related character of the gene silencing plant after the salt stress processing; and if the gene silencing plant after the salt stress processing shows the salt resisting character, determining that the target gene has the salt resisting function. Experiments demonstrate that: the method disclosed by the invention offers correct identification results, and has important significance on quickly identifying and exploring the salt-resistance-related gene resources.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving currant tomato endogenous gene silencing efficiency by viruses through induction
InactiveCN103146743AHigh speedImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionPlant virusMulti aspect
The invention discloses a method for improving currant tomato endogenous gene silencing efficiency by viruses through induction. According to the method, multi-aspect elements affecting virus induced gene silencing (VIGS) efficiency are comprehensively considered, through different inoculation methods and inoculation agrobacterium bacterium concentration, through combination of the silencing efficiency, namely silencing frequency, silencing effectiveness and silencing effects, an evaluation method obtains the optimal system that currant tomato viruses induce the gene silencing, and an appropriate inoculation method and concentration improve the silencing efficiency. Evaluation for the VIGS efficiency by means of the method is short in time, high in speed and high in efficiency, the method can be applied to evaluation for an optimization system that other plant viruses induce gene silencing, and an effective method is provided for rapid verification of a gene function.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Virus induced gene silencing system and use thereof
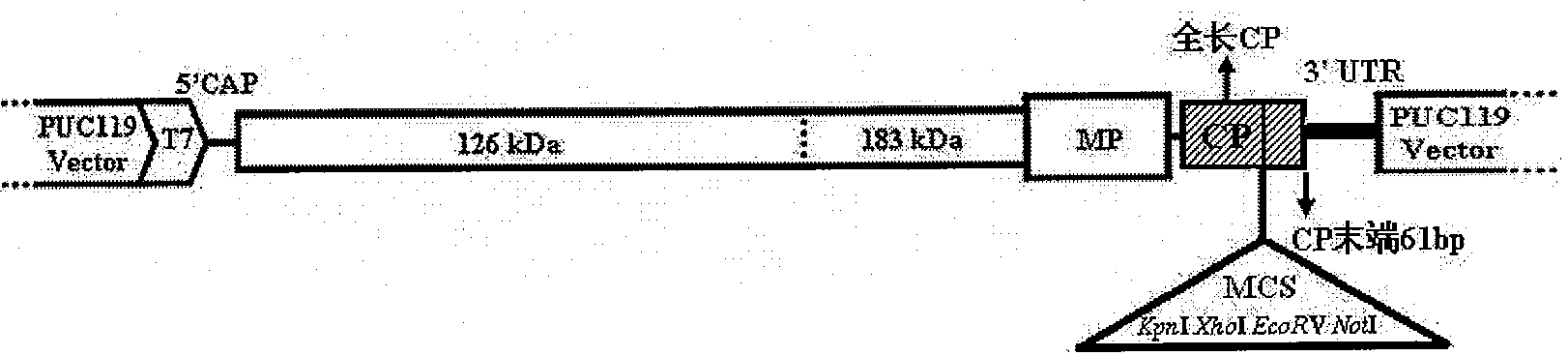
The invention relates to a virus-induced gene silencing system in particular using tobacco mosaic virus TMV as a vector. In the system, a DNA segment of a target gene is inserted between a termination codon and a 3' untranslated region of coat protein CP of the tobacco mosaic virus TMV; a polyclonal restricted endo enzyme cutting point is introduced between the termination codon and the 3' untranslated region of the coat protein CP of the tobacco mosaic virus TMV and is used for the insertion of the DNA segment of the target gene; and a section of a basic group sequence on the bottom end of CP3' is introduced in the front of the 3' untranslated region so as to strengthen the stability of the silencing vector. The DNA segment of the target gene is not more than 1 kb. The gene silencing system is utilized to carry out silencing on the target gene and is economic, feasible, convenient and effective.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for improving efficiency of eggplant virus induced gene silencing (VIGS)
InactiveCN108624617AEfficient Silencing MethodsFast silent methodVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genetic engineeringVirus
The invention discloses a method for improving efficiency of eggplant virus induced gene silencing (VIGS), belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The method comprehensively considers various factors affecting the efficiency of the eggplant VIGS; a recombinant vector is silenced by constructing a TRV2 virus containing a target gene fragment; a vacuum infiltration method is adopted to infect seeds at the stage in germination so as to induce silencing of an endogenous target gene. The silenced plants treated by the method are rapid in phenotype appearance, high in efficiency and long in phenotypic change duration, and the problems of injury, caused by injection and inoculation, to plants, difficulty in injection and inoculation of smaller eggplant cotyledons, and the like can be solved; therefore, an effective method is provided for rapid verification of gene functions.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
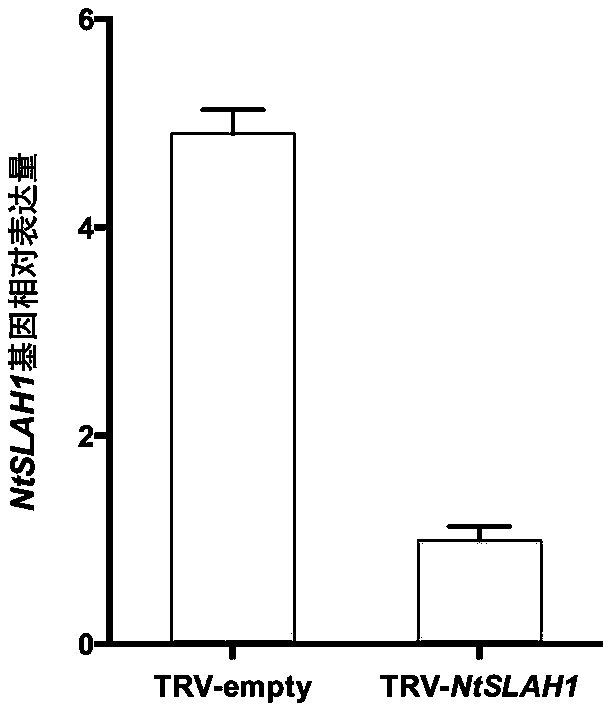
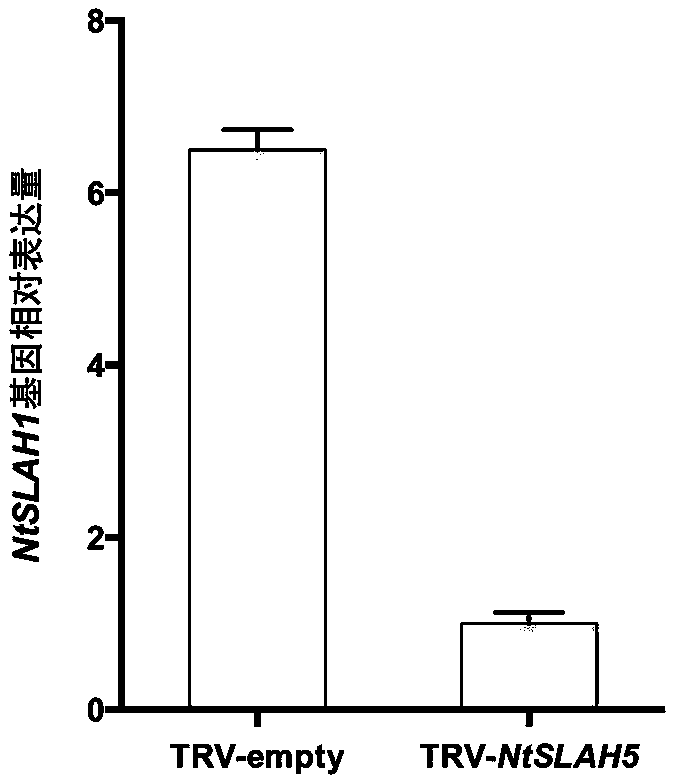
Nicotiana tabacum slowly activating anion channel homologue (NtSLAH1) and application thereof
ActiveCN108192896AReduce Chloride ContentQuality improvementPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
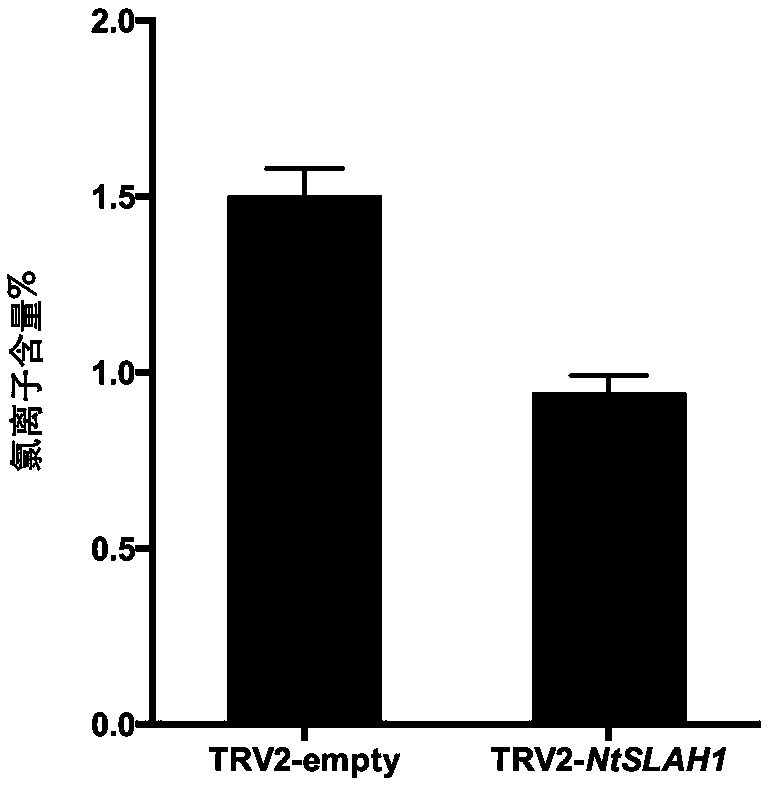
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco genetic engineering, and in particular relates to a nicotiana tabacum slowly activating anion channel homologue (NtSLAH1) and application thereof. The CDS sequence of the gene comprises 1107 bp basic group, and the sequence of the basic group is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, wherein the 270th-615th nucleotides are specific nucleic acid fragments. The NtSLAH1 is a key protein of tobacco chlorine ion metabolism; after the expression of the NtSLAH1 gene is inhibited by using a virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) technology, the chloride ion contentin transgenic silencing plants is significantly reduced. Therefore, a good foundation is laid for cultivating new varieties of low-chlorine tobacco, and a fundamental technical support is also provided for the stability of tobacco quality and the improvement of cigarette quality.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Viral vectors useful in soybean and methods of use
ActiveUS20070214518A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousBean pod mottle virus
The invention provides Bean pod mottle virus (BPMV) vectors useful for expression of heterologous proteins in plants such as soybean. The BPMV vectors are also useful for virus-induced gene silencing. The invention also provides methods for expressing a heterologous polypeptide in a plant such as soybean. The invention additionally provides methods for virus-induced gene silencing, particularly in a soybean plant, which can be used to determine the function of a gene of interest.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Virus induced gene silencing (VIGS) for functional analysis of genes in cotton
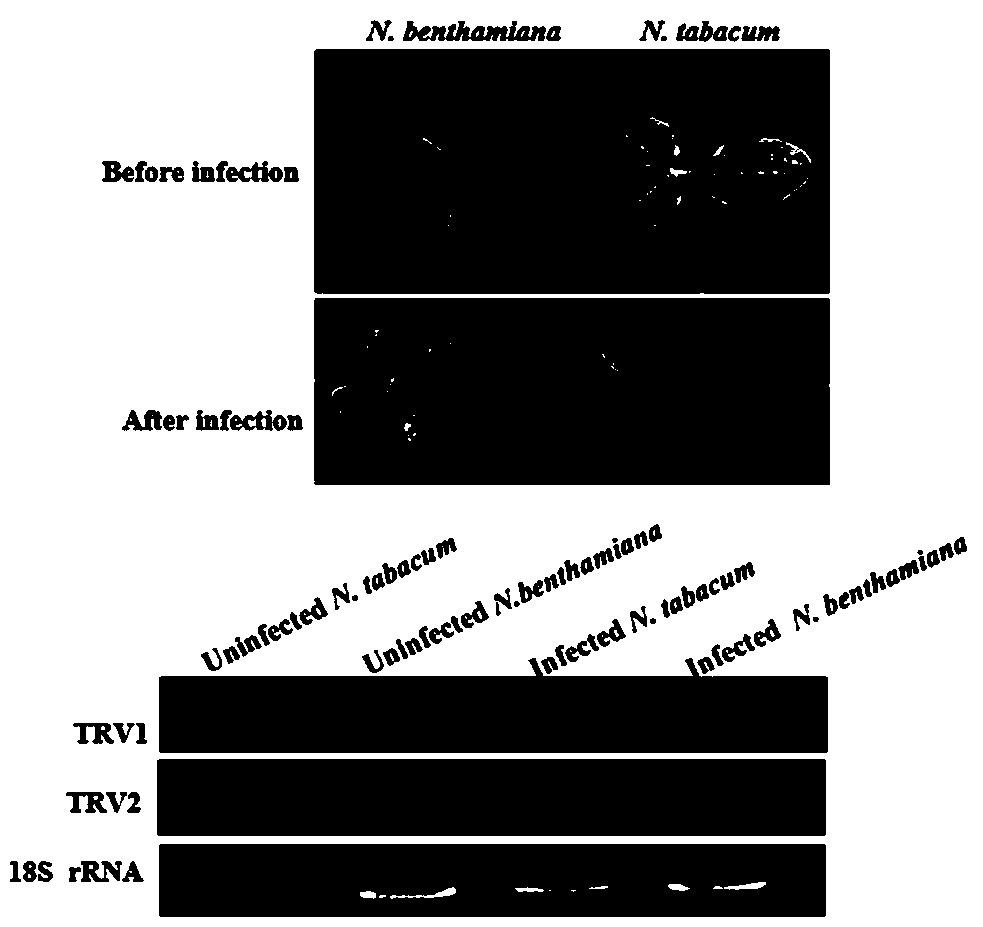
ActiveUS20120096595A1Rapid silencing procedureImprove cotton agronomic traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationPlant tissueFunctional analysis
The invention relates to the functional analysis of genes in cotton by employing the Virus Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) method. More specifically this method induces gene silencing in cotton with the help of the Tobacco Rattle Virus (TRV) vectors RNA1 and RNA2 and phenotypic effects on the cotton plant can be analysed Moreover this invention also provides transient expression vector TRV RNA2 in order to transiently express genes in cotton plants and plant tissue under the influence of a strong subgenomic promoter.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Gene silencing method Si-VIGS (Seed imbibition-virus-induced gene silencing) in early stage of cotton
ActiveCN110172473AEasy to operateLong silencePlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumSilencing gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton breeding, and specifically relates to a gene silencing method in early germination and seedling stage of cotton. The method comprises the steps of preparing agrobacterium liquid for transfection, performing virus amplification by utilizing tobacco, infecting cotton seeds and the like. According to the invention, a cotton gene silencing technology is optimized and improved by taking a tobacco rattle virus (TRV) as a virus vector. It is proved by a result that a gene silencing phenotype can be obtained through inoculating cotton cotyledon orseeds with TRV homogenate or agrobacteria. Through comparing the similarities and differences of TRV homogenate and agrobacteria inoculation, it is discovered that through applying a seed imbibition(Si) method to inoculation of any infection liquid, the virus inoculation time can all be advanced to the inflorescence primordial formation stage of the seeds; functional genes during germination ofthe seeds can be efficiently silenced within 3 days; virus homogenate-mediated gene silencing can last till the seedling stage of the cotton. Si-VIGS (Seed imbibition-virus-induced gene silencing) involved in the invention can efficiently silence the genes from the early germination stage of the cotton; the operation is simple; the phenotypes are unified; a relatively good application prospect isshown.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Functional Analysis of Jatropha Genes
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Agroinoculation method for virus induced gene silencing
The invention provides novel methods and compositions for modulating gene function in plants. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions that allow efficient induction of virus-induced gene silencing in plants. The invention is significant in that it allows high throughput analysis of gene function in plants.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
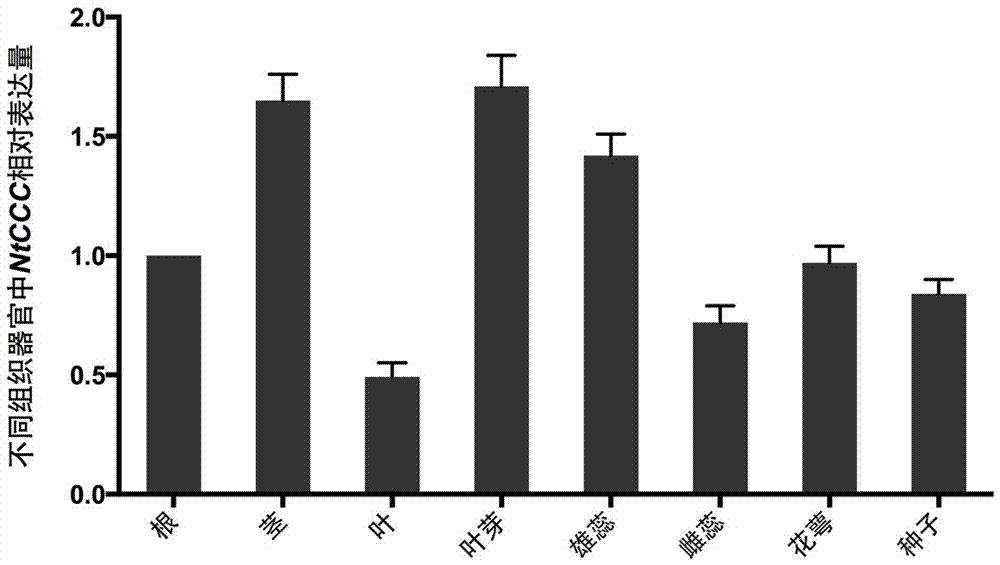
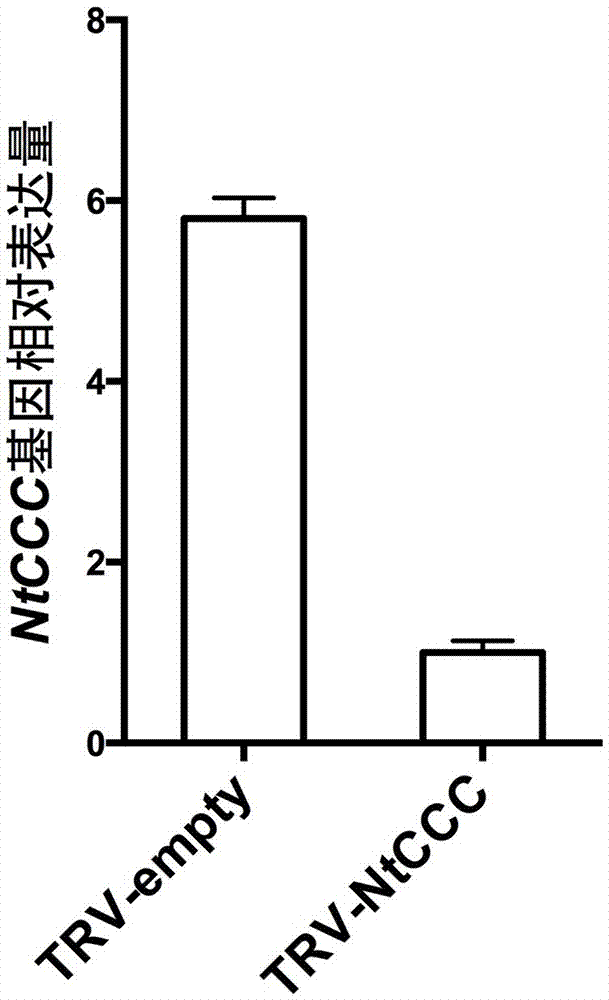
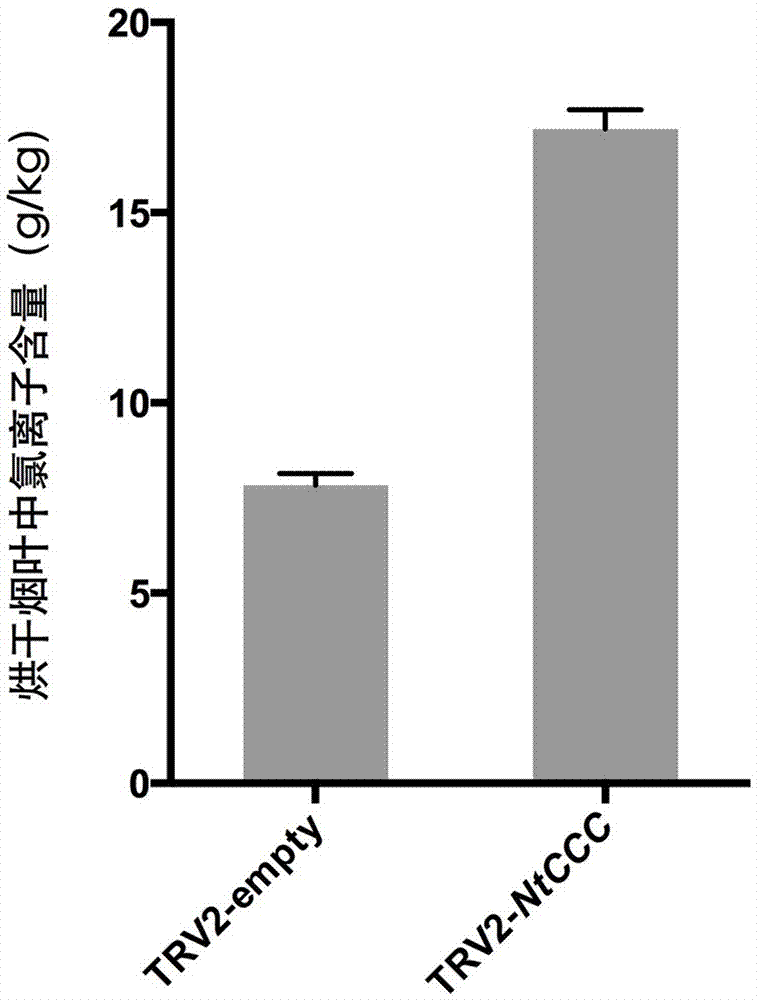
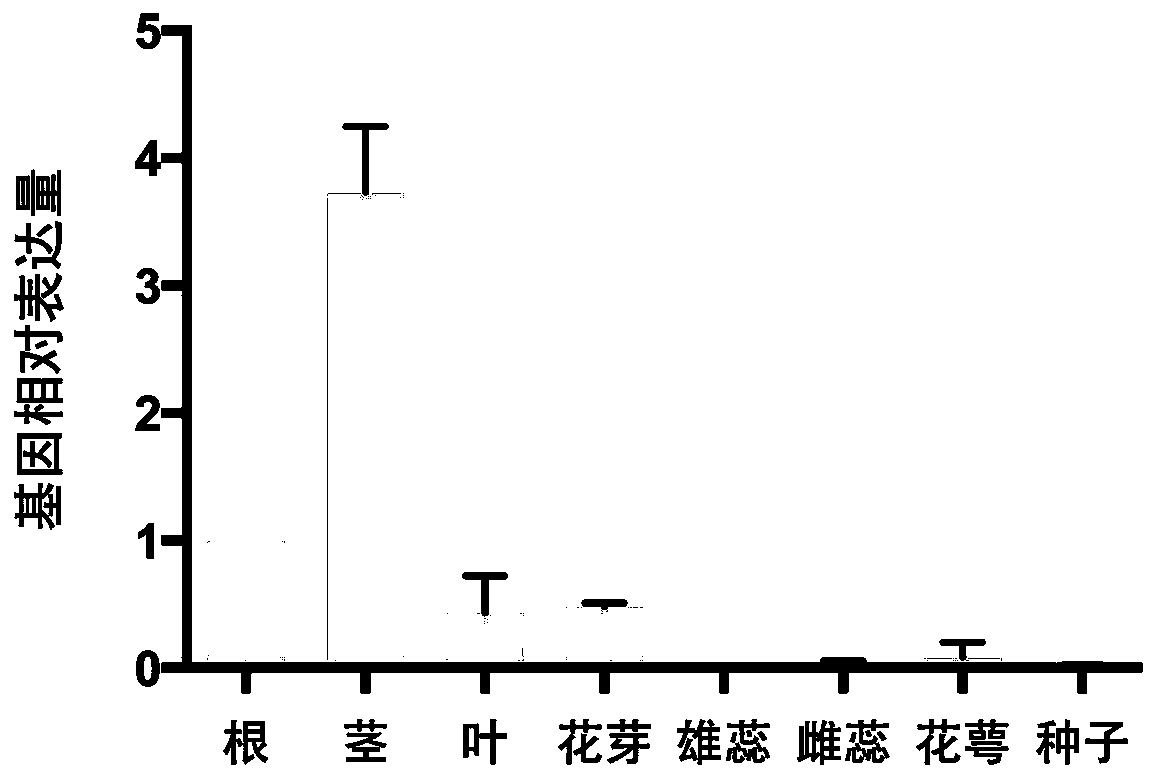
NtCCC (nicotiana tabacum cation/chloride cotransporter) and application thereof
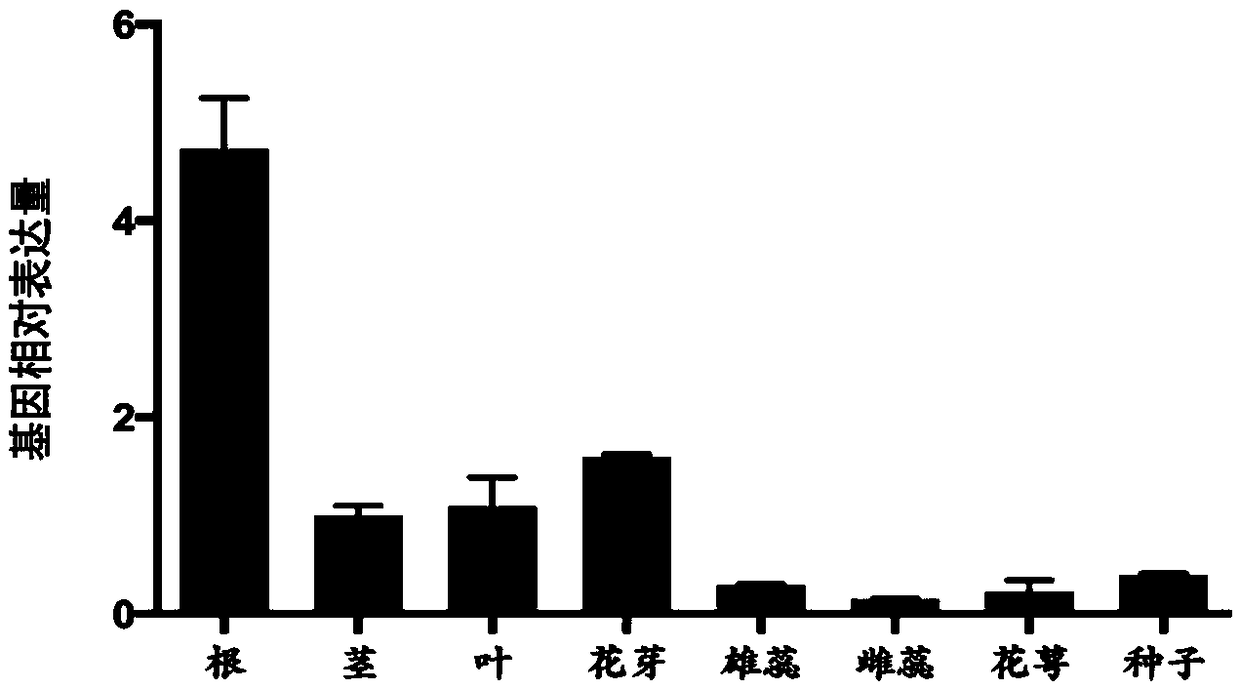
The invention relates to nicotiana tabacum chloride transport related genes, in particular to an application of an NtCCC (nicotiana tabacum cation / chloride cotransporter) in improvement of saline-alkali soil. The contransporter is related to chloride transport and has a base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein nucleotides at 5-477 sites are specific nucleic acid fragments. The NtCCC is a key regulator in nicotiana tabacum chloride metabolism, is found to be expressed in all tissue of nicotiana tabacum through real-time PCR and has higher expression in stems and leafbuds of nicotiana tabacum. Gene silenced plants with increased chloride content can be obtained through VIGS (virus-induced gene silence) or NtCCC knockout, making breeding of the nicotiana tabacum with higher chloride content possible, and a new technological approach is provided for adaptation of the nicotiana tabacum to different planting environments and improvement of saline-alkali soil.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
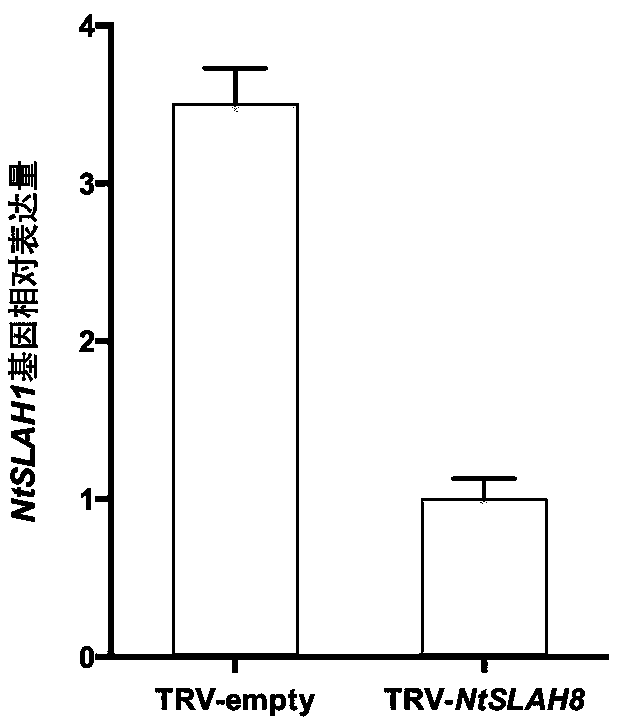
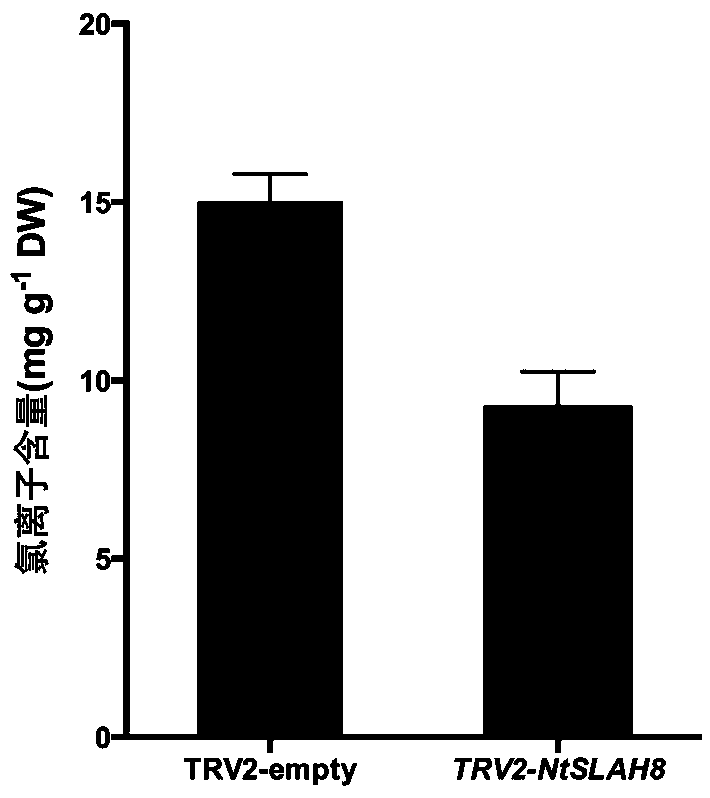
Tobacco slowly activating anion channel protein NtSLAH8 and application thereof
InactiveCN109337914AReduce Chloride ContentQuality improvementPlant peptidesFermentationIon contentNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco genetic engineering, and particularly relates to tobacco slowly activating anion channel protein NtSLAH8 and application thereof. A gene CDS sequence comprises 579bp basic group, with the base sequence being as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the first to 388th nucleotide for a specific nucleic acid fragment. The tobacco slowly activating anion channelprotein NtSLAH8 belongs to key protein for metabolism of tobacco chlorine ion, and the chlorine ion content in transgenic silencing plant is obviously reduced after NtSLAH8 gene expression is inhibited through a virus induced gene silencing (VIGS) technology, so that a good foundation can be laid for cultivation of low chlorine content novel varieties, and meanwhile a fundamental technical support for the stabilizing of tobacco leaf quality and improvement of cigarette quality.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Gene silence indicating gene and virus induced silencing vector and construction method and infection method
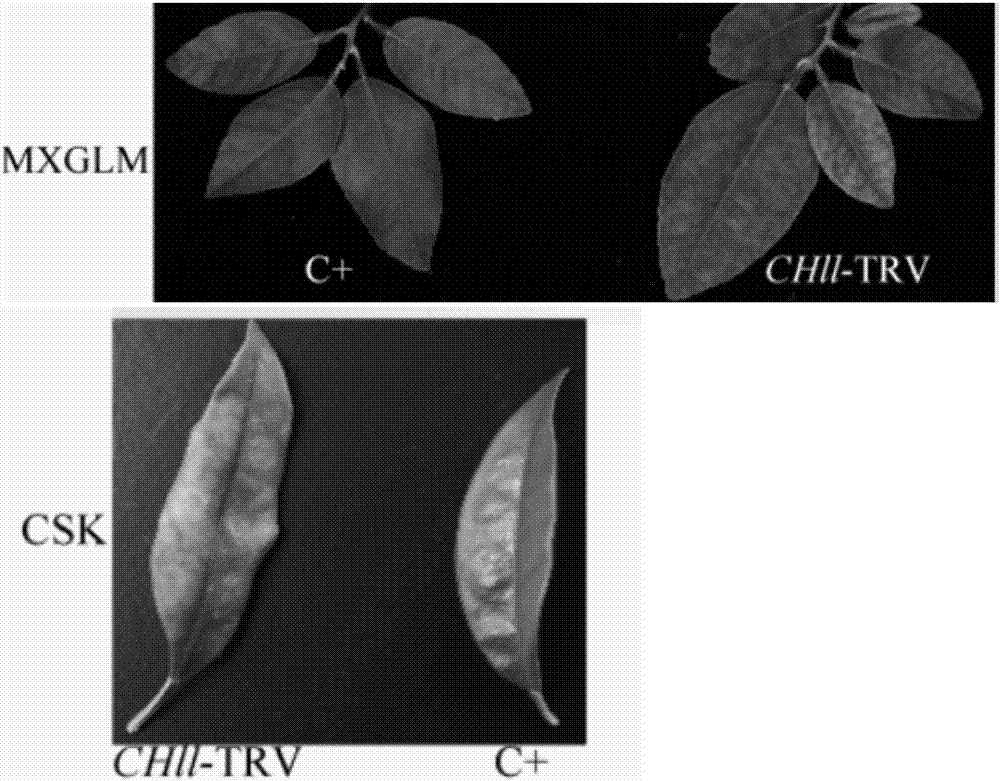
ActiveCN106939313AEasy to buildSignificant silent phenotypeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesTransformation efficiencyNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses an indicating gene used in a TRV-mediated gene silencing system, the nucleic acid sequence of the indicating gene is as shown in SEQIDNo:1, and the invention discloses a virus induced silencing vector comprising the sequence and a construction method thereof and an infection method of citrus seedlings by use of the virus induced silencing vector. The effective indicating gene is provided for the TRV-mediated virus induced gene silencing system, the TRV-mediated gene silencing system is firstly successfully established in citrus fruits, and the indicating gene in the citrus fruits is successfully silenced. The silencing system constructed by the silencing vector has the advantages of simple operation and high conversion efficiency, can rapidly carry out functional verification of the gene in the citrus fruits, and can effectively inhibit the expression of endogenous genes in the citrus fruits, and the phenotype is remarkable. The silencing vector provides a reliable technique for rapid and effective performing of gene function verification in the citrus fruits.
Owner:CITRUS RES INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
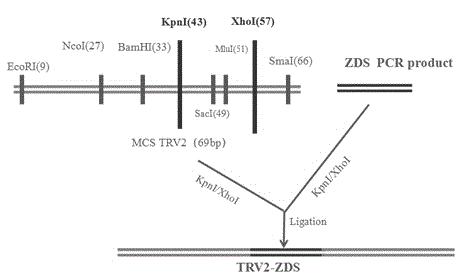
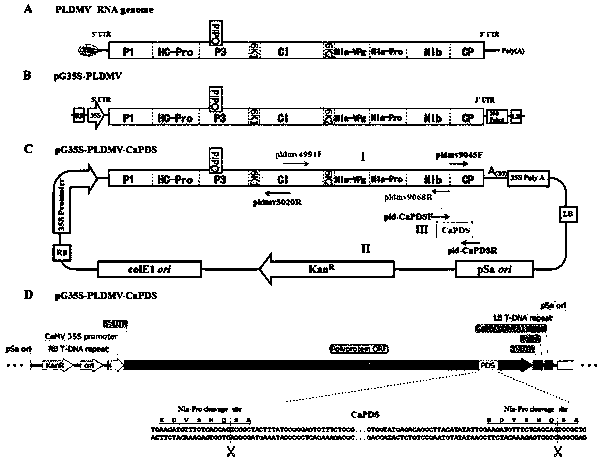
Potyvirus virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system and application thereof
ActiveCN110951763AGood silence effectGood effectSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesGenus DependovirusPlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses a potyvirus virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system with a papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus (PLDMV) as avirus vector. According to the system, a target gene is inserted between Nib and coat protein (CP) of the PLDMV, and a NIa-Pro digestion site is introduced between the target gene and the CP. By in-vitro splicing methods such as Gibson splicing or In-Fusion cloning, target gene fragments are seamlessly cloned and inserted between the Nib and the CP to construct a recombinant virus silence vector containing a plant target gene. Plants are inoculated with the recombinant virus silence vector by agrobacterium injection, and phenotypic changes of the plants are observed after the target gene silencing the plants is induced. The potyvirus VIGS system provides a powerful tool to study gene functions of papaya by using the PLDMV silence vector, and has great scientific significance and application prospects.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Verticillium dahliae phospholipase target gene fragment and interference vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105255918AImprove disease resistanceStrong disease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumPhospholipase
The invention discloses a verticillium dahliae phospholipase target gene fragment and an interference vector and application thereof, and belongs to the fields of clone and application of verticillium dahliae disease course key genes. A gene sequence of a verticillium dahliae phospholipase target gene is introduced into transient expression ds RNA of nicotiana benthamiana through a virus-induced gene silencing technology, and the target gene which can extremely significantly improve the plant disease resistance is screened; an RNAi technology is further utilized to establish the stably inherited interference vector and transform the nicotiana benthamiana, and transforming results show that transgenic tobacco plants extremely significantly improve the disease resistance of tobaccos to verticillium dahliae, show the highly resistance and even reach the immune level. The verticillium dahliae phospholipase target gene fragment and the RNA interference vector can be applied to improving the disease resistance of the plants to the verticillium dahliae and cultivating new transgenic plant species with the verticillium dahliae resistance.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cotton ascorbic acid peroxidase gene APX and application thereof
The invention provides a cotton ascorbic acid peroxidase gene APX and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. A nucleotide sequence of the gene APX is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or shown in a sequence which has 80% of homology with the sequence. The cloned gene APX has the advantages that the expression is different after the gene APX is induced by verticillium dahliae in different corn varieties; the up-regulated expression is presented in the anti-disease variety in the whole tendency, and the down-regulated expression is presented in the disease-susceptible land cotton variety, namely that the expression is inhibited; a VIGS (virus induced gene silencing) carrier PYL156-APX is built, the gene APX in cotton is silenced, and the resistance reaction of the gene APX on the verticillium dahliae of the cotton is reversely demonstrated; the gene is converted into tobacco, and the resistance reaction of the gene APX on the verticillium dahliae of the cotton is positively demonstrated; the gene APX is used for improving the resistance of the crop on the verticillium dahliae, and the broad application prospect is realized in the crop germplasm resources improving and genetic breeding aspects.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
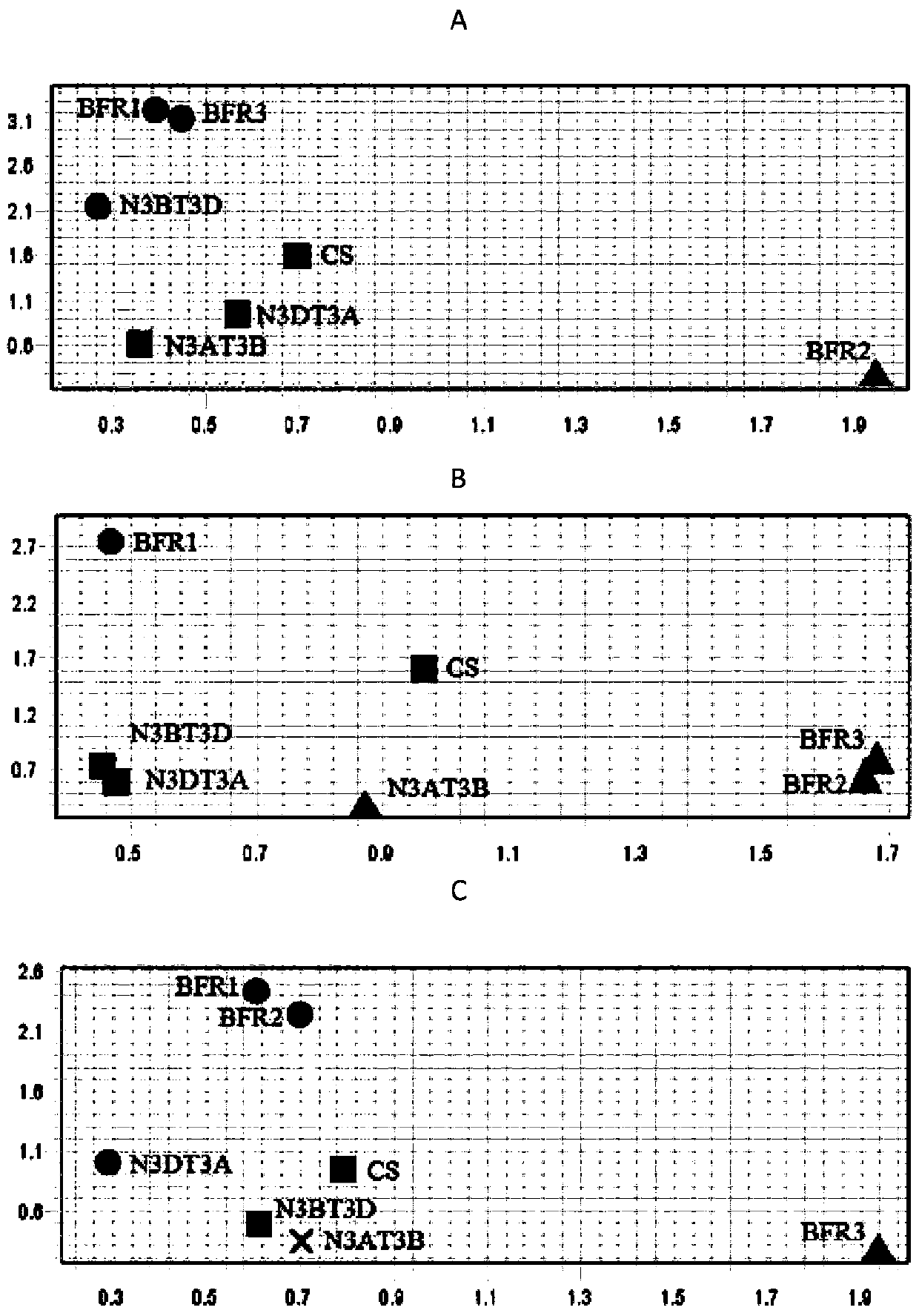
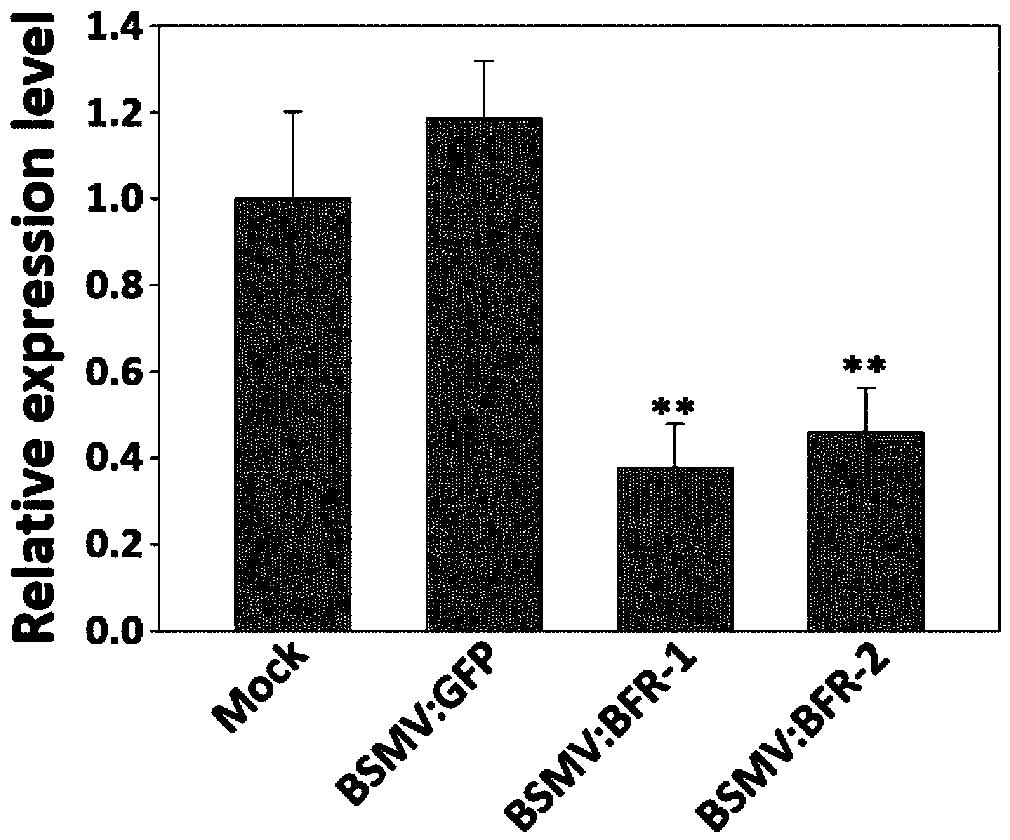
BFR protein associated with resistance of wheat to powdery mildew, and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN110229223AReduce expressionInhibition of germinationPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologySpore germination
The invention relates to the field of wheat disease resistance, and specifically relates to a BFR protein associated with resistance of wheat to powdery mildew as well as a coding gene and applicationthereof. The BFR protein associated with resistance of wheat to powdery mildew has an amino acid sequence as shown in sequence 7, or a sequence constructed by replacing one or more amino acids in theamino acid sequence shown in sequence 7. Expression of the BFR protein in wheat leaves is reduced by adopting a virus-induced gene silencing technology and a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology so asto have reaction type of infection of a powdery-mildew-resistant wheat variety, xiao-bai-dong (Triticum aestivum L.), on an avirulent strain E18 changed from grade 0-1 to grade 3-4. Over-expression of the BFR gene in wheat leaves is allowed by adopting biolistic transformation; and thus, pathogen spore germination of a virulent strain E18 on leaves of the wheat variety Kelong-199 is significantlyinhibited.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for mediating virus-induced gene silencing by TRV vectors in forsythia suspensa leaf
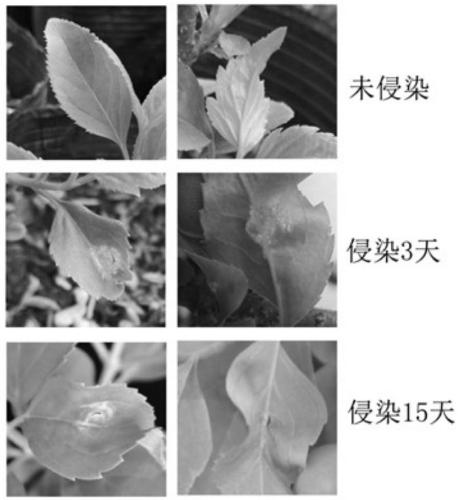
ActiveCN108949809AImprove the success rate of infectionOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionForsythia suspensaGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and concretely discloses a method for mediating virus-induced gene silencing by TRV vectors in a forsythia suspensa leaf. The method includes the following steps: transforming the TRV2 vector and the TRV1 vector containing specific target gene fragments into an agrobacterium competent state; performing screening to obtain a positive strain, and performing proliferation culture to obtain two monoclonal cells containing the different vectors; centrifuging the two monoclonal cells, resuspending the two monoclonal cells until OD600 is equal to 0.9-1.1 by using an infection solution, and then mixing the two monoclonal cells in equal volume to obtain a mixed infection solution; and injecting the mixed infection solution into the forsythia suspensa to silence the target genes. The method deeply deeply explores key factors that can improve a success rate of the infection and screens out an optimal infection solution composition formula and an OD value of the infection solution containing the cells during the infection. The method of the invention is used to infect the forsythia suspensa leaf, and so the success rate of the forsythia suspensa leaf VIGS infection can be more than 90%.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
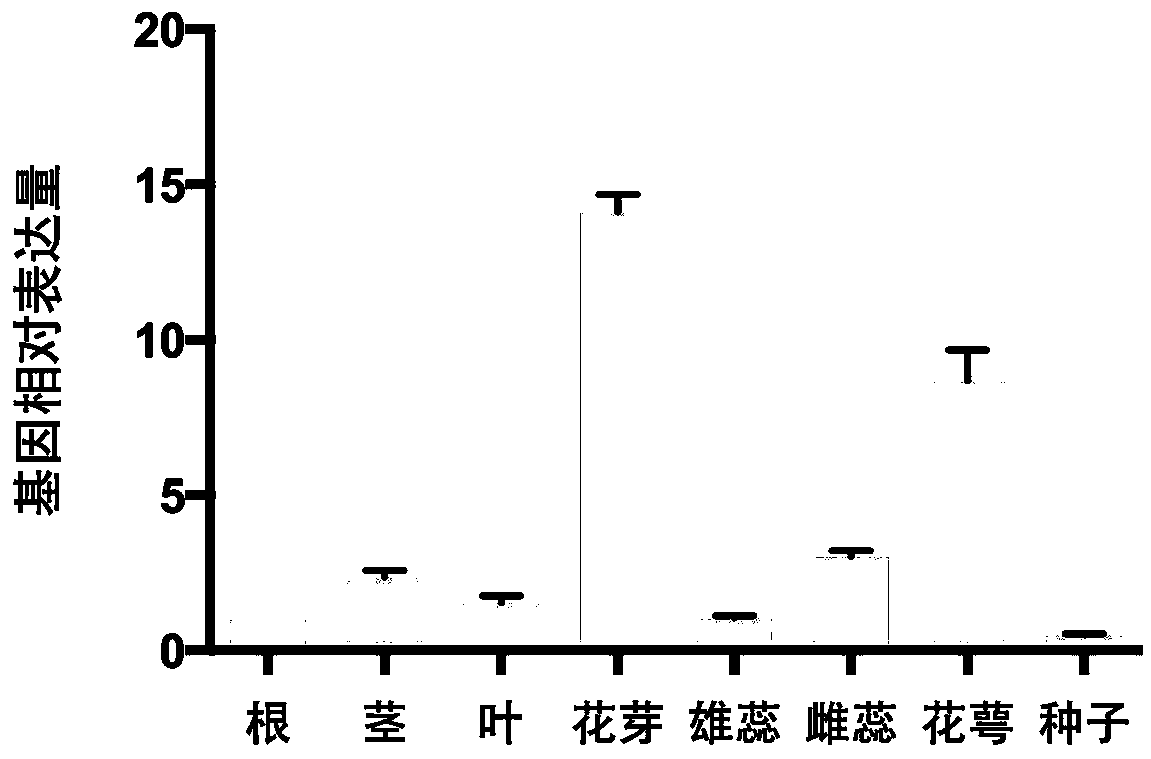
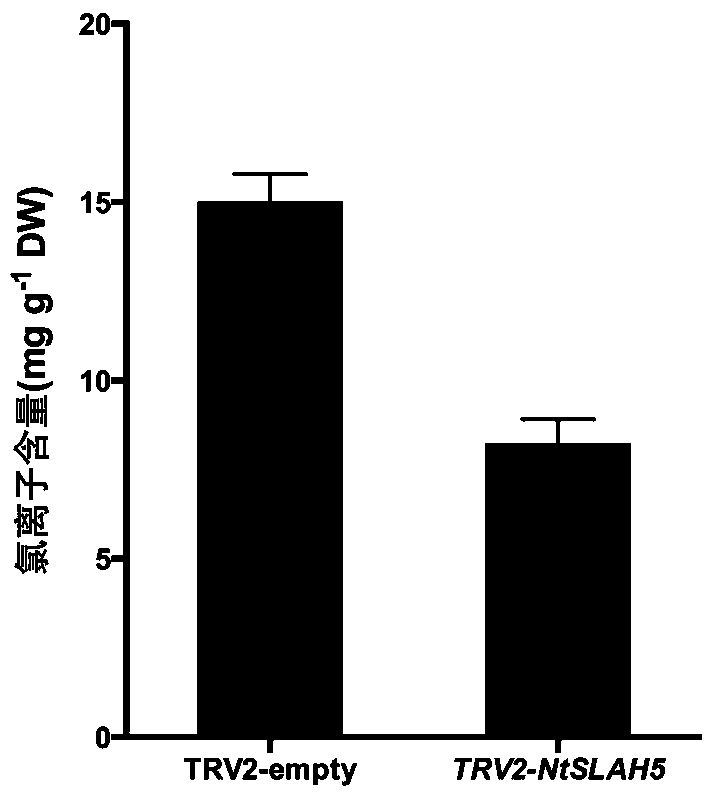
Slowly activating anion channel homologue NtSLAH5 for tobaccos and application of NtSLAH5
ActiveCN109517828AReduce Chloride ContentQuality improvementPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco gene engineering and particularly relates to slowly activating anion channel homologue NtSLAH5 for tobaccos and patent application of the NtSLAH5. The CDS sequence of the gene contains an 1821bp basic group, the sequence of the basic group is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and nucleotides 1112-1448 are specific nucleic acid fragments. The slowlyactivating anion channel homologue NtSLAH5 for the tobaccos is a key protein for the metabolism of chloride ions of the tobaccos, and the expression of the gene of the NtSLAH5 is inhibited by virtueof a virus induced gene silencing (VIGS) technique, so that the content of the chlorine ions in a transgenic silenced plant. Therefore, a good foundation can be laid for the cultivation of new speciesof low-chlorine-content tobaccos, and meanwhile, the basic technical support is provided for the quality stabilization of the tobacco leaves and the quality improvement of cigarettes.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Gene for regulating plant height of Gossypium hirsutum, and application thereof
InactiveCN108396031AStrong specificityRealize regulationPlant peptidesFermentationGenomic sequencingMolecular breeding
The invention relates to the field of plant height genes, and concretely relates to a gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum, and an application thereof. The base sequence of the CDS of the gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and a specific base sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. A large number of SNPs covering the whole genome of Gossypium spp. are developed based on an SLAF-seq reduced representation sequencing technology by utilizing 355 natural populations of Gossypium hirsutum, genetic genes of theplant height are parsed by adopting a GWAS technology through the 3-year and 2-site phenotypic identification of plant height traits, and the genetic screens are screened to obtain the gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum. A result of verification of the functions of the gene by using a virus-induced gene silencing technology shows that the plant height can be controlled by regulating the expression of the gene, so the gene lays a foundation for developing the molecular breeding of the Gossypium hirsutum.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV +1
Virus-induced gene silencing vector, application thereof and citrus disease prevention and control method
PendingCN114317598AGood ulcer control effectLow costFermentationGenetic engineeringCitrus volkamerianaGene terminator
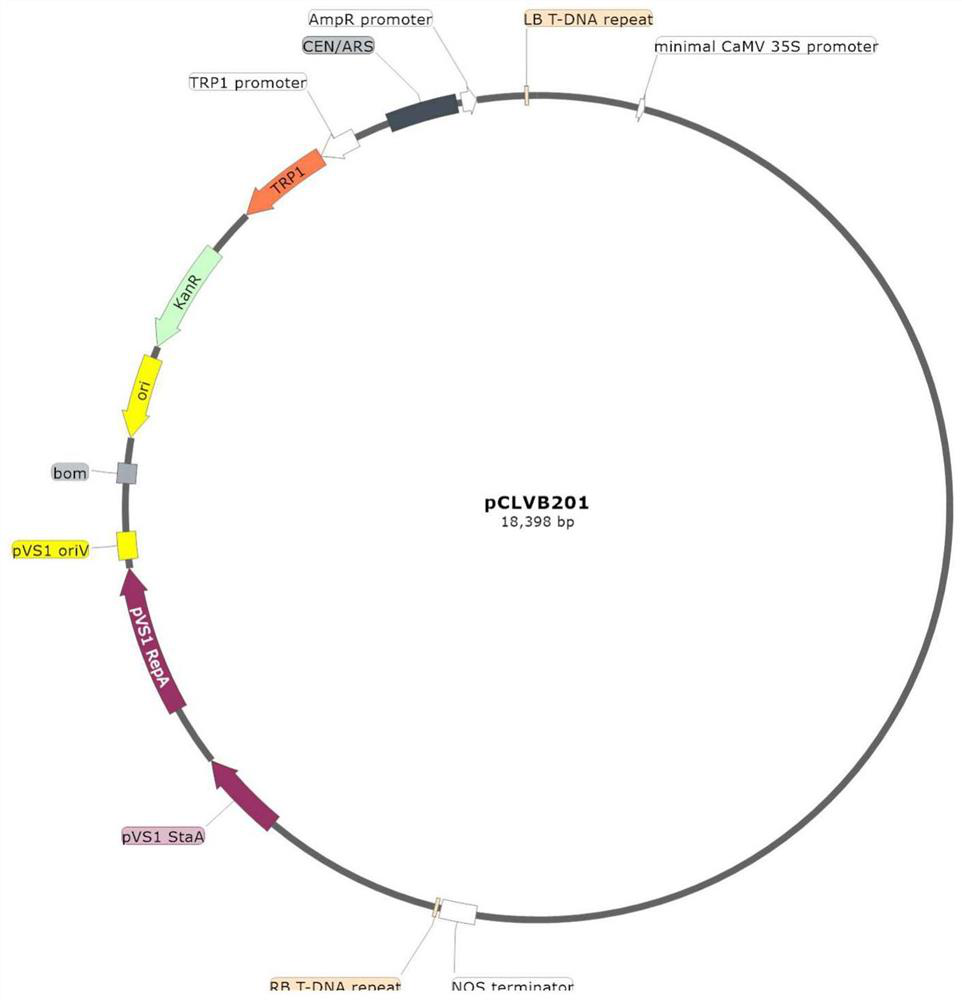
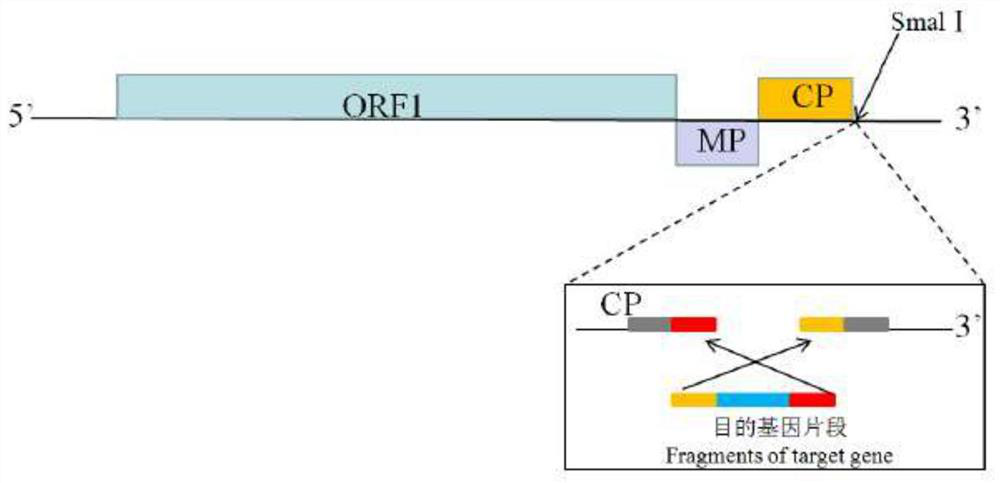
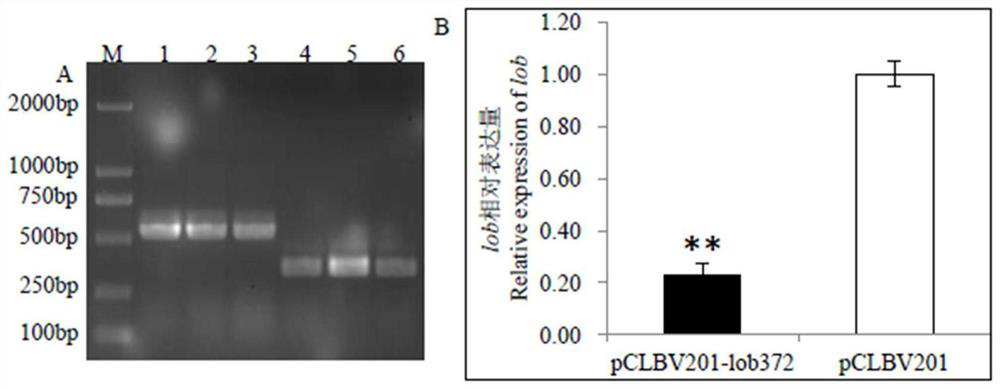
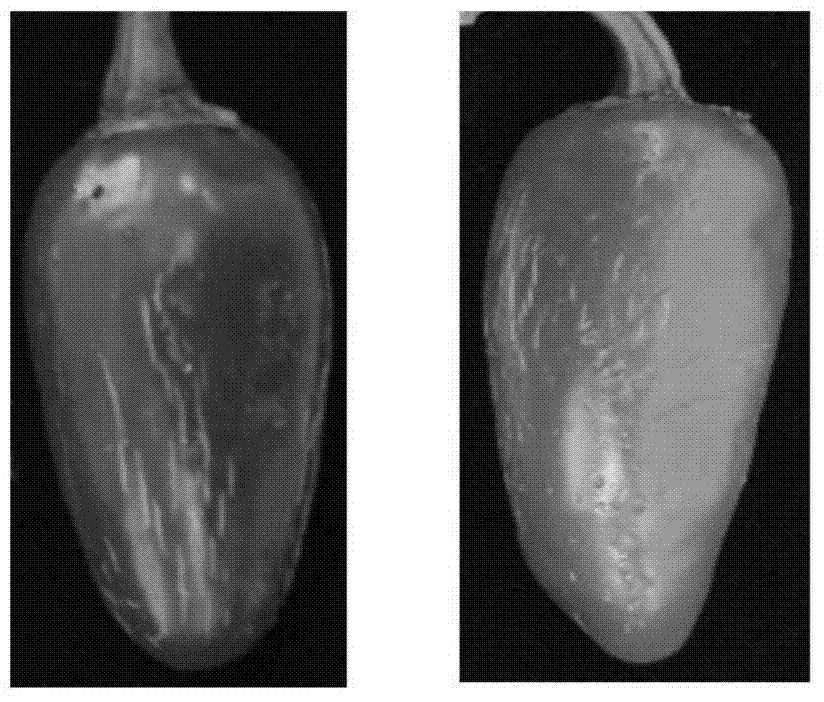
The invention provides a virus-induced gene silencing vector, application thereof and a method for preventing and controlling citrus diseases. The gene silencing vector is constructed on the basis of infectious clone plasmids of the citrus leaf mottle virus. The gene silencing vector is a recombinant plasmid vector constructed by integrating a target gene segment into a CLBV infectious cloning plasmid pCLBV201, and the target gene segment is preferably and reversely connected between a CLBV genome cp gene terminator and 3 'UTR in the plasmid vector pCLBV201. The gene silencing vector of the targeted citrus lob gene provided by the invention blocks the combination of citrus canker pathogen and the target gene, can achieve a good canker prevention and control effect, and is low in cost and environment-friendly. The constructed gene silencing vector targeting different ORFs of the CYVCV genome can effectively inhibit transcription expression of CYVCV in plants, and then prevention and control of the citrus yellow vein disease are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Method for rapidly identifying functions of pepper fruit color development related genes
InactiveCN103695537ARapid identificationValid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFunctional identificationYellow symptom
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
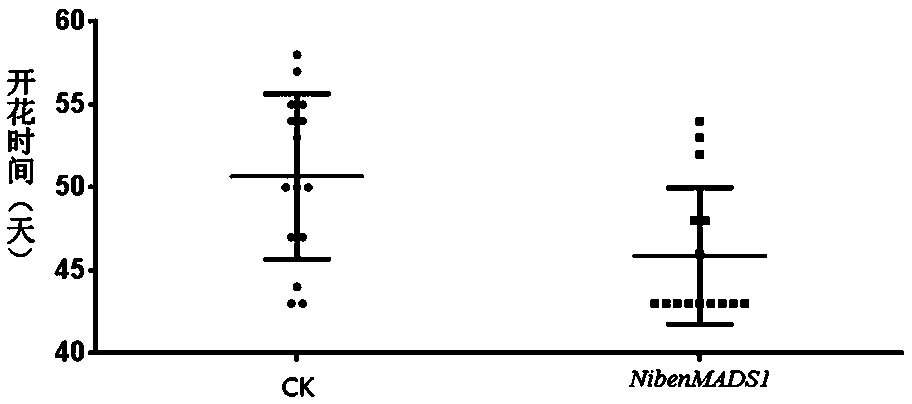
Regulatory gene NtMADS1 during tobacco flowering period as well as cloning method and application thereof
The invention discloses a regulatory gene NtMADS1 during a tobacco flowering period as well as a cloning method and application thereof. A sequence of nucleotide contained in the regulatory gene NtMADS1 during the tobacco flowering period is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; a sequence of amino acid contained in a polypeptide coded by the regulatory gene NtMADS1 during the tobacco flowering period is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2. In tobacco, by reducing the expression of the regulatory gene NtMADS1, the tobacco flowering period can be ahead of time; in addition, by comparing a polypeptide sequence of the regulatory gene NtMADS1, homologous genes having the same functions can be searched, and the functions of the homologous genes can be verified by utilizing a VIGS (Virus-induced Gene Silencing) technology, so that the regulatory gene NtMADS1 has a wide application range; through the regulatory gene NtMADS1 during the tobacco flowering period, genetic and technical supports are provided for optimizing breeding of the tobacco during the flowering period.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Application of solanum lycopersicum SlTRXz gene as restraining target to defence of meloidogyne incognita
InactiveCN111718955AIncrease resistanceRoot knot index decreasedOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyRoot-knot nematode
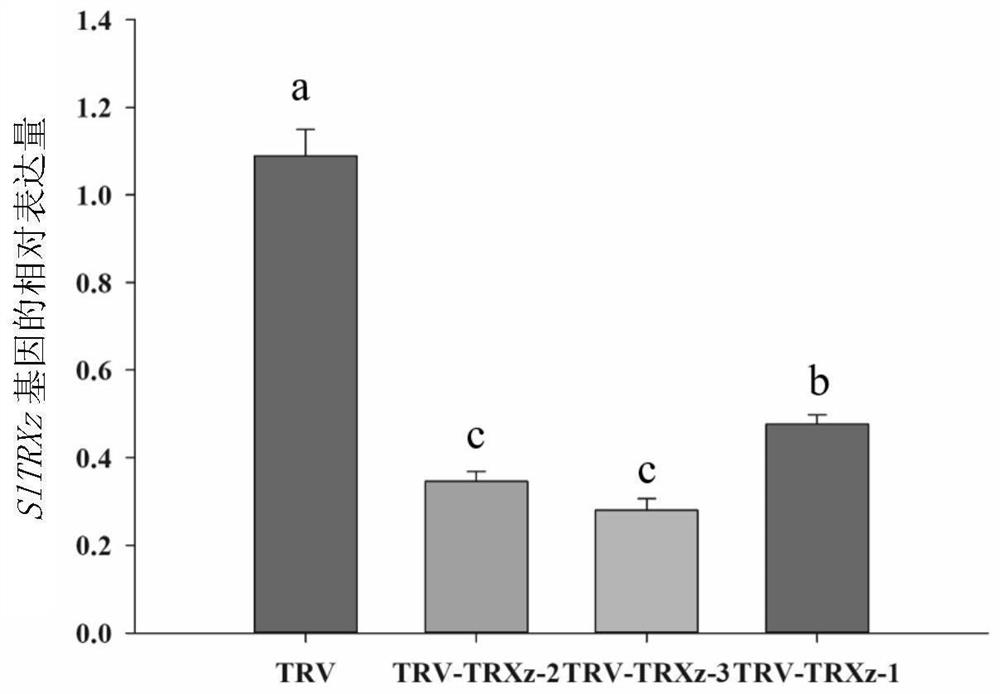
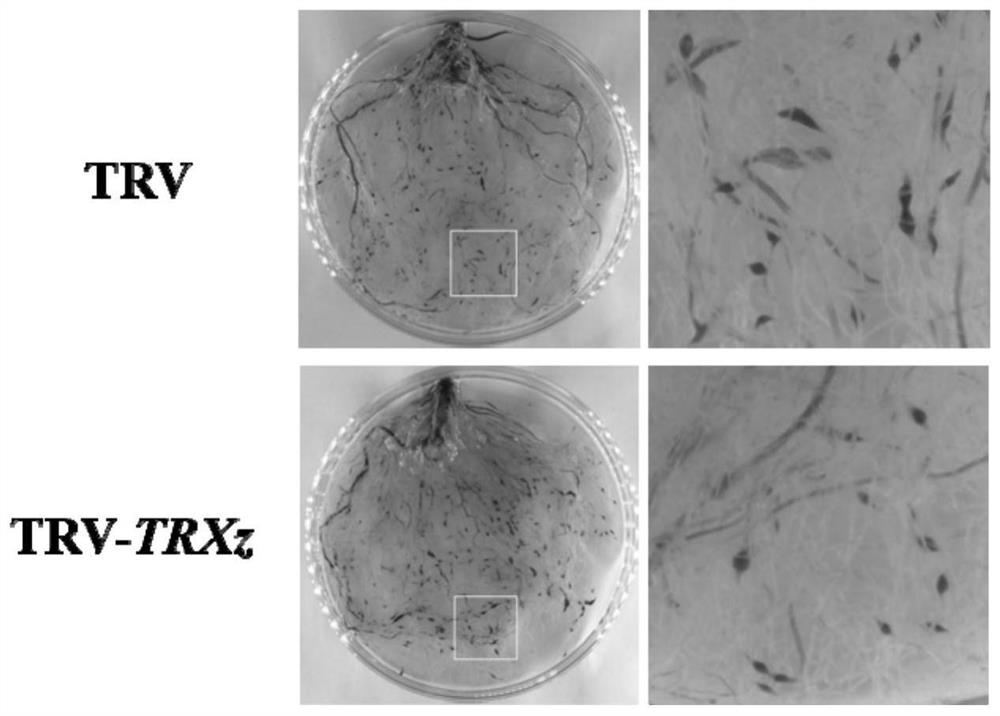
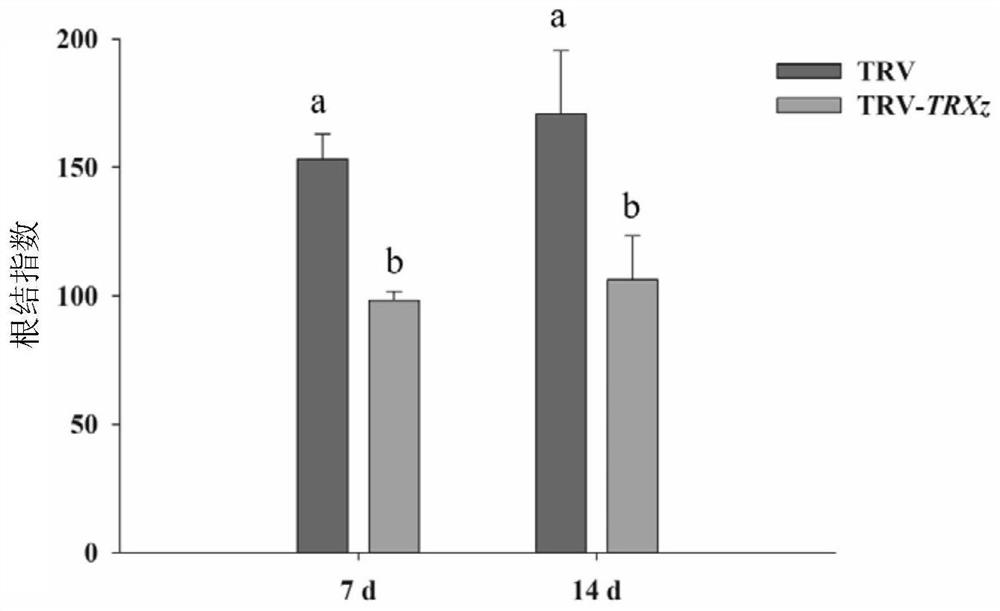
The invention discloses an application of a solanum lycopersicum SlTRXz gene as a restraining target to defence of meloidogyne incognita. The invention claims protection of a method for cultivating plants capable of improving resistance to root-knot nematode. The method comprises the following steps of restraining expression of an SlTRXz gene in plants to obtain the plants capable of improving resistance to root-knot nematode. The content and / or activity of SlTRXz proteins in the plants is reduced, and the resistance of the plants to the root-knot nematode is improved. The expression quantityof the SlTRXz gene in the plants is reduced, and the resistance of the plants to the root-knot nematode is increased. The abundance of the SlTRXz gene in transcription products in the plants is reduced, and the resistance of the plants to the root-knot nematode is improved. A solanum lycopersicum SlTRXz instantaneous silencing strain is obtained through a virus induced gene silencing technique, after the root-knot nematode is inoculated, the inventor finds that the root knot index is significantly, that is to say, the resistance of the plants to the root-knot nematode is improved. Related genes of solanum lycopersicum for adjusting and controlling the resistance to the root-knot nematode are enriched, and reference is provided for solanum lycopersicum breeding and increase of yield in biological adverse circumstances.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Root agroinoculation method for virus induced gene silencing
The invention provides novel methods and compositions for modulating gene function in plants. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions that allow efficient induction of virus-induced gene silencing in plants. The invention is significant in that it allows high throughput analysis of gene function in plants.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com