Power semiconductor device
A semiconductor and power technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of depletion layer elongation obstruction, withstand voltage drop, variation, etc., to achieve the effect of suppressing the drop of withstand voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0024]
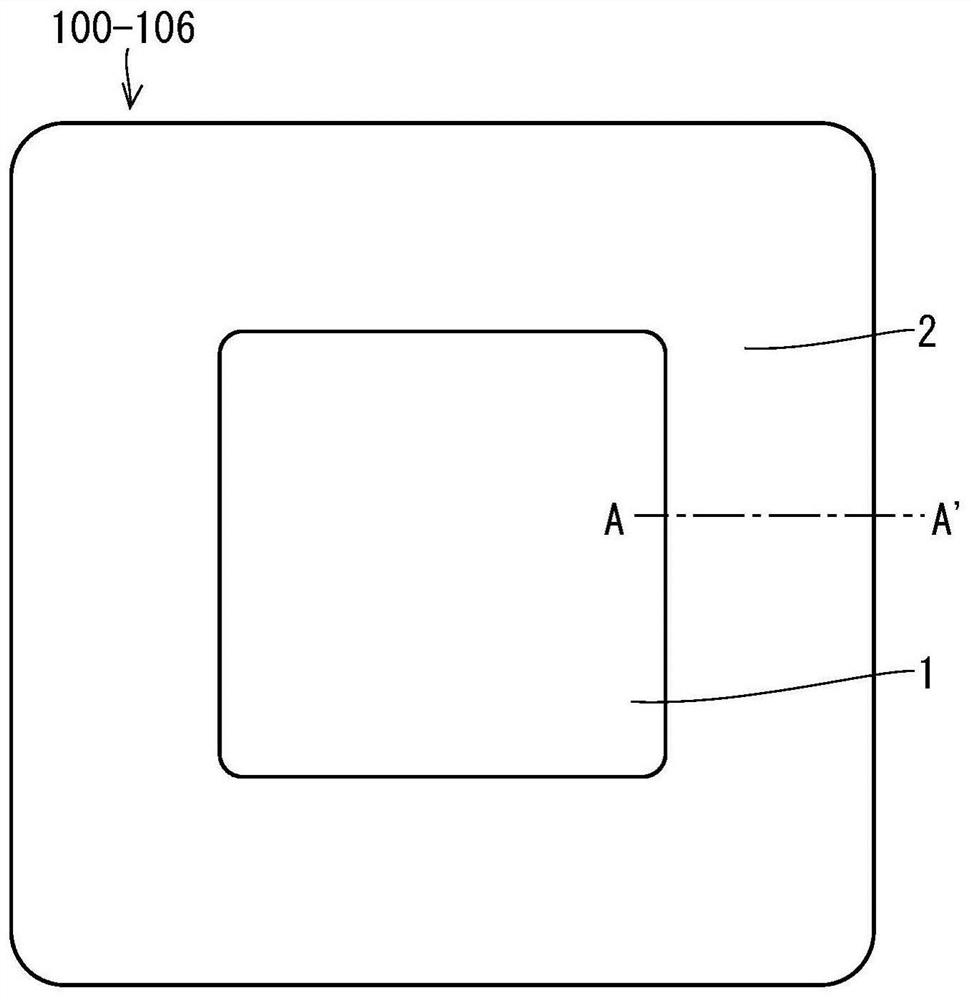
[0025] figure 1 It is a plan view of the power semiconductor device 101 according to the first embodiment. also, figure 1 The illustrated plan views are also used as plan views of the power semiconductor devices of the embodiments and the power semiconductor devices of the comparative examples described later. Such as figure 1 As shown, the power semiconductor device 101 is configured to have a cell region 1 and a termination region 2 surrounding the cell region 1 .
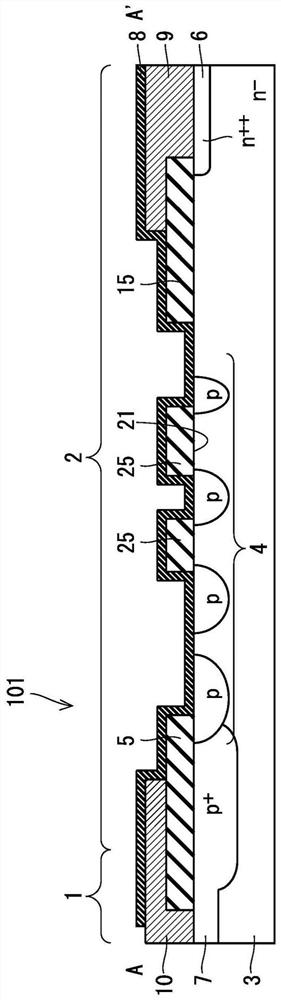
[0026] figure 2 is along figure 1 A cross-sectional view of the power semiconductor device 101 taken along the line A-A'. Such as figure 2 As shown, the power semiconductor device 101 is divided into a cell region 1 and a terminal region 2 when viewed from above, and the power semiconductor device 101 has an n-type semiconductor substrate 3, insulating films 5, 15, n++ type diffusion layers 6, p+ type diffusion layer 7, semi-insulating film 8, electrodes 9, 10 and at least one p-type diffusion...
Embodiment approach 2
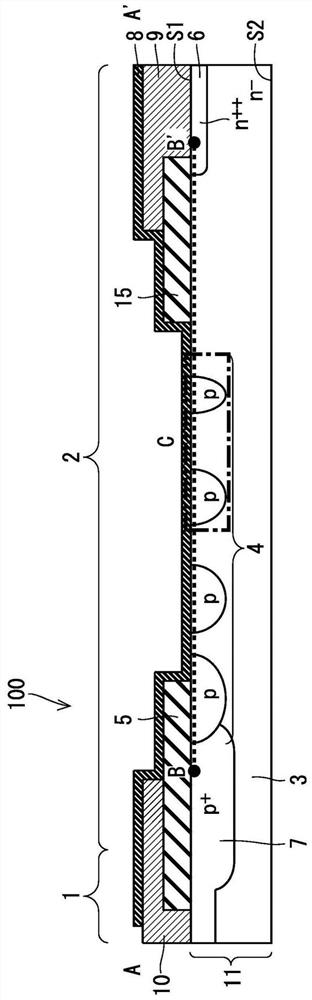
[0052] Figure 8 It is the edge of the power semiconductor device 102 of Embodiment 2. figure 1 A cross-sectional view of line A-A'. The power semiconductor device 102 differs from the power semiconductor device 101 only in the arrangement of the insulating film 25 and the contact form between the semi-insulating film 8 and the semiconductor base 11 accompanying the arrangement. Hereinafter, only the parts different from those of the power semiconductor device 101 in the structure of the power semiconductor device 102 will be described.
[0053] In the power semiconductor device 102 , the insulating film 25 is formed on a region of the substrate exposed region 21 excluding both ends in contact with the p-type diffusion layer 4 . Therefore, semi-insulating film 8 is in contact with p-type diffusion layer 4 and the end of substrate exposed region 21 in contact with p-type diffusion layer 4 .
[0054] That is, in the power semiconductor device 102 according to Embodiment 2, th...
Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Figure 9 It is the edge of the power semiconductor device 103 according to the third embodiment. figure 1 A cross-sectional view of line A-A'. The power semiconductor device 103 differs from the power semiconductor device 101 only in the arrangement of the insulating film 25 and the contact form between the semi-insulating film 8 and the semiconductor base 11 accompanying the arrangement. Hereinafter, only the parts different from those of the power semiconductor device 101 in the structure of the power semiconductor device 103 will be described.
[0057] In the power semiconductor device 103 , the insulating film 25 is formed across the entire exposed substrate region 21 and end regions of the p-type diffusion layer 4 adjacent to both sides of the exposed substrate region 21 . Therefore, the semi-insulating film 8 is in contact only with the p-type diffusion layer 4 on the first main surface S1 of the semiconductor base 11 , and is not in contact with the semiconduc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com