Mechanism for controlling deflection of snakelike joint and multi-degree-of-freedom flexible instrument applied by mechanism
A joint and serpentine technology, applied in the field of multi-degree-of-freedom flexible instruments, can solve the problems of tearing the end effector, driving the end effector left and right deflection, and difficulty in design.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
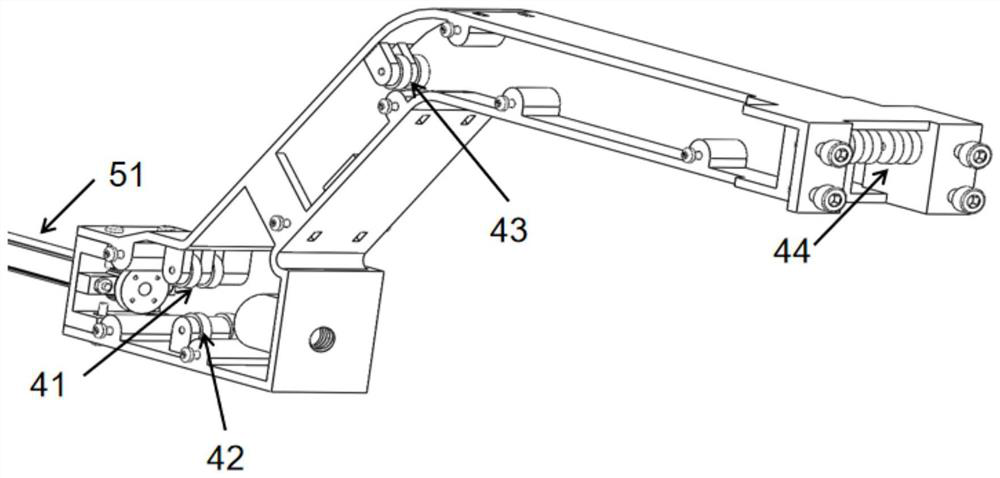
[0054] Such as Figure 6 and Figure 7 , a mechanism for controlling the deflection of the serpentine joint, the proximal end of the serpentine joint 60 is connected to the shaft tube 50, and the distal ends of the four strands of silk thread are connected to the serpentine joint through through holes evenly arranged around the central channel 92 of the serpentine joint 60 Around the far end of 60, the through holes are located at the four corners of the central channel 92: upper left, upper right, lower left, lower right; two strands of silk 8a, 8c and two strands of silk 8d, 8b which are in a diagonal relationship among the four strands of silk respectively form a combination And combination 2, the proximal ends of the silk threads of combination 1 and combination 2 pass through the shaft tube 50 and are respectively wound and fixed on two winding discs 38b, 38a. The winding directions of the two strands of silk in the same combination are opposite, and the two strands of si...
Embodiment 2
[0067] As an improvement to Example 1 on the basis of Example 1, such as Figure 14 The two winding disks 38a, 38b can also be respectively set on a pair of rotatable shafts 34d, 34c on the main frame, and the pair of shafts 34d, 34c are symmetrically arranged and concentric with the axis parallel to the revolution axis, and located at Figure 4 Above the pair of shafts three 32d, 32c, the opposite sides of the pair of shafts three 32d, 32c and the pair of shafts four 34d, 34c are driven by mutually coupled transmission parts, such as mutually meshing gears (33a and 36a, 33b and 36b). Brake discs are respectively fixed on opposite sides of a pair of shaft three 32d, 32c or a pair of shaft four 34d, 34c, and two symmetrical joint locking clips 35a, 35b are also arranged on the main frame, joint locking clips 35a, 35b accommodates the brake disc between the clamps that can be relatively close and separated. When the joint locking clamps 35a and 35b are clamped, the pair of sha...
Embodiment 3
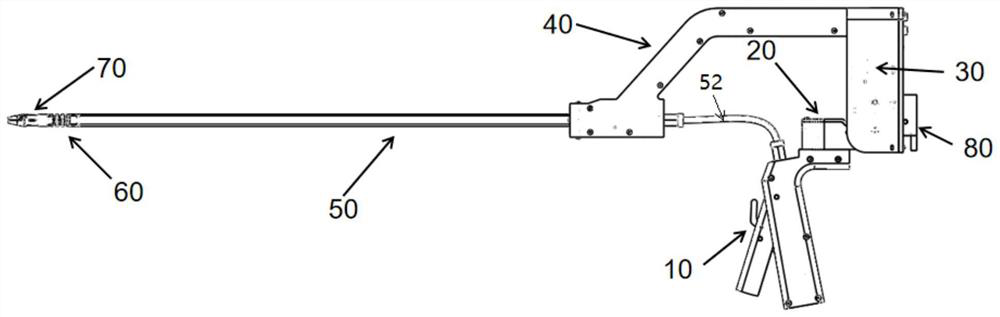
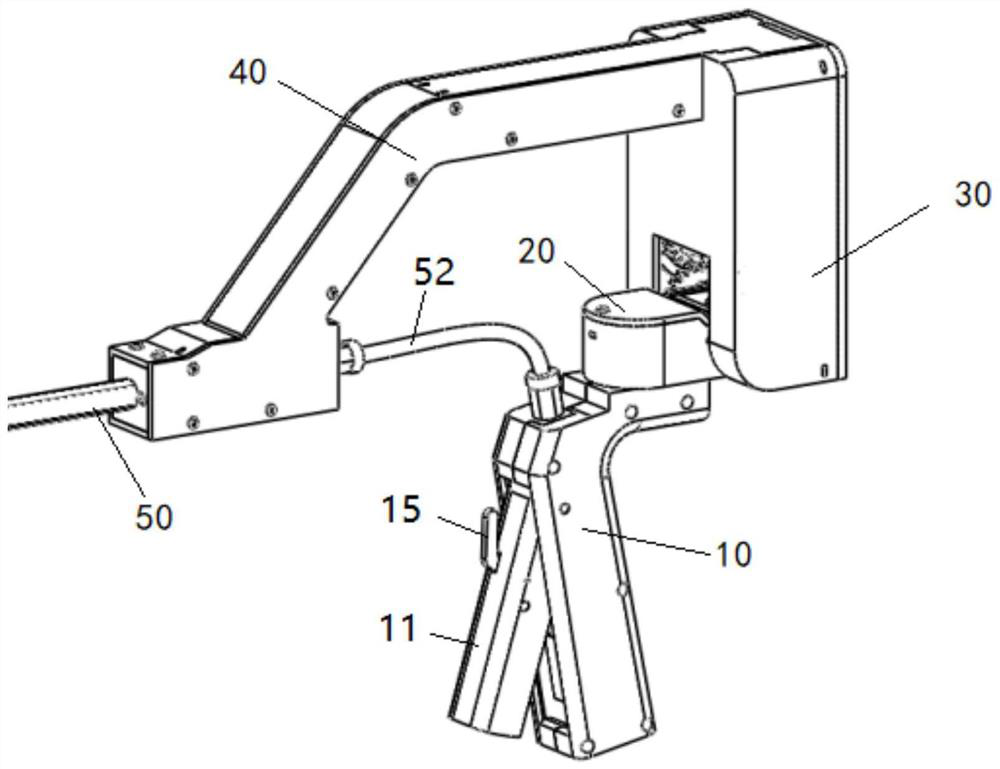
[0071] figure 1 An overall view showing an embodiment of the multi-degree-of-freedom flexible minimally invasive surgical instrument of the present invention, figure 2 A partial perspective view showing an embodiment of the multi-degree-of-freedom flexible minimally invasive surgical instrument of the present invention, which has a hollow shaft tube 50, and the distal end of the shaft tube 50 is connected to the front-end actuator 70 through a serpentine joint 60, in the extension direction of the shaft tube 50 The proximal end of the formed first plane in-plane shaft tube 50 is equipped with an upwardly bent fixed bracket 40 and a main frame arranged vertically downward from the proximal end of the fixed bracket 40, and the main frame is provided with a control serpentine joint 60 horizontally deflected. The swing control assembly one 20 and the swing control assembly two 30 of pendulum and vertical direction deflection, the swing control assembly two 30 are fixed on the mai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com