Property modeling for real time human being visual system
A performance, normalization technique, used in television, image analysis, instrumentation, etc., to solve problems such as lack of instantaneous effects of spatial frequency sensitivity, model adoption, and obvious complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
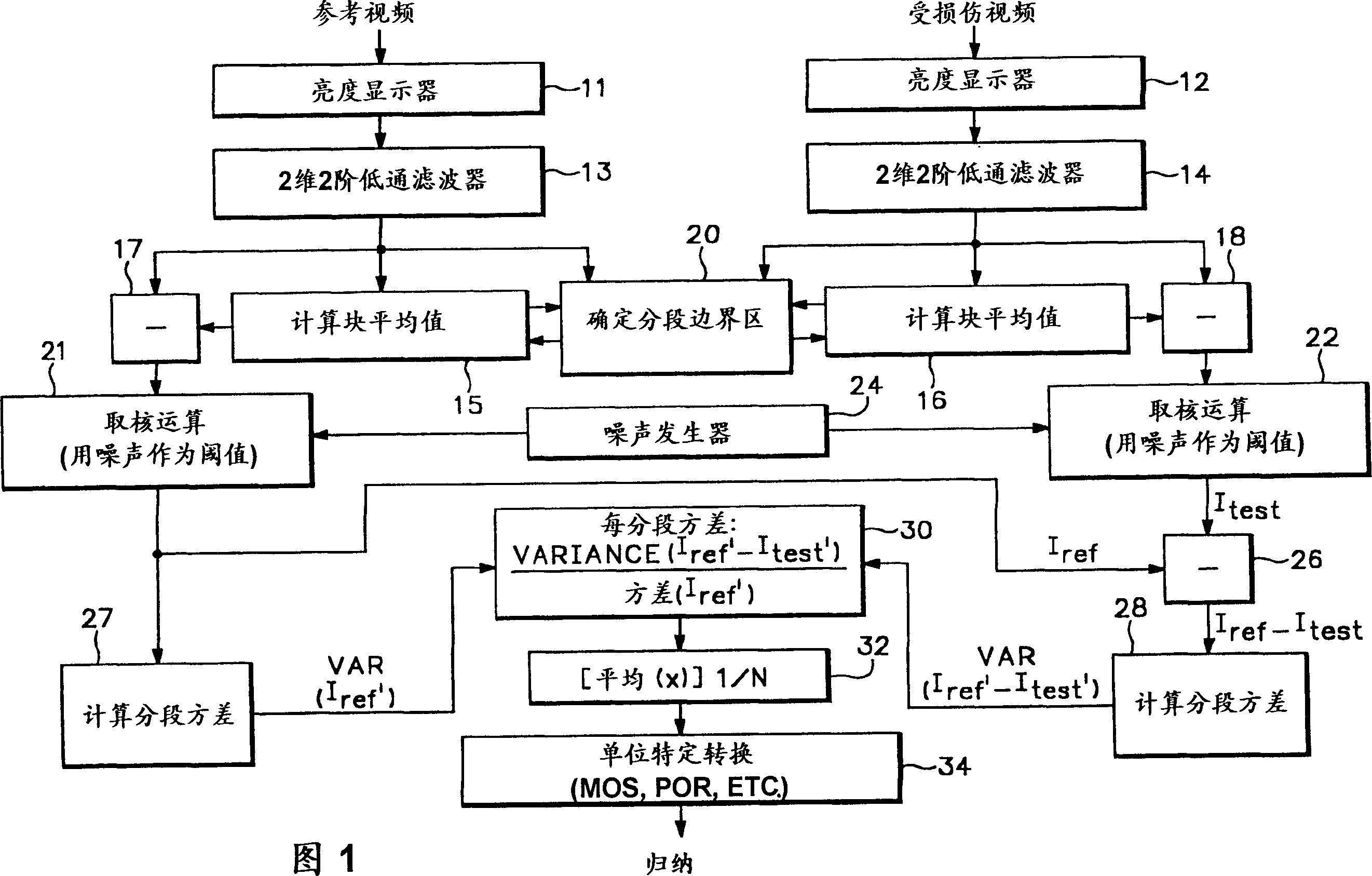
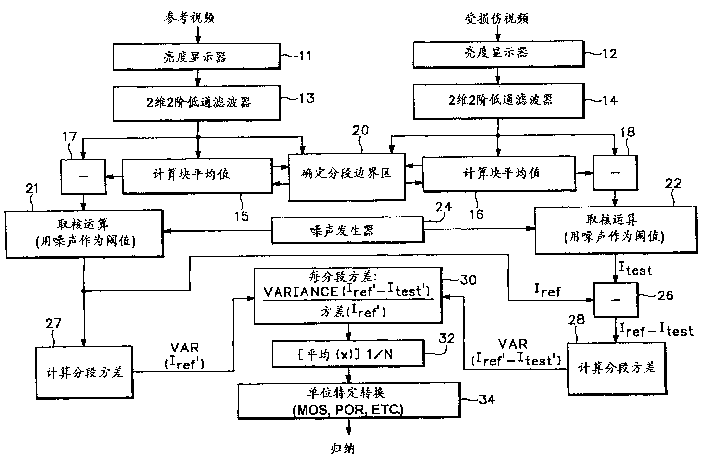
[0036] When examining the performance of the human visual system revealed by data from the literature in conjunction with historical data on the effects of various noise sources on the human visual system, the following observations can be made:
[0037]1. In the higher spatial frequency range, the amplitude sensitivity in the linear region of the influence of brightness on the contrast sensitivity function is insensitive to the changing average brightness, but decreases according to the square of the frequency. This corresponds to a second order low pass filter.
[0038] 2. Weber and Devries-Rose areas [see Taylor et al., "Contrast Detection and Discrimmation for Visual Models" and N. Gray Graham, and "Visual pattern Analyzers", Oxford U. press 1989] both correspond to the low frequency range where amplitude sensitivity is most affected by varying average luminance. Examination of the amplitude versus frequency plots at various mean luminances reveals behavior similar to a v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com