Human hybrid host cell for mammalian gene expression
A kind of cell, cell line technology, applied in the field of engineering host, mammalian cell line
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
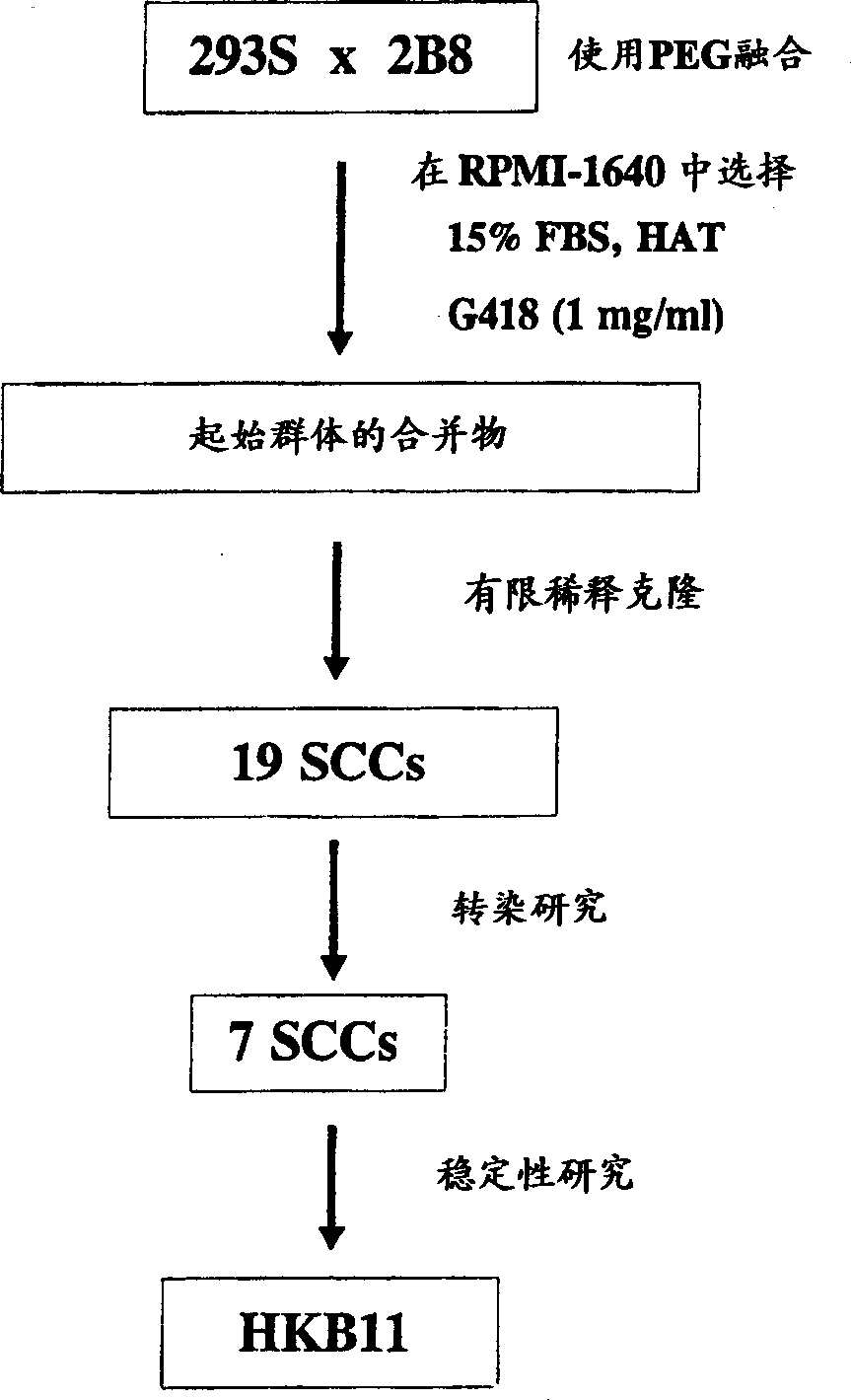
[0034] Cell fusion and derivation of single cell clones
[0035] Cell fusion was primarily performed according to the polyethylene glycol (PEG) fusion method described by Kenentt (1979, Meth Enzymol 58:5-359). 5,000,000 293S and 2B8 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were washed with PBS without calcium and magnesium ions (Life Technologies, Rockville, MD), and seeded into 6-well plates pretreated with peanut agglutinin (Sigma, 5 μg / ml) in one of the holes. The 6-well plate loaded with cells was centrifuged at 400 g for 6 minutes in a Beckman J-6M / E centrifuge (Beckman, Palo Alto, CA). After removing PBS from the cells, the cells were treated with 2 ml of 40% (w / v) PEG (Sigma) for 1 min. One well was not treated with PEG as a control. Cells were washed 3 times with 5 ml of PBS containing 5% DMSO, then 3 times with PBS. Cells were incubated for 25 minutes with fresh medium supplemented with 15% FBS. Cells were inoculated into 96-well plates (1.2 × 10 6 cells / plate). C...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Identification of HKB clones
[0039] Although all heterozygous cells were selected under selection conditions, heterozygous status was confirmed by counting the number of chromosomes in the cells. Indeed, all HKBs have a chromosome number of 90-110. These numbers are similar to the sum of the 293S and 2B8 chromosome numbers (64 and 47, respectively, according to ATCC data). 293S (Stillman et al., 1985, Mol Cell Biol 5:2051-2060) is 293 (ATCC CRL-1573) adapted for suspension culture.
[0040] All heterozygous cell clones were assayed for expression of endogenous Ig ([mu] and [kappa]) by direct immunofluorescence assay using methanol-fixed cells to determine which cell clones secreted endogenous Ig. In longer term repeat experiments, these cells were observed to be negative for mu and kappa chain expression by immunofluorescence assay (Table 1) and ELISA (data not shown).
[0041] cell
gene expression
heavy chain (μ)
light chain (κ)
...
Embodiment 3
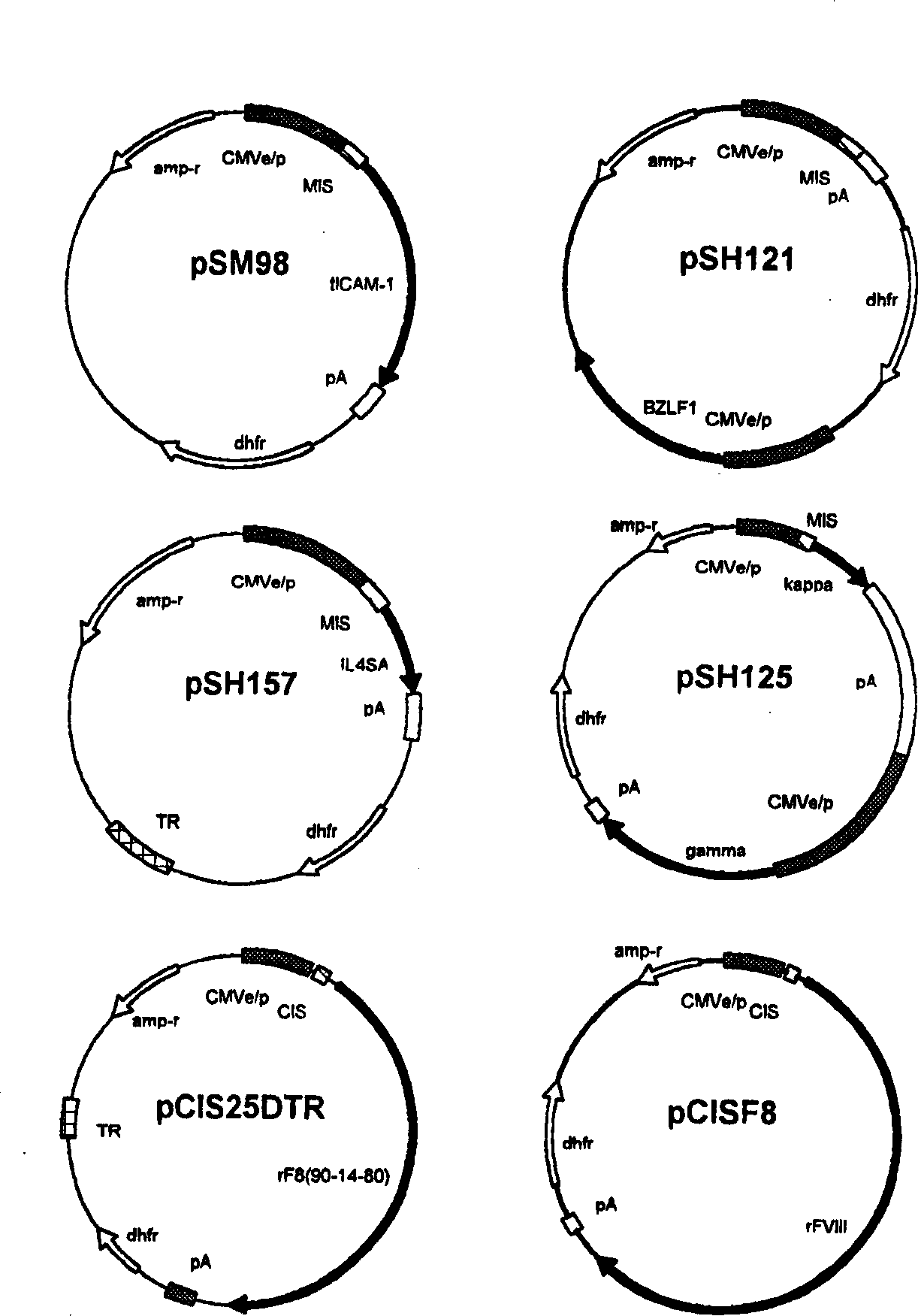
[0052] Derivation of HKB clones stably secreting heterologous proteins
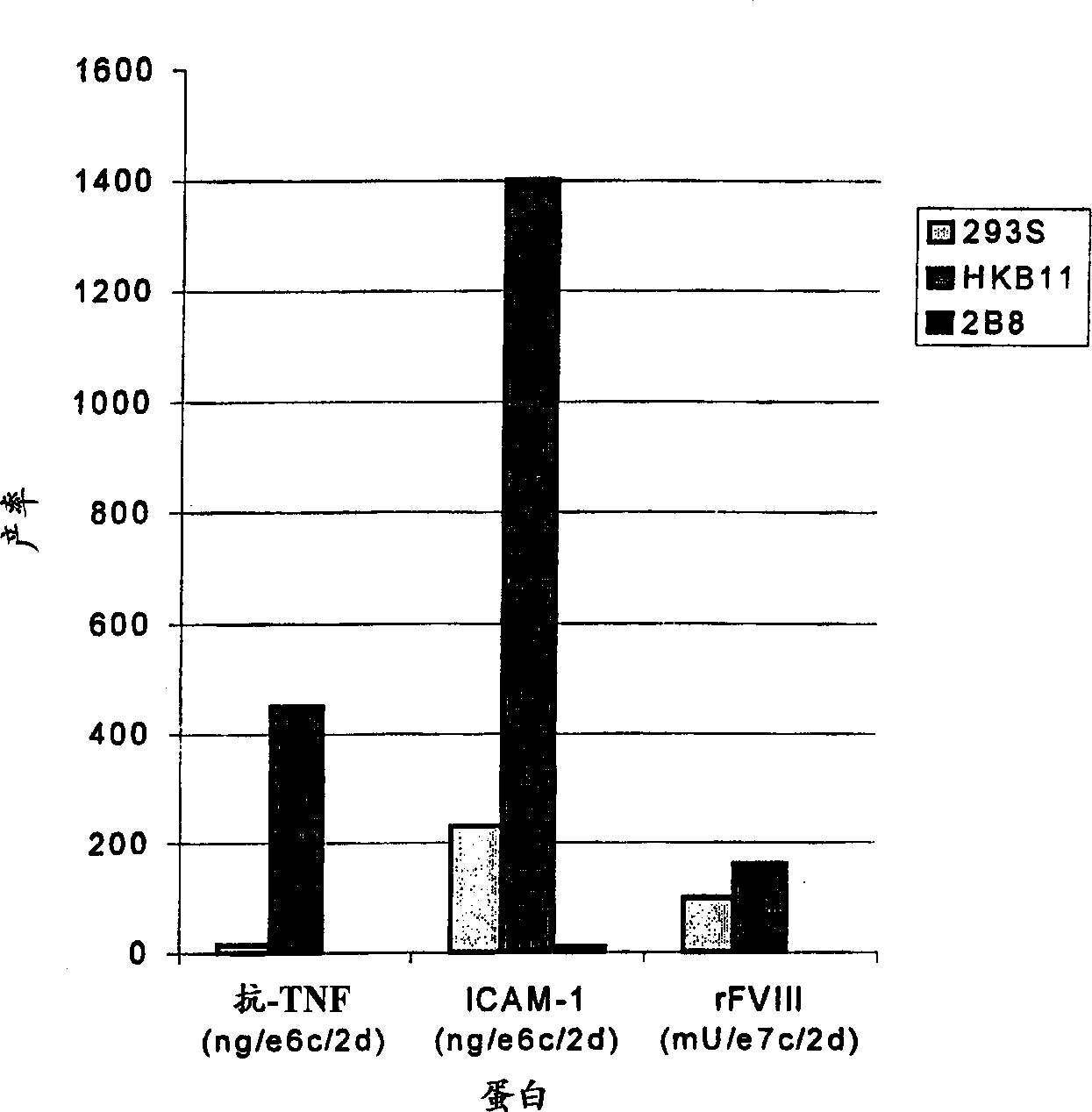
[0053] Hybrid clones were tested for stable protein expression in a gene amplification system (dhfr / MTX). Cells are first transfected with an appropriate expression vector, and then the transfected cells (usually 10 per 96-well plate) 6 cells) were seeded in selection medium without hypoxanthine and thymidine but supplemented with FBS and MTX (50nm) for selection / expansion. After the first round of screening on the plates, cells from high-secretion wells were selected and transferred to 6-well plates. Cells in 6-well plates were further expanded in media containing higher concentrations of MTX (100, 200 and 400 nM). The starting population on 6-well plates was further screened to derive the final population. Finally, these populations are used to clone single cell-derived clones. As shown in Table 4, HKB11 cells are the most suitable for producing high levels of heterologous human proteins. HKB11 cel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com