Visual attention location system
A technique of visual attention, relation, applied in the field of systems used by image compression systems, to achieve the effect of avoiding the use of processing correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
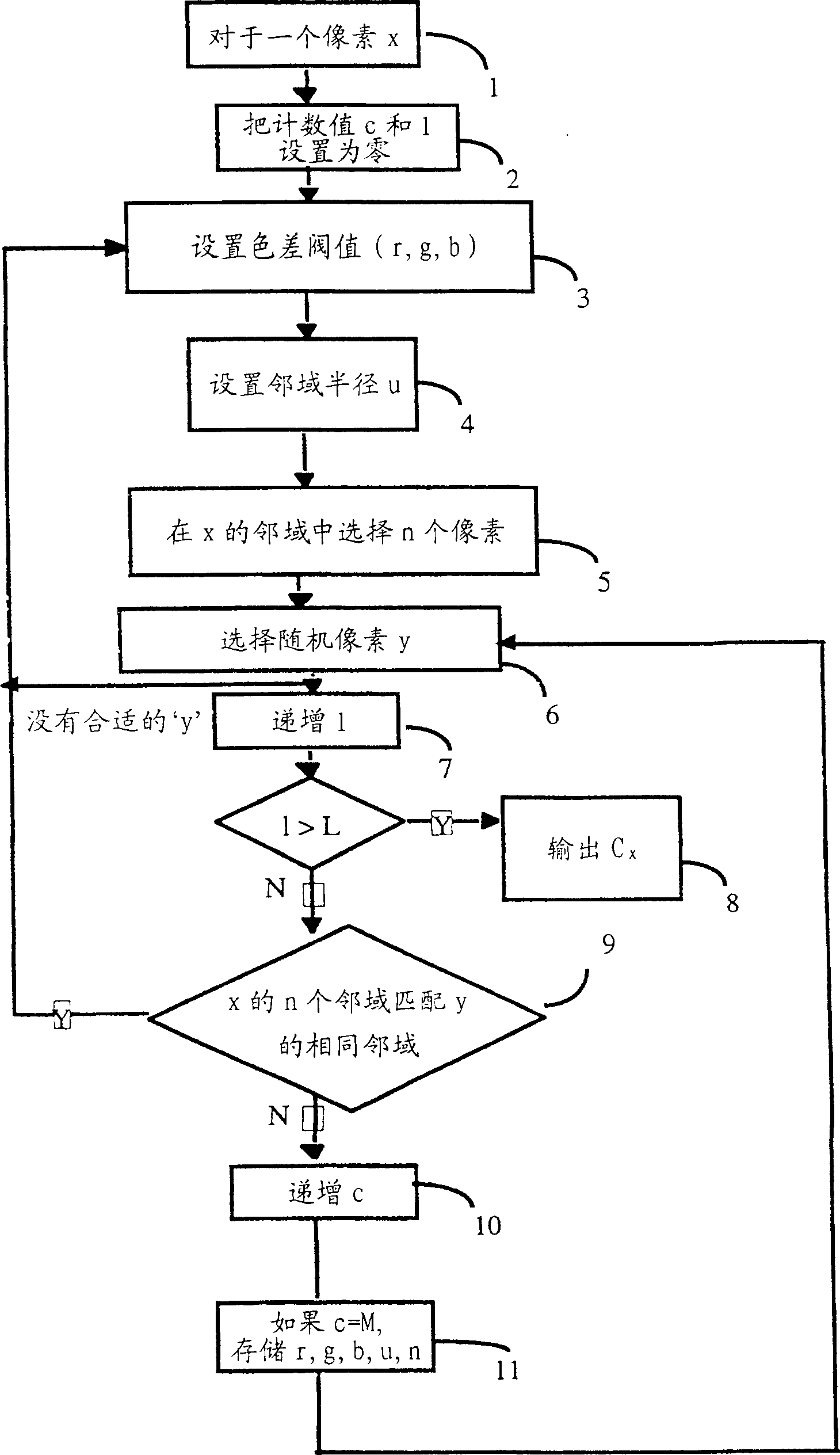
[0056] The components illustrated in Fig. 4 include: an input device 41, such as a scanner; a central processing unit (CPU) 42; an output unit, such as a visual display unit (VDU) or printer 43; a memory 44; computing processor 45 . The memory includes memories 440,444-446, registers 441,447-449 and counters 442,443. Data and programs for controlling the computer are stored in the memory 44 . The CPU 42 uses this information to control the functions of the computer.
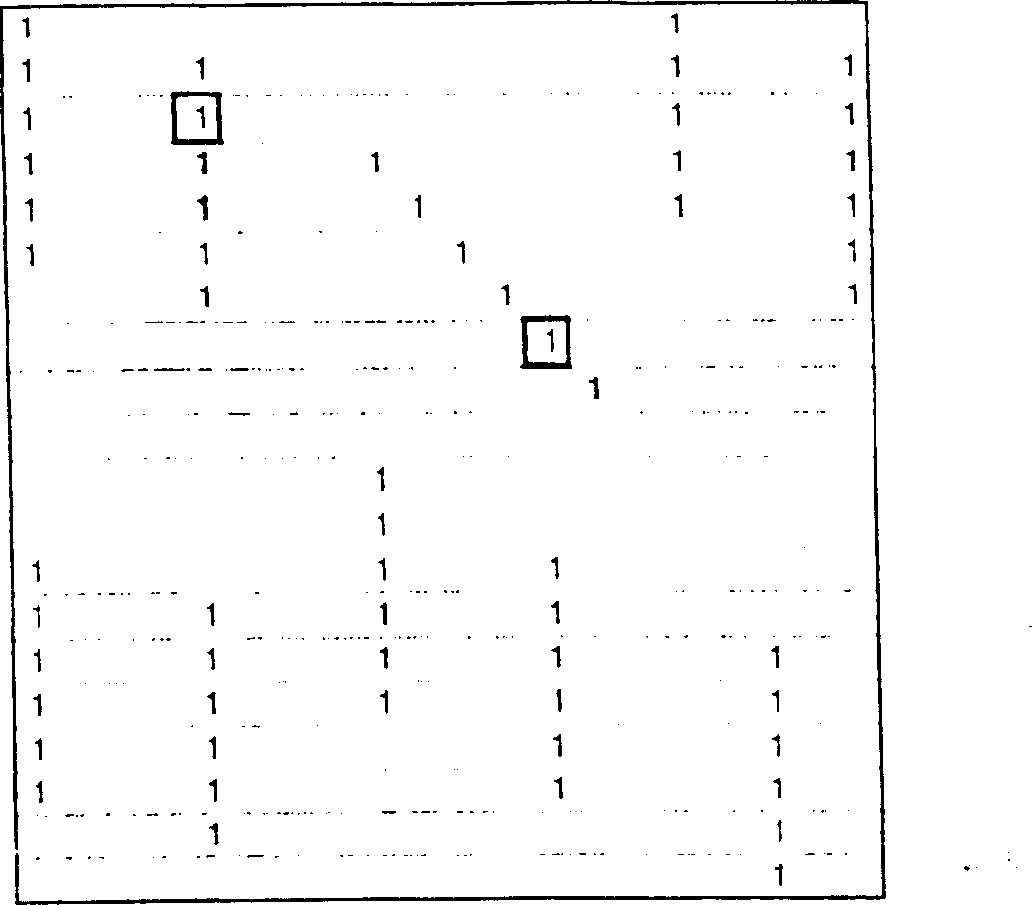
[0057] now consider figure 1 and 4, the image 40 to be analyzed is accessed by the input device 41 and stored digitally in an image memory 440 as an array A of pixels x, where each pixel has the color intensity (r x , g x , b x ), in the case of a grayscale image, a single grayscale intensity value t x .
[0058] Then select a pixel x from array A (step 1) and assign its intensity value (r x , g x , b x ) or t x stored in a test pixel register 441. Several test pixels can be processed in parallel, but...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com