Bias voltage forming circuit, amplifying circuit, streamline type AD adaptor
一种偏压电压、偏压电路的技术,应用在模数转换器、直流耦合的直流放大器、改进放大器以提高效率等方向,能够解决电路面积增大、消耗超过功率等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
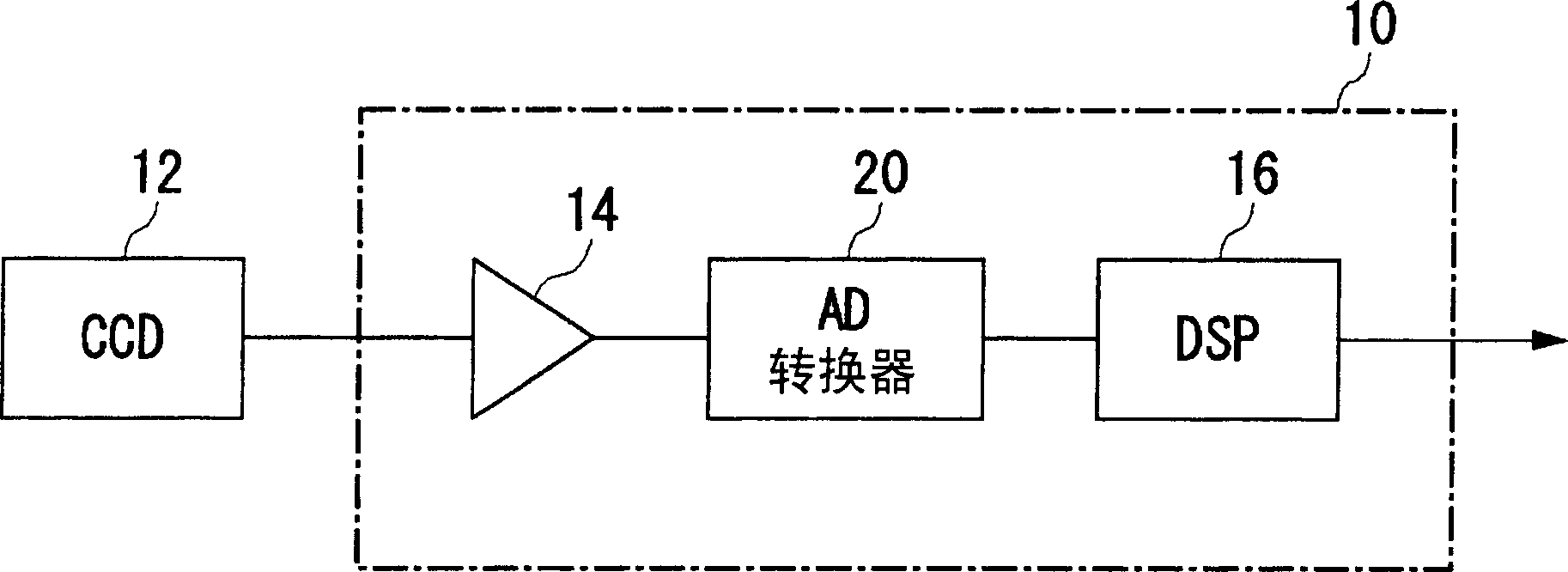
[0026] figure 1 It shows the basic configuration of an image processing circuit partially including the bias voltage generating circuit of this embodiment. An image sensor 12 such as a CDD (Charge Coupled Device) or a CMOS sensor takes in light from a subject, converts it into an electrical signal, and inputs it to a single-chip LSI (Large Scale Integration) 10 . In the single-chip LSI 10 , an AGC (Auto Gain Control) 14 , an AD converter 20 , and a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) 16 are incorporated. The AGC 14 amplifies the electrical signal received from the image sensor 12, the AD converter 20 converts the amplified analog signal into a digital signal, and the DSP 16 performs processing such as compression on the converted digital signal. Each structure built in the monolithic LSI 10 is powered by a predetermined voltage power supply.
[0027] The AD converter 20 includes a bias voltage generating circuit for realizing low power consumption, and realizes low power consumpt...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0043] The difference between the bias voltage generation circuit of this embodiment and the first embodiment lies in the control timing of the first bias circuit and the second bias circuit of the control unit, but the other configurations are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0044] The implementation is the same.
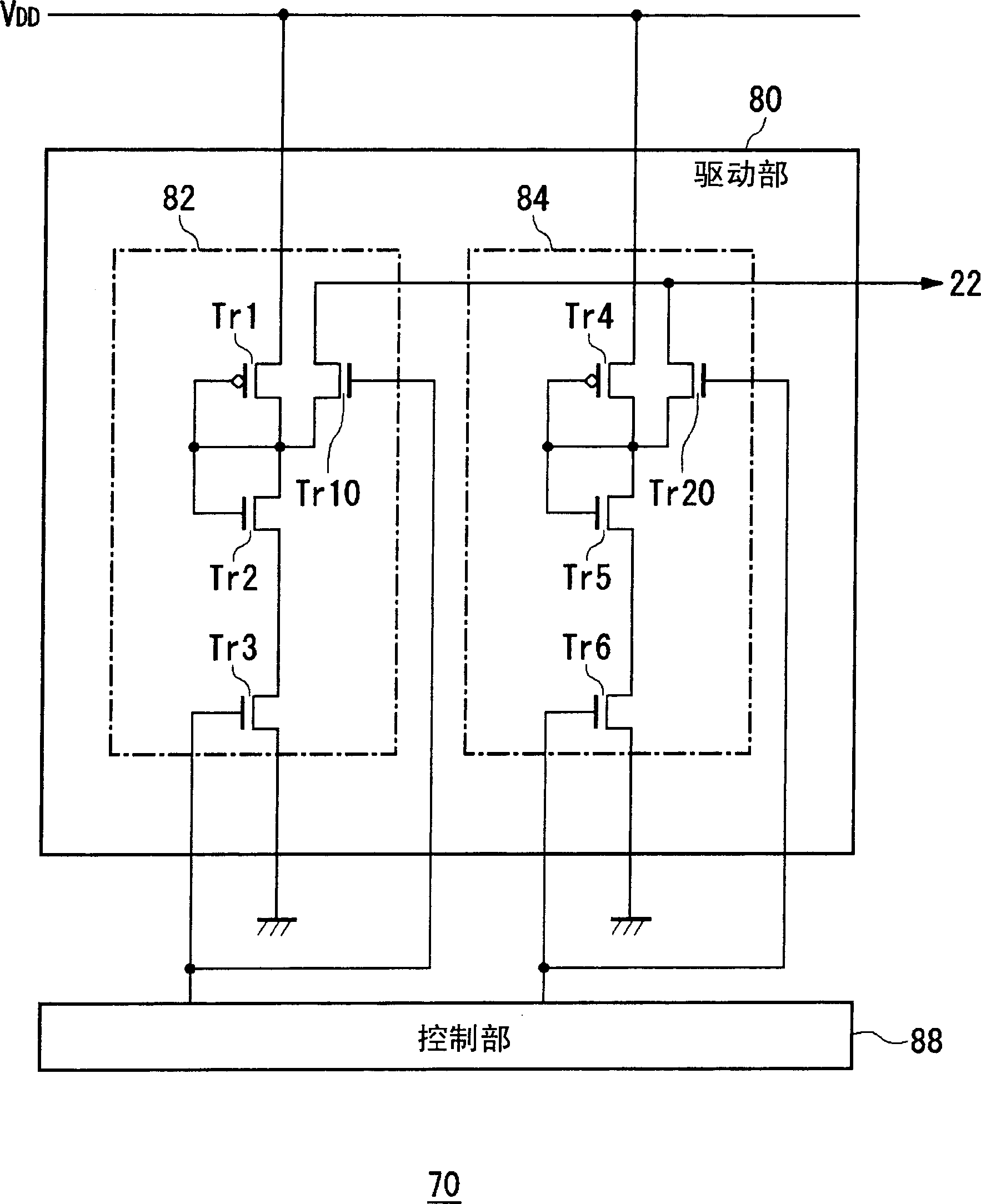
[0045] Figure 5 It is a timing chart showing the relationship between the change in the operation of the first conversion unit 22 and the control of the control unit 88 in the second embodiment. In the present embodiment, during the auto-zero operation period, especially immediately after the auto-zero start, a large current is required, and a small current is sufficient for the remaining auto-zero period. Correspondingly, the control unit 88 turns on both the third transistor Tr3 and the sixth transistor Tr6 during the period immediately after the auto-zero start, turns off the third transistor Tr3 during the remaining auto-zero period, and turns on...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
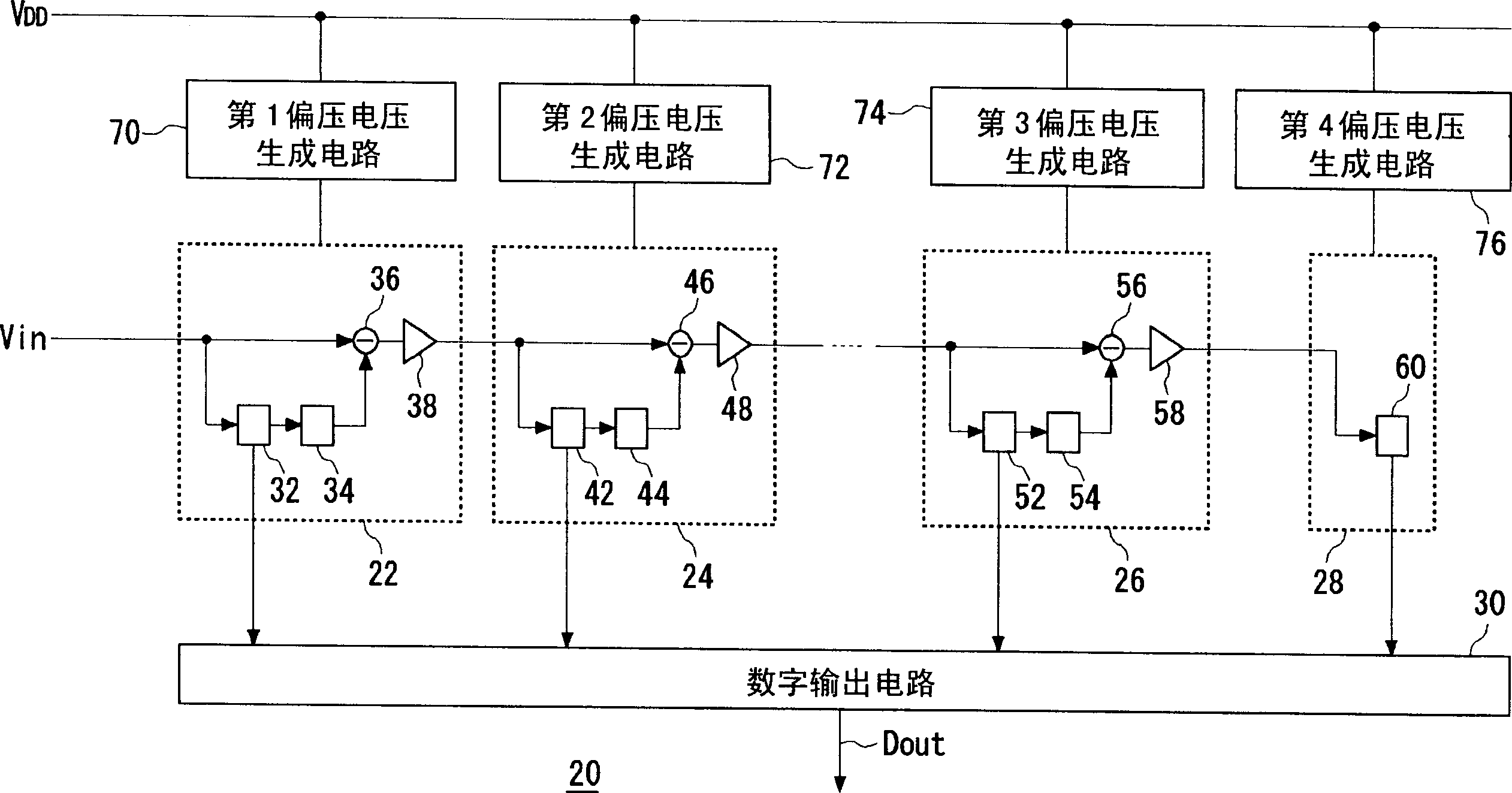
[0047] The bias voltage generating circuit of the present embodiment differs from the first and second embodiments in that the current driving capabilities of the plurality of bias circuits constituting the drive unit are all the same, but the other configurations are the same as those of the first or second embodiments. same.
[0048] Figure 6 The configuration of the first bias voltage generating circuit 70 is shown. In the first bias generation circuit 70 , the drive unit 80 includes a first bias circuit 82 , a second bias circuit 84 , and a third bias circuit 86 . These bias circuits have the same current drive capability. That is, the element sizes and size ratios of the first and second transistors Tr1 and Tr2 constituting the first bias circuit 82, the element sizes and size ratios of the fourth and fifth transistors Tr4 and Tr5 constituting the second bias circuit 84, and the configuration The element sizes and size ratios of the seventh and eighth transistors Tr7 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com