Moving picture coding apparatus
A moving image and coding device technology, applied in image communication, television, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of not disclosing the amount of calculation and maintaining high-resolution reference images, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
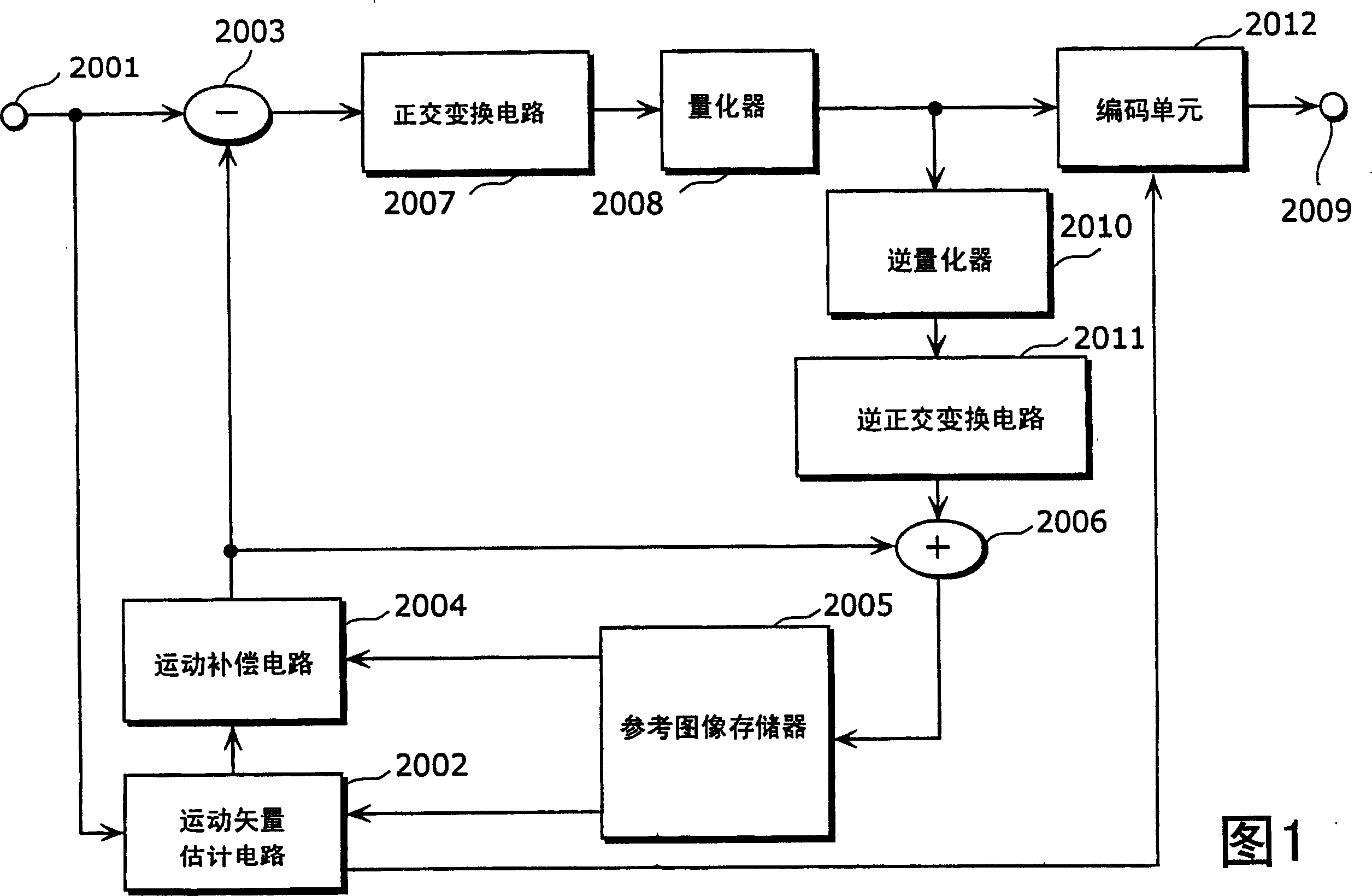
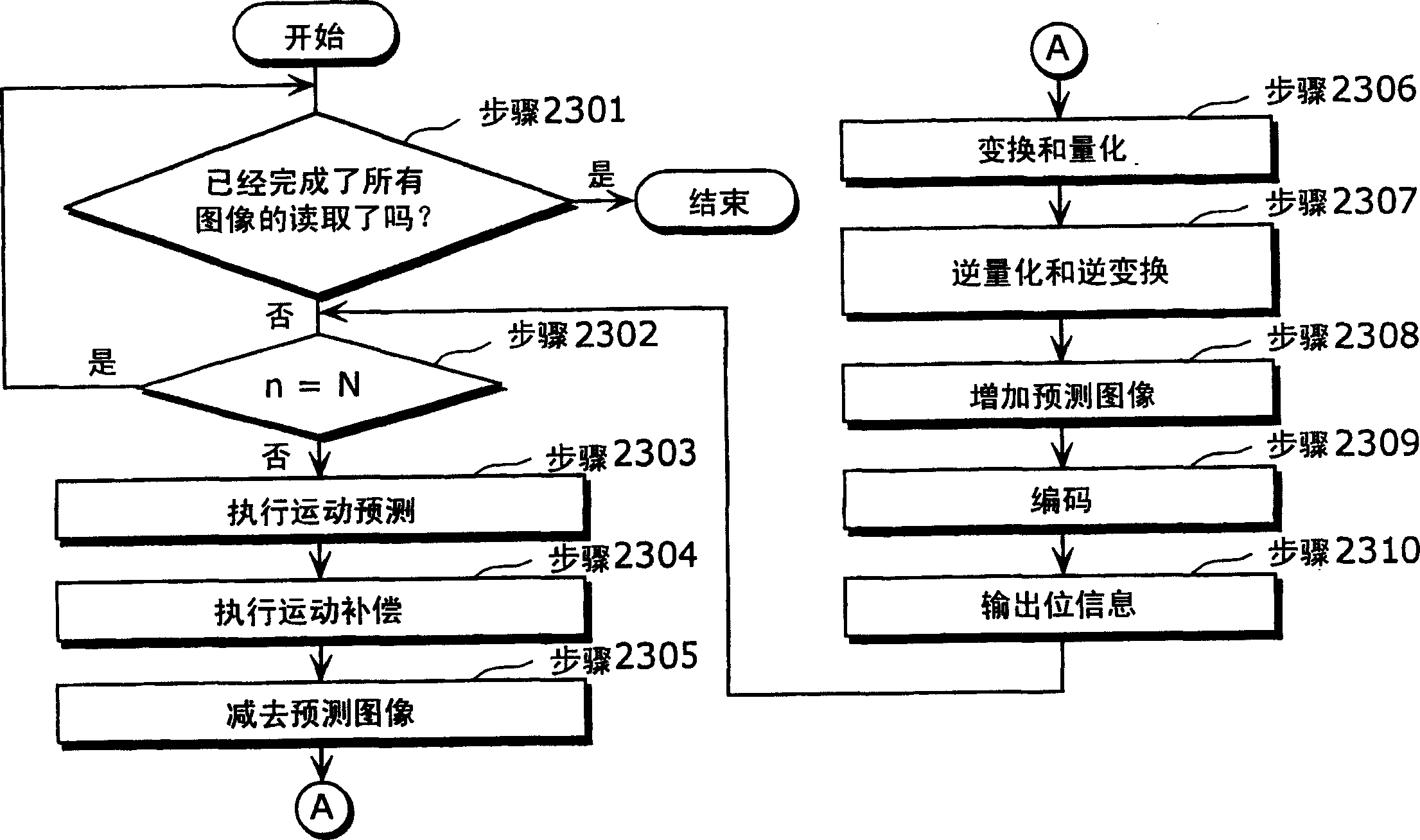
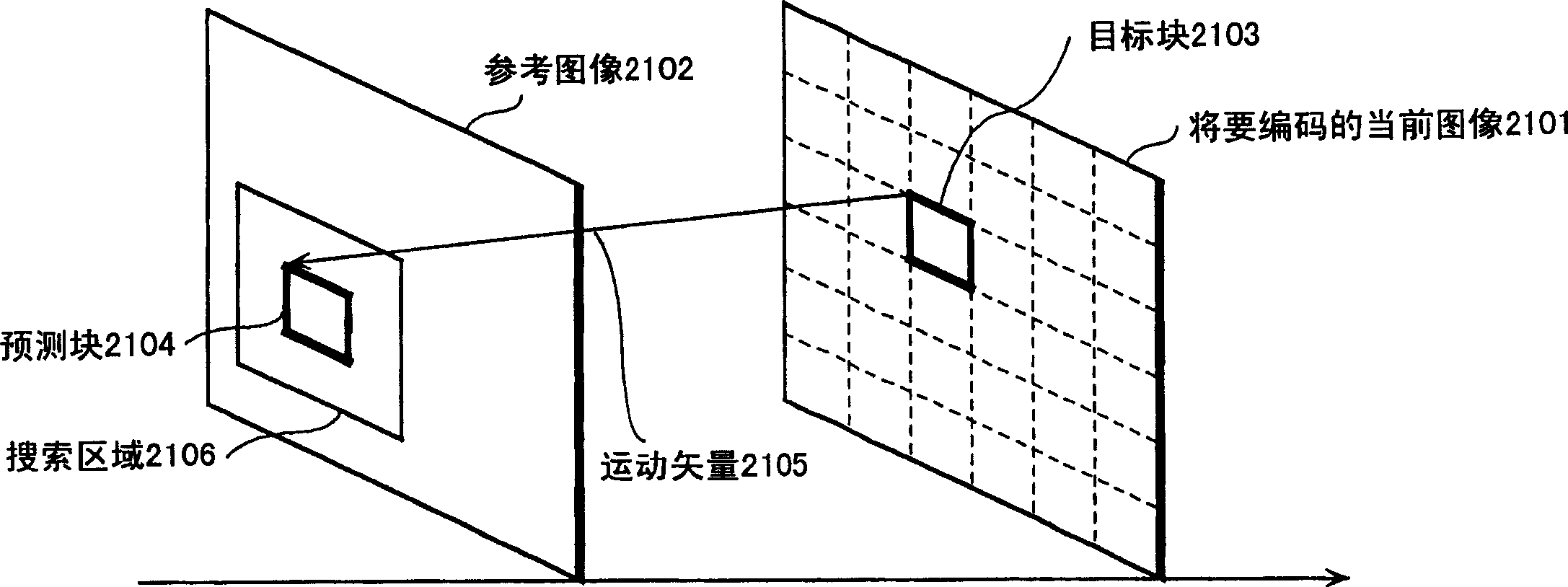
[0074] A moving picture coding apparatus in a first embodiment of the present invention will be described. The moving picture encoding device of the present invention is a device which receives a moving picture signal as an input signal; encodes the picture; and outputs encoded information. It has wide applicability in combination with video storage devices or video delivery devices.
[0075] Fig. 7 is a block diagram showing the structure of the moving picture coding apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The same reference numerals are assigned to constituent elements performing the same operations as those of the conventional moving image encoding device shown in FIG. 1 . The motion picture coding apparatus in this embodiment limits the search of the motion vector to the search area generated in advance by the 2-tap filter, and for these motion vector candidates obtained as the search results, finally interpolated using the 6-tap filter Moti...
no. 2 example
[0147] If the programs for realizing the moving picture coding method and the moving picture decoding method shown in the above first embodiment are recorded on a recording medium such as a floppy disk, the above first embodiment can be easily executed in an independent computer system processing shown in .
[0148] 17A, 17B and 17C are diagrams showing a situation in which the moving picture coding method and the moving picture decoding method in the first embodiment described above are executed in a computer system using a computer program recorded on a storage medium such as a floppy disk.
[0149] FIG. 17B is a front view showing the appearance of a floppy disk, a cross-sectional view thereof, and the floppy disk itself, and FIG. 17A shows an example of the physical format of a floppy disk as a storage medium main body. The floppy disk FD is contained in the casing F, and a plurality of tracks Tr are provided annularly from the outer circumference to the inside in the radi...
no. 3 example
[0153] Furthermore, applications of the moving image coding method and moving image decoding method as shown in the first embodiment described above and a system using these methods will be described.
[0154] FIG. 18 is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of a content providing system ex100 for realizing content distribution services. The area for providing communication services is divided into cells of desired size, and base stations ex107 to ex110, which are fixed radio base stations, are provided in each cell.
[0155] In this content providing system ex100, devices such as a computer ex111, a personal digital assistant (PDA) ex112, a mobile phone ex114, and a camera-equipped mobile phone ex115 are connected via an Internet service provider ex102, a telephone network ex104, and base stations ex107 to ex110 to the Internet.
[0156] However, the content providing system ex100 is not limited to the configuration shown in FIG. 18, and any combination of them c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com