Method for updating dynamic field name in IPv6 network
A dynamic domain name, ipv6 network technology, applied in the field of communication, to achieve huge economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
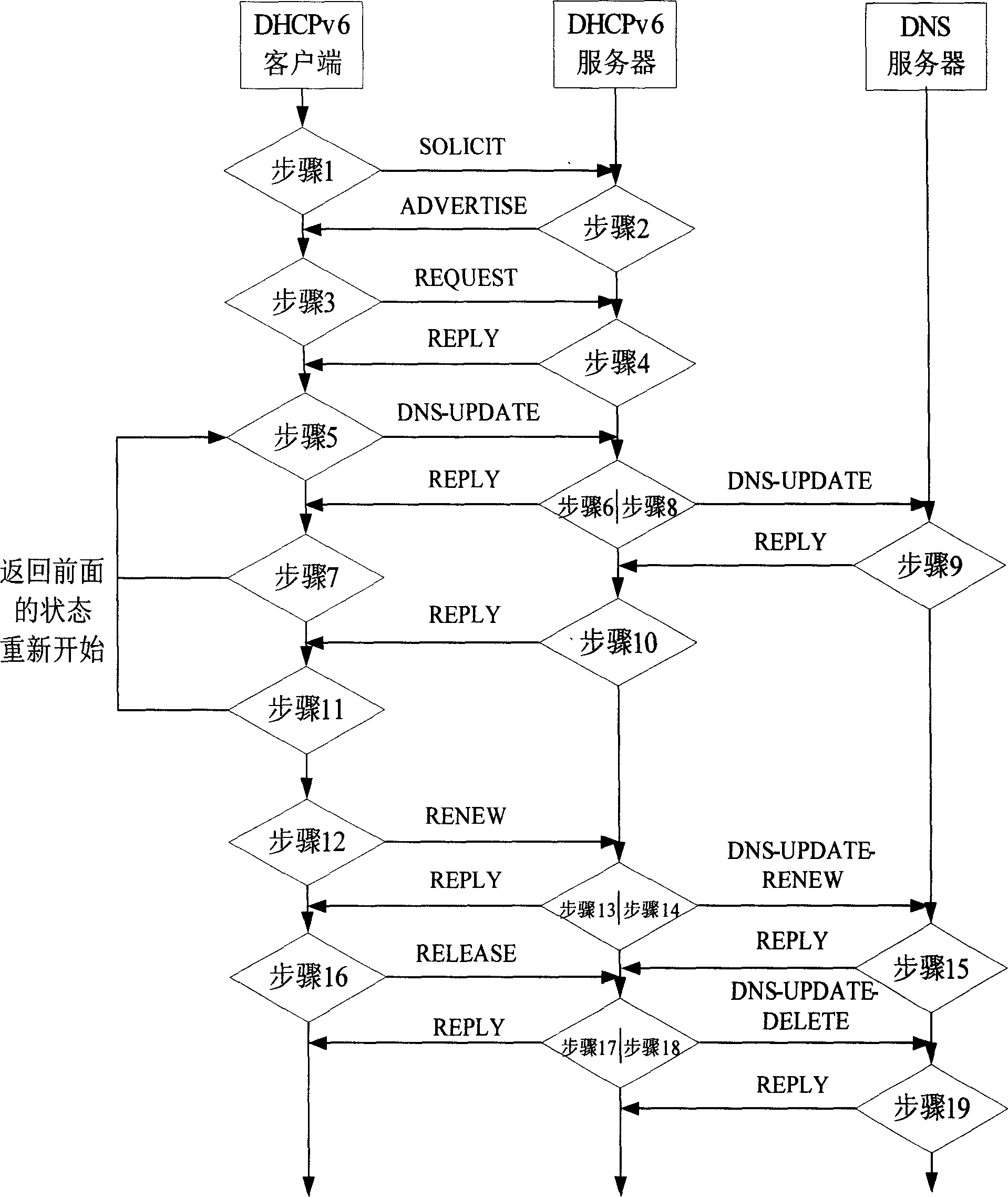
[0053] Embodiment 1, a method for realizing dynamic domain name update in an IPv6 network has the following steps:
[0054] Below is the description of the three stages of the program of the present invention;
[0055] Step 1: The DHCPv6 server and the client host interactively assign addresses;
[0056] According to rfc3315, the message format of the DHCPv6 protocol is: the first 4 bytes, which are 1 byte message type (msg-type) and 3 bytes transmission identifier (transaction-id), and the rest Sections all consist of different types of option fields. Currently, there are 29 option fields that have been determined by rfc according to different functions.
[0057] The inventive scheme proposes two types of options in the first stage:
[0059] The specific format is as follows:
[0060] 0 1 2 3
[0061] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
[0062] +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- +-+-+-+-...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Embodiment 2, the following is a detailed description of the three stages of the program of the present invention,
[0111] The first stage: the DHCPv6 server and the client host interact to assign addresses
[0112] The DHCPv6 protocol defines 13 packet types in total. Compared with DHCPv4, its protocol function has many extensions, but the working principle of the function of DHCPv6 protocol address allocation is roughly the same as that of DHCPv4.
[0113] In the first step, after the client host is connected to the network, if it needs one or more IPv6 addresses, it will first send a Solicit message to all DHCPv6 servers and relay agents to find an available server. The Solicit message uses Client The Identifier option field carries the DUID that identifies this client host.
[0114] In the second step, all DHCPv6 servers that receive the Solicit message will reply with an Advertise message. The Advertise message uses the Server Identifier option field to carry th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com