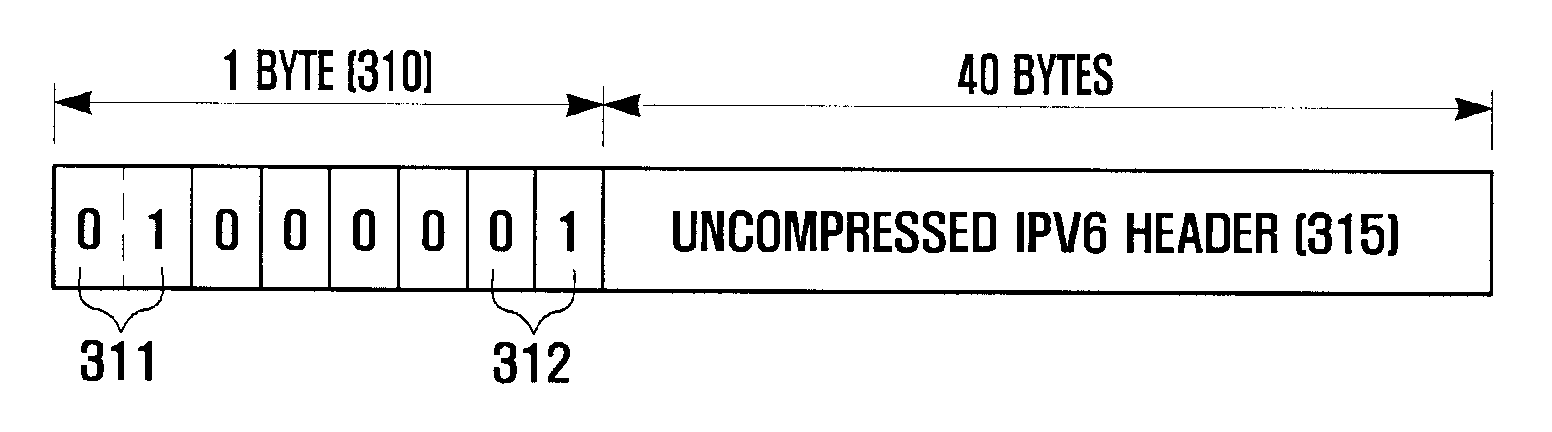
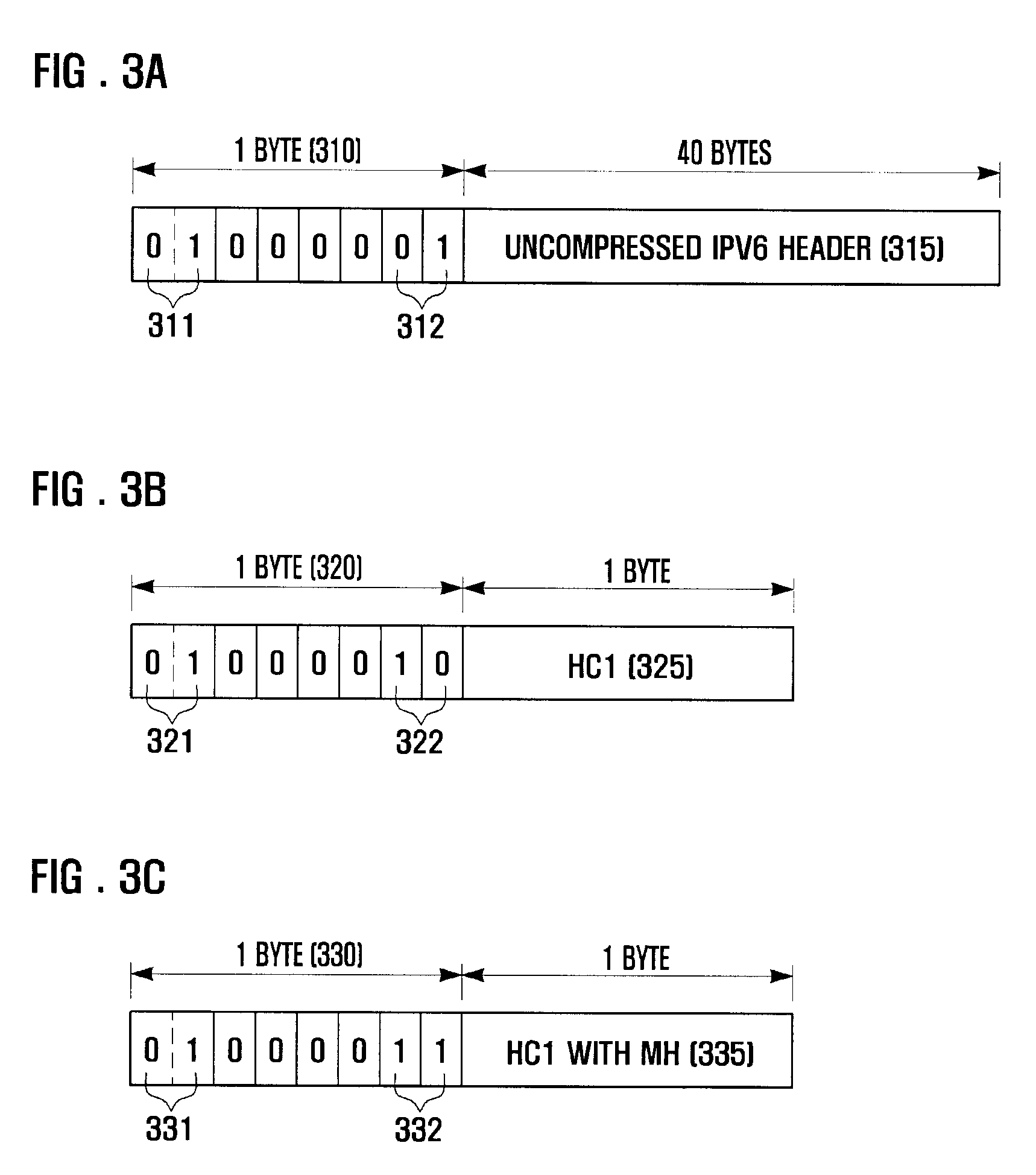
Patents
Literature
1283 results about "IPv6" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion. IPv6 is intended to replace IPv4. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, who subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017.
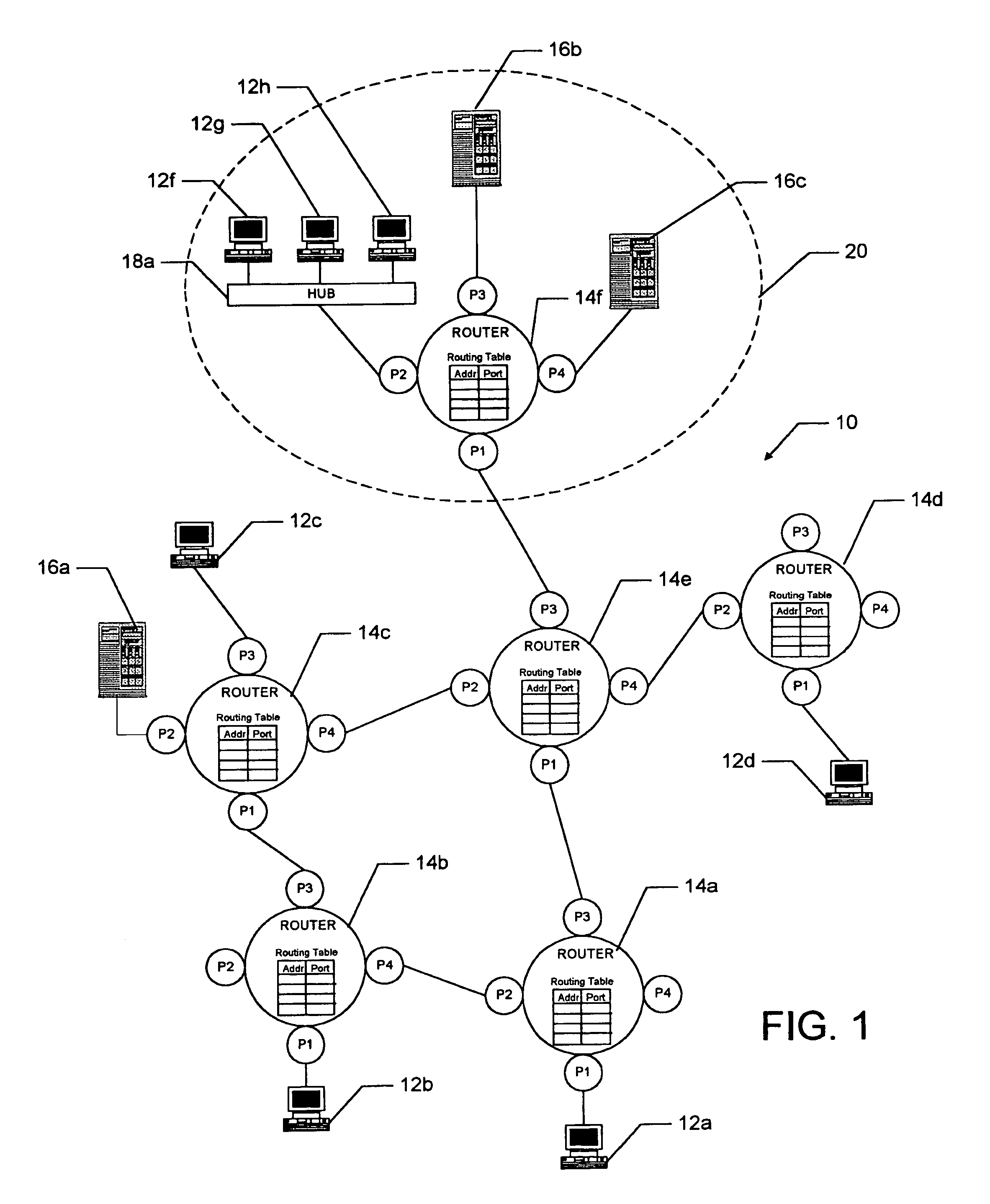
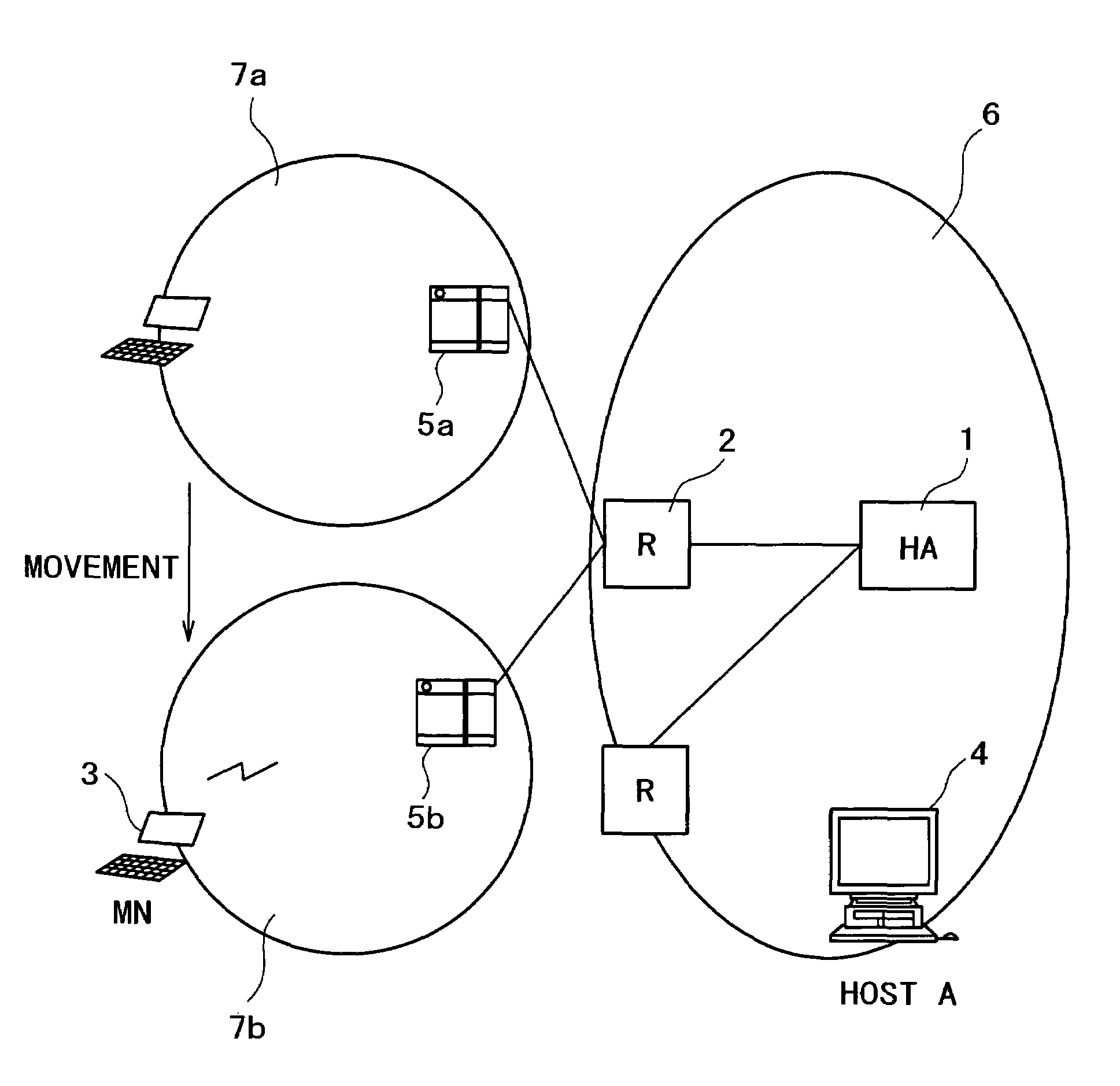
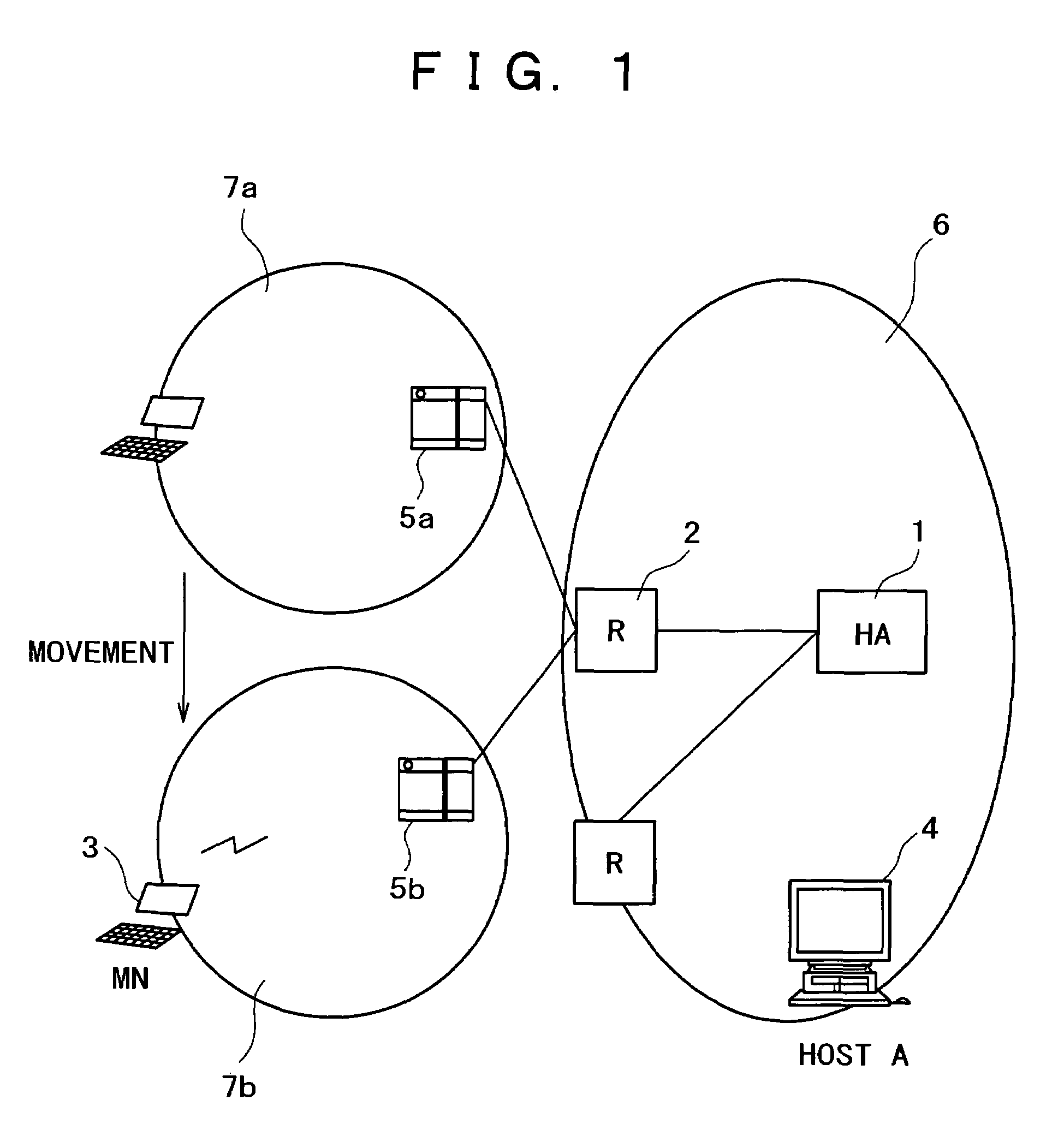
Home agent management apparatus and method
InactiveUS7626957B2Raise countTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkAnalysis data
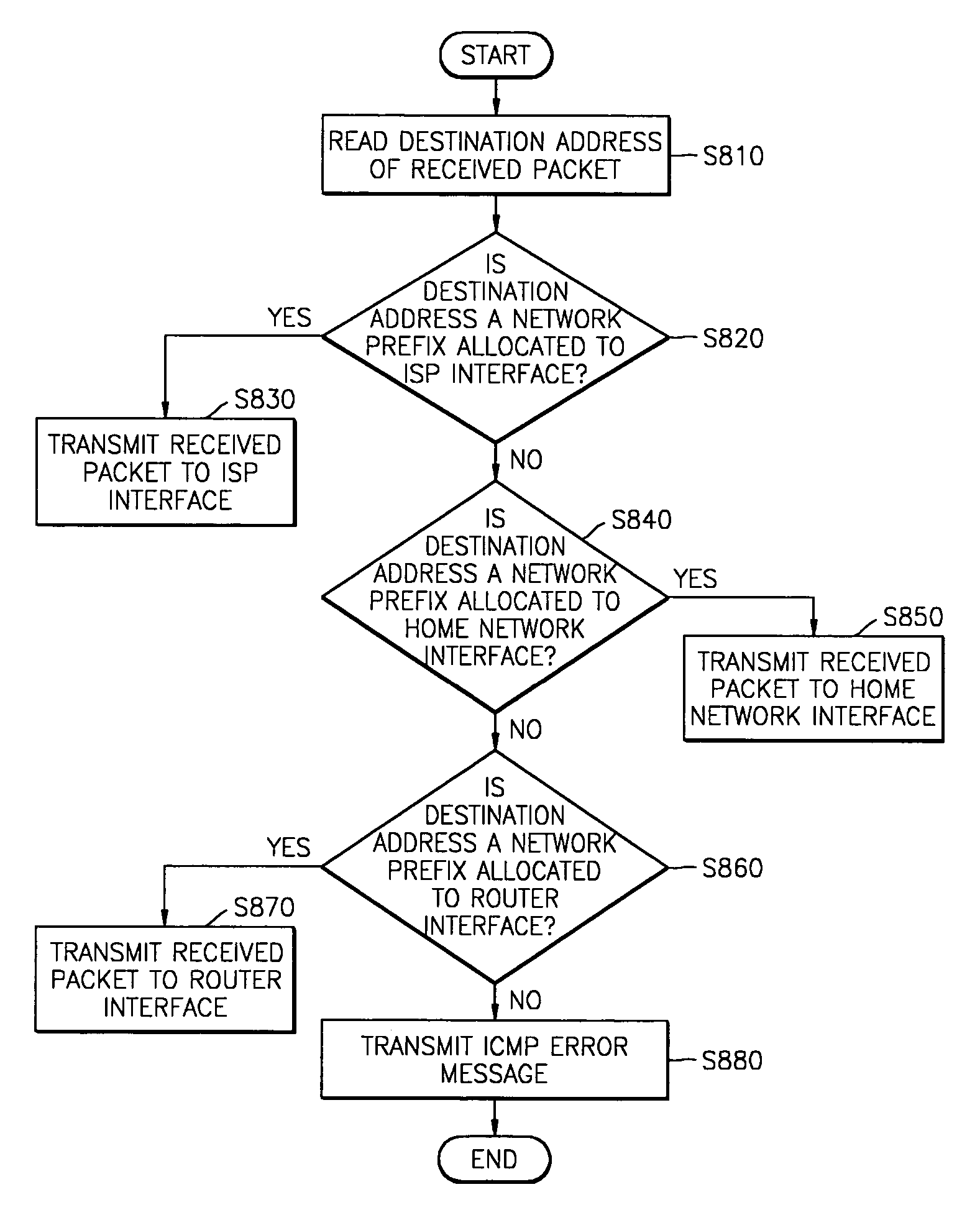
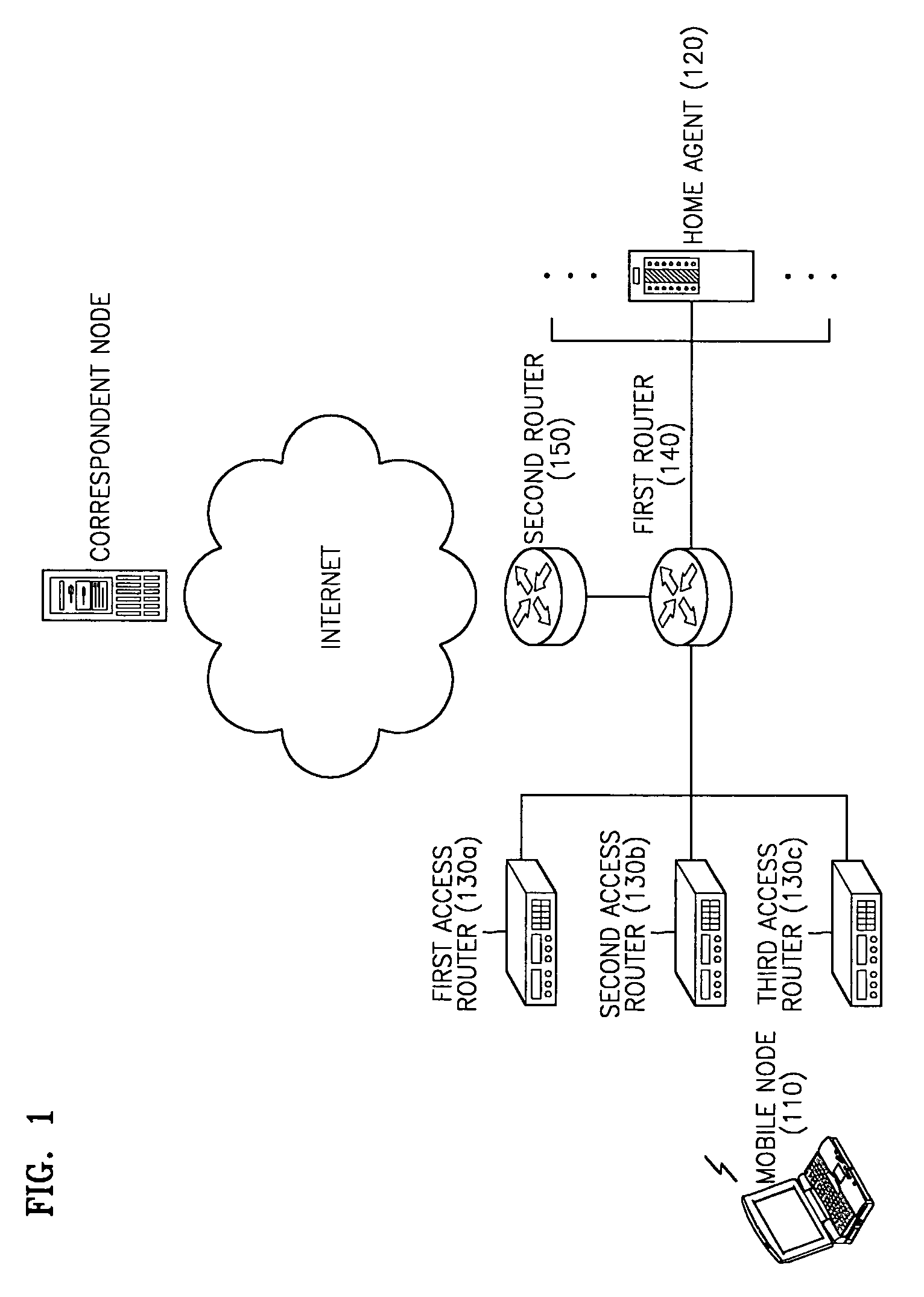
A home agent management apparatus and method for routing a packet using a home network equipment as a home agent in a mobile Inter Protocol version 6 (IPv6) are provided. The home agent management apparatus includes a packet analyzer, which receives a packet and analyzes the packet; a database, which stores information indicating whether a home agent of a home network operates normally according to the result of the analysis; and a home agent function executor, which performs a home agent function in place of the home agent when the home agent does not operate normally. Accordingly, a load concentrated on a home agent of an Internet Service Provider (ISP) can be split.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
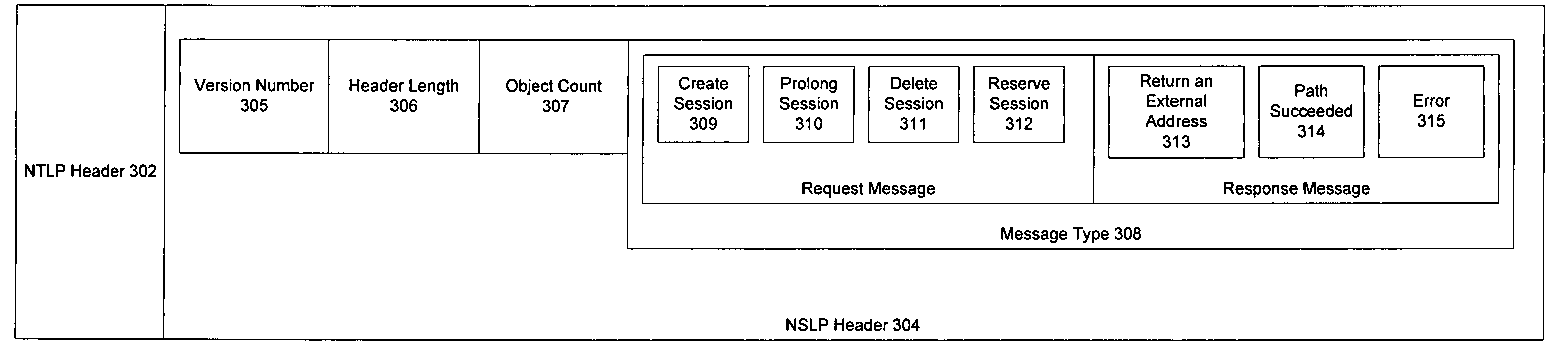
Load Balancing and Session Persistence in Packet Networks
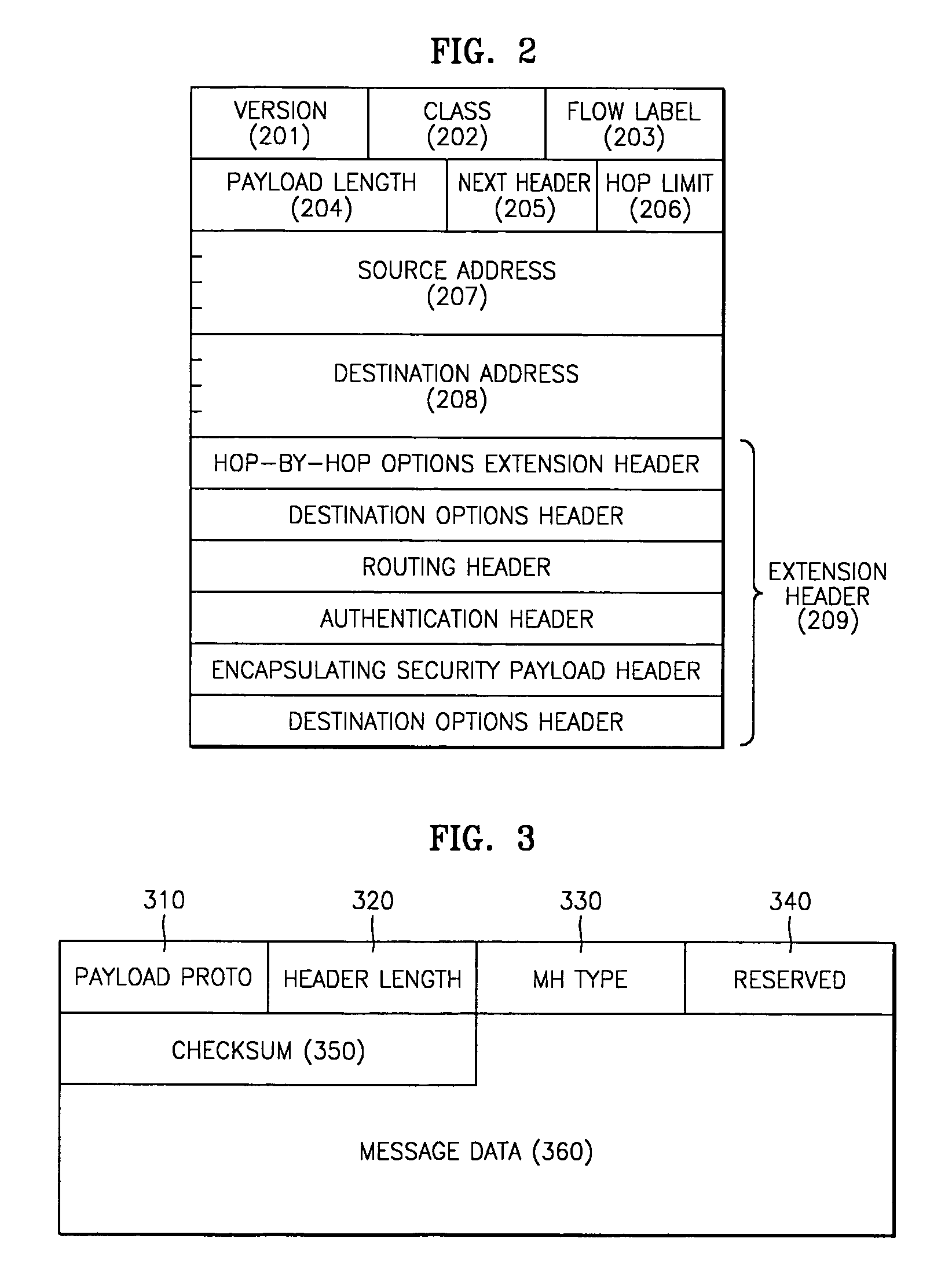
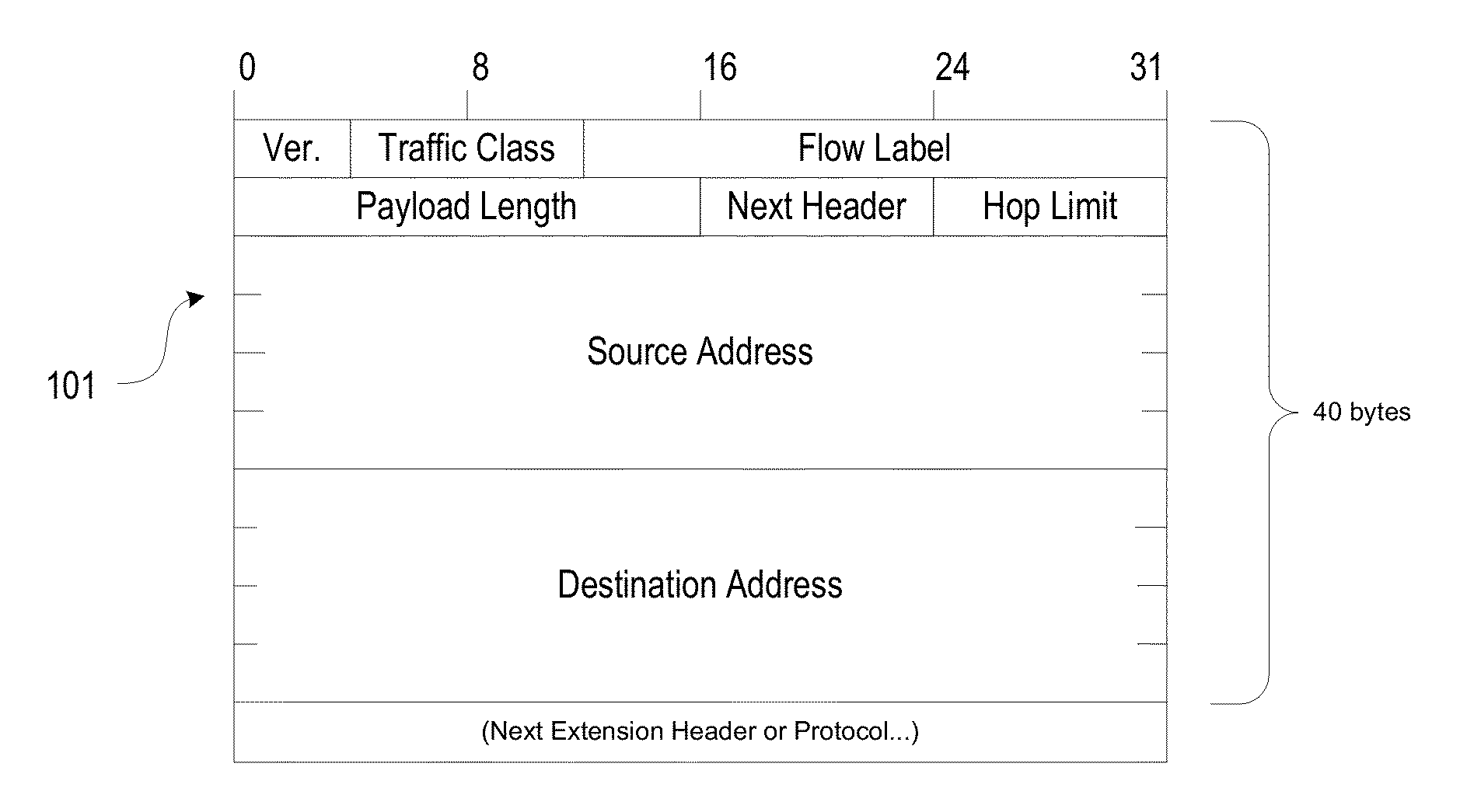
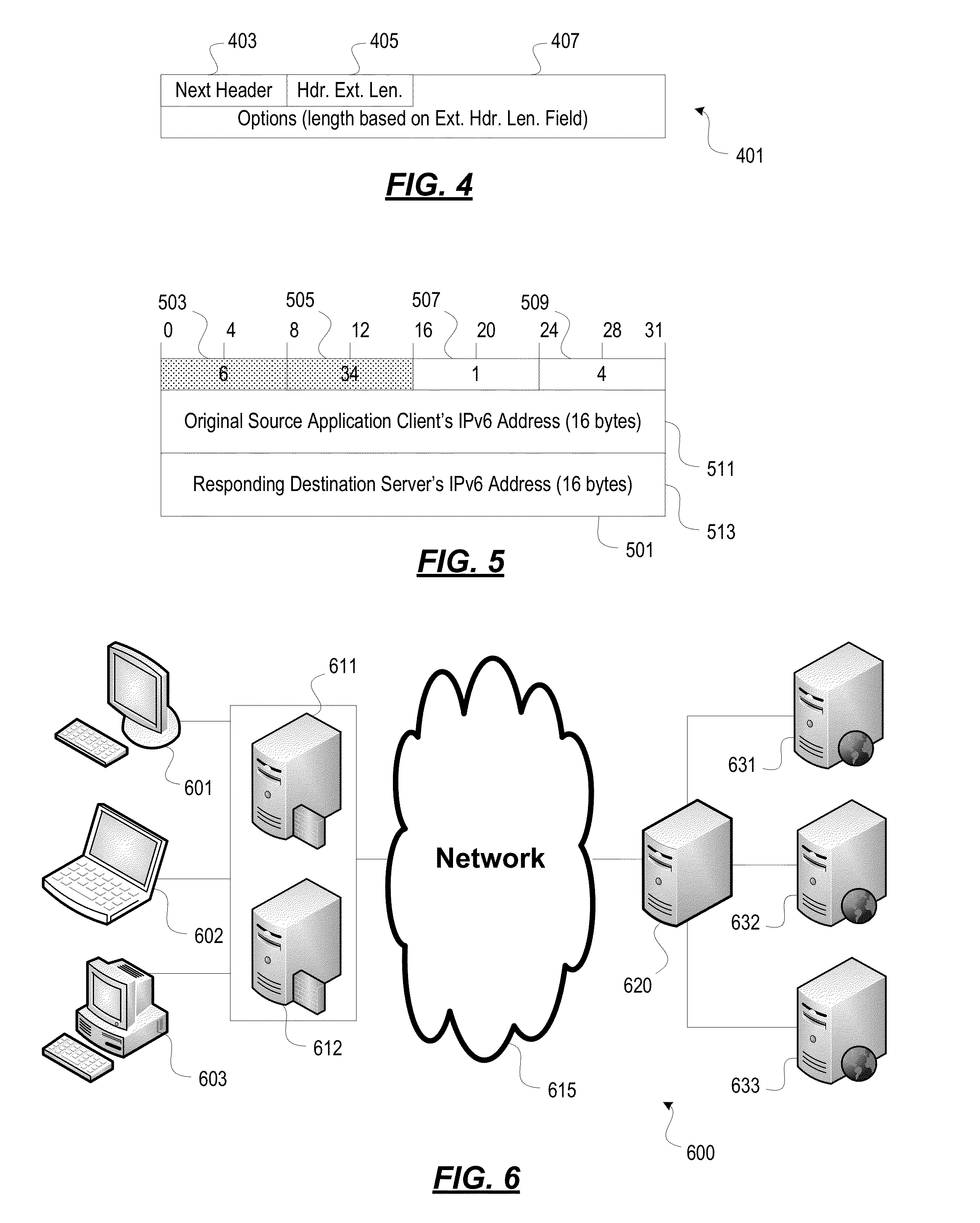
Methods and systems for performing load balancing and session persistence in IP (e.g., IPv6) networks are described herein. Some aspects relate to a destination options extension header that may be defined as a load balancing session persistence option (LBSPO) for storing a client identifier and a server identifier for each of a client and a server during a session. Packets sent between the client and the server may include the LBSPO with the client and server identifiers. A load balancer with a virtual IP address of a target application can perform session persistence and assign a destination server to a client based on a preexisting session between the server and the client, as determined by the LBSPO information. While a target VIP node may process data packets based on the LBSPO information, once established, the LBSPO information may remain unchanged for the duration of the session.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Methods and apparatus for achieving route optimization and location privacy in an IPV6 network
ActiveUS20060018291A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsTelecommunicationsMobile IP
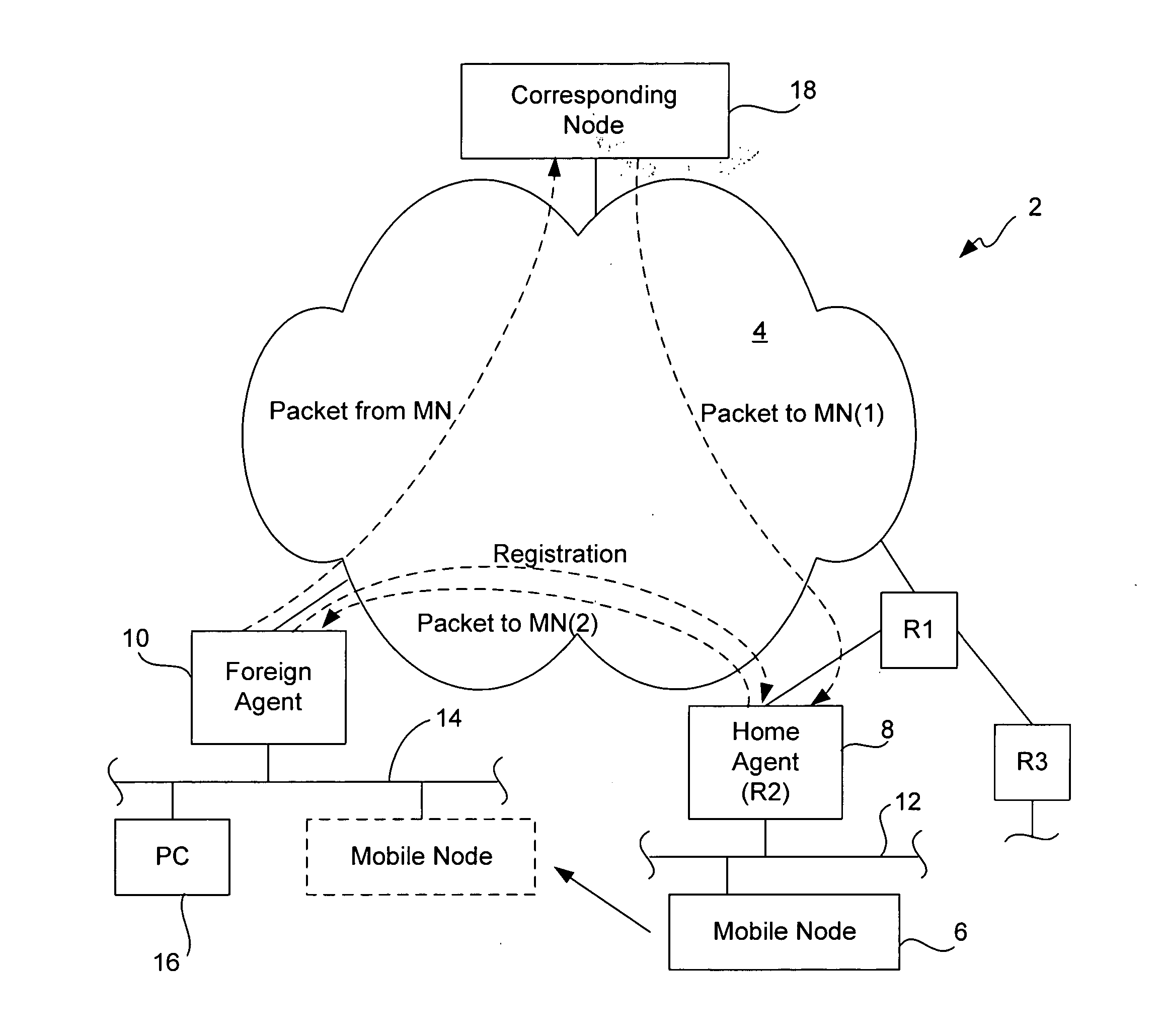
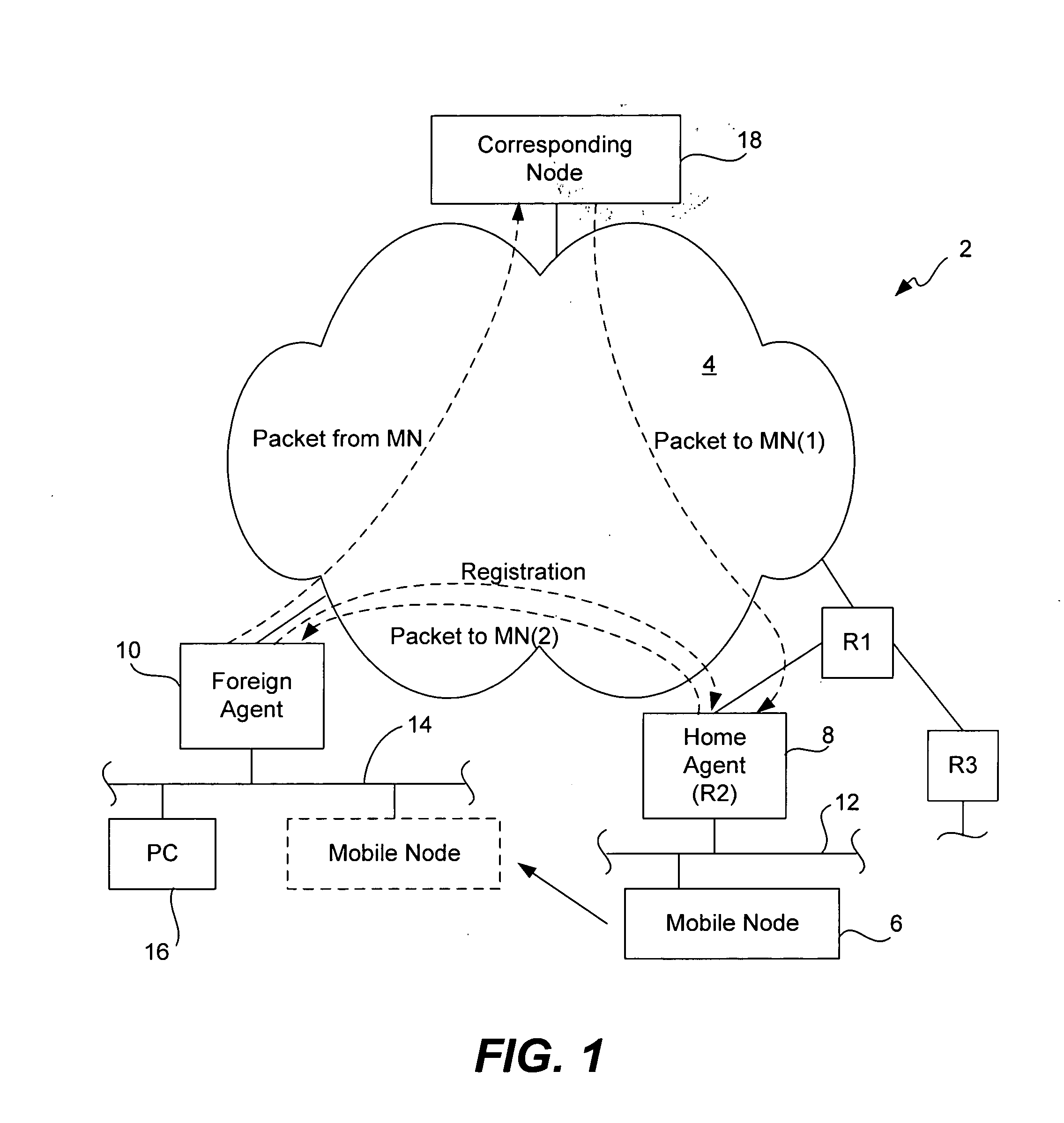
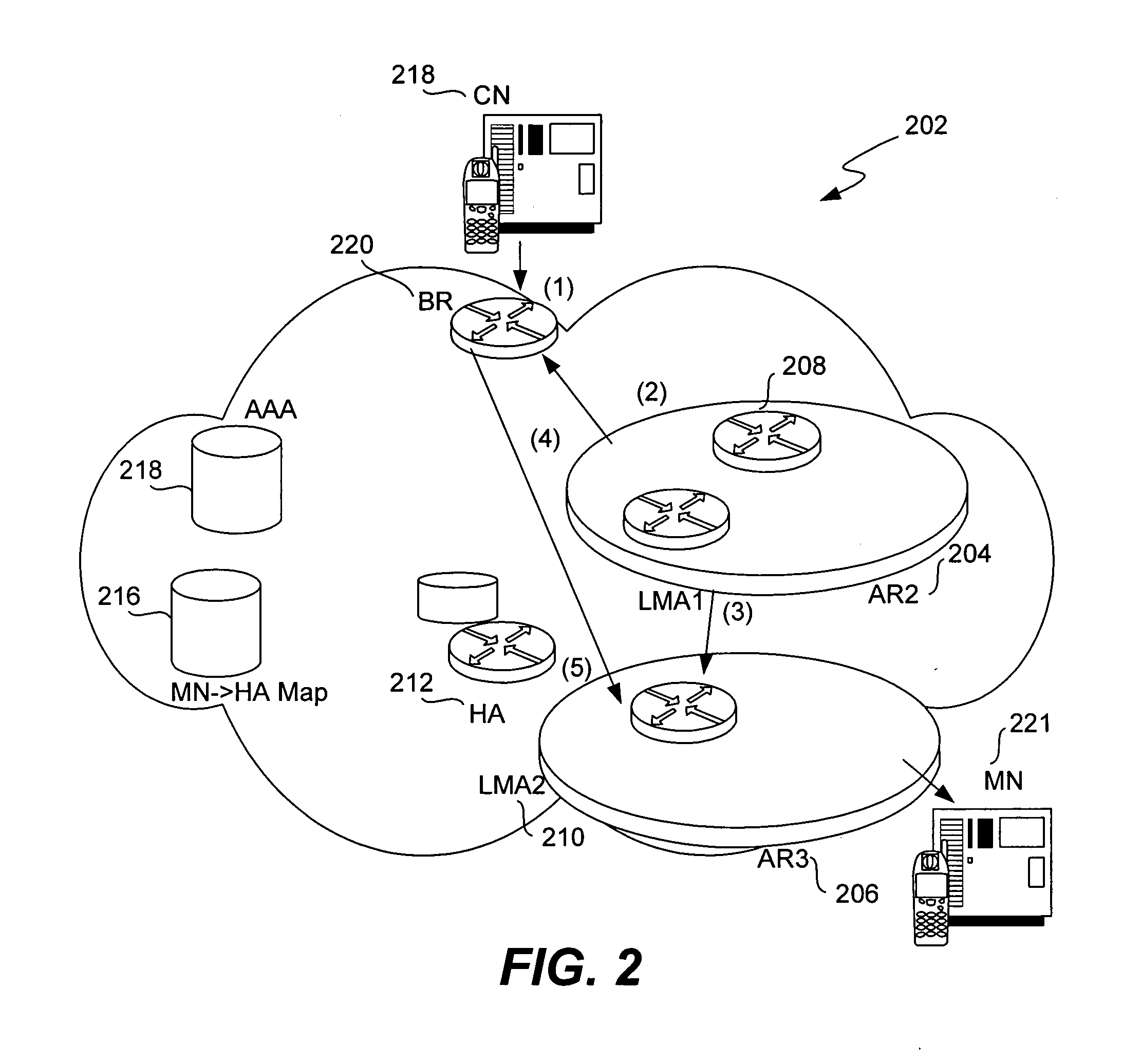
Methods and apparatus for performing proxy registration on behalf of a node with a Home Agent supporting Mobile IP are disclosed. A first registration request is composed on behalf of the node and transmitted to the Home Agent via a first Local Mobility Anchor, wherein the first Local Mobility Anchor is a regional controller via which registration is performed when the node moves within a region associated with the first Local Mobility Anchor. When the node moves within a region or between regions, the node is re-registered. Specifically, a second registration request is composed and transmitted to the first Local Mobility Anchor when the node moves within the region associated with the first Local Mobility Anchor. When the node moves into a second region associated with a second Local Mobility Anchor and outside the first region associated with the first Local Mobility Anchor, a second registration request is composed and transmitted to the Home Agent via the second Local Mobility Anchor, wherein the second Local Mobility Anchor is a regional controller via which registration is performed when the node moves within a region associated with second first Local Mobility Anchor.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mobile node, router, server and method for mobile communications under ip version 6 (ipv6) protocol
InactiveUS20050020265A1Smooth handoverQuick eliminationWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDelayed timeMobile communication systems
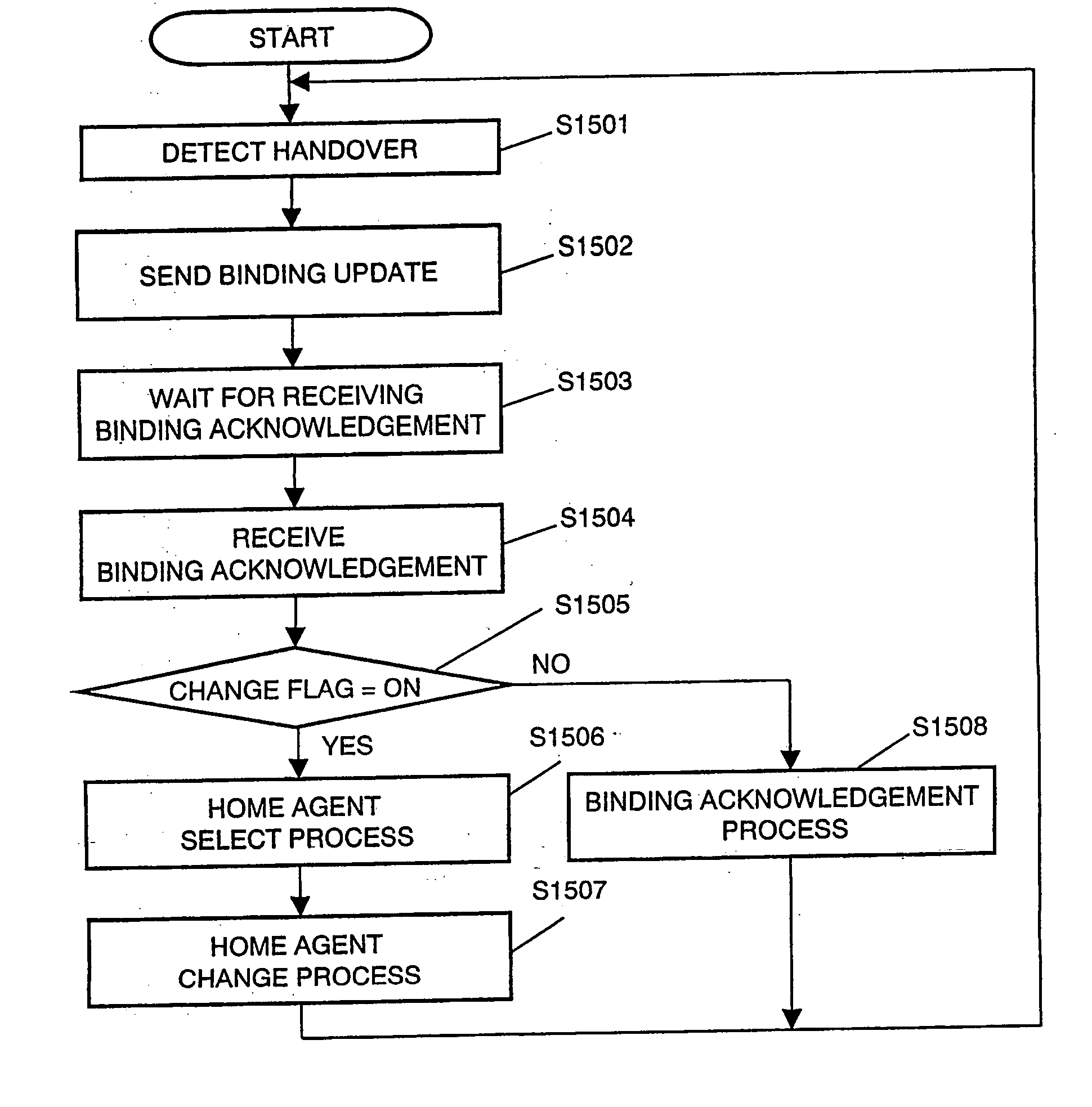
In a mobile communication system supported with IP version 6, a mobile node measures at least one of a hop number or communication delay time to a belonging home agent. When the result of measurement is equal to or greater than a predetermined value, registration deletion is requested to the belonging home agent while registration is requested to a new home agent. The belonging home agent deletes the registration of mobile node, and the new home agent registers the mobile node. This can reduce the load on an IP network and decrease data delay.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method, Communication Device and System for Detecting Neighboring Nodes in a Wireless Multihop Network Using Ndp
InactiveUS20070274232A1New featureData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsTraffic capacityCommunications system
A method is presented for neighbor discovery in a wireless multihop packet based communication network using Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) wherein the network is built up by client and / or server devices and / or infrastructure devices, network traffic is based on using NDP forwarding and rebroadcasting to locate devices in such a network architecture. The invention also includes devices for such a network and the complete communication system is described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Address translation equipment, terminal equipment and mobile communication method
InactiveUS7328281B2Multiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsMobile ip protocolNetwork packet
A packet sent in a mobile IP communication between different regions passes through a particular address translation unit, so that the communication route cannot be optimized. The packet cannot be delivered to a mobile node not having a fixed home address. To overcome the difficulties, the address translation unit includes a function to process the mobile IPv6 protocol. The mobile node includes a function to dynamically acquire a home address. A first network and a second network each identify the mobile node by a SIP (session initiation protocol) identifier. The mobile node acquires a home address on the second network and registers a corresponding relation between the identifiers and the home address thereof. A terminal on the second network acquires the home address of the mobile node from information of the mobile node registered to the SIP server according to a SIP procedure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Coordinator, gateway, and transmission method for IPv6 in wireless sensor network
InactiveUS20090146833A1Reduce overheadCircuit arrangementsNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
Provided are a coordinator, a gateway, and a transmission method for applying IPv6 in a wireless sensor network (WSN). Dual addressing of a link local address using a short address used in the WSN and a global unicast address using an extended unique identifier (EUI) of a node makes it possible to support mobility of the WSN and communicate data with an external network.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Filter based longest prefix match algorithm
InactiveUS20050175010A1Reduce in quantityFaster and less-costly to implementData processing applicationsNetworks interconnectionSlide windowIp address
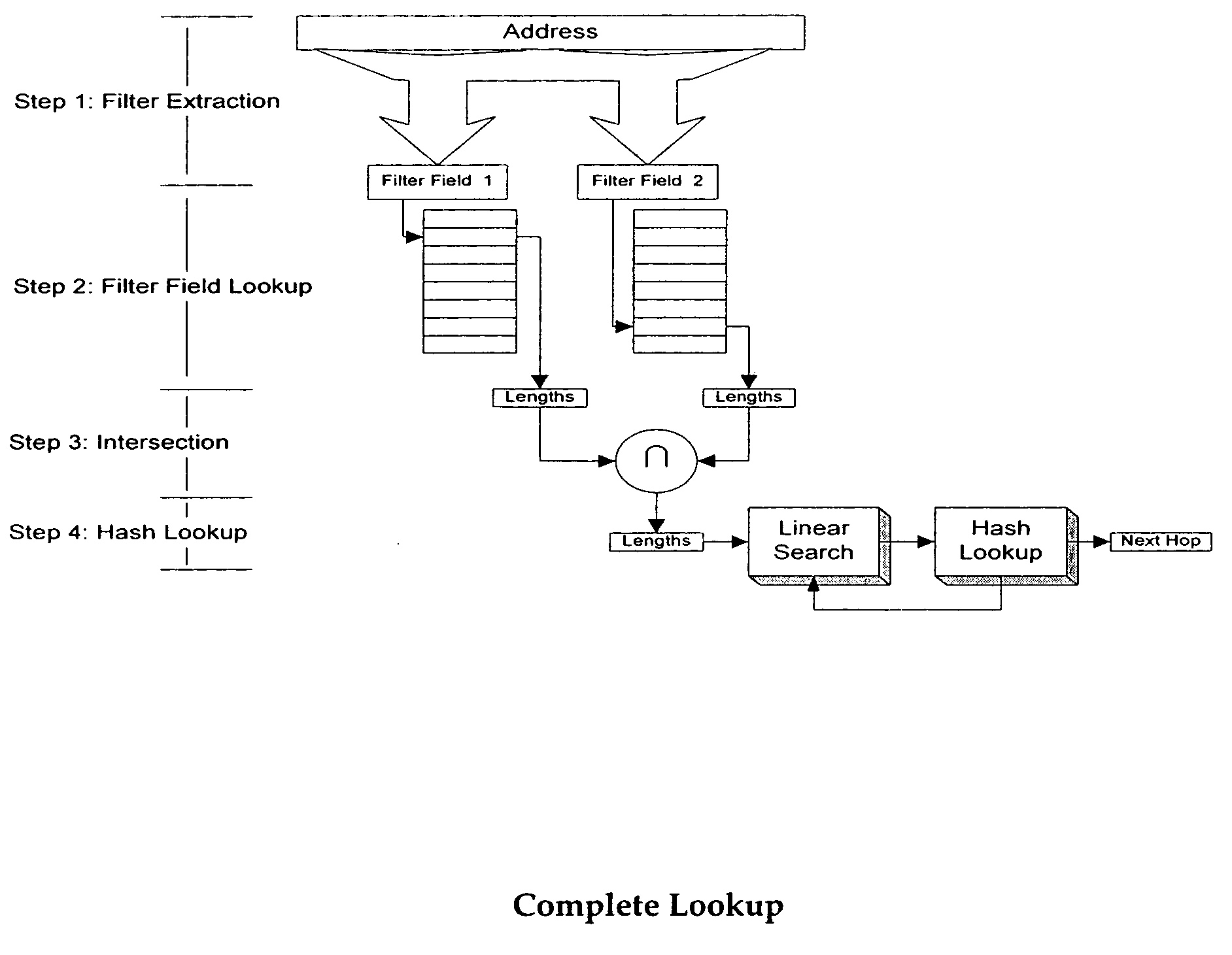
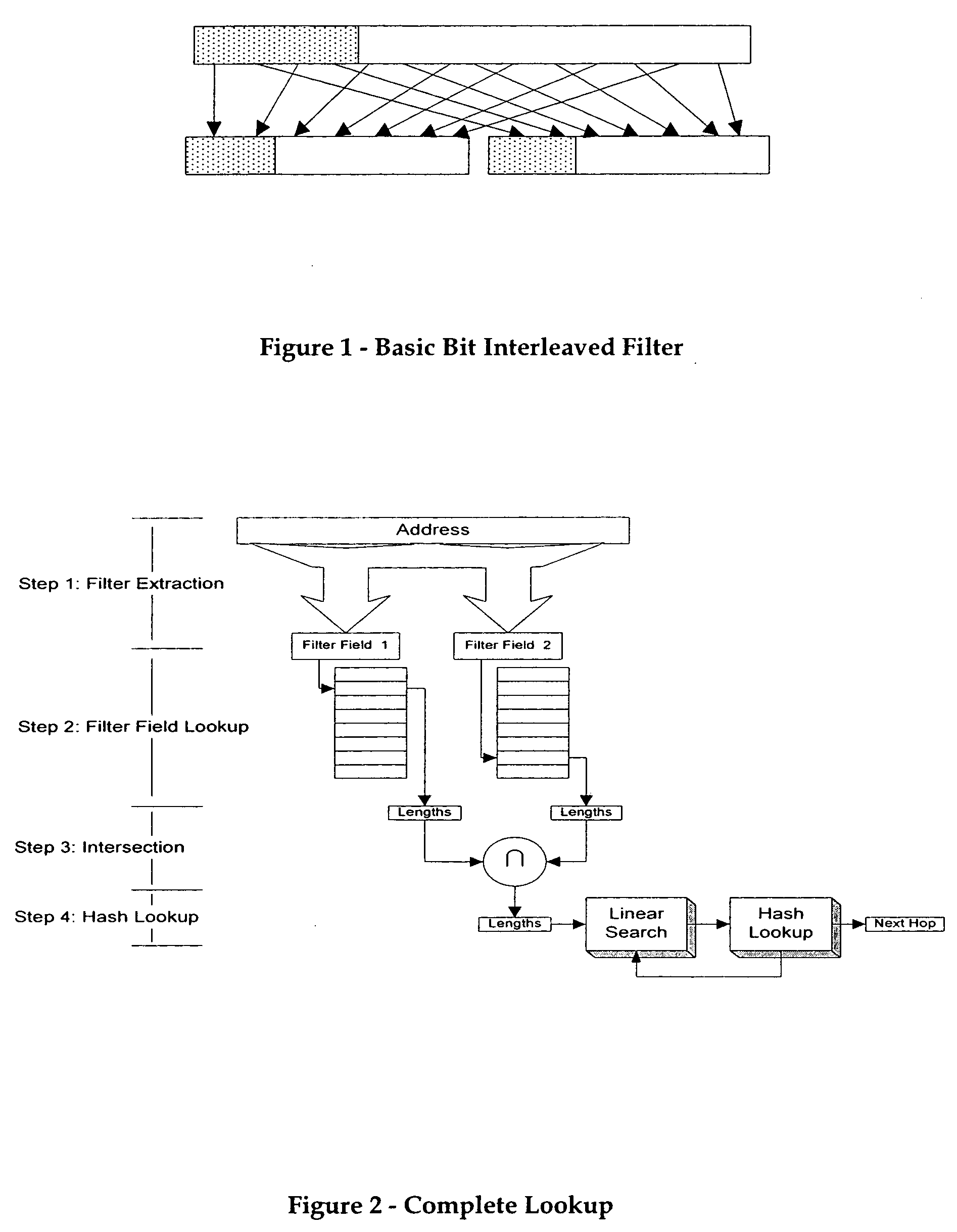
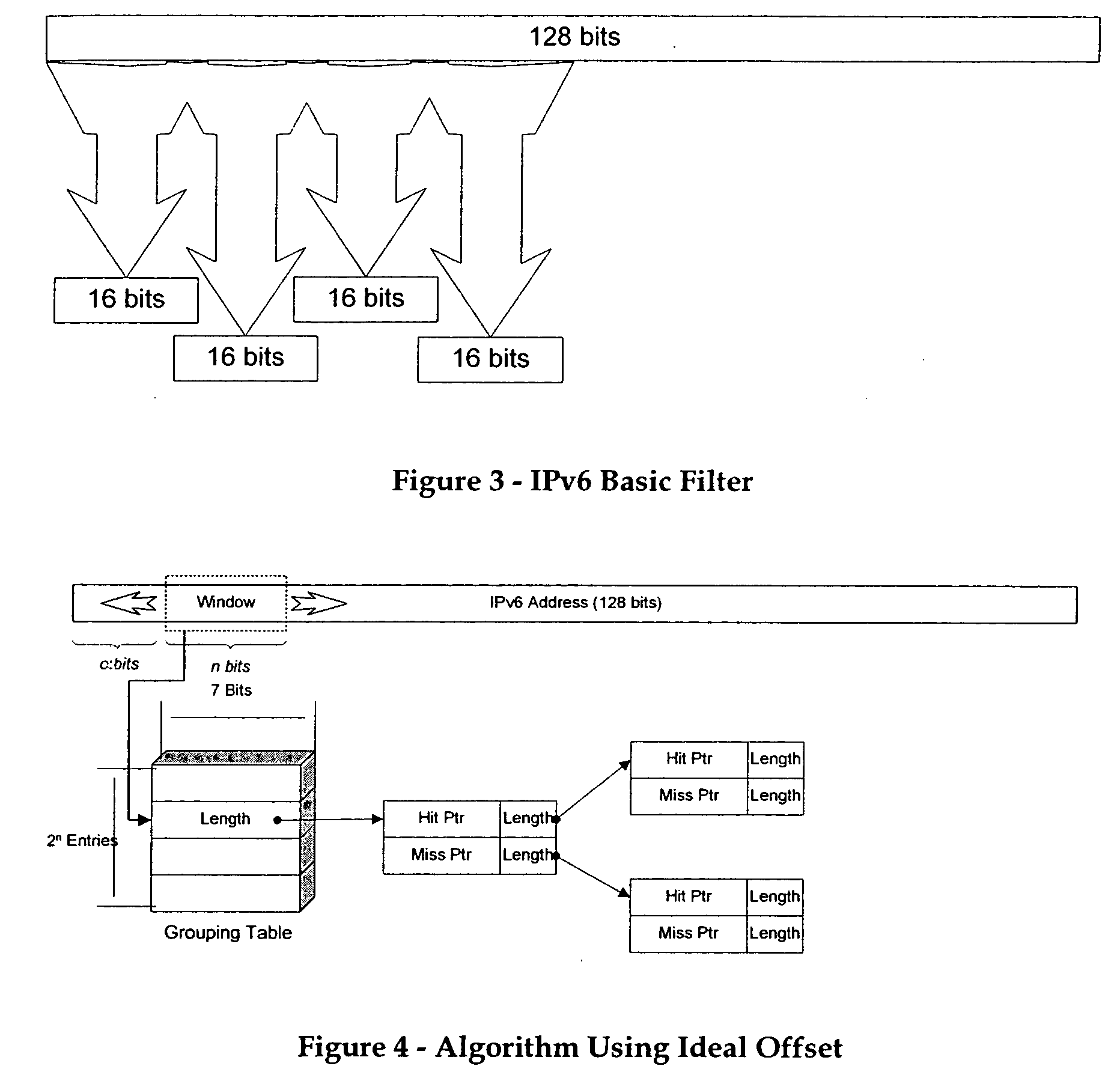
Methods directed to longest prefix matching and systems directed to IP address lookups are presented. The methods and systems relate in particular to IPv6 and comprise finding the longest prefix match (LPM) for an IP address. The method of the invention results in the use of filters to perform LPM. In embodiments of the invention, partial address filtering is used to further reduce filtering requirements. Reducing the number of filtering operations has the advantage of making the LPM algorithm faster and less costly to implement than prior art approaches. Also described is an “ideal offset filter” that extracts a fixed sized sliding window of bits from the IP address being processed.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
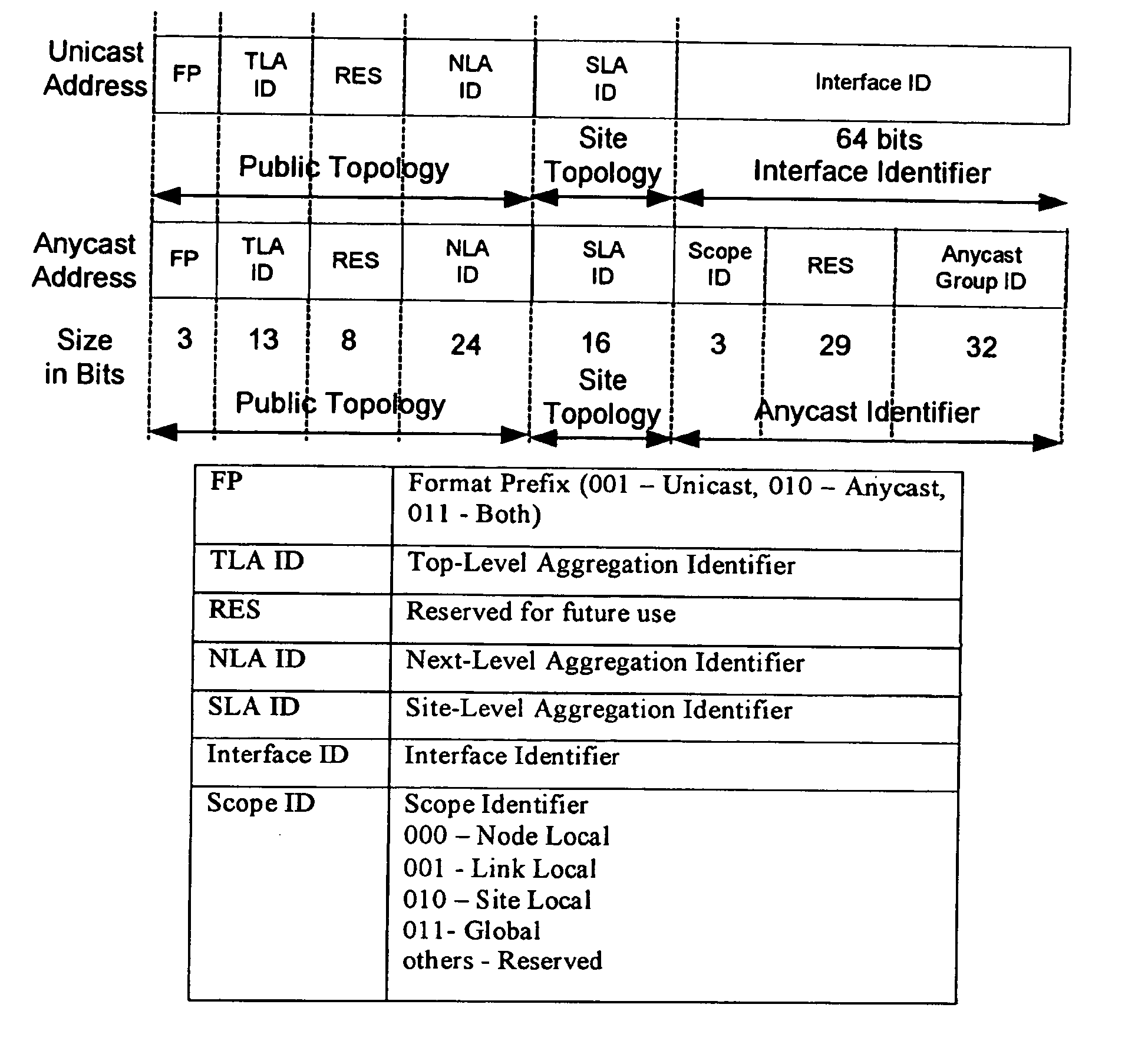
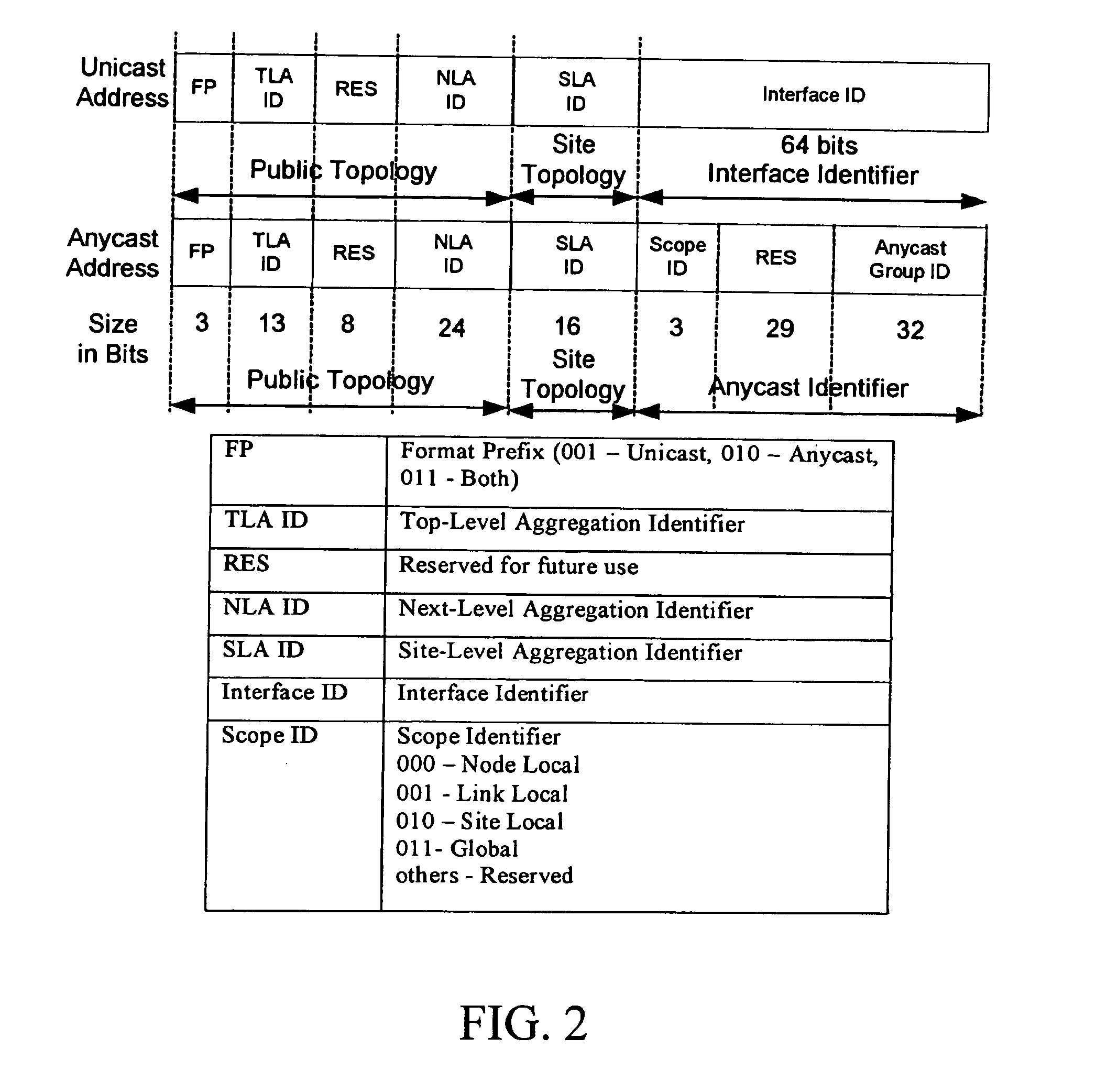
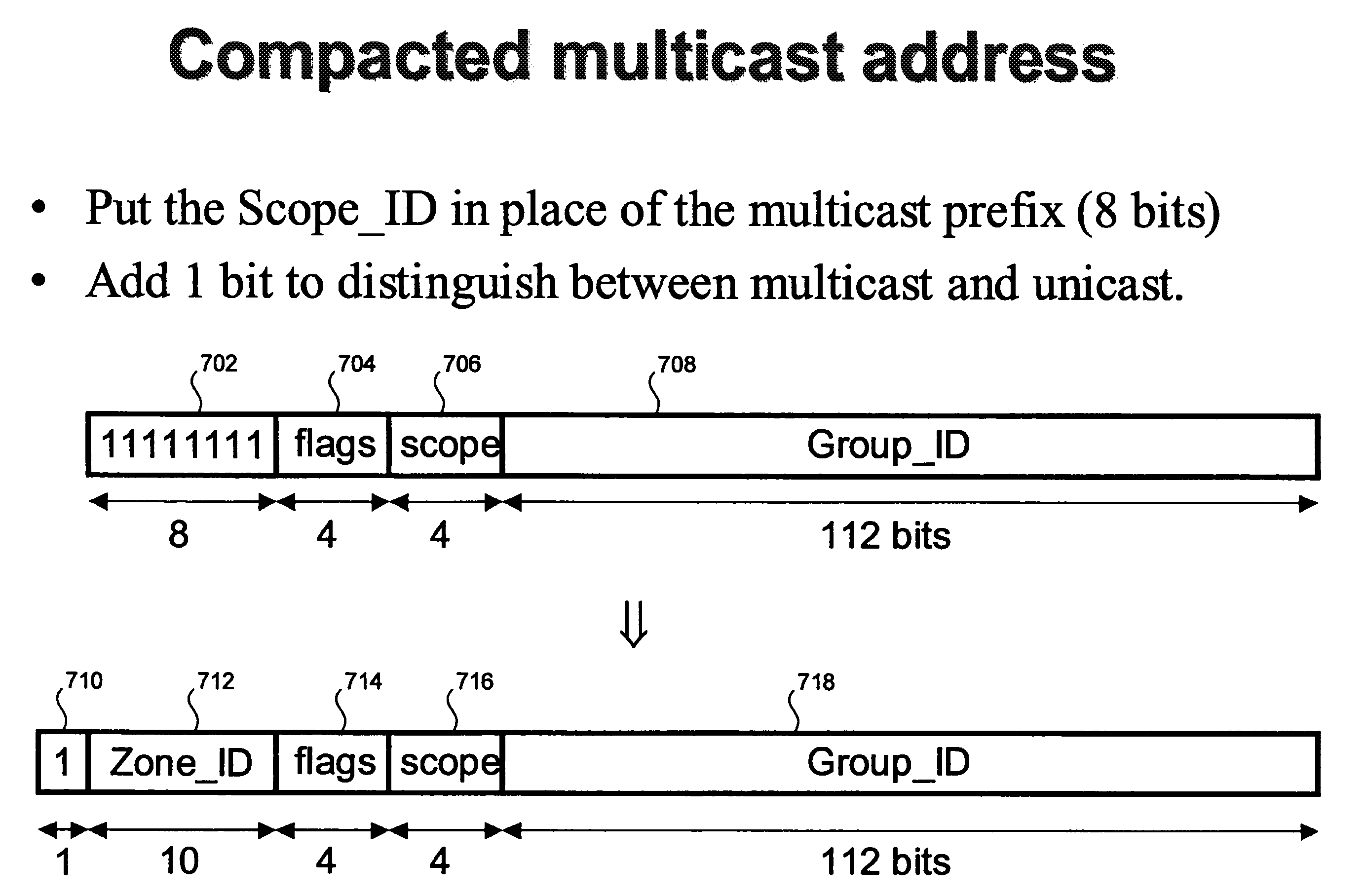
Anycast addressing for internet protocol version six
ActiveUS20050198367A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworking protocolRouting table
A protocol associated with an Internet protocol version six (IPv6) network address included within a network packet provides both unicast and anycast addressing, while having the same bit locations and bit functions associated with a top-level aggregation identifier, a next-level aggregation identifier, and a site-level aggregation identifier. A prefix associated with the three most significant bits of the network address identifies the network address as being a unicast address, an anycast address, or both a unicast and an anycast address. The prefix that identifies the network address as being both a unicast and an anycast address allows routers to have smaller routing tables.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
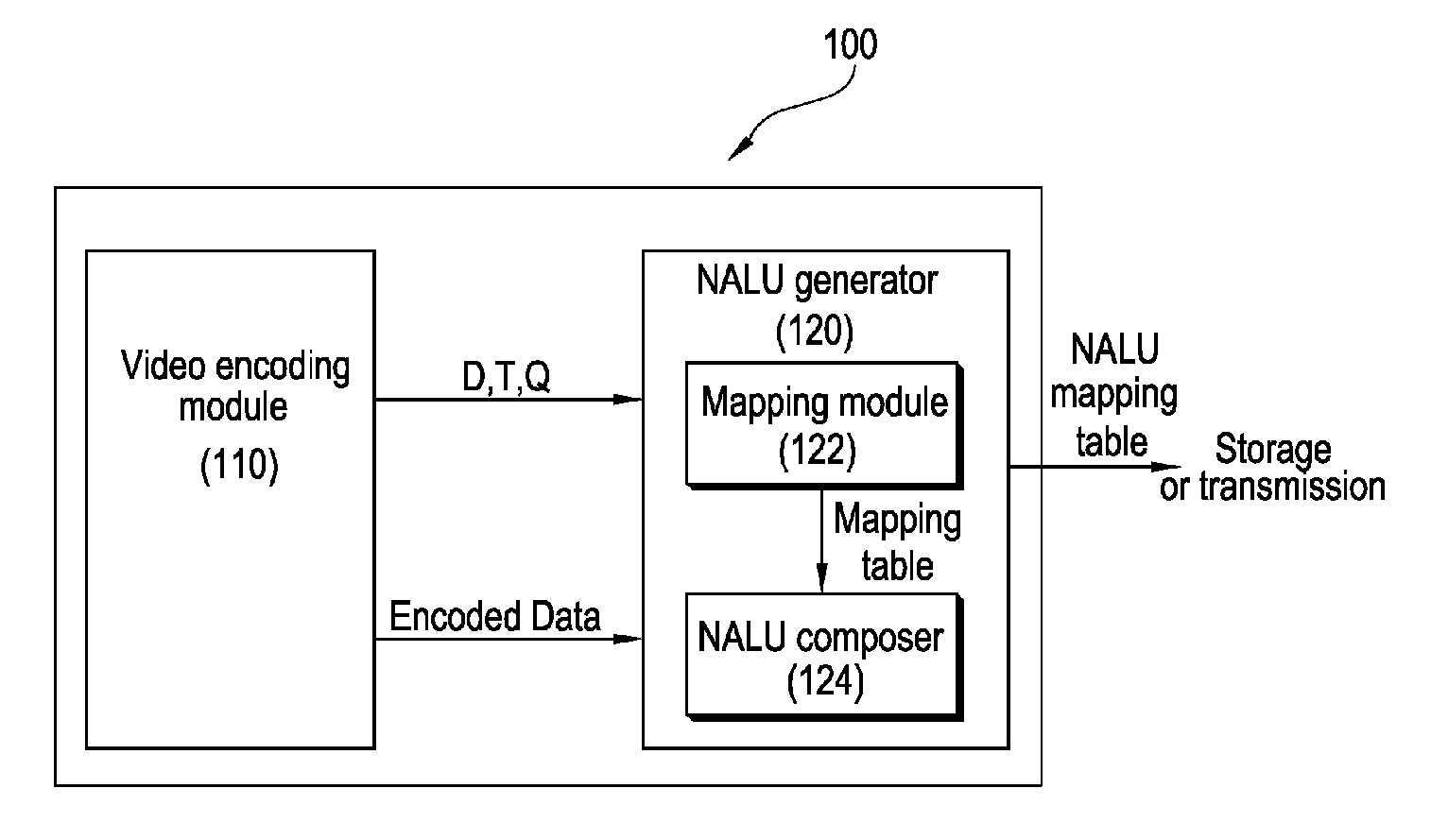
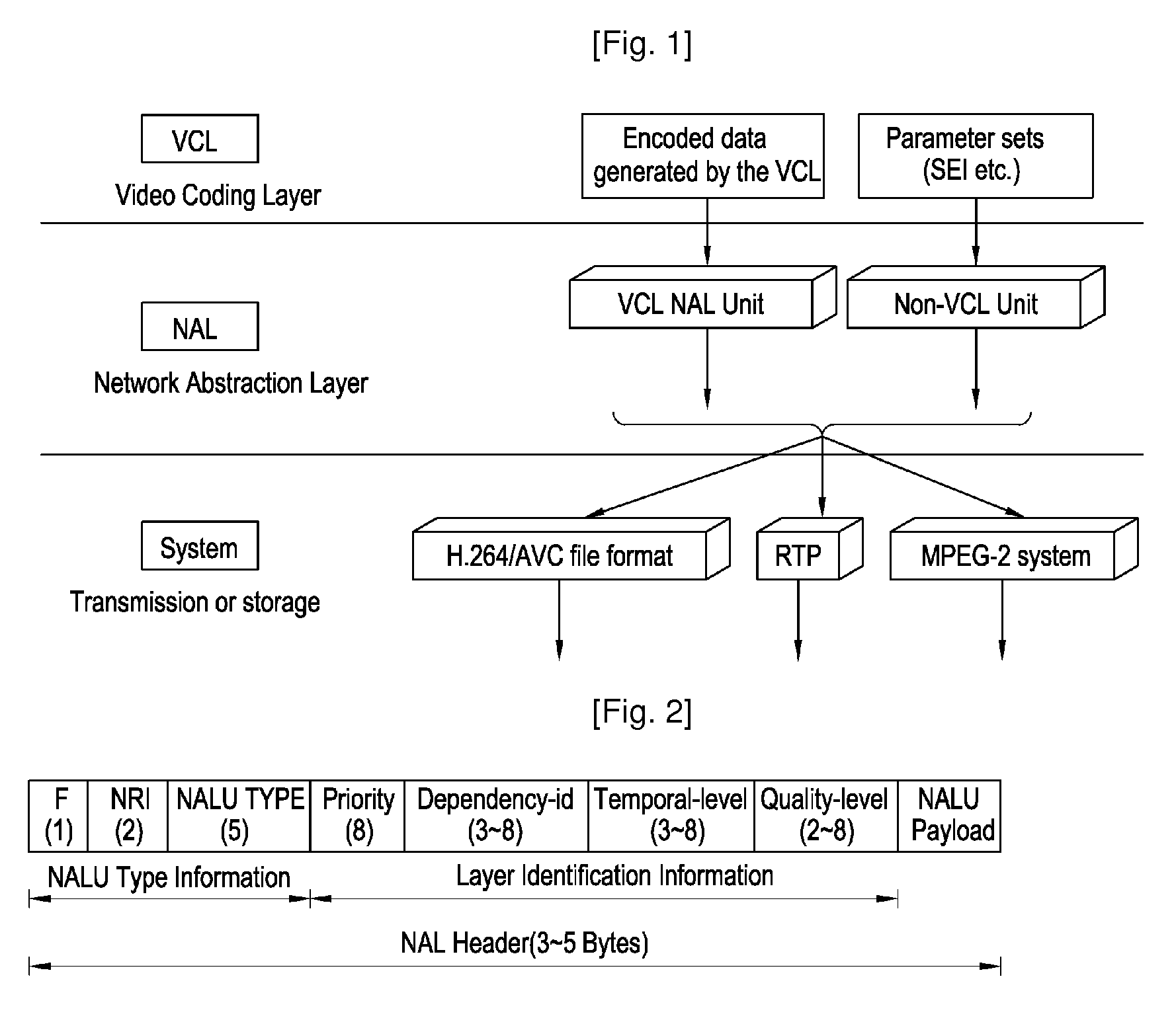
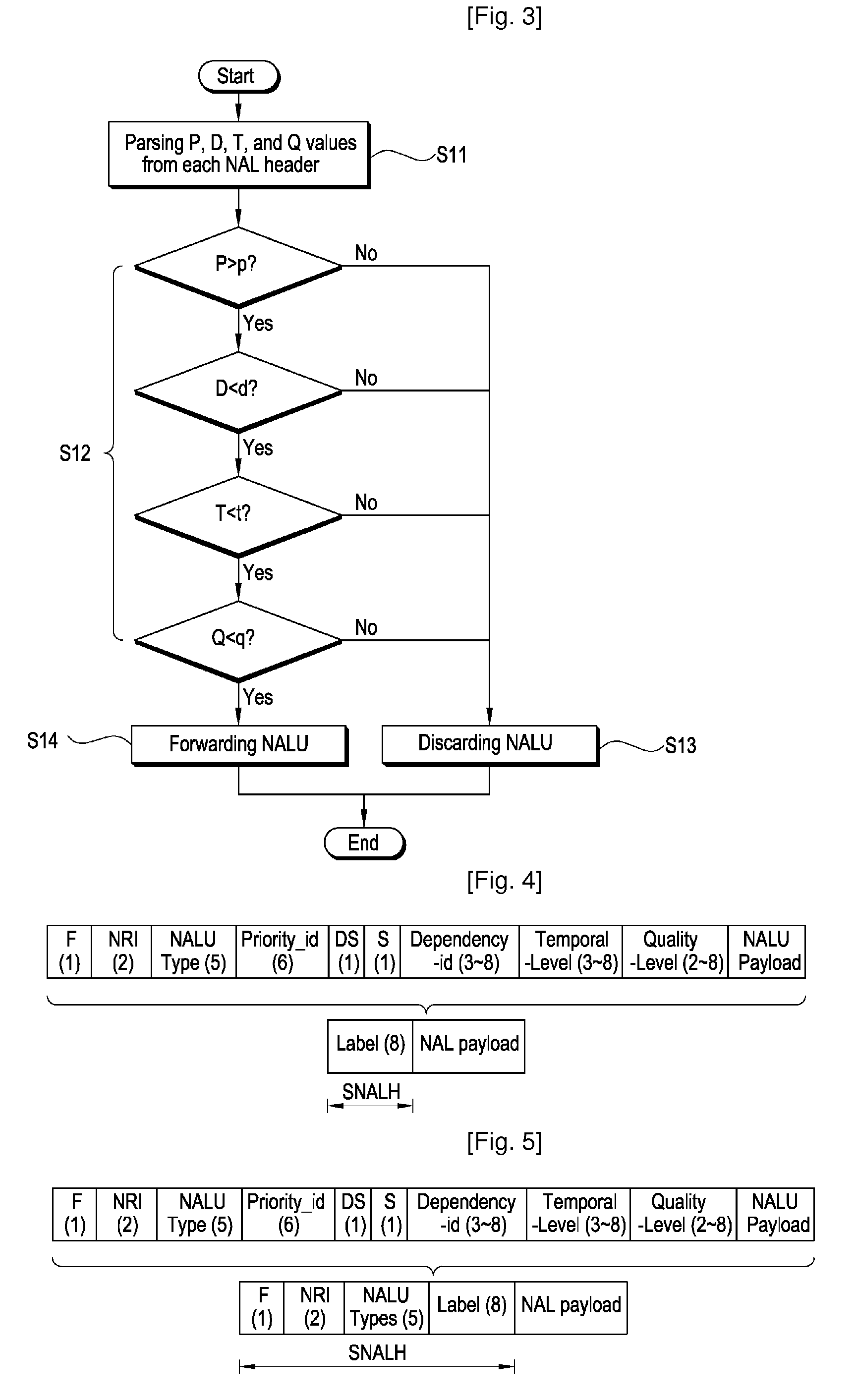
Packet format of network abstraction layer unit, and algorithm and apparatus for video encoding and decoding using the format, QOS control algorithm and apparatus for ipv6 label switching using the format
ActiveUS20090175353A1Reduce complexityReduce controlPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData packVideo encoding
The construction method of NALU (Network Abstraction Layer Unit) for IPv6 label switching and its using algorithms of video encoding, QoS control, and decoding are provided. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the NALU format is composed of the NALH (Network Abstraction Layer Header) including the label and the NAL (Network Ab straction Layer) payload. Here, the label is determined based on layer information which is combination of a spatial scalable level, a temporal scalable level, and a quality scalable level of the encoded data. The decoder uses the label to decide which one of multiple decoding modules is used to decode the current NAL payload. Moreover, the label can be included in the packet header so that the MANE (Media Aware Network Element) can use the label to decide whether to forward the packet or drop it. For example, the label in the packet header can be used for QoS control of video service by using the flow label field in IPv6 packet header The IPv6 router can identify priority of the video packet by using the 20 bit long flow label, into which the label in NALH can be inserted. According to the embodiment, the MANE assumed in the MPEG and JVT (Joint Video Team) can be implemented effectively.
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV
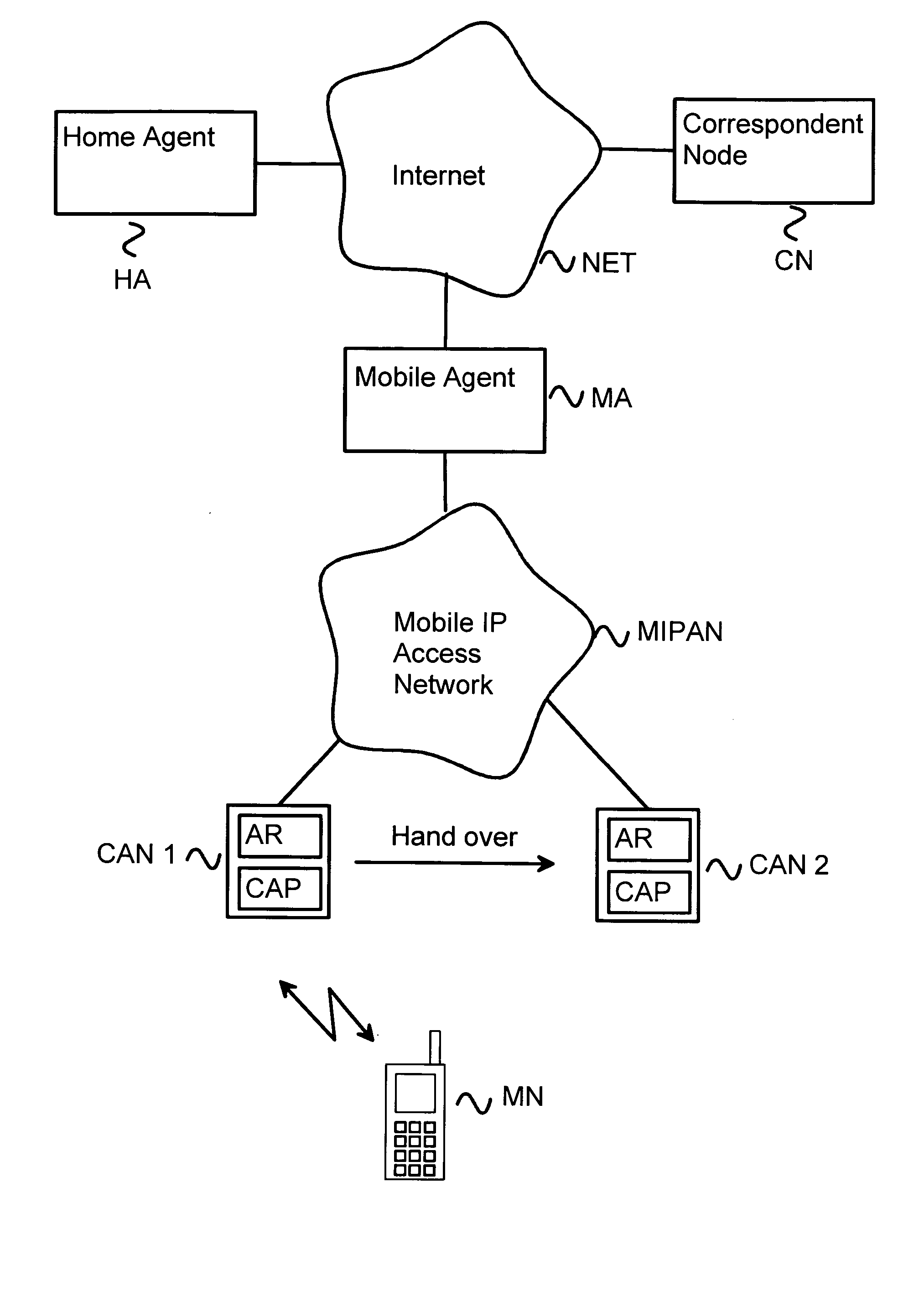
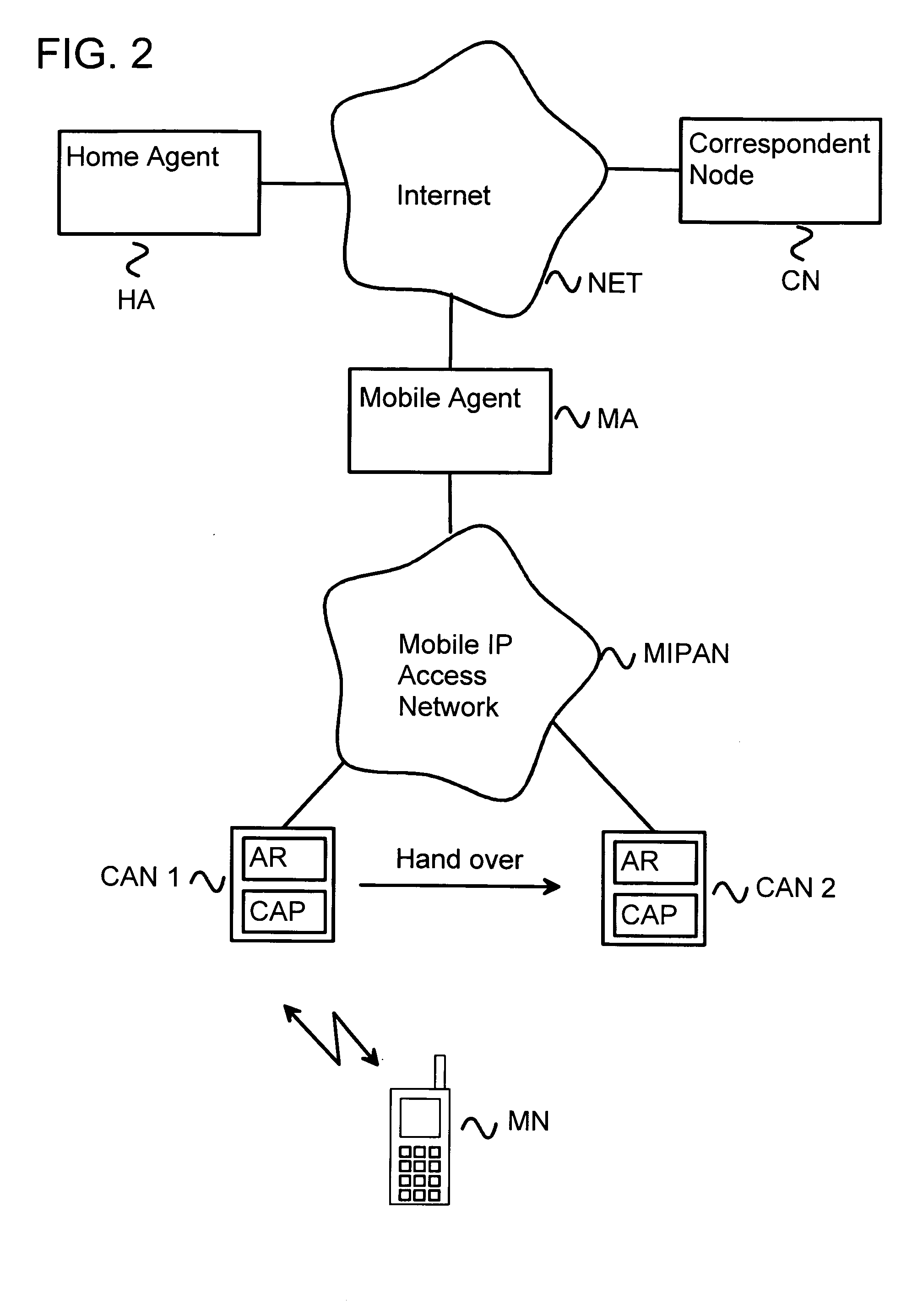
Method and system for local mobility management
ActiveUS20050088994A1Reduce air interfaceEnhanced signalWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAir interfaceMobility management
The present invention describes a method and system for local mobility management in which the mobility management taking place inside the mobile agent (MA) domain is hidden from the home agent (HA) and correspondent node (CN). In the method the mobile agent (MA) prefix information is broadcast over the air interface. An access router is implemented in the cellular access node (CAN). The cellular access node (CAN) also comprises a cellular access point (CAP). Proxy functionality is arranged to the cellular access point (CAP). Binding entries are created to the mobile agent (MA) so that only basic mobile IPv6 needs to be supported in the mobile node (MN).
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Mobility header compression method and system for internet protocol-based low power wireless network
ActiveUS20090185549A1Improve transmission efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer networkRobust Header Compression
A mobility header compression method and system for an IPv6-based LoWPAN is provided for supporting IPv6 mobility to the IPv6-based LoWPAN checks a packet carrying data and a first and a second headers containing transmission information about the data to determine whether the second header contains a compressed Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) information. When the second header contains a compressed IPv6 information, ands followed by a mobility header, a mobility support-indicative field of the first header is set to indicate that the second header is followed by the mobility header and the rest of the fields of the second header are compressed except for the mobility header-indicative field. A mobility information-indicative field of the mobility header is set to indicate inclusion of mobility information; and the rest of the fields of the mobility header are compressed except for the mobility information-indicative field.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND KYUNG HEE UNIV +1
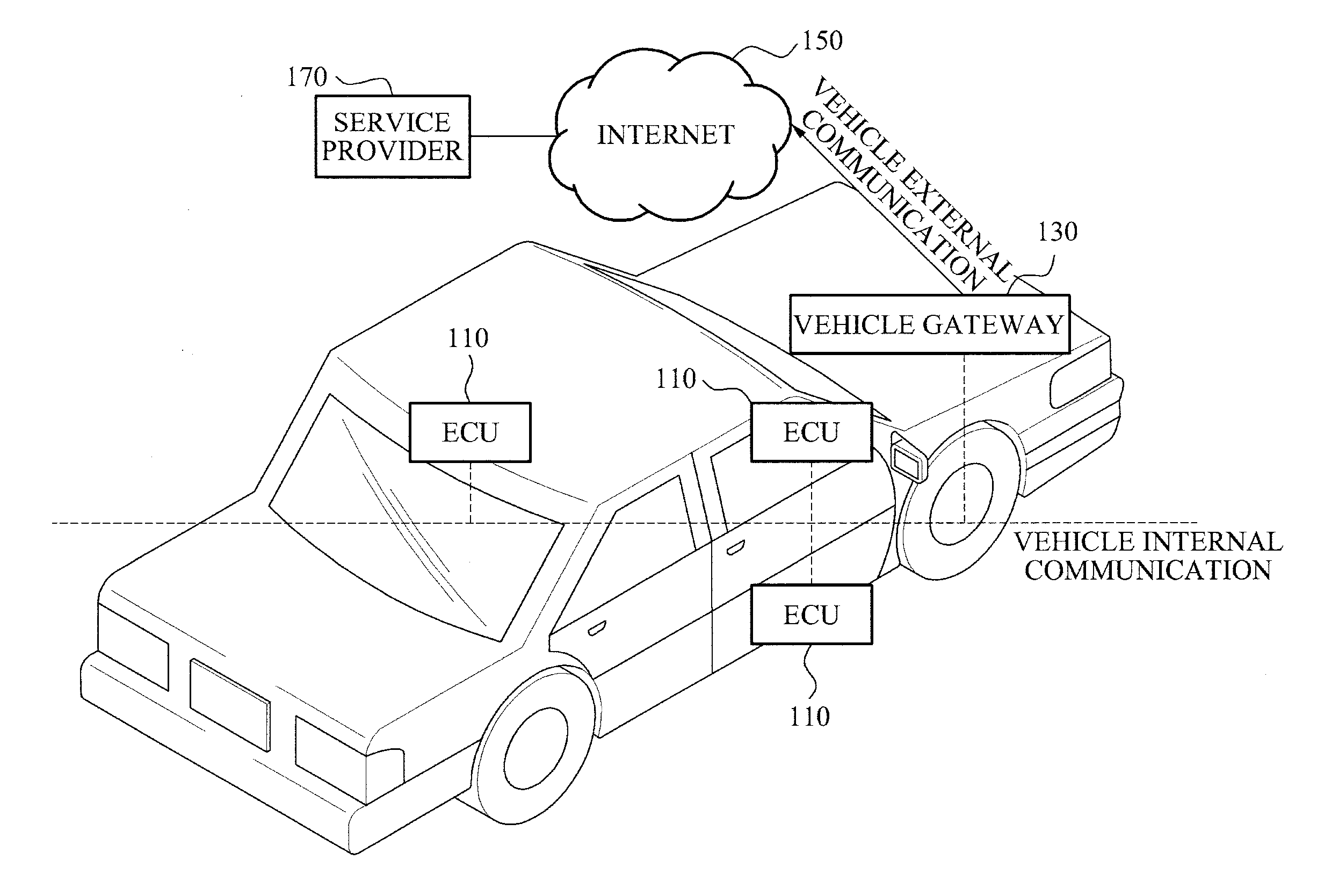
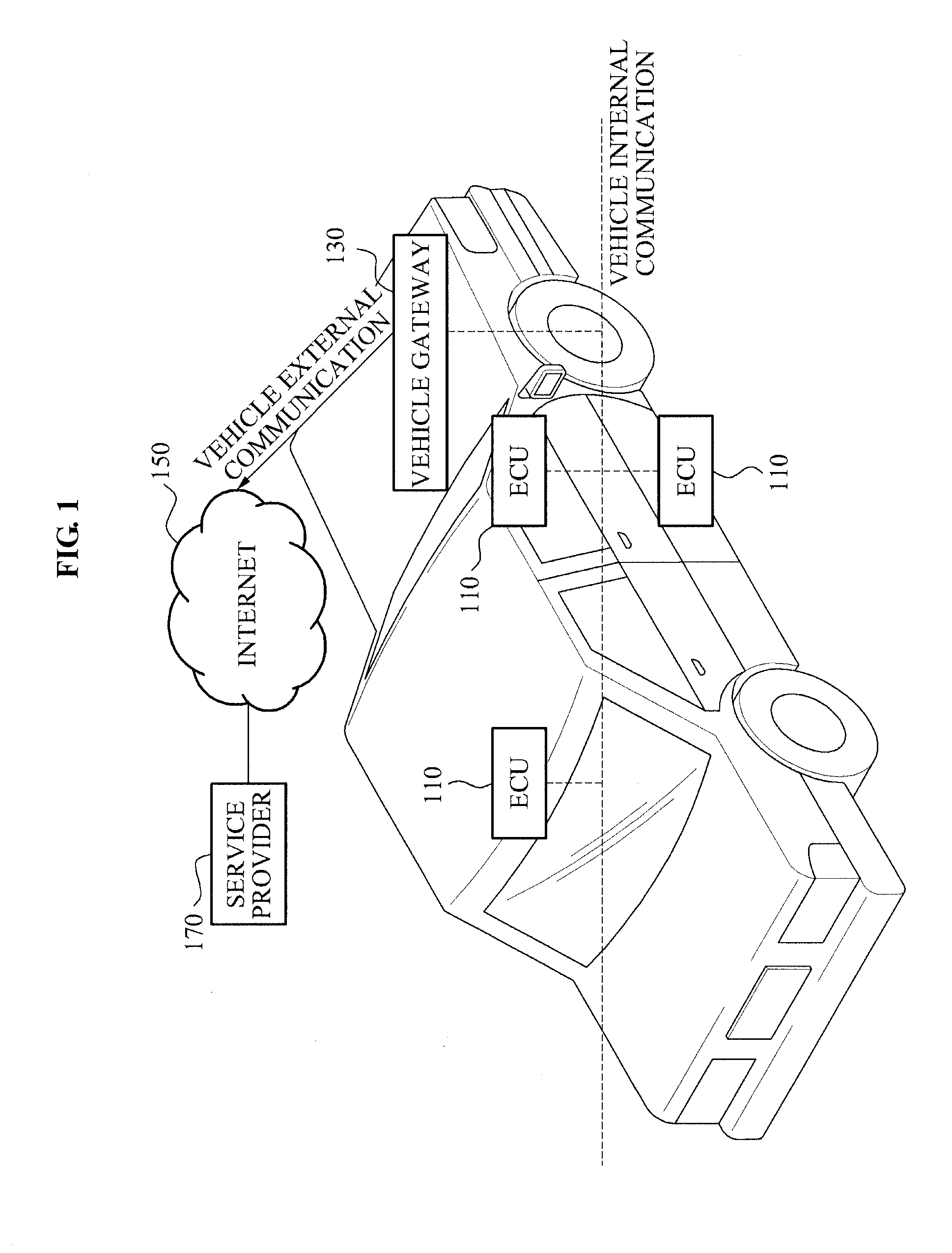
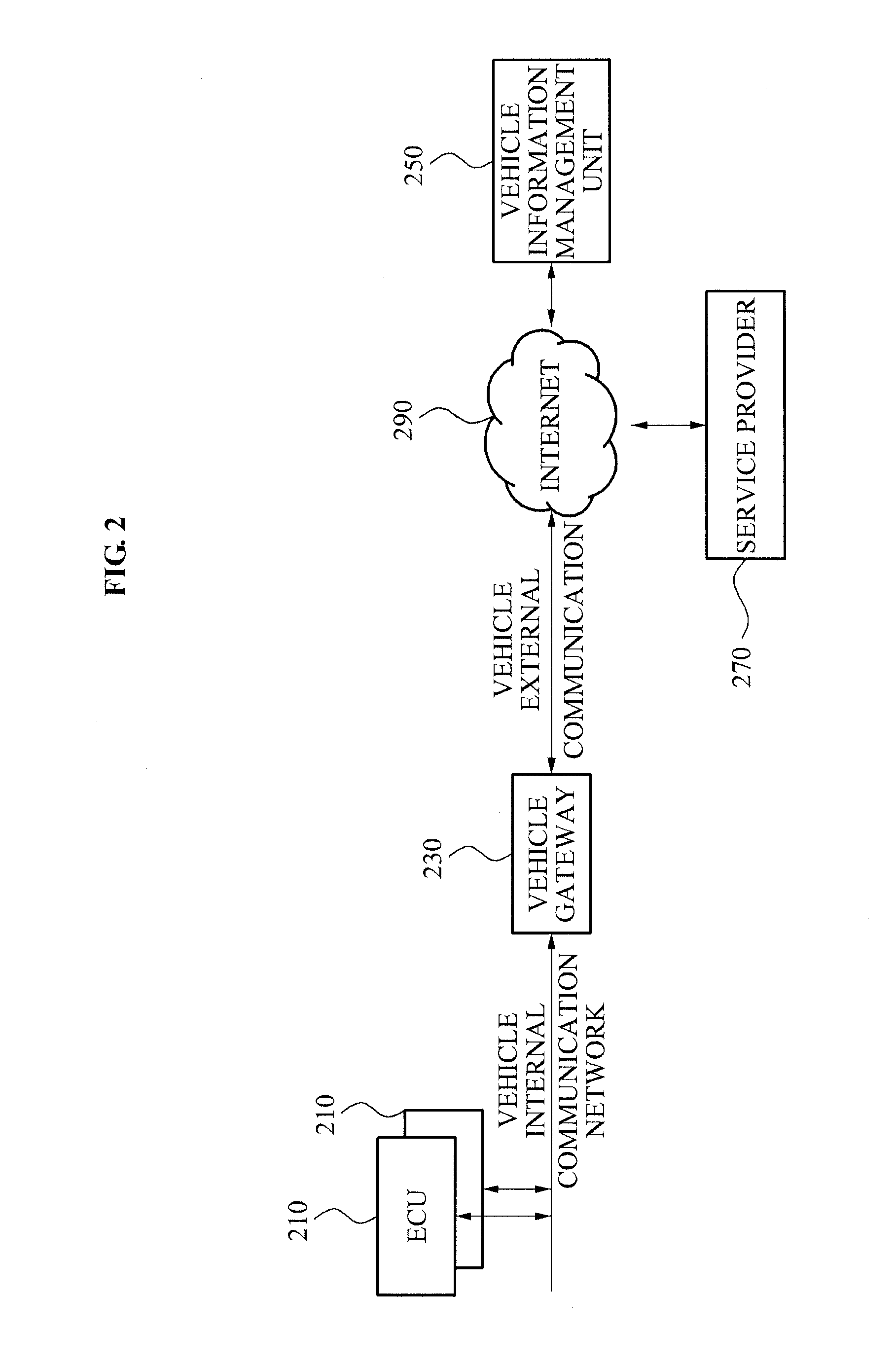
COMMUNICATION APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR VEHICLE USING IPv6 NETWORK
InactiveUS20110153149A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesService provisionNetwork communication
A communication apparatus for a vehicle using an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) network is disclosed. The communication apparatus may include at least one Electronic Control Unit (ECU) having an IPv6 network communication function, and a vehicle gateway to support vehicle internal communication network to communicate with the at least one ECU and to support vehicle external communication network for a communication with a terminal of a service provider.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Access list key compression
ActiveUS20080165783A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkIPv6
Methods and apparatus for implementing an access list key for accessing information associated with a packet from an access list are disclosed. The packet includes an IP source address field and an IP destination address field, the IP source address field including an IP source address and the IP destination address field including an IP destination address, the IP source address and the IP destination address each having a number of bits (e.g., 128 bits in the case of IPv6). An IP source address is obtained from the IP source address field of the packet and an IP destination address is obtained from the IP destination address field of the packet. A modified IP source address is generated from the obtained IP source address such that the number of bits in the modified IP source address is less than the number of bits in the obtained IP source address. In addition, a modified IP destination address is generated from the obtained IP destination address such that the number of bits in the modified IP destination address is less than the number of bits in the obtained IP destination address. The access list key is then composed from the modified IP source address and the modified IP destination address.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway
InactiveCN102448202AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce power consumptionHigh level techniquesWireless communicationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceTransceiver
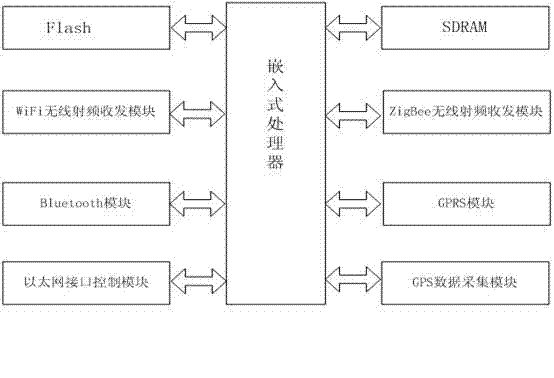
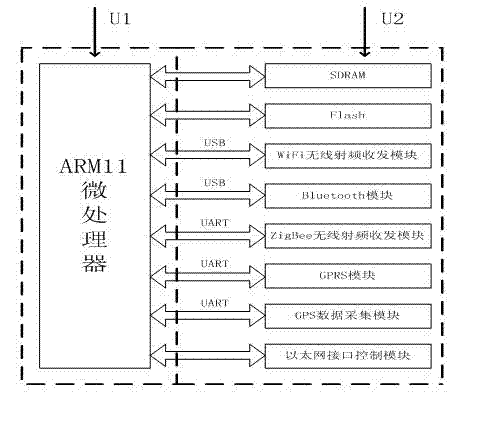
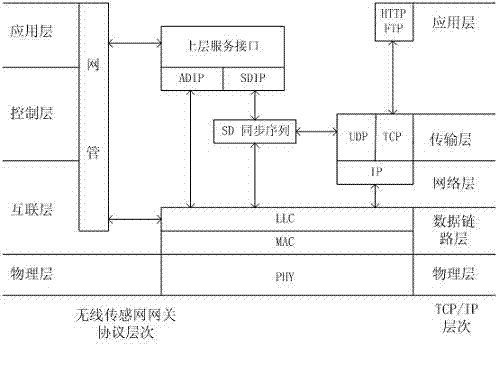
The invention discloses a multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway and relates to the technical field of a wireless sensor network. The gateway mainly consists of an embedded processor, an SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory), a Flash memory, a WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) wireless radio frequency transceiver module, a ZigBee wireless radio frequency transceiver module, a GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) module, a Bluetooth module, a GPS (Global Positioning System) data acquisition module and an Ethernet interface control module. A networked operating system Linux is used as an operating system of the multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway and can be compatible with a TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) protocol IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6). The multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway has the advantages that conversion among various protocols is completed by treatment of a design protocol conversion program; the multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway can be used for setting up networks with various architectures, interconnecting the networks with various architectures and transmitting data; various network access schemes are provided for the wireless sensor network; the multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway has strong anti-interference capability, low power consumption and small volume; and portable equipment is provided for interconnection among the networks with various architectures and building of an integrated network.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
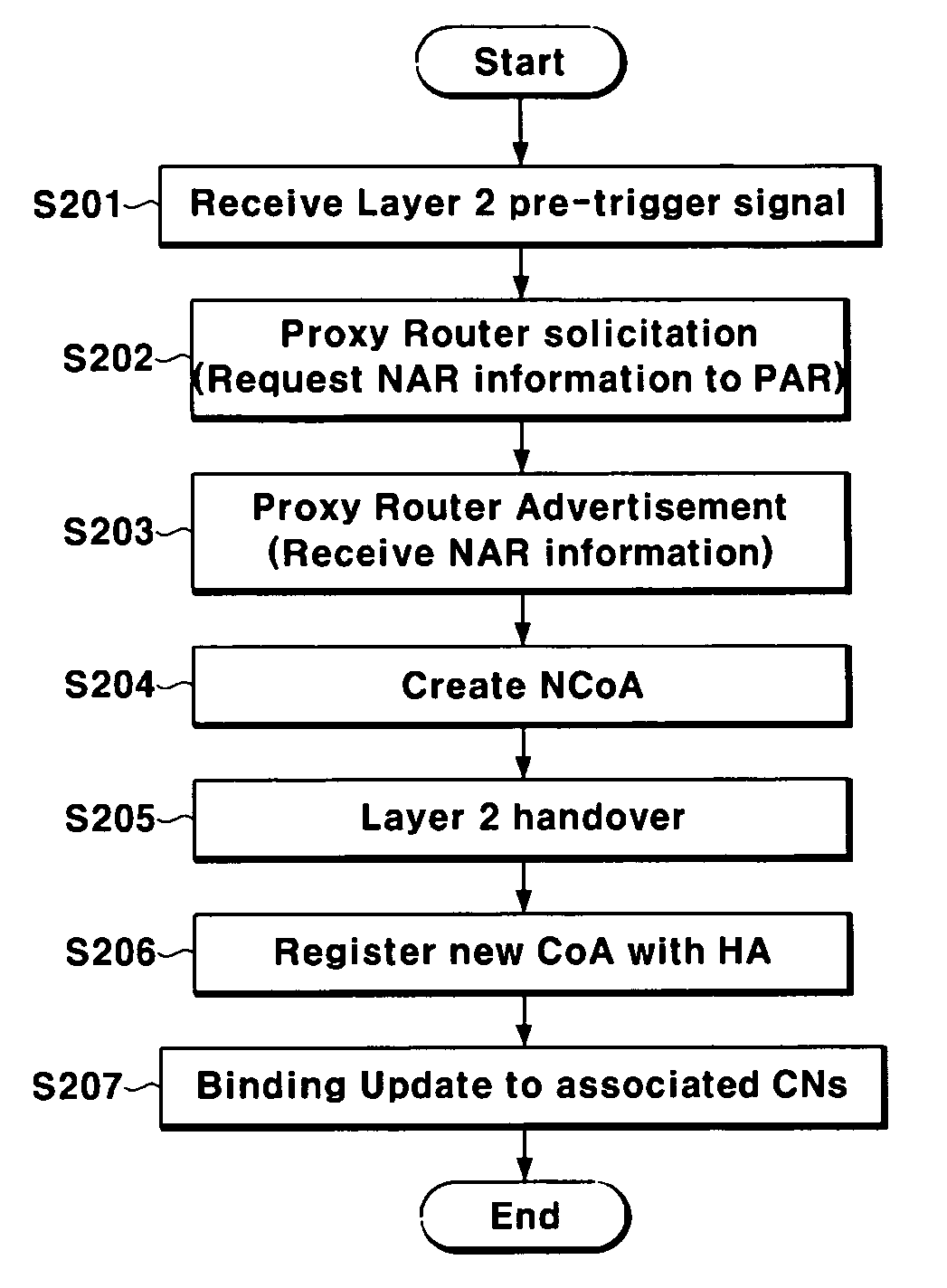
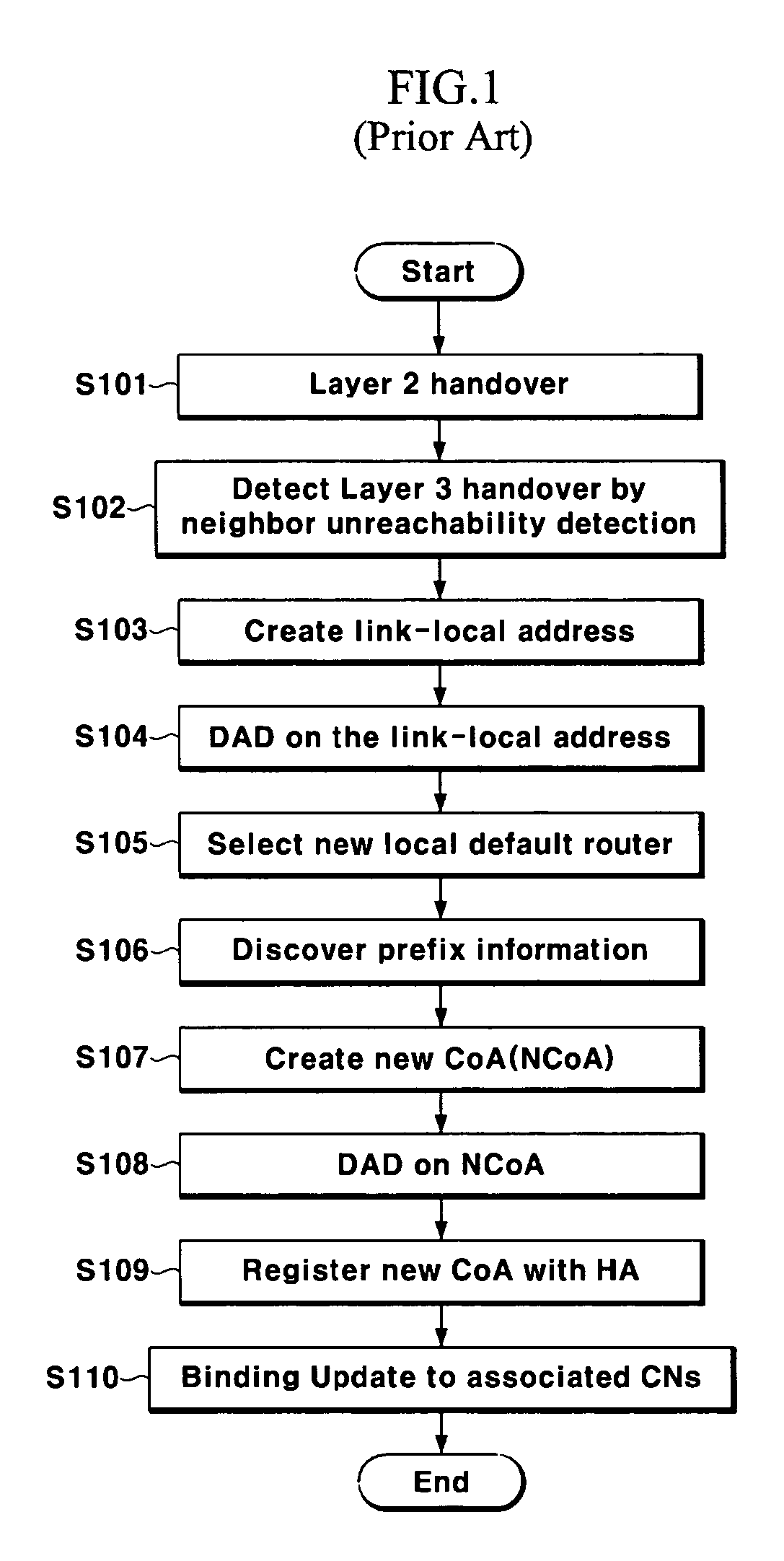
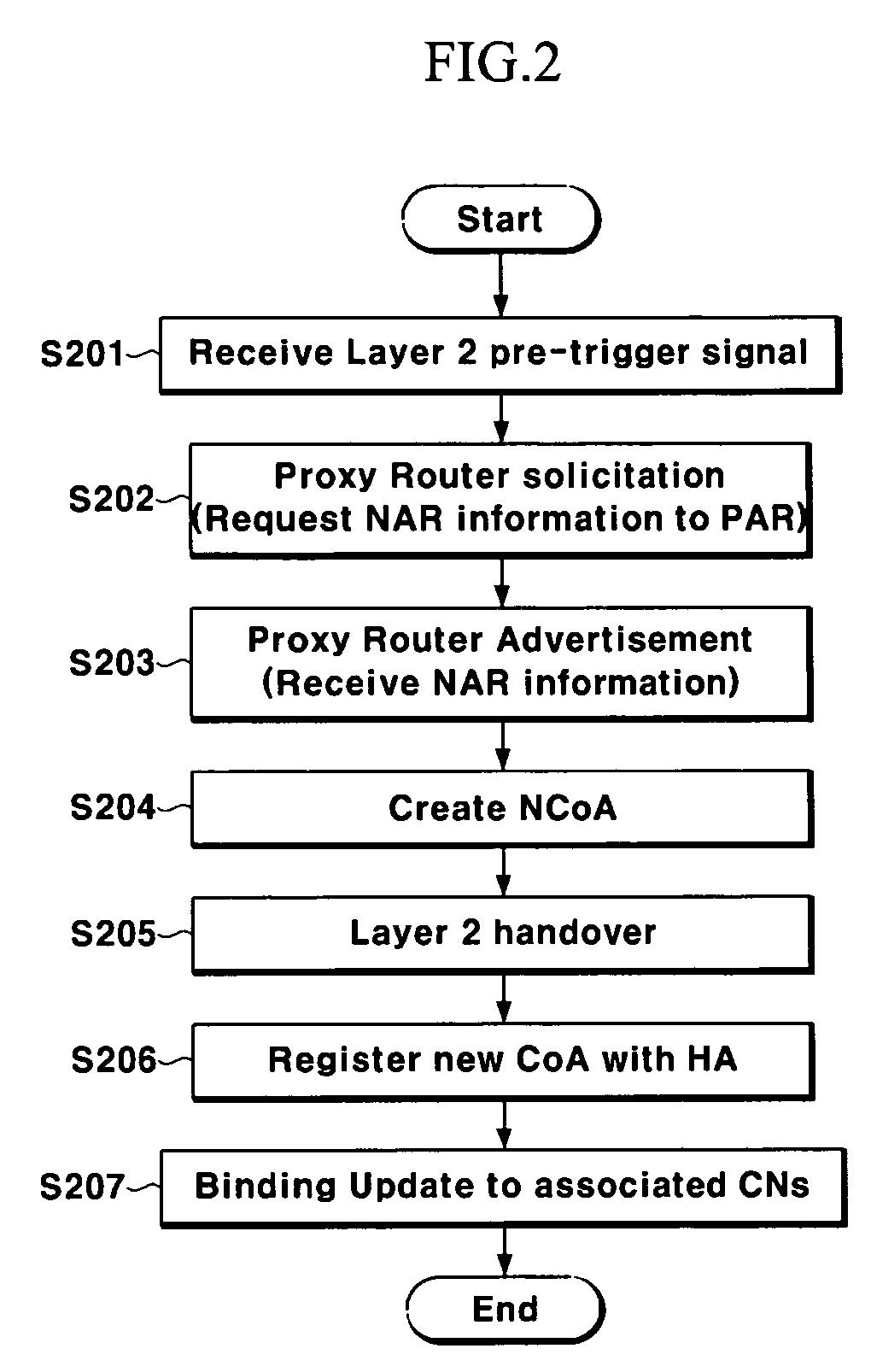
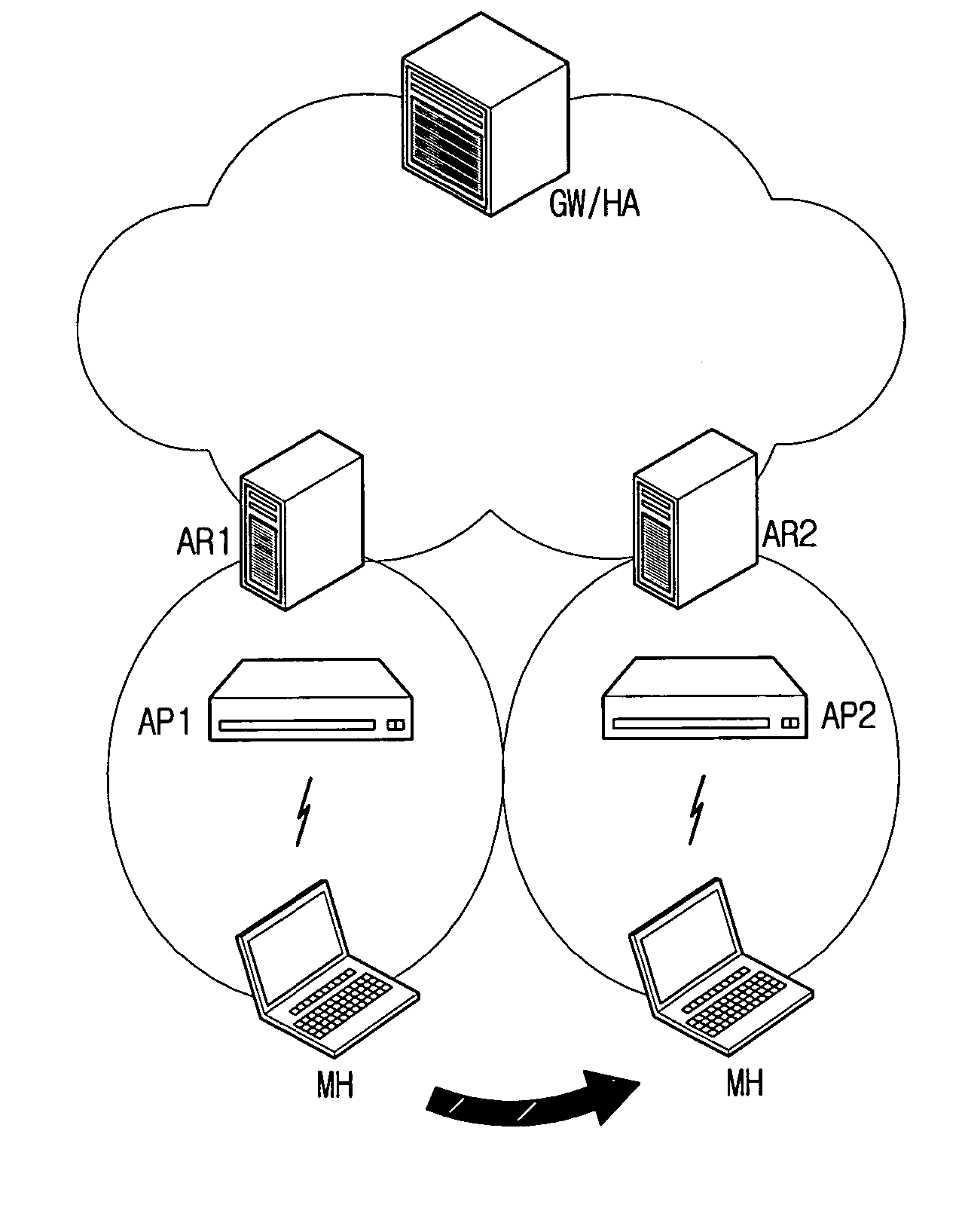
Handover method
InactiveUS20060029020A1Reduce switching delayWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsIp addressHandover
In a handover method, a mobile node receives a Layer 2 trigger message; requests information on Layer 3 of a new access router (NAR) from a previous access router (PAR) by using information included in the Layer 2 trigger message and information on an IP address of the NAR and a new Care of Address (NCoA) to be used when moving to the NAR; and performs registration with a Home Agent (HA) of the mobile node and sending binding update to an associated correspondence node by using the NCoA when a Layer 2 handover is occurred. With this configuration, the present invention provides a handover method automatically creating an address using a MAC (Medical access control) address in the mobile IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
VPN services using address translation over an IPv6 network
A method and system for translation of virtual private network (VPN) addresses over a provider network are disclosed. The method includes creating a multipoint tunnel extending between customer edge routers in a VPN network and over the provider network. The multipoint tunnel is identified with a multicast address and multicast packets are sent over the tunnel to identify tunnel endpoints at customer edge routers within the VPN. The method further includes converting, at one of the customer edge routers, a VPN join message to a provider join message and sending it over the provider network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Dynamic intelligent bidirectional optical access communication system with object/intelligent appliance-to-object/intelligent appliance interaction
ActiveUS20110158653A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsPersonalizationSoftware modules
Reduced Rayleigh backscattering effect enables a longer-reach optical access communication network-thus it eliminates significant costs. Furthermore, a wavelength to an intelligent subscriber subsystem can be dynamically varied for bandwidth on-Demand and service on-Demand. A software module renders intelligence (and context awareness) to a subscriber subsystem and an appliance. An object can sense / measure / collect / aggregate / compare / map and connect / couple / interact (via one or more or all electrical / optical / radio / electro-magnetic / sensor / bio-sensor communication network(s) within and / or to and / or from an object) with another object, an intelligent subscriber subsystem and an intelligent appliance utilizing an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) and its subsequent versions.A construction of a near-field communication (NFC) enabled intelligent micro-subsystem and / or intelligent appliance with key applications (e.g., an intelligent, location based and personalized social network and an intelligent, location based and personalized direct and peer-to-peer marketing) are also described.
Owner:MAZED MOHAMMAD
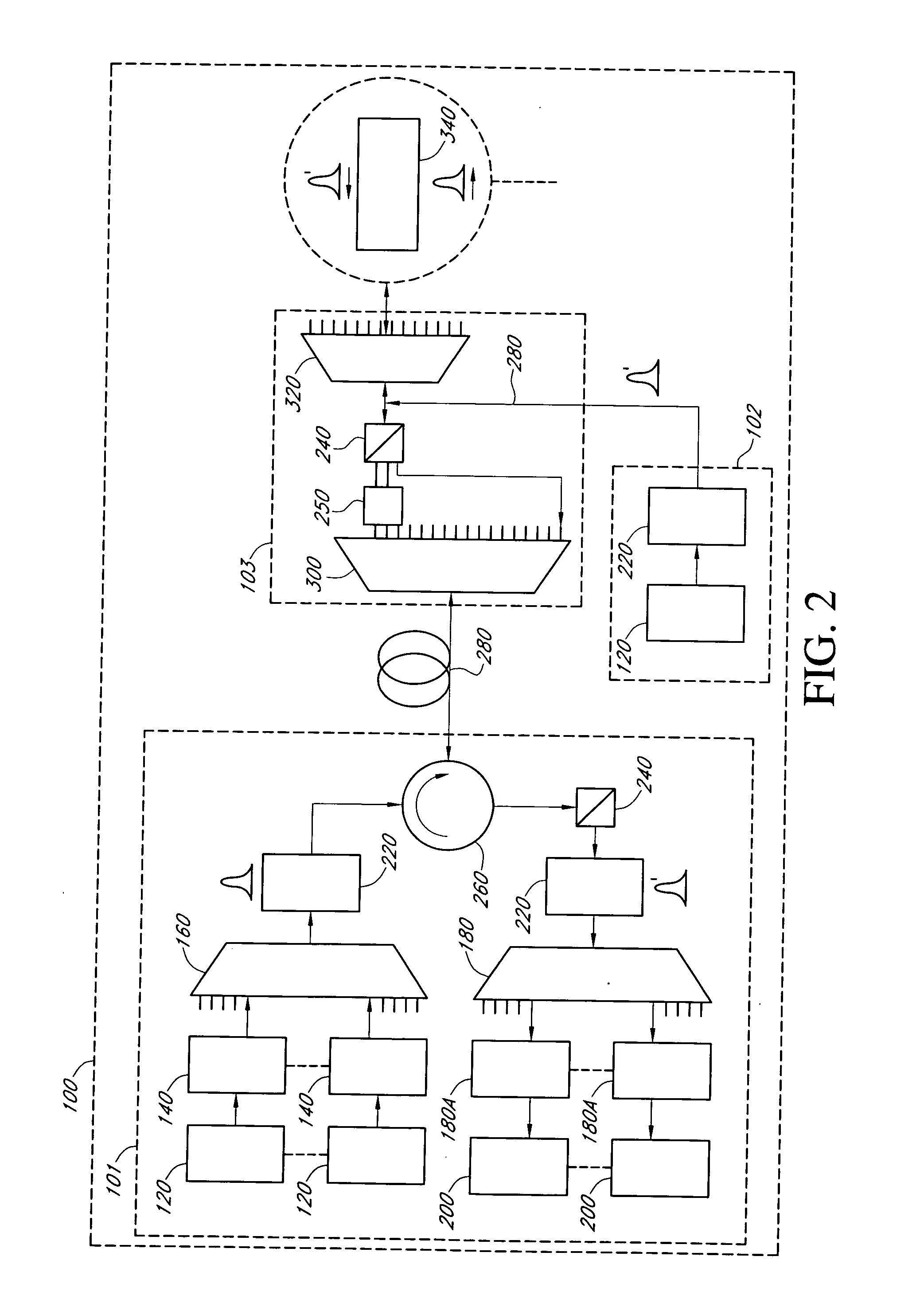
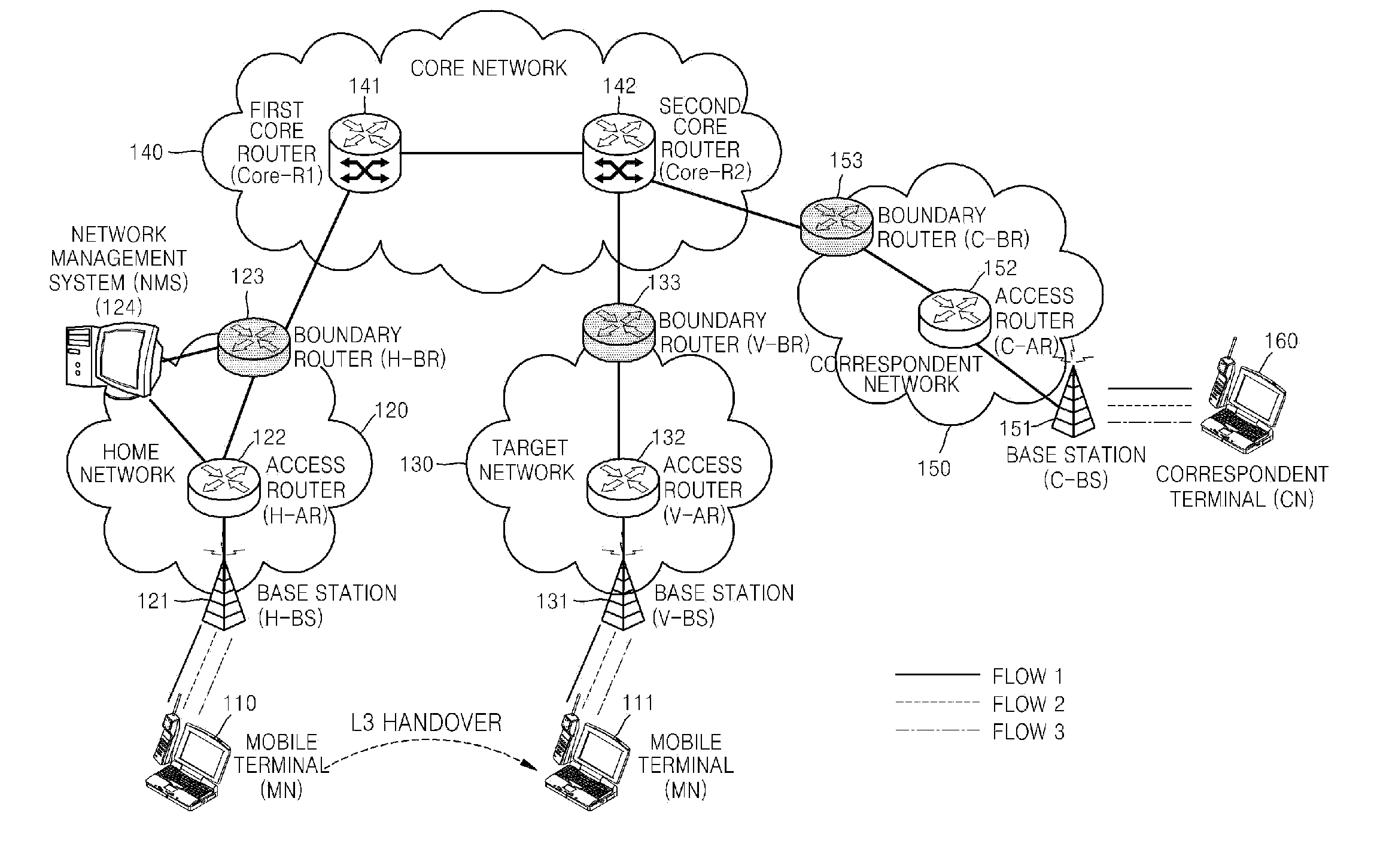
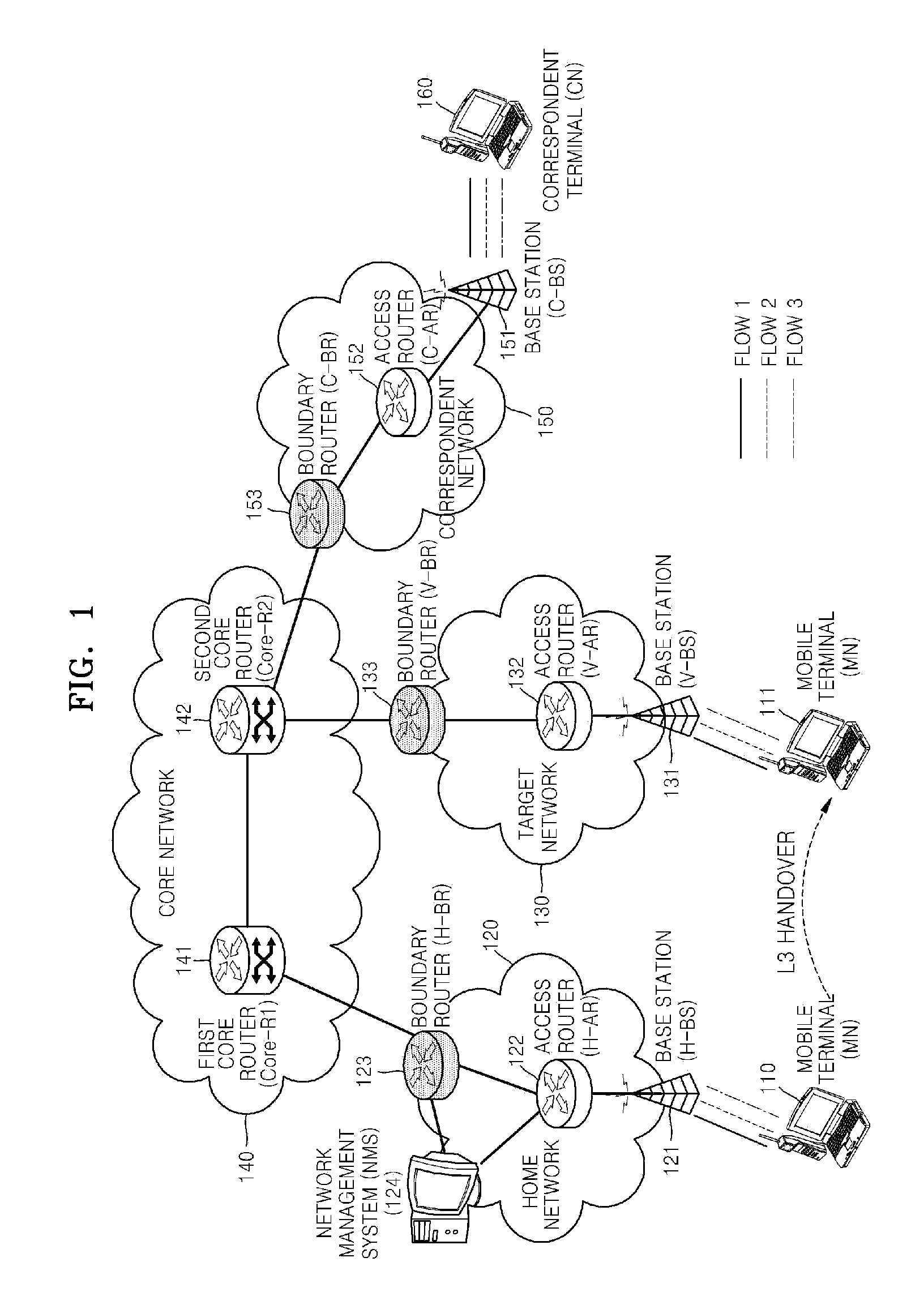
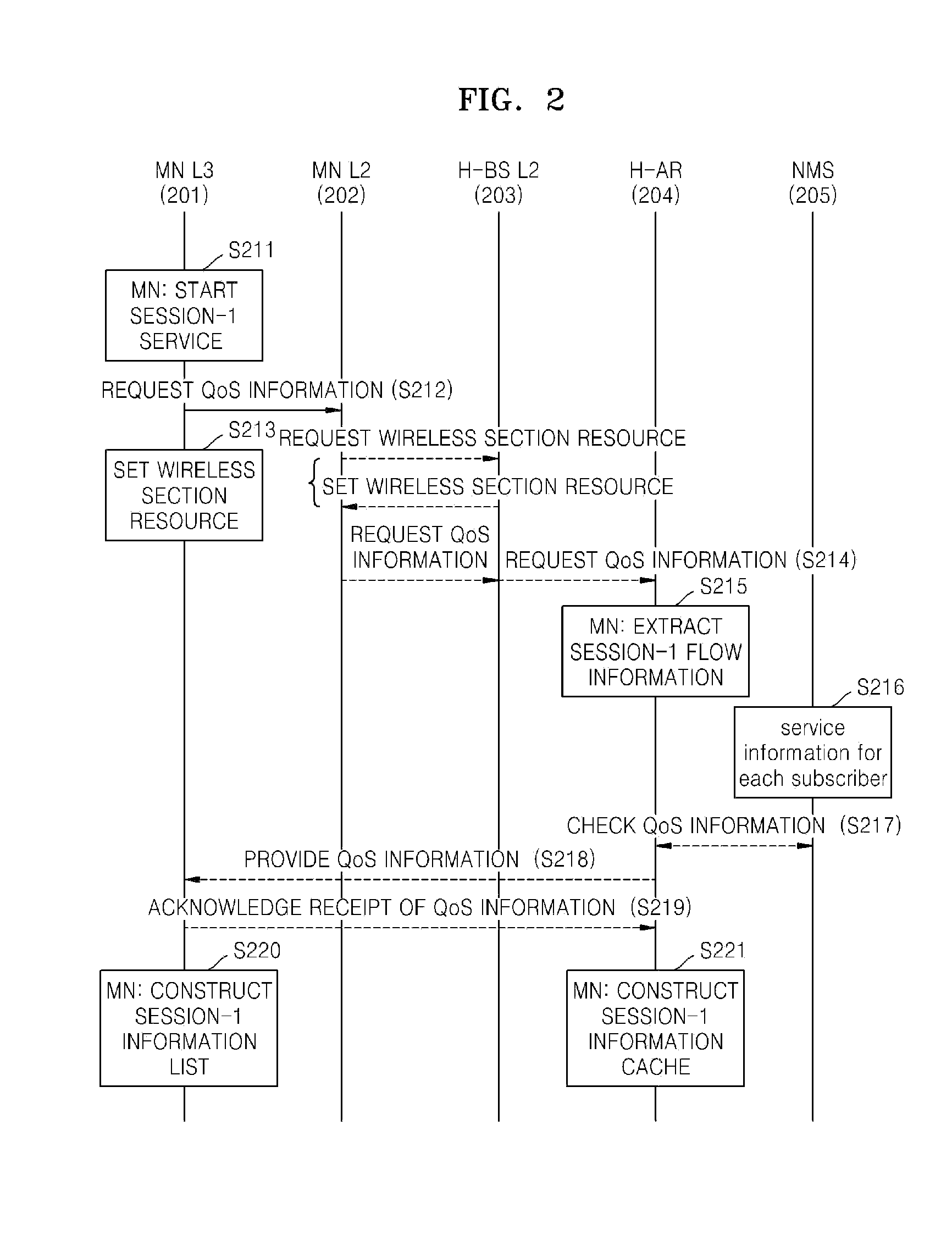
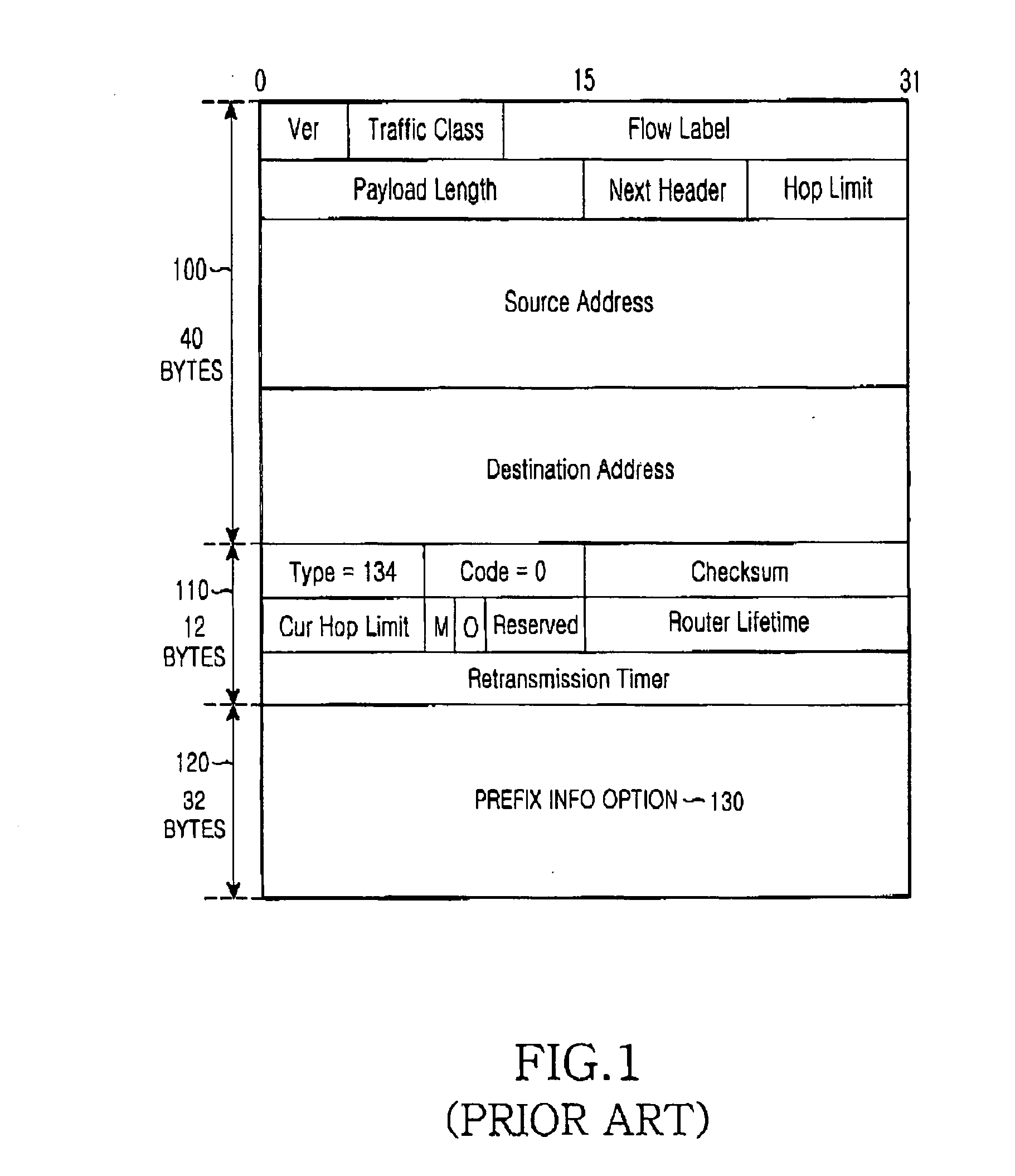
METHOD OF SETTING L3 HANDOVER PATH GUARANTEEING FLOW-BASED QoS IN MOBILE IPv6 NETWORK
InactiveUS20080137615A1Network traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
Provided is a method of setting a layer 3 (L3) handover path in a mobile IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) network while guaranteeing a flow-based QoS (Quality of Service). The method includes receiving verification of QoS-related information and flow information of a mobile terminal in a home network from a network management system, constructing a flow list storing the verified flow information in the mobile terminal, and constructing a flow cache storing the verified flow information in an access router in the home network; transmitting the flow information by using a hop-by-hop extension header of a packet that is to be transmitted in order to allow a plurality of routers in a path between the mobile terminal and a correspondent terminal to sequentially construct a flow cache; if the mobile terminal moves to a target network, reconstructing the flow list of the mobile terminal and the flow cache in the access router in the target network, between the mobile terminal and an access router of the target network; adding the hop-by-hop extension header to a binding update message in order to allow a plurality of routers in a path between the mobile terminal which has moved to the target network and the access router in the home network to sequentially construct the flow cache; and adding the hop-by-hop extension header to a binding update message in order to allow a plurality of routers in a path for establishing direct communication between the mobile terminal and the correspondent terminal to sequentially construct the flow cache.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
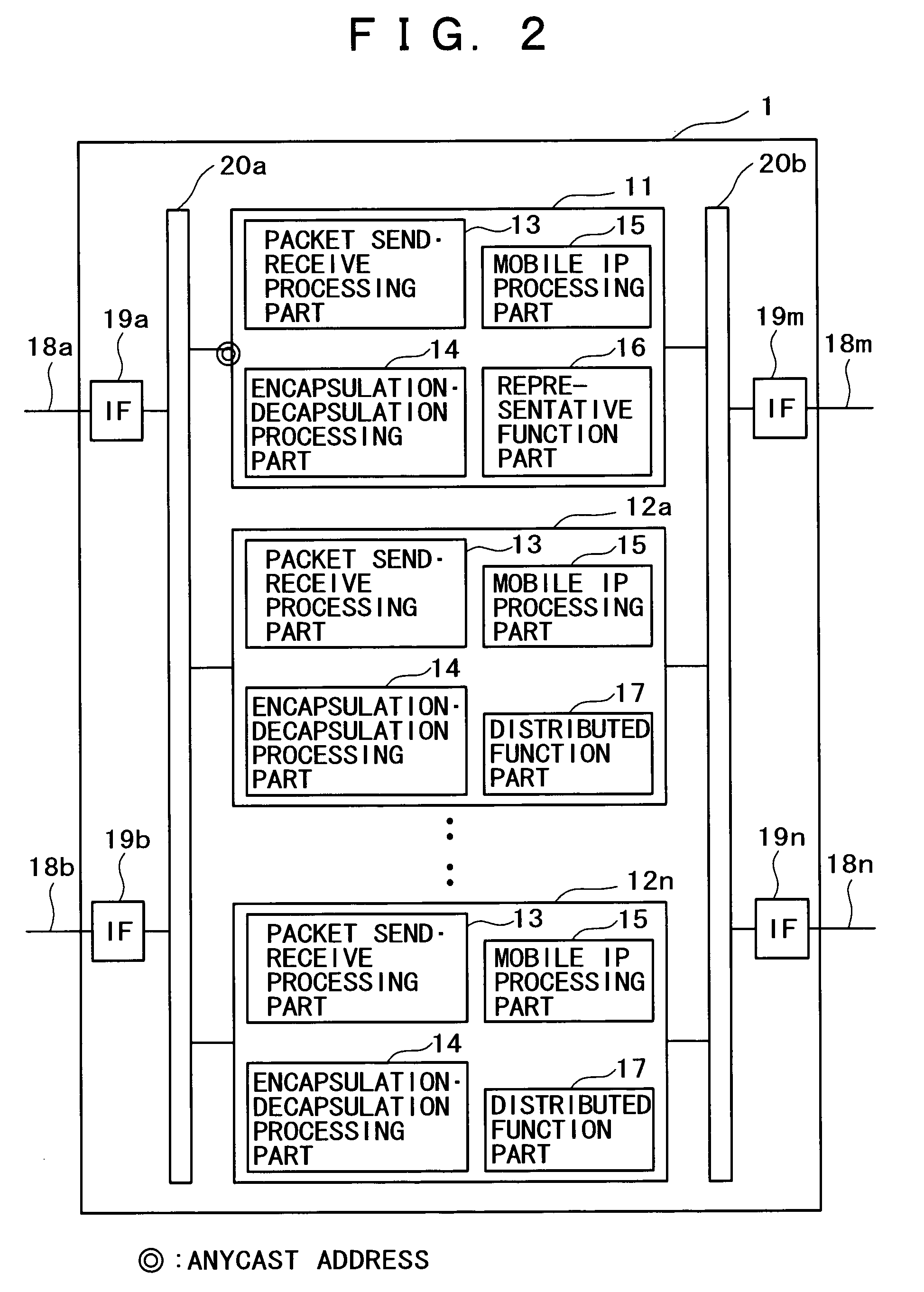
Method and apparatus for mobile communication utilizing load balancing
InactiveUS7328009B2Efficient loadingIncrease or decrease the numberNear-field transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed computingIPv6
A method and apparatus are provided for mobile communication utilizing load balancing. When a home agent (HA) consists of one or more servers with each server being assigned a Mobile IPv6 Home-Agents Anycast Address, a nearby router does not store the link-layer addresses with respect to the Anycast addresses of the servers in its neighbor cache. Consequently, load balancing between or among the servers could not be performed. To solve this problem, in one example, an HA is provided that comprises a representative HA and distributed HAs. The representative HA is assigned an Anycast Address. The representative HA includes a collecting device configured to collect HA lists and load information from the distributed HAs. The representative HA dynamically creates a HA list and sends the HA list to a mobile node (MN). The MN registers its current location with an HA from the HA list included in a Home Agent Address Discovery Reply message. The load on the HA can then be shared by the servers constituting the HA.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
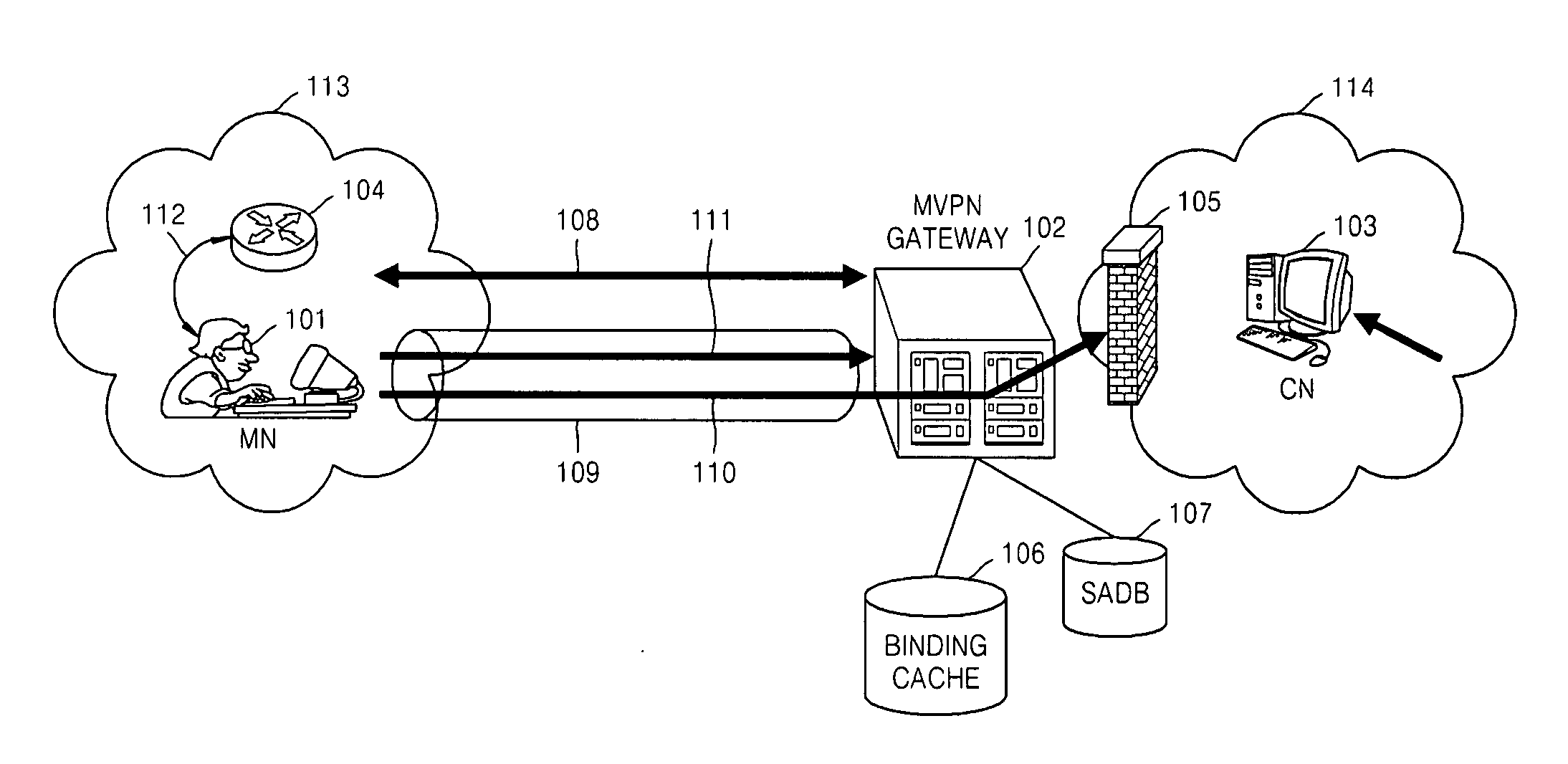
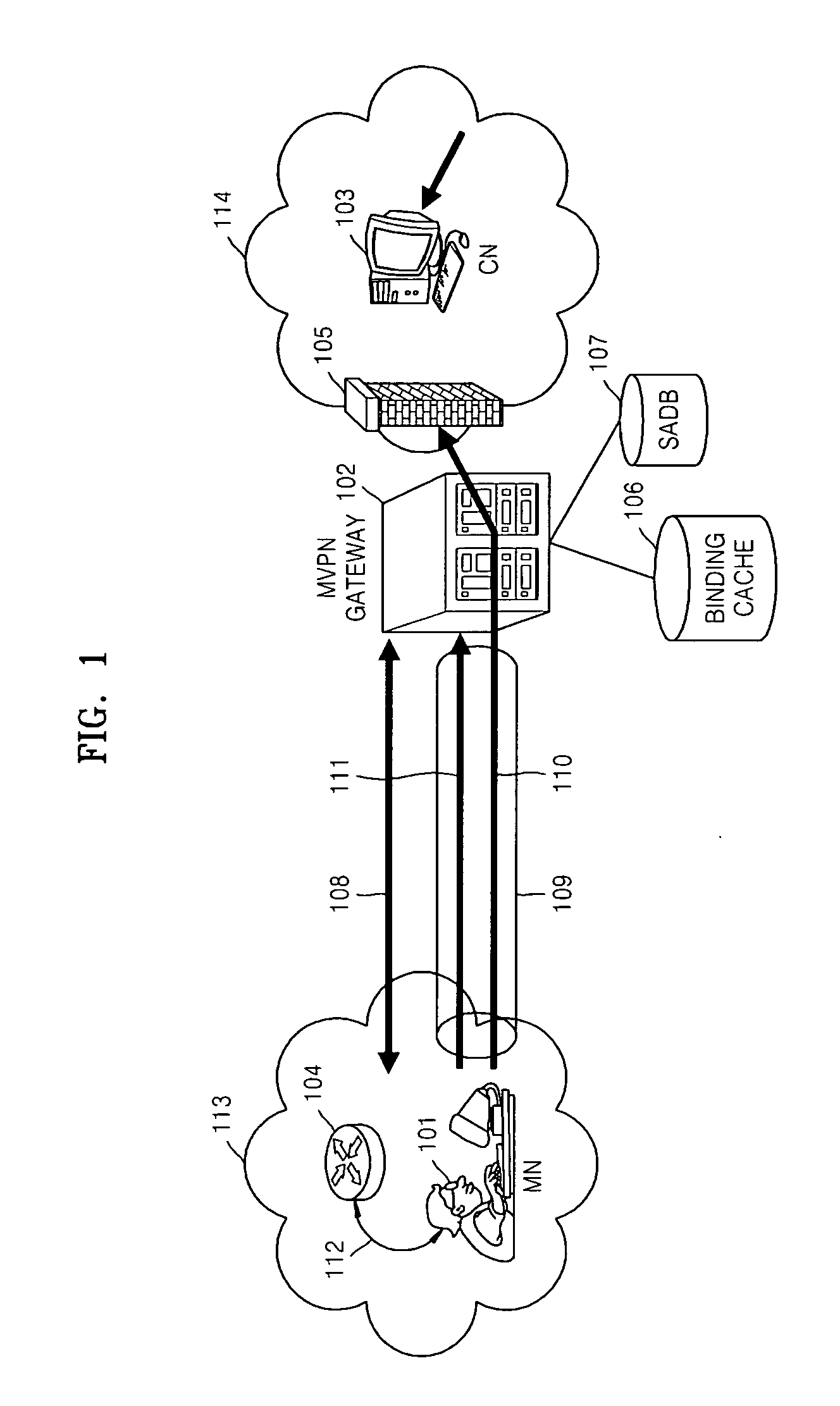
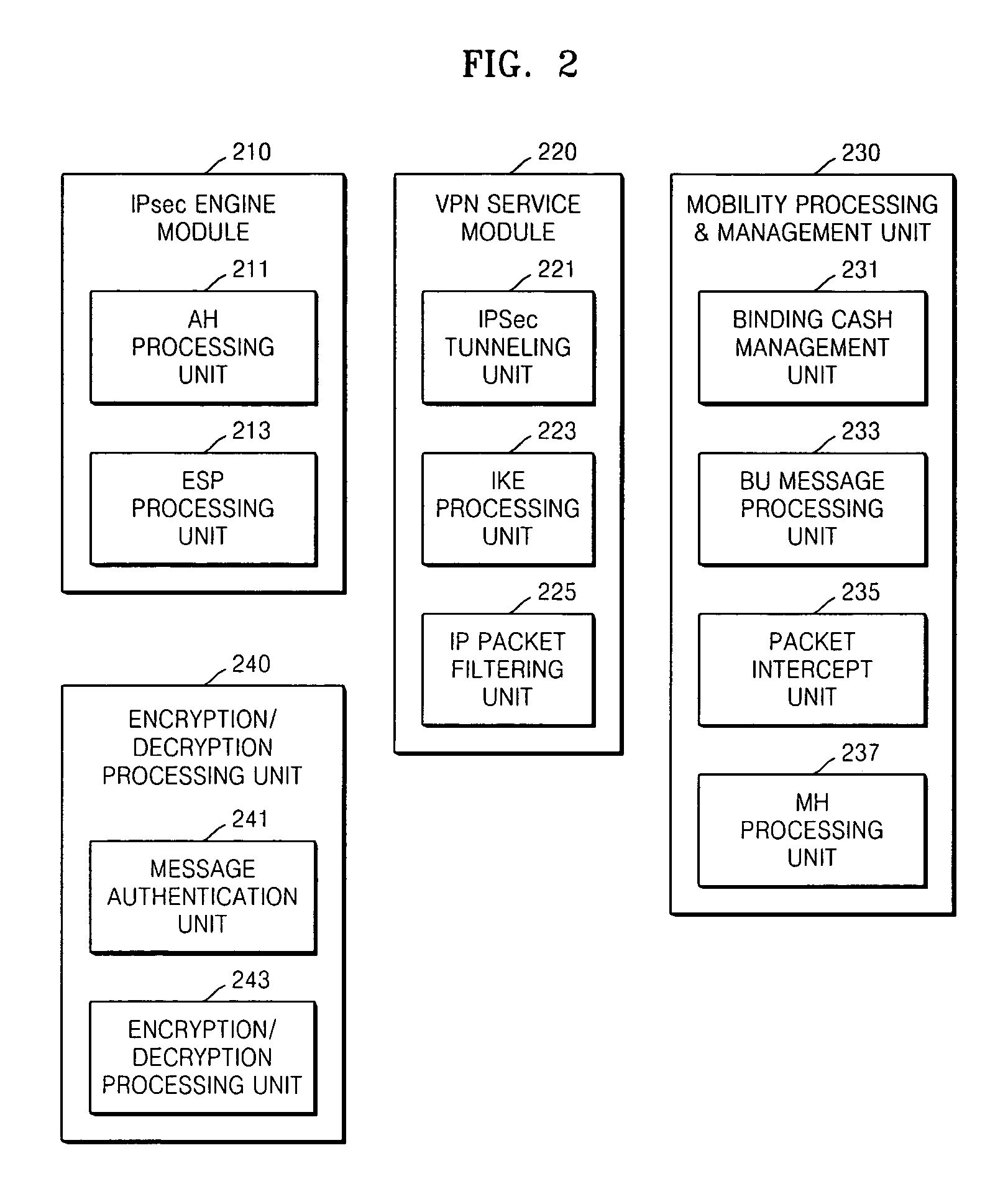
Method for providing virtual private network services to mobile node in IPv6 network and gateway using the same
InactiveUS20070177550A1Support mobilityUser identity/authority verificationWireless network protocolsInternet Key ExchangeSecurity association
Provided are a method for providing virtual private network (VPN) services to a mobile node (MN) in an IPv6 network and a gateway using the same. The method includes: performing IKE (Internet key exchange) negotiation with an MN (mobile node) which has performed handover, acquiring SA (security association) and then authenticating a terminal of the MN; receiving a BU (binding update) message from the MN and verifying the BU message, storing new position information of the MN, transmitting a BA (binding acknowledgement) message and performing mobility processing; if the mobility processing is completed, performing IPsec processing on packets which the MN transmits to a CN (correspondent node), and transmitting the packets; and re-configuring and transmitting packets so that packets which the CN transmits to a home address of the MN can be transmitted to a CoA (Care-of-Address) of the MN. A function performed by a home agent (HA) of Mobile IPv6 is performed so that IP mobility in VPN services can be provided and both mobility inside a VPN domain of the MN and mobility outside the VPN domain can be supported.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
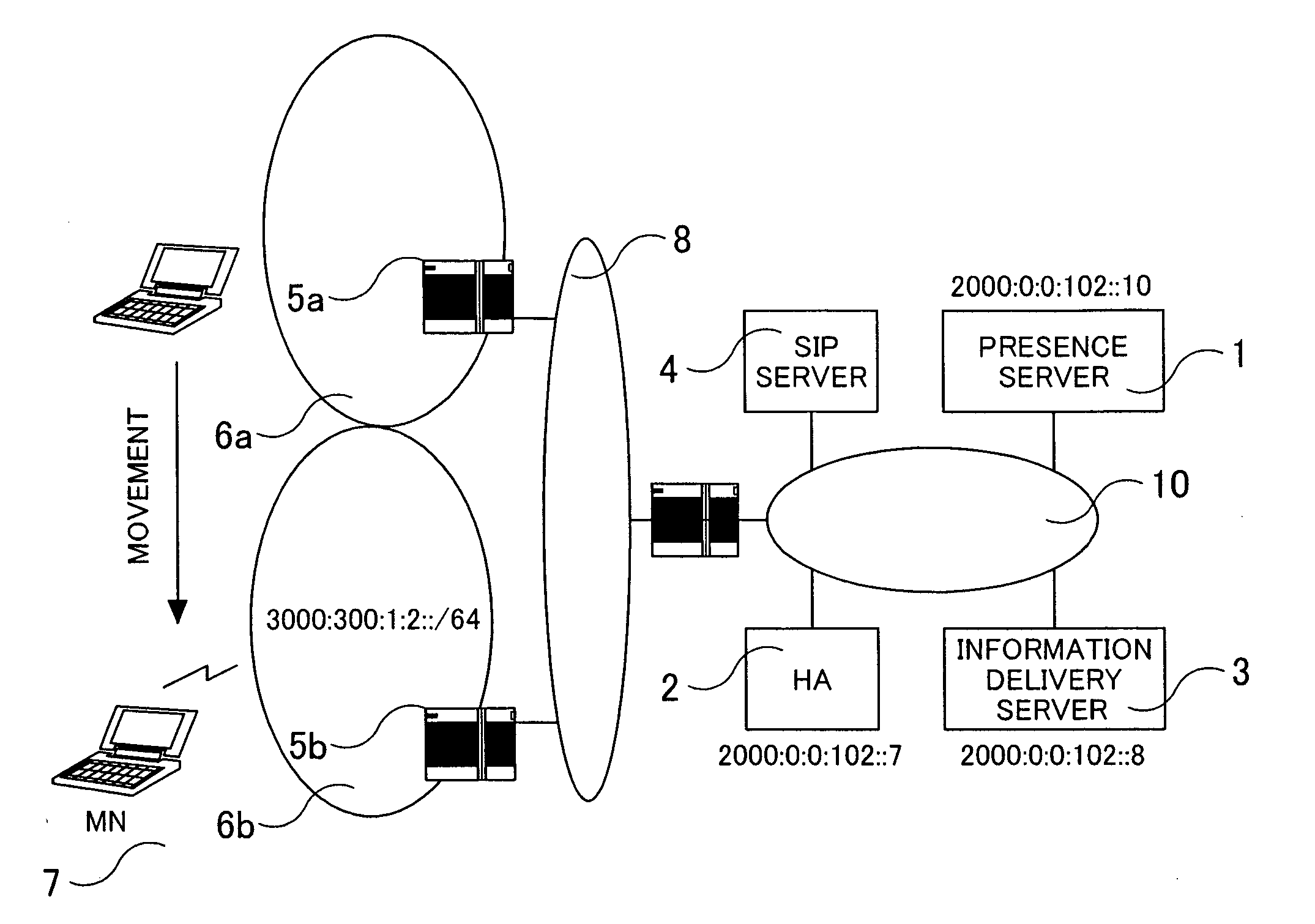
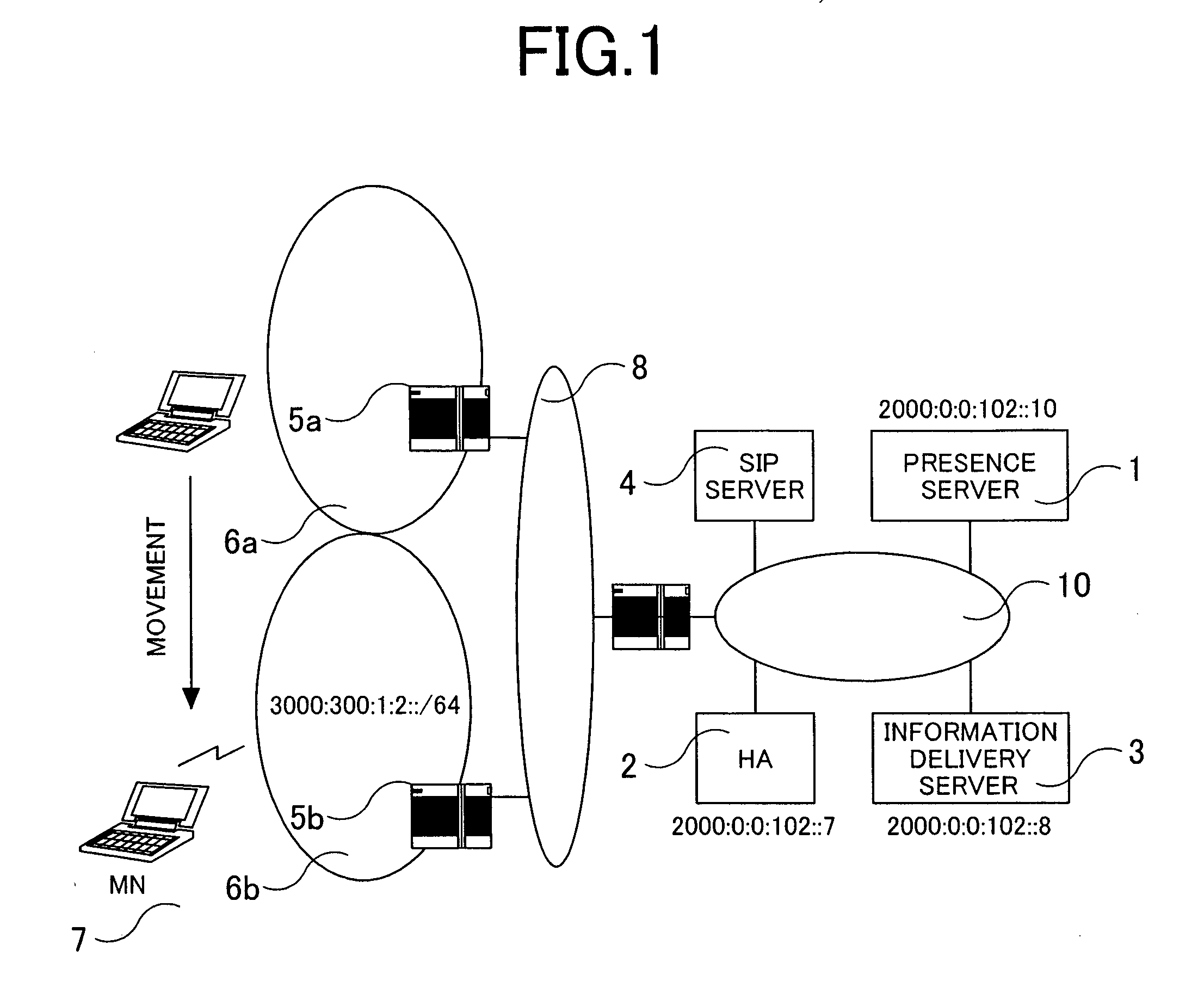
Communication system and communication control equipment
InactiveUS20050265276A1Maintain securityTime-division multiplexWireless network protocolsCommunications systemPresence service
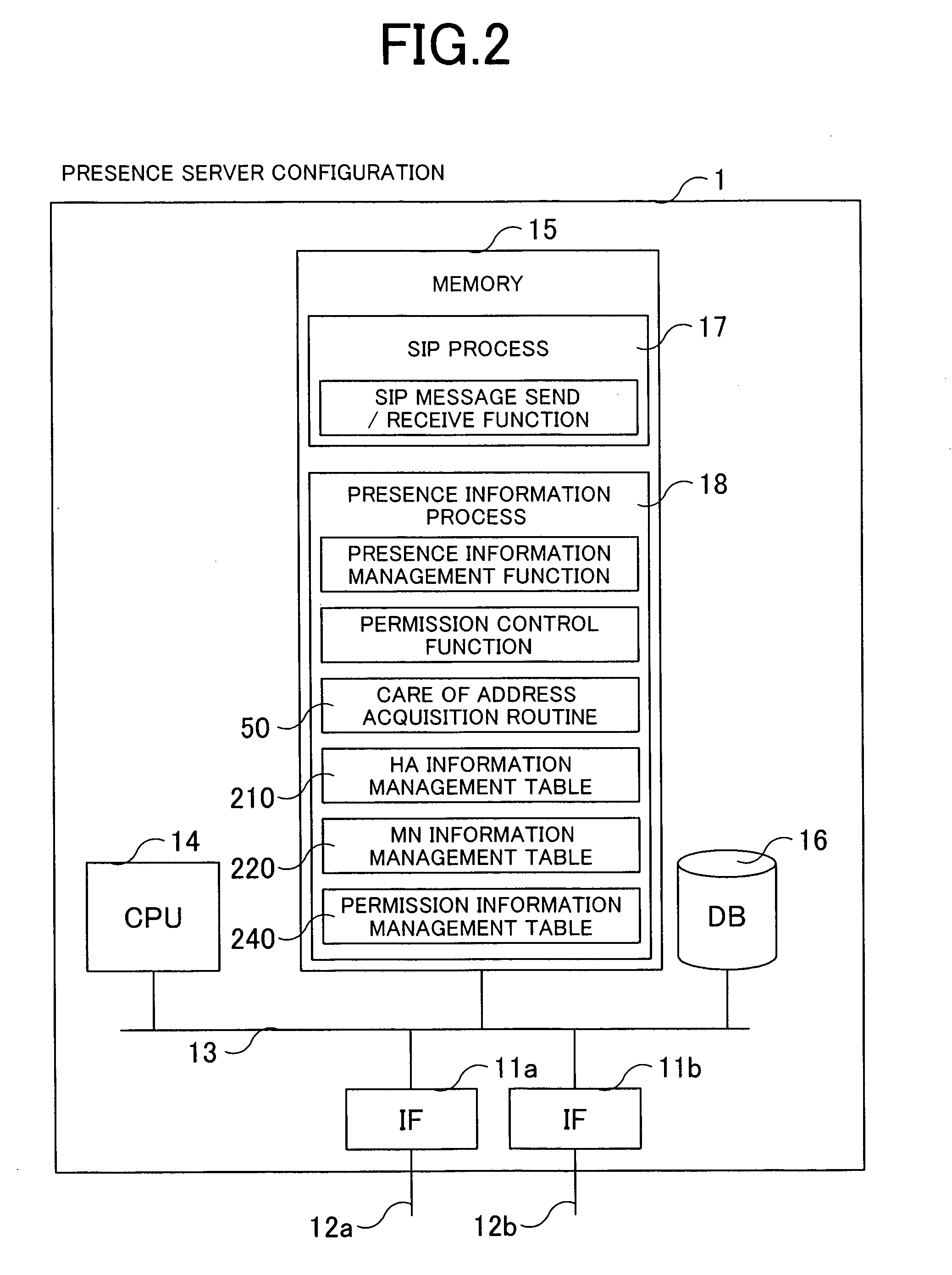
Mobile IPv6 assigns MN (Mobile Node) with a fixed home address in order to guarantee an arrival to MN 7. A SIP process of HA (Home Agent) 2 is provided with a unit for notifying Binding information of MN to a presence server 1. Alternatively, the presence server 1 is provided with a unit for requesting HA 2 for the Binding information of MN. An information delivery server 3 is provided with a unit for acquiring a Care of Address of MN from the presence server 1 and selecting information corresponding to the Care of Address. Presence service can be provided to MN existing in a network other than a home network.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
VPN services using address translation over an IPv6 network
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
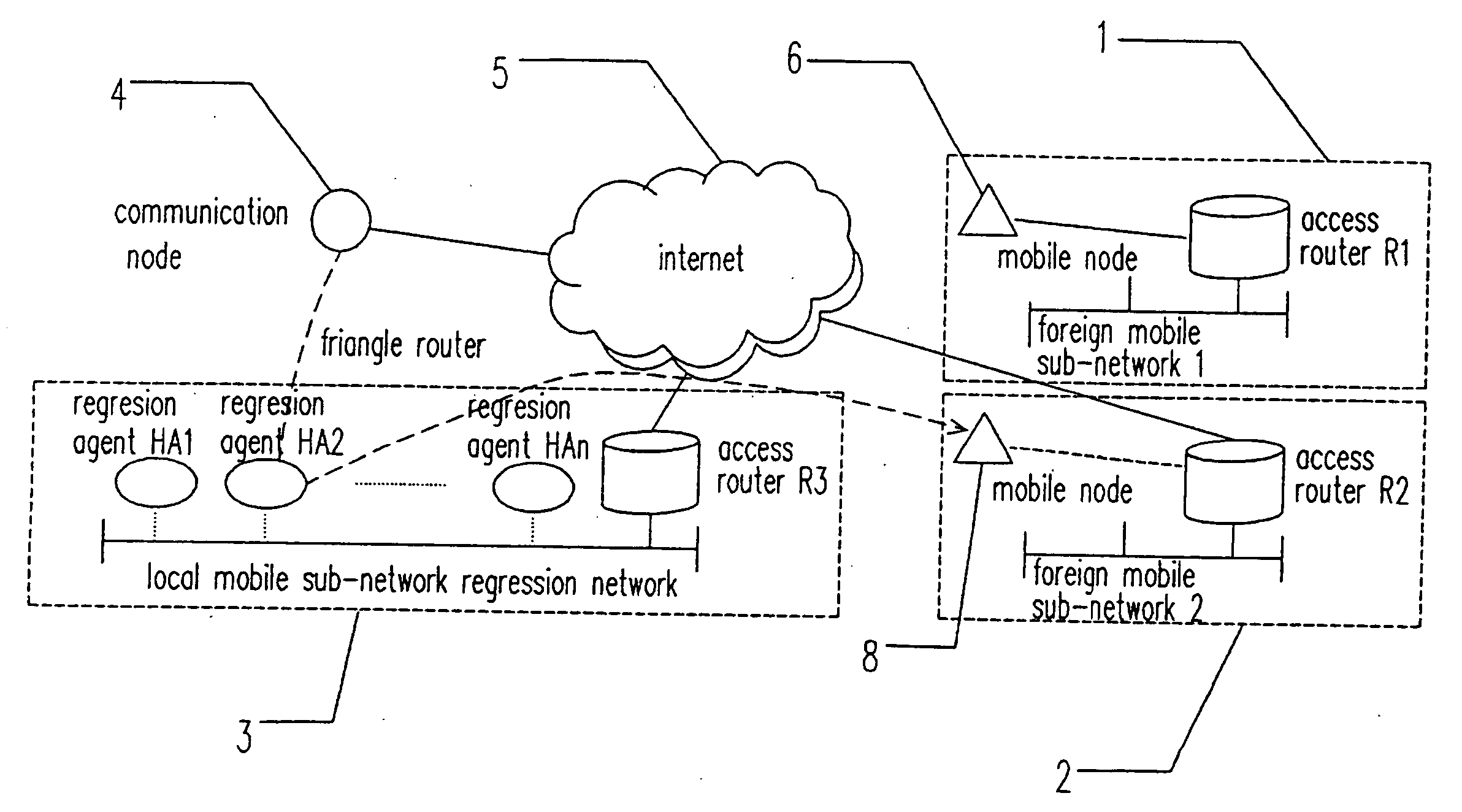
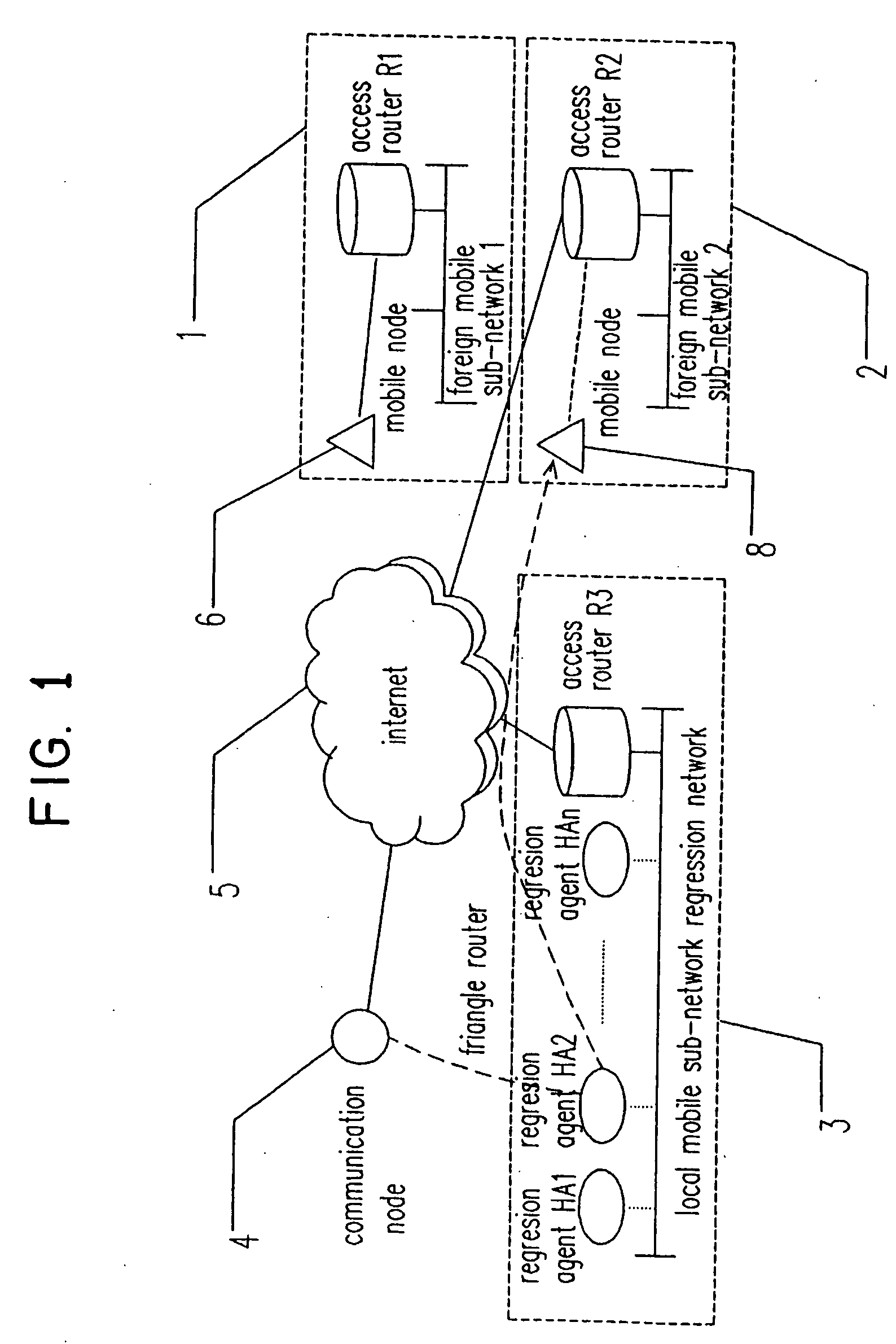
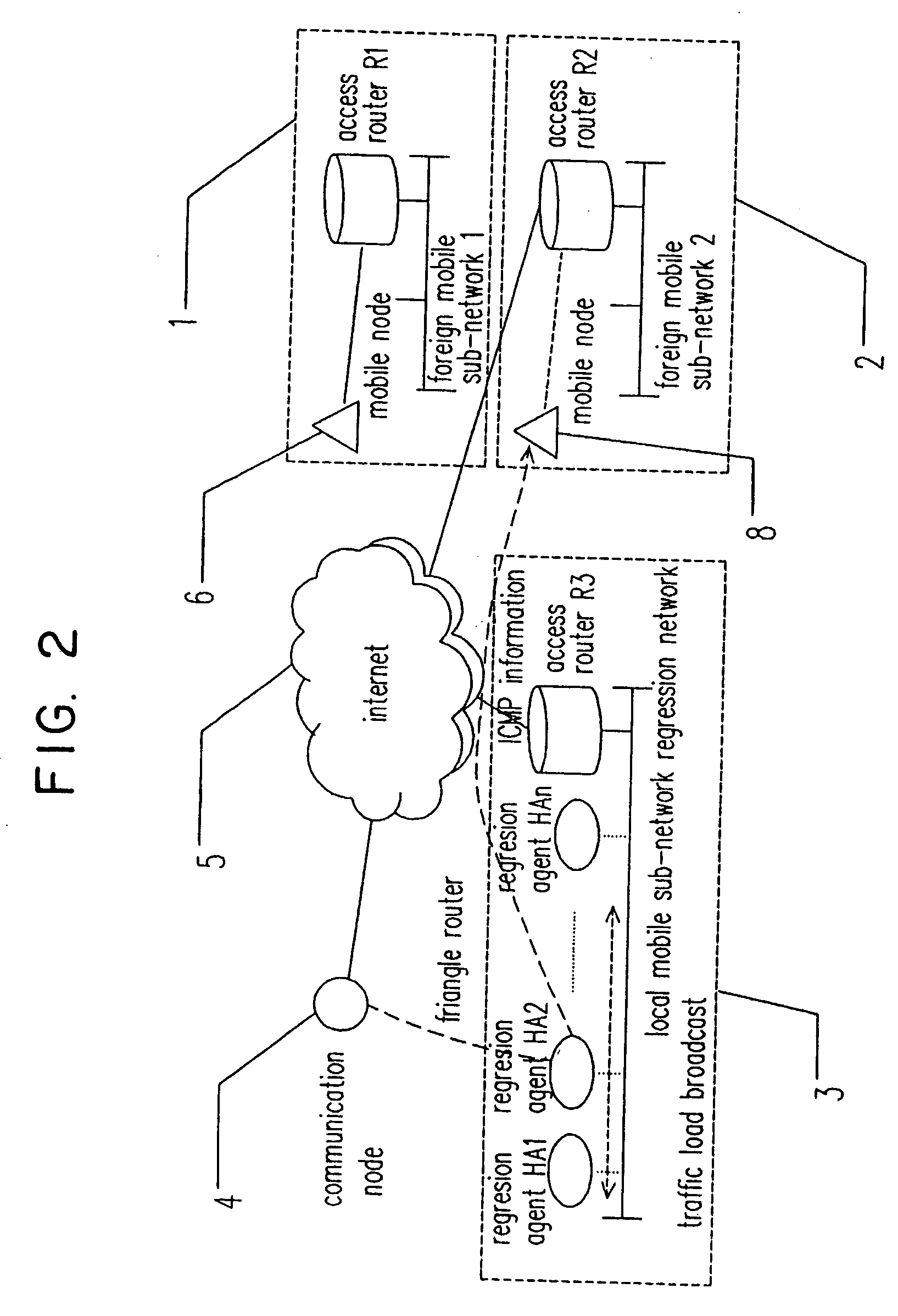
Mobile IPv6 network having multiple home agents and method of load balance
InactiveUS20050047420A1Network traffic/resource managementConnection managementLoad SheddingTraffic load
In a mobile IPv6 network having multiple distributed regression home agents and a load balance method for the multiple regression home agents, the network comprises a plurality of mobile subnets connected to each other through an Internet. Each mobile subnet comprises an access router, a plurality of mobile nodes, and a plurality of regression agents. The regression agents are arranged in a distributed topology structure. The regression agents exchange information with each other by performing a broadcast of traffic load information (table) among the regression agents. Further, each of the regression agents has a traffic load table to perform the load balance operation accordingly.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Wireless local area network system capable of supporting host mobility and an operation method therefor
ActiveUS20040240445A1Support mobilityNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless lanIPv6
A wireless local area network system capable of supporting host mobility services and an operation method therefor are disclosed. The wireless local area network system includes a gateway performing the functions of a home agent in mobile wireless communication environments and sending prefix information; and access points, each access point allocating an Internet Protocol (IP) address to a mobile host within a range thereof by using prefix information of the gateway. Thereafter, each access point produces and sends a Binding Update list that corresponds to the mobile hosts to the gateway. Thus, the present invention supports the mobility for mobile hosts with or without a mobile IPv6 stack, in a wireless local area network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
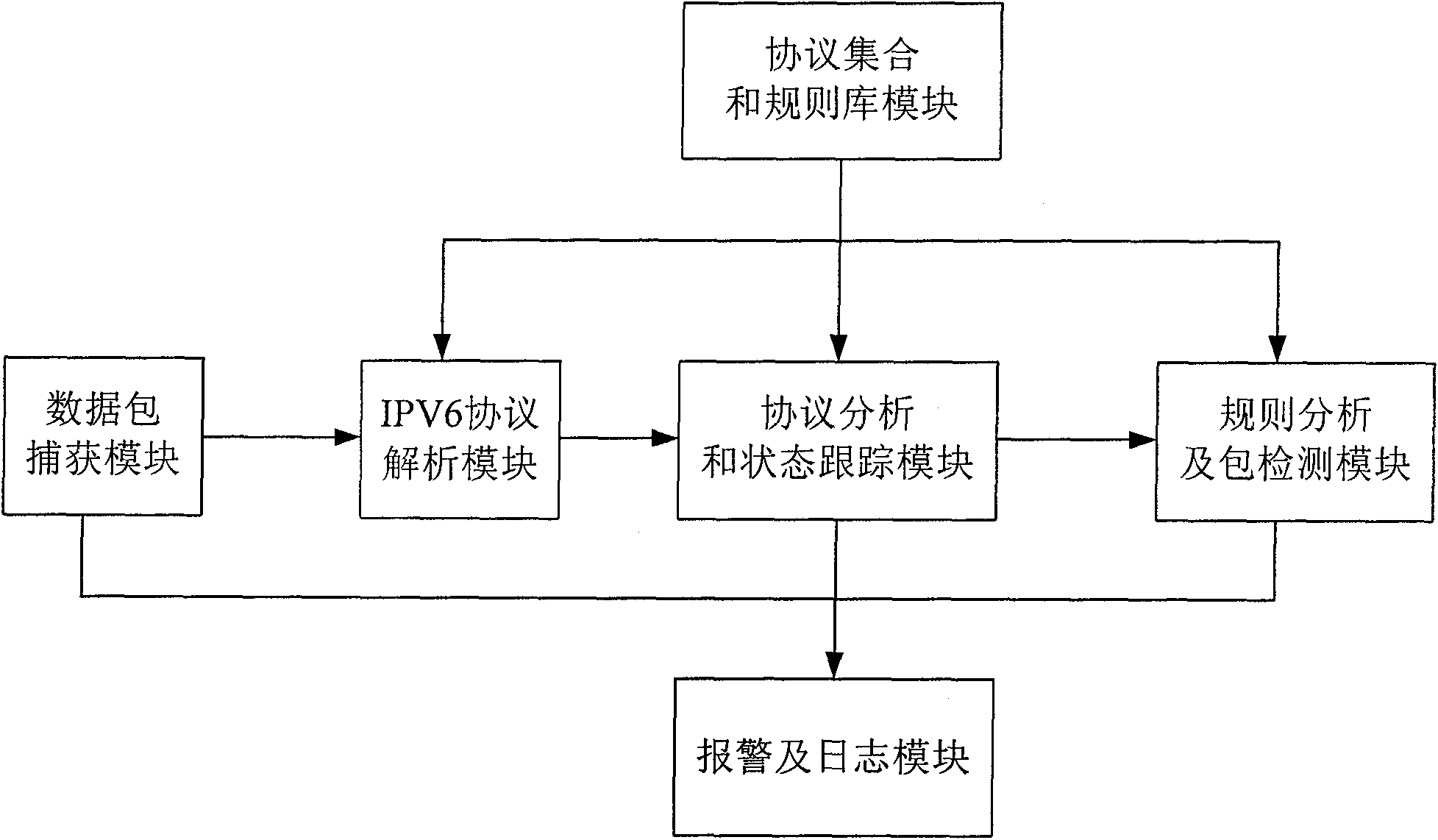
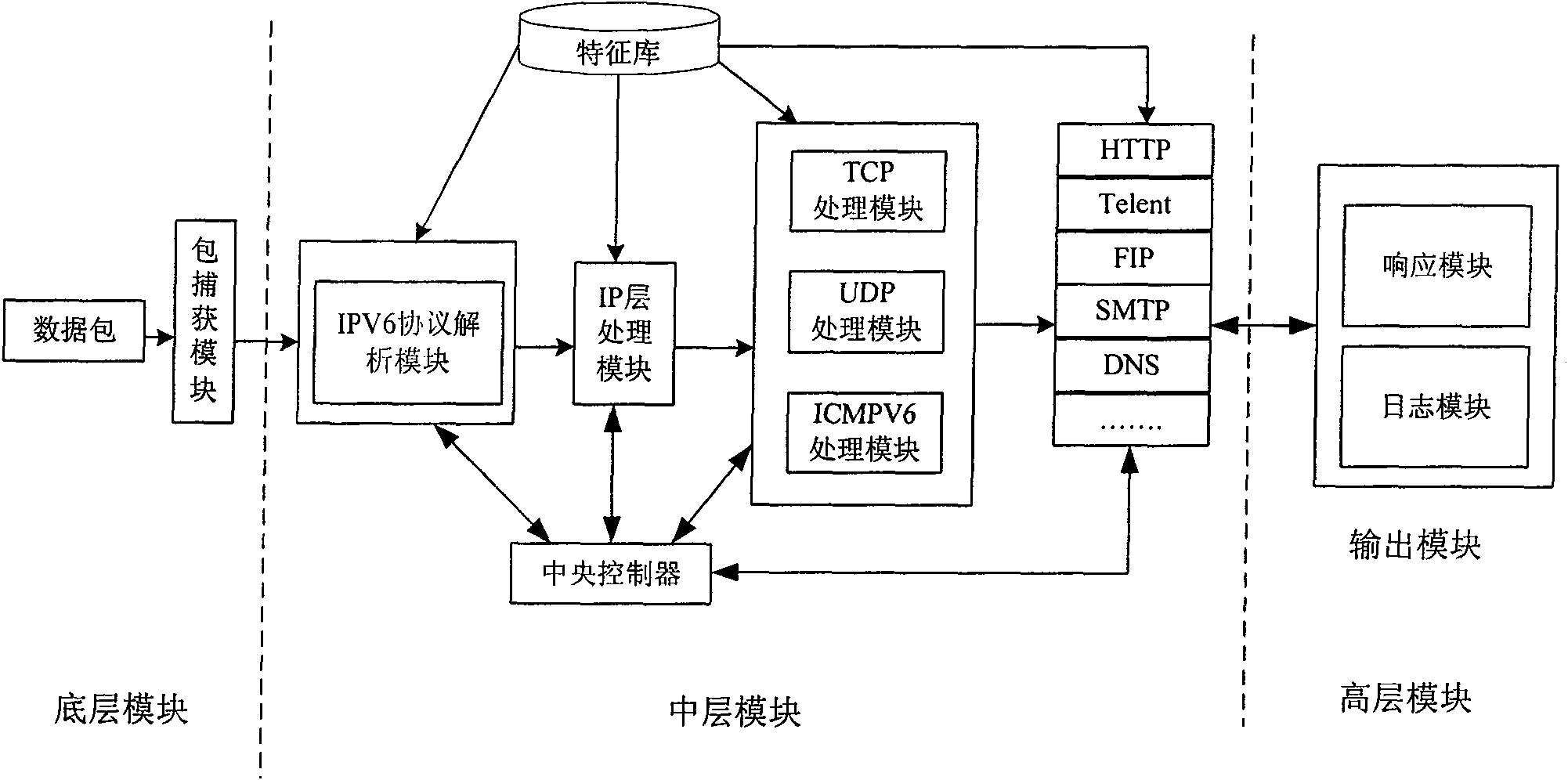
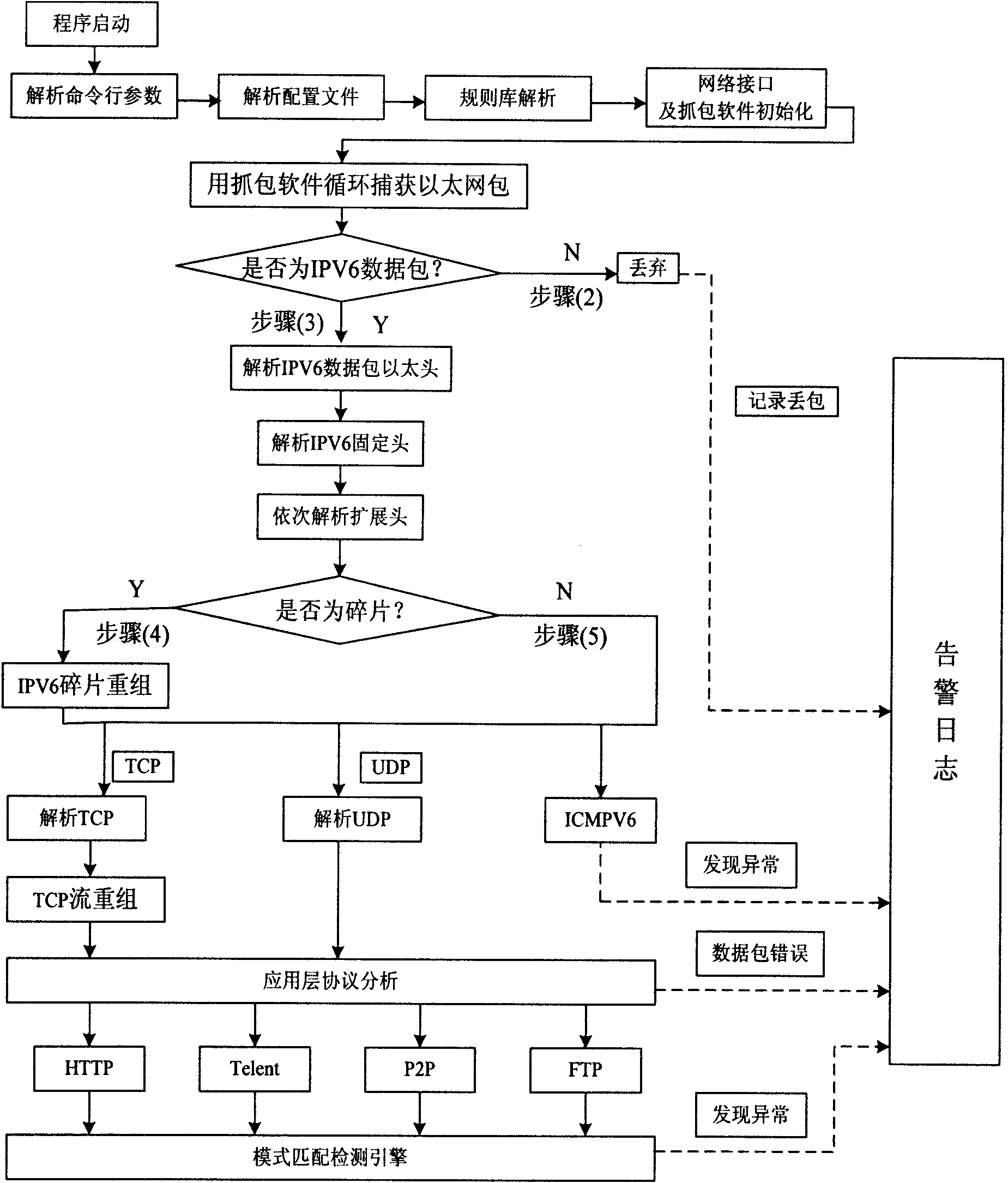
Intrusion detection system and method based on IPv6 network environment
The invention provides an intrusion detection system (IDS) and a method based on IPv6 network environment. The system comprises a protocol set and rule base module, a data packet capture module, an IPV6 protocol analysis module, a protocol analysis and state tracking module, a rule analysis and packet detection module and a warning and logging module. The invention well solves the new problem of transplant of the IDS, brought about by the new IPv6 standards and characteristics, and improves the capture ability of the data packet, the detection means of the IDS and the safety detection abilityof the IDS.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
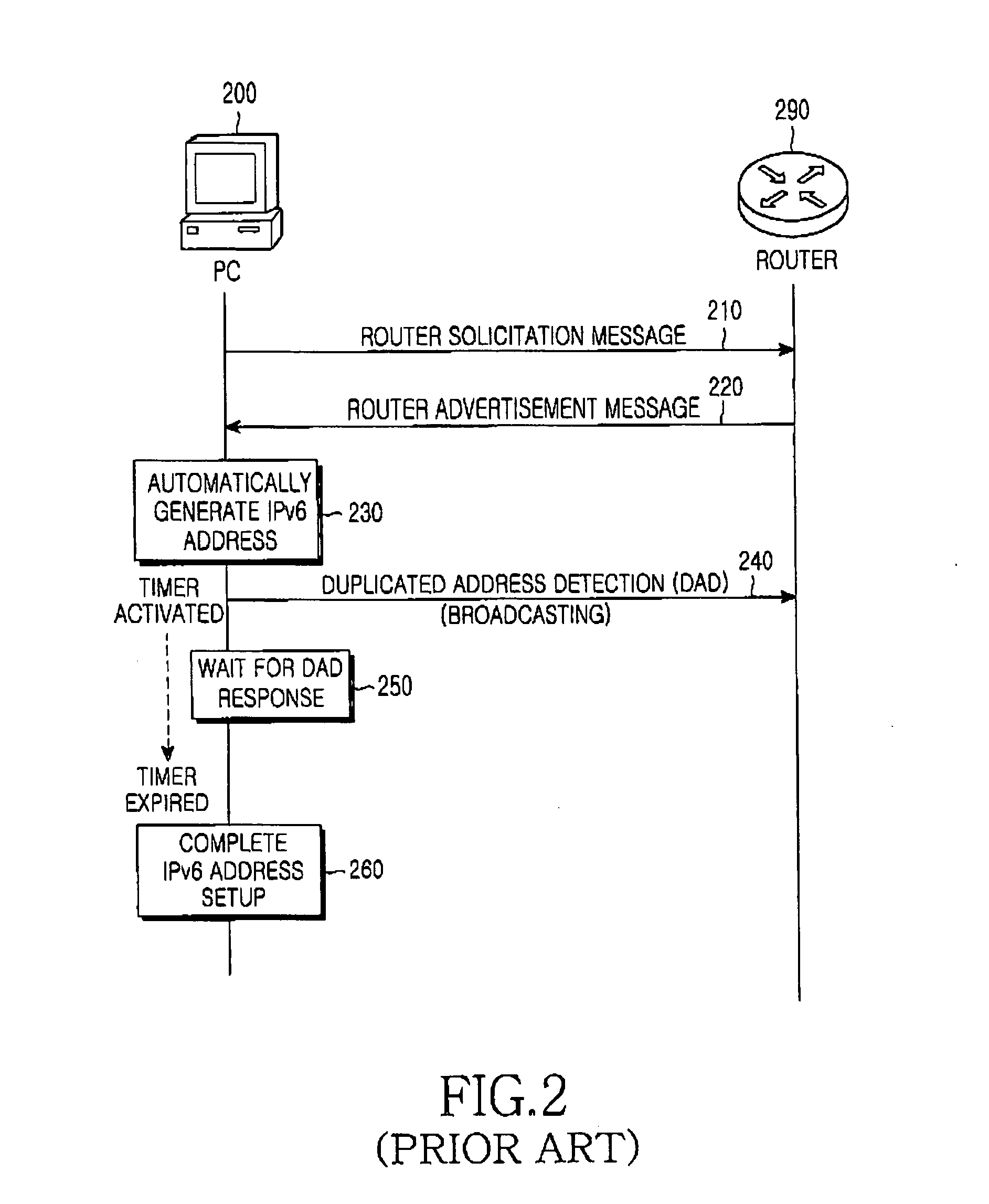
Method and system for generating IP addresses of access terminals and transmitting messages for generation of IP addresses in an IP system
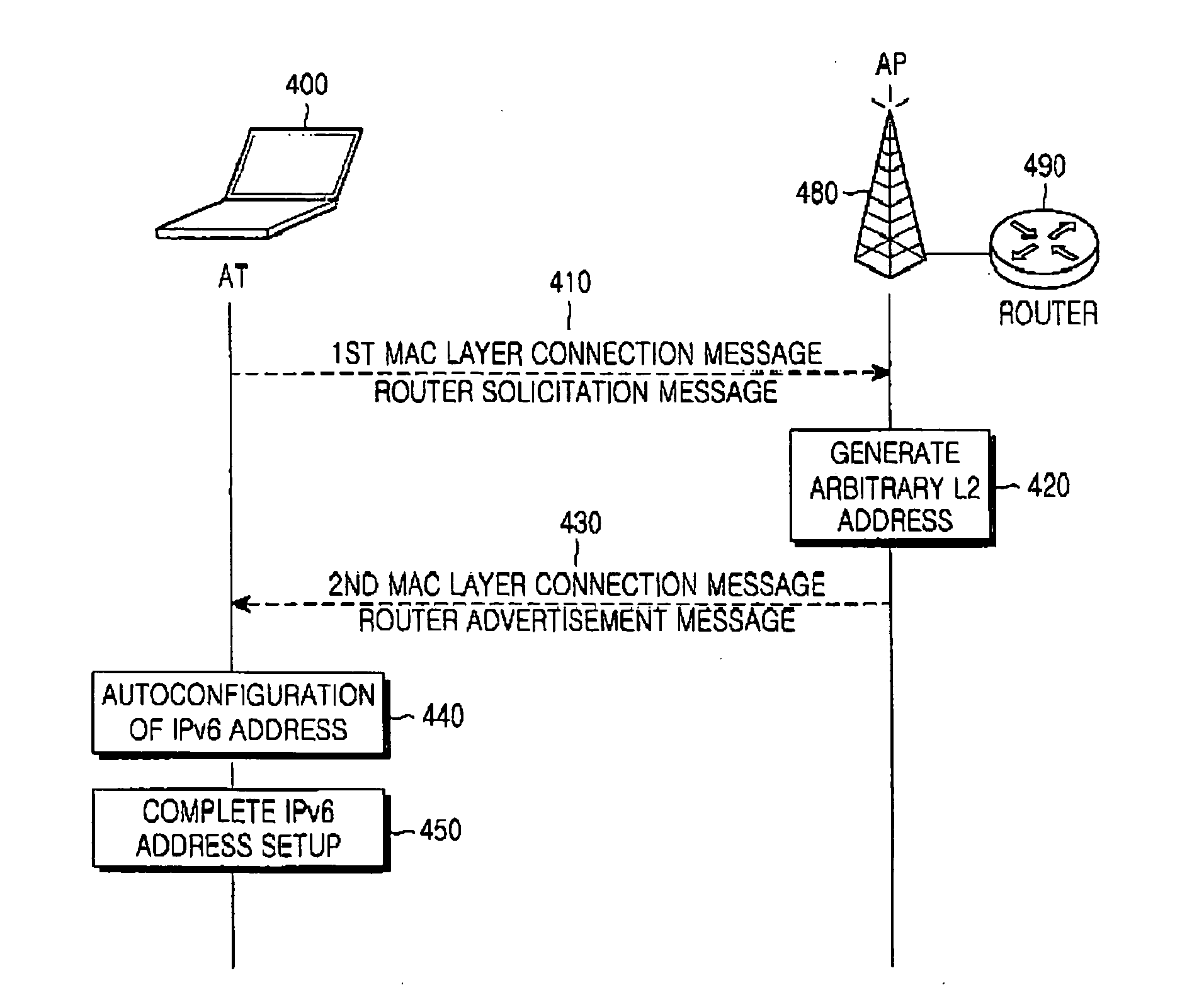
InactiveUS20050018677A1Quick buildEasy accessData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsIp addressMedia access control
A system for transmitting a message for generating an Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address is provided. The system includes at least one access terminal, an access point, and a router. The access terminal transmits a first medium access control (MAC) layer connection message including its own MAC address and a fast address setup indication field to the access point. The access point receives the first MAC layer connection message from the access terminal, and determines whether a duplicate MAC address of the MAC address of the access terminal exists in the same sub-network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Segment routing forwarding method and device based on IPv6 data plane
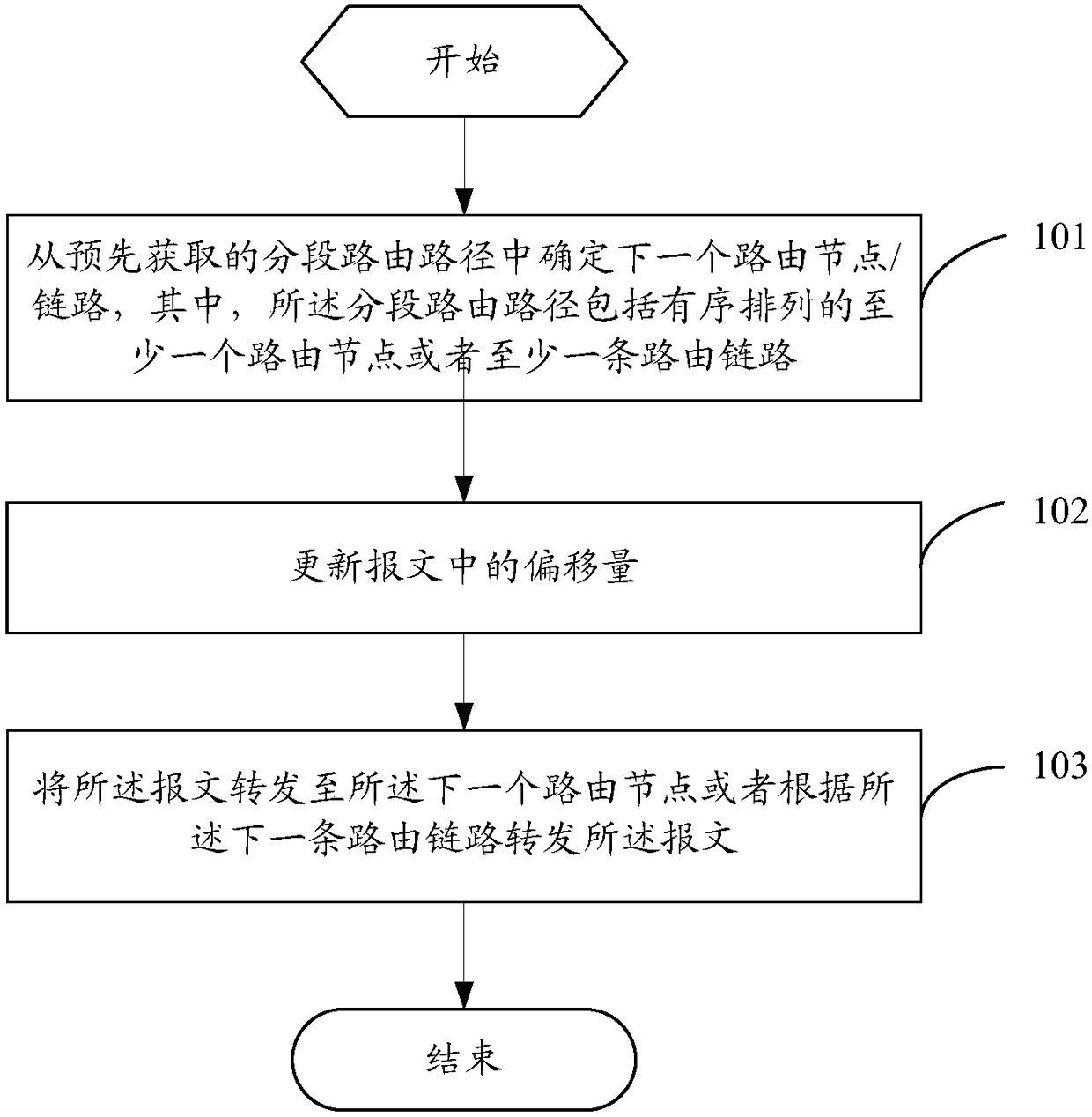
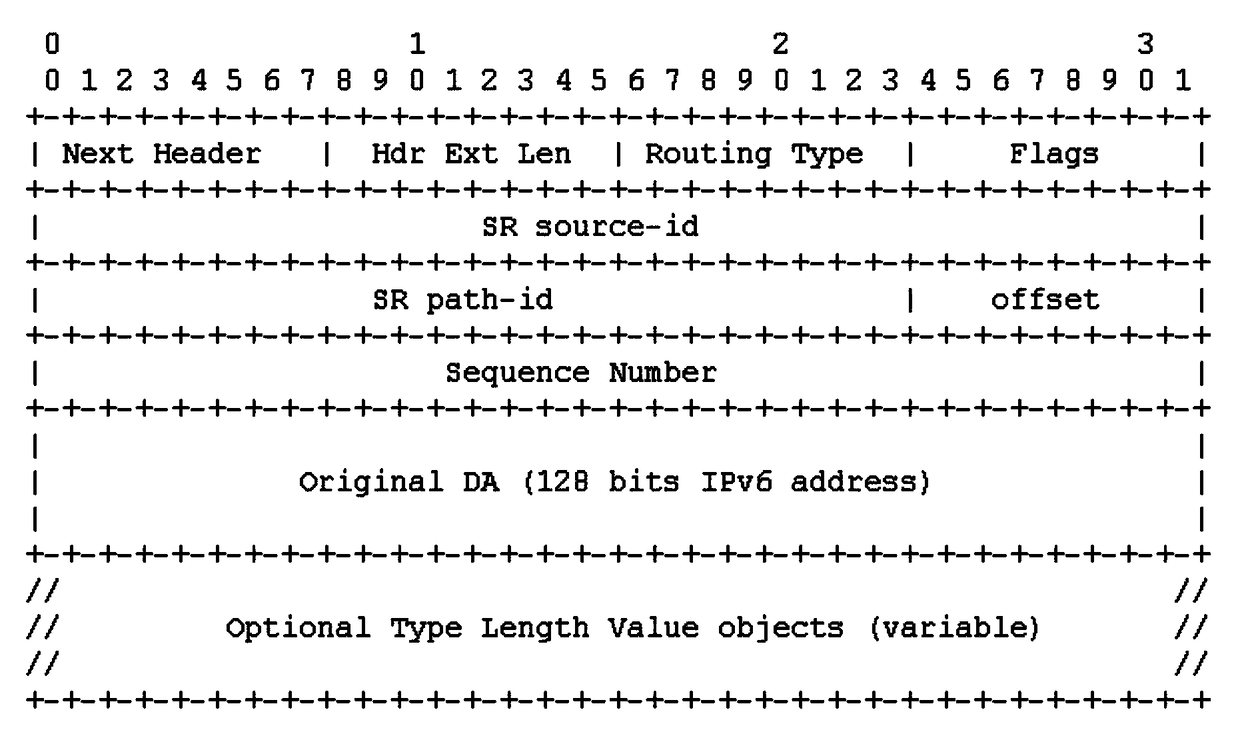
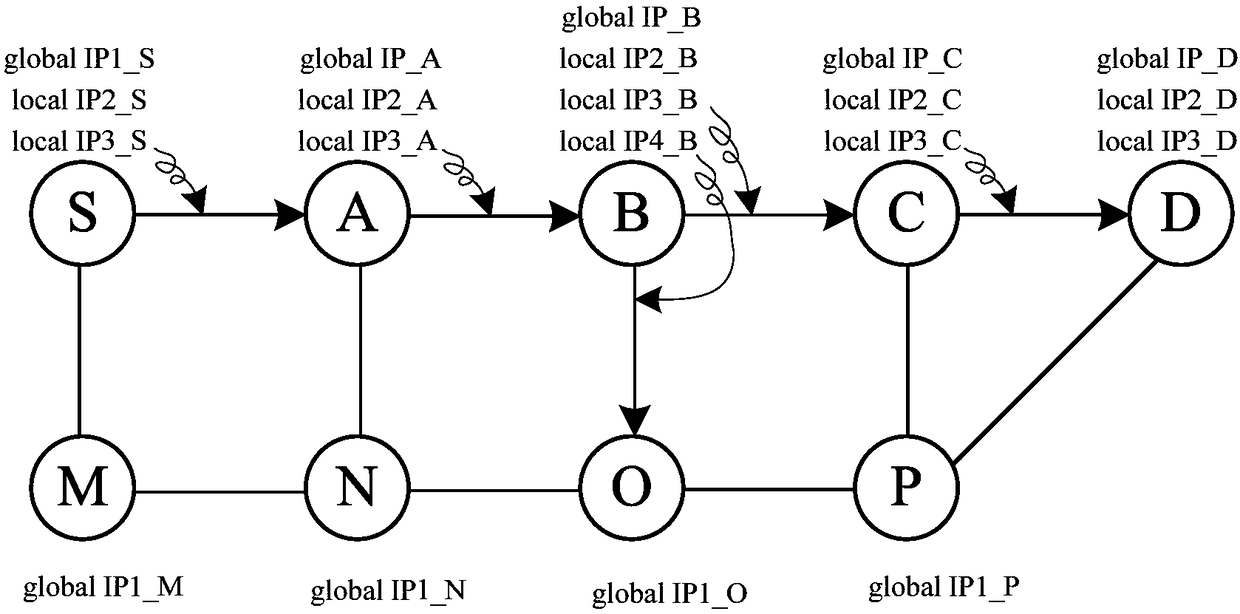
ActiveCN108156077AImprove loading efficiencyReduce overheadData switching networksDistributed computingIPv6
Owner:ZTE CORP
Extensions to filter on IPv6 header
InactiveUS20050268332A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlDistributed computingIPv6
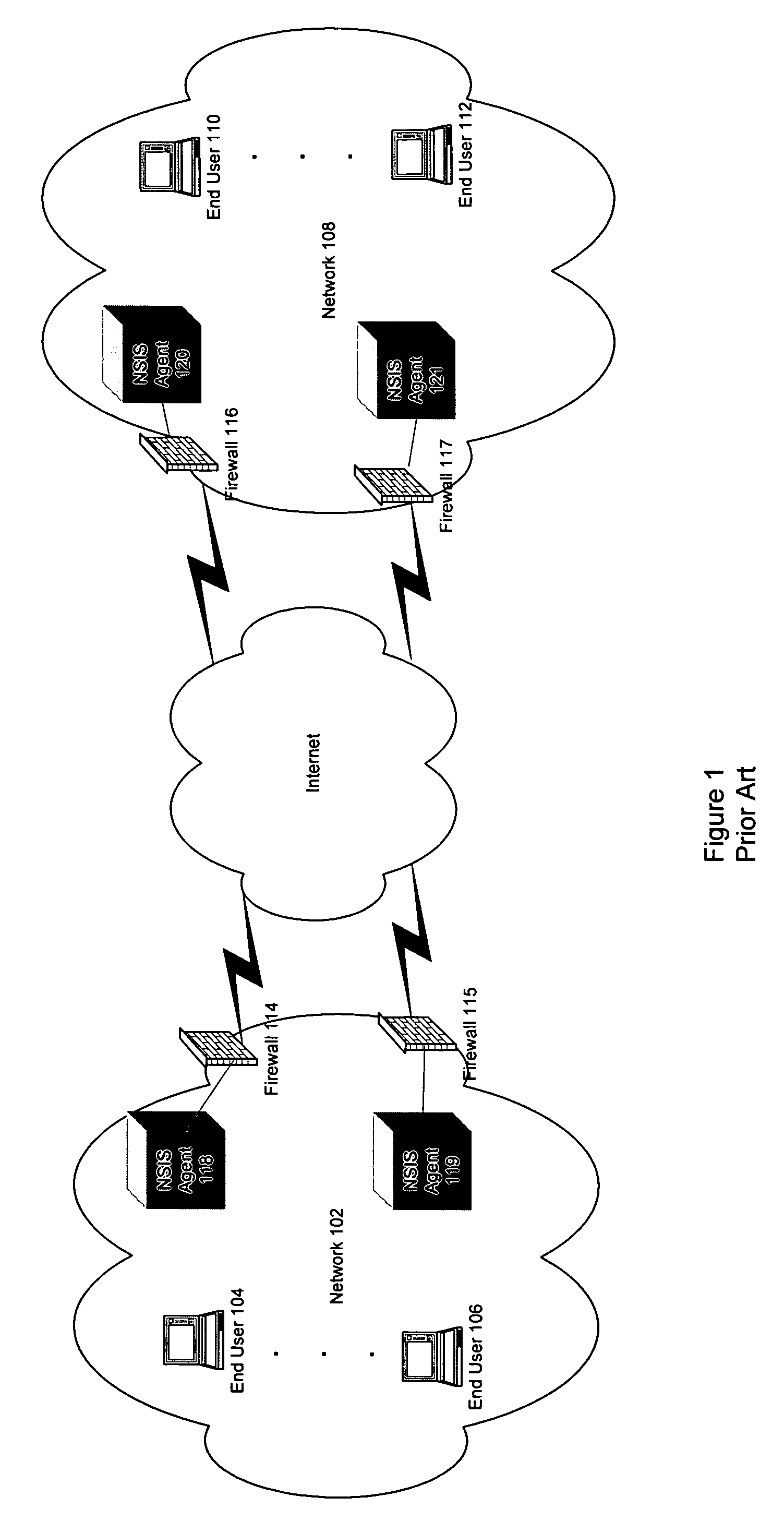
A network implementing at least one firewall for providing protection for users on the network. The network includes at least one host system protected by the at least one firewall, the host system being configured to send and receive information from external host systems through the at least one firewall. The at least one firewall including installation means for installing policy rules that are transmitted from at least one network entity to the at least one firewall. The policy rules include an option field for allowing the at least one network entity to send additional information to the firewall. The additional information relating to at least one type of information used in at least one of a Internet Protocol version 6 protocol or a mobile Internet Protocol version 6 protocol. The additional information is optionally used by the at least one firewall to filter on data travelling through the at least one firewall.
Owner:SPYDER NAVIGATIONS L L C
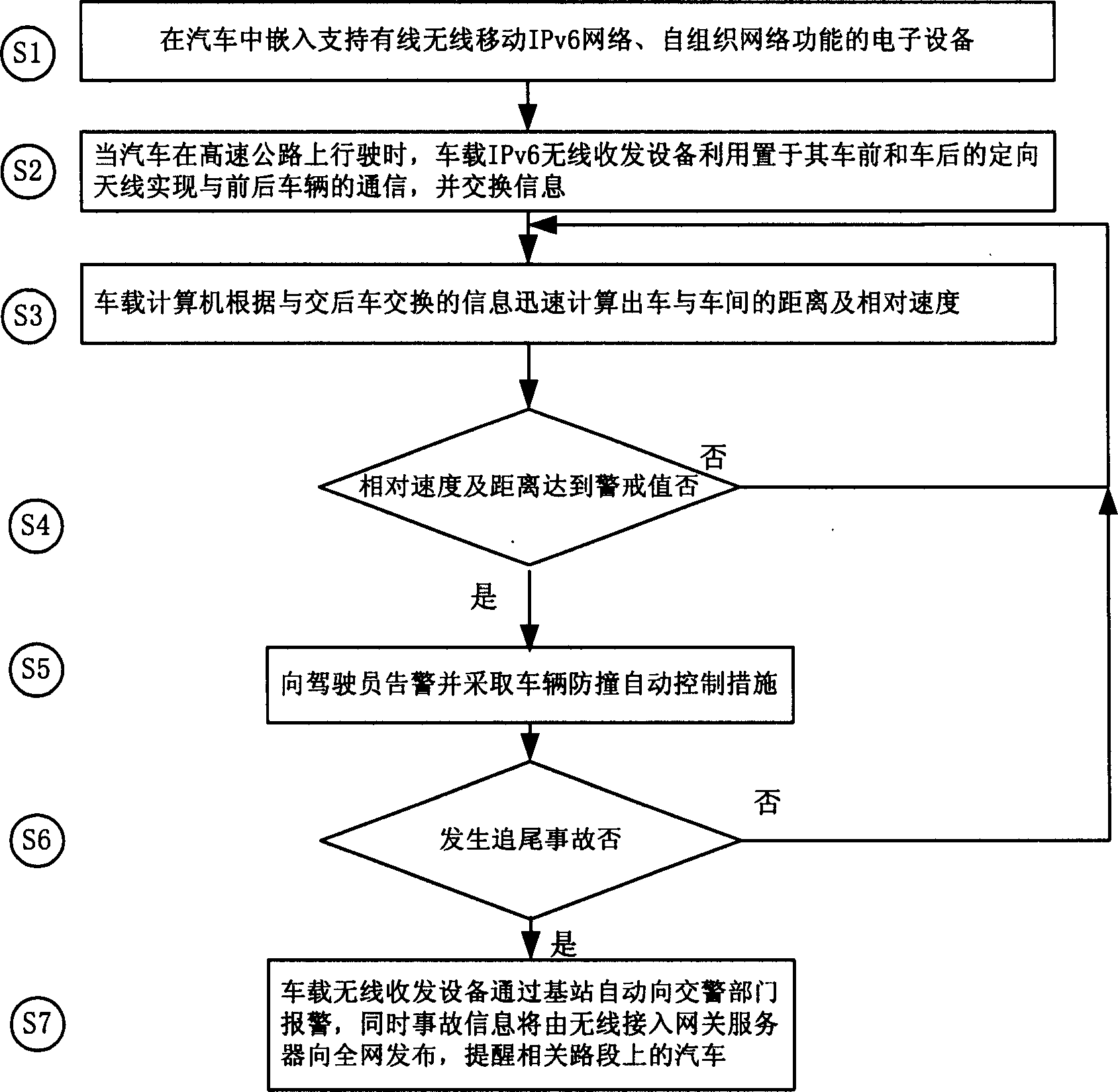
Method of realizing automobile anticollision on high speed highway by using radio self organizing network technology
InactiveCN1534553AAvoid rear-end accidentsReduce rear-end collisionsNetwork topologiesAnti-collision systemsNetworking protocolWireless mesh network
A method for using wireless self-organizing network technique to prevent collision of car on expressway includes installing an electronic device in car, which supporting mobile IPv6 network functions and self-organizing communication, communicating in self-organizing mode, generating warning information, judging if the distance reaches the warning value, generating warning information, and sending the collision accident to relative department via wireless network if a rear collision occurs.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com