Method of driving a non-volatile flip-flop circuit using variable resistor elements
A multivibrator, non-volatile technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, static memory, etc., can solve problems such as increasing current consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
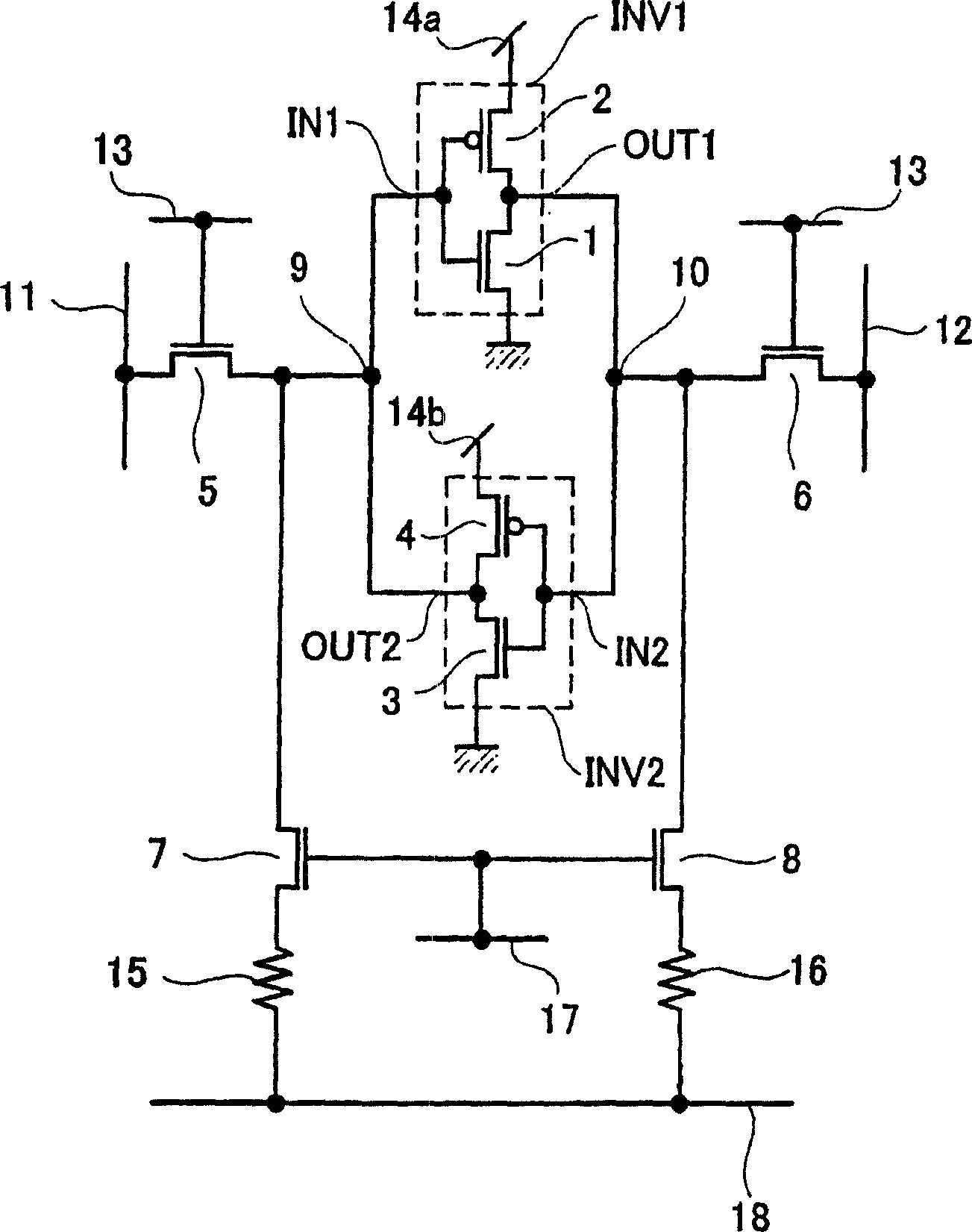
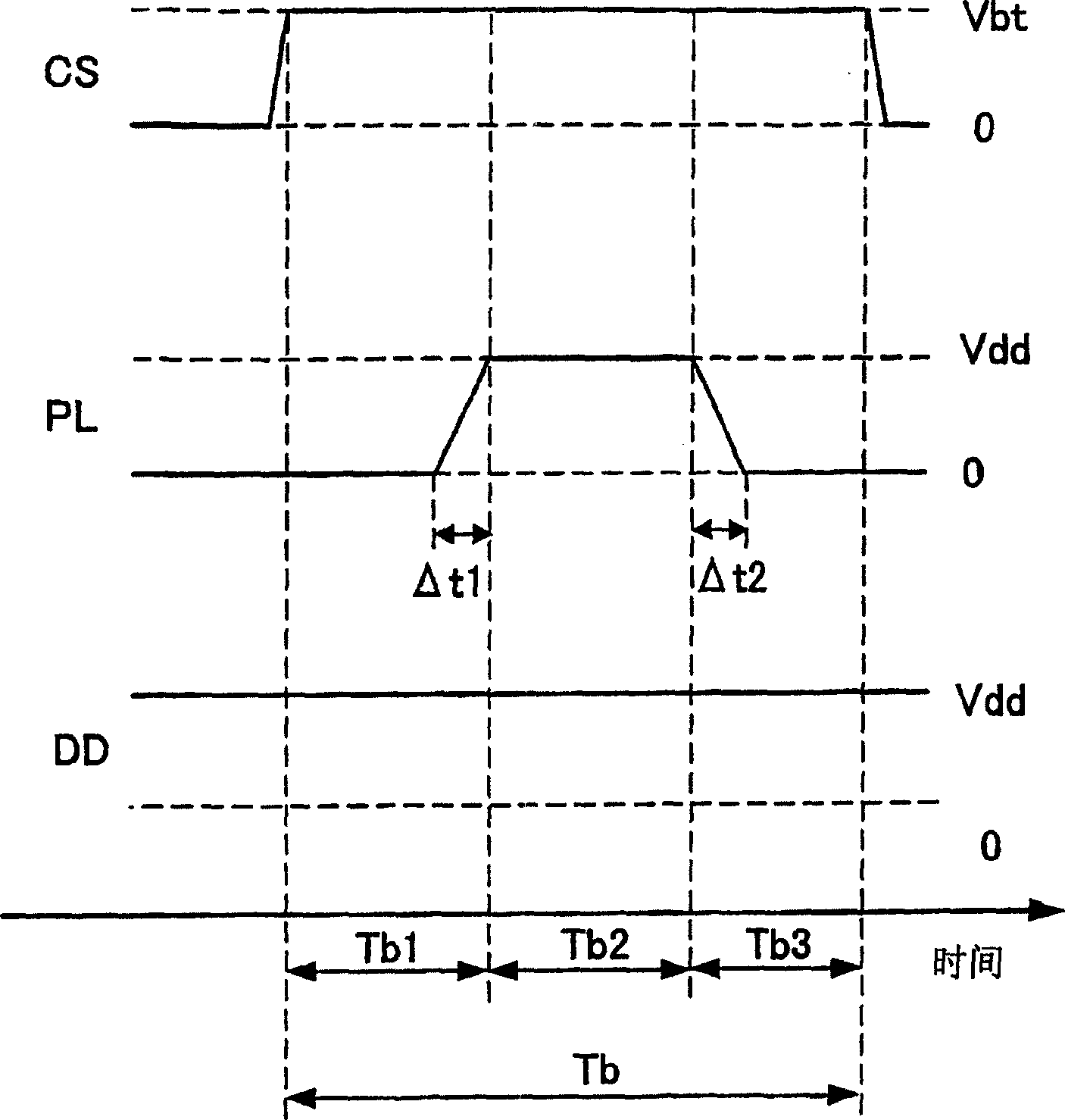
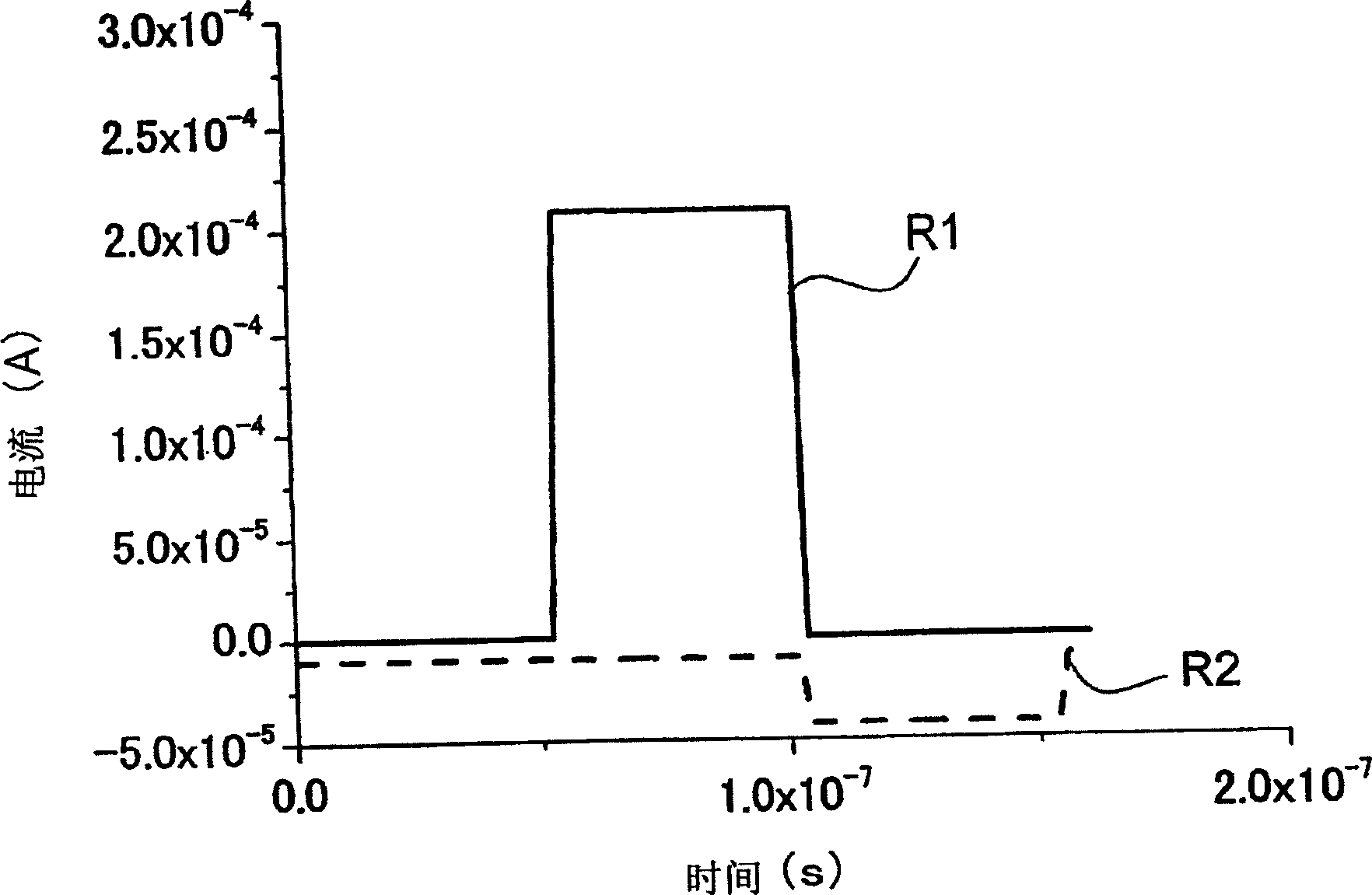
[0021] Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing a nonvolatile flip-flop circuit according to an embodiment of the present invention. This nonvolatile flip-flop circuit has a first transistor 1 and a second transistor 2 constituting a first inverter INV1, a third transistor 3 and a fourth transistor 4 constituting a second inverter INV2, The fifth transistor 5 and the sixth transistor 6 of the first and second bypass transistors, the first storage node 9 and the second storage node 10, the word line 13, the first bit line 11 and the second bit line 12, the first and the second power supply lines 14a and 14b, the seventh transistor 7 and the eighth transistor 8 of the first and second control switching elements, the first variable resistance element 15 and the second variable resistance element 16, and the CS of the control signal line. Line 17 and Plate Line 18. The first and second transi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com