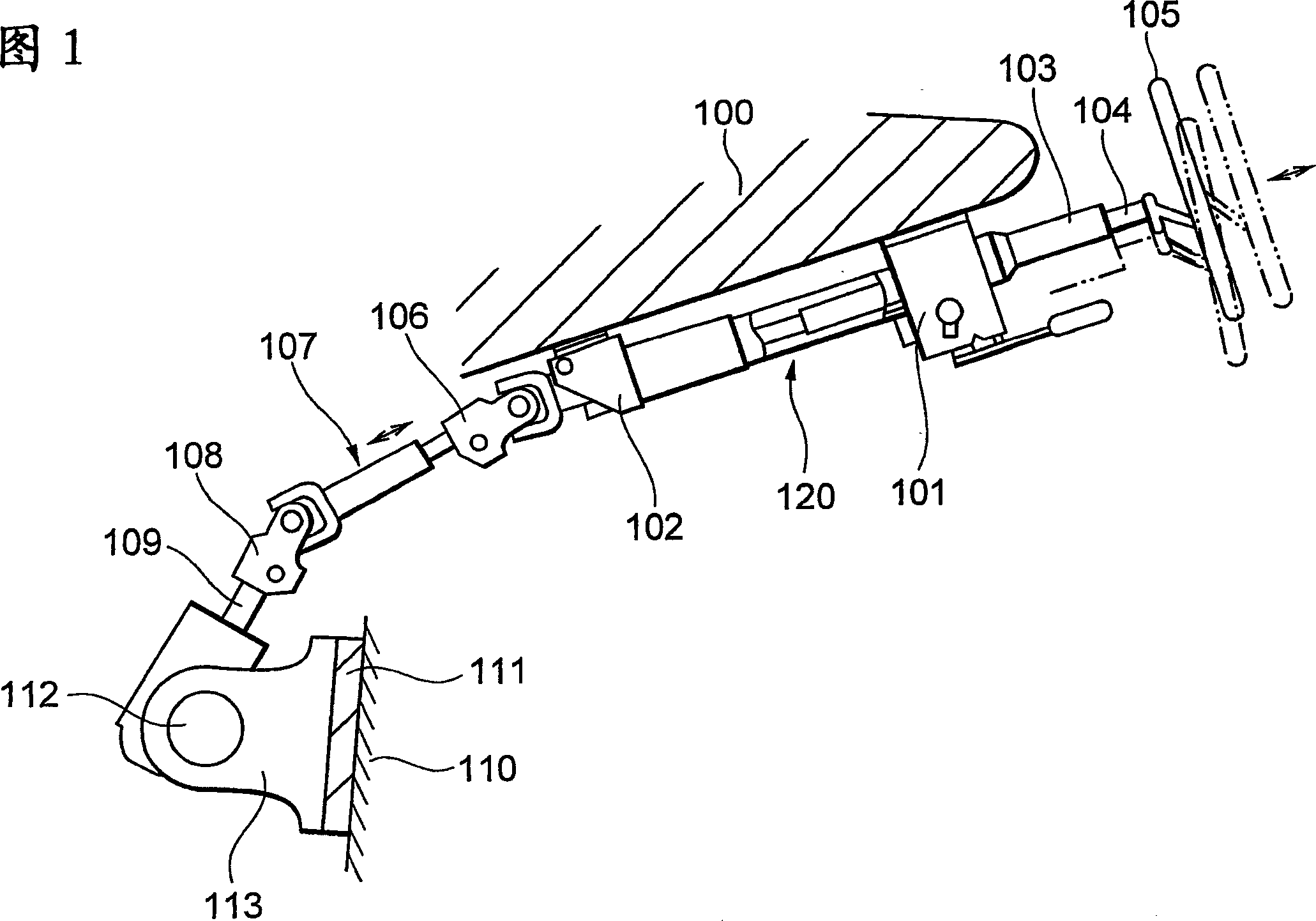
Telescopic shaft for motor vehicle steering
A telescopic shaft and steering shaft technology, which is applied to the steering column, steering control mounted on the vehicle, steering control, etc., can solve the problems of torque reduction, affecting the long life of the steering shaft, and inability to obtain hysteresis. High-rigidity feel steering characteristics, prevent excessive hysteresis, and ensure the effect of deflection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
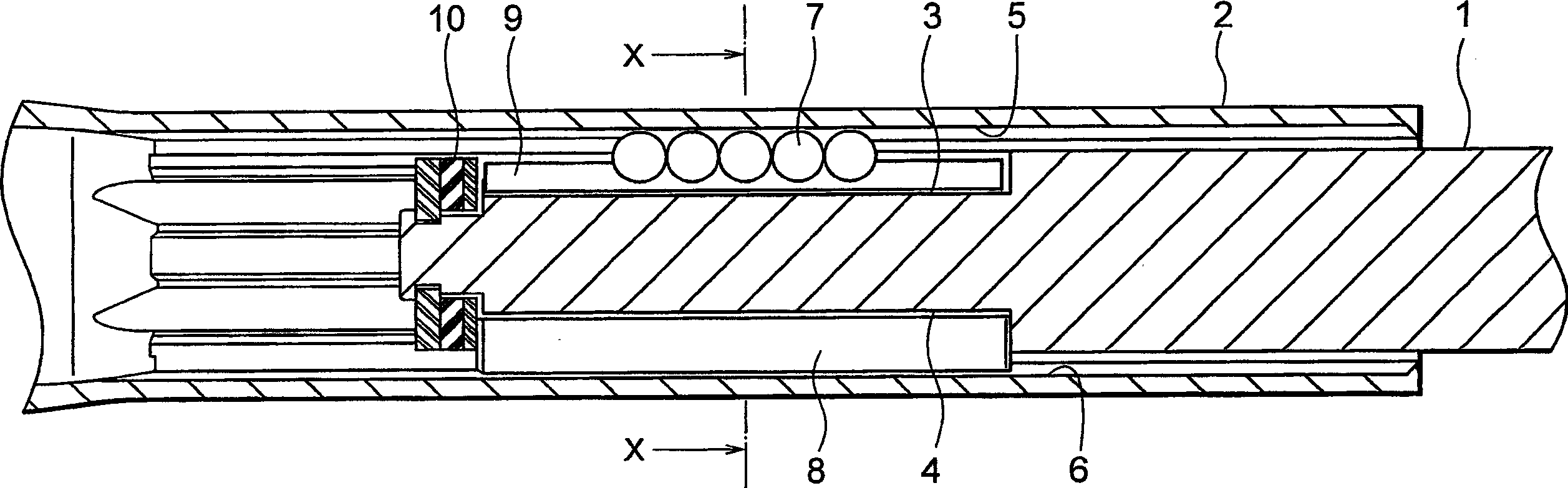
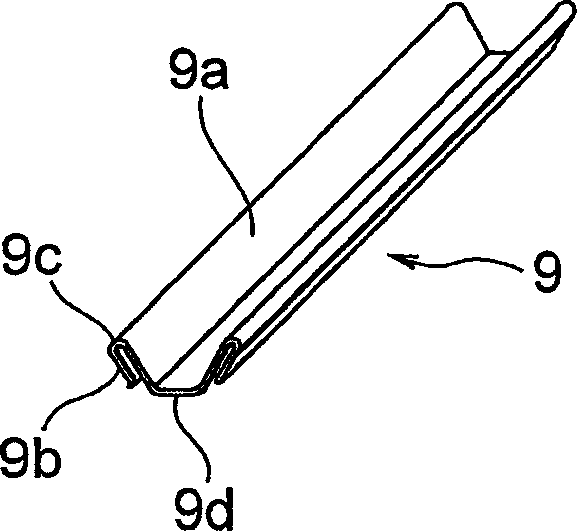
[0072] Figure 2A It is a longitudinal sectional view of a vehicle steering telescopic shaft according to a first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 2B is a perspective view of a leaf spring used as an elastomer / component. image 3 is along Figure 2A A cross-sectional view taken along the line X-X.
[0073] Such as Figure 2A As shown, the telescopic shaft for vehicle steering (hereinafter referred to as the telescopic shaft) includes a male shaft 1 and a female shaft 2 that cannot rotate with each other but are slidably engaged with each other.
[0074] Such as image 3 As shown, three grooves 3 extending in the axial direction are provided on the outer peripheral surface of the male shaft 1 at equal intervals of 120 degrees in the circumferential direction. Correspondingly, three axially extending grooves (hereinafter referred to as axial grooves) 5 are provided on the inner peripheral surface of the female shaft 2 at equal intervals of 120 degrees in the cir...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0147] Figure 8 is a cross-sectional view showing a vehicle steering telescopic shaft according to a second embodiment of the present invention (corresponding to the Figure 2A Cross-sectional view taken along the line X-X).
[0148] The second embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment described above, in that the bottom surface 3b of the axial groove 3 is separated from the bottom 9d of the leaf spring 9 by a predetermined distance.
[0149] Therefore, in this case, as described above, the hysteresis can be controlled without friction when the axial groove 3 and the leaf spring 9 move relative to each other, so that the hysteresis can be set to be small.
no. 3 Embodiment
[0151] Figure 9 is a cross-sectional view showing a vehicle steering telescopic shaft according to a third embodiment of the present invention (corresponding to the Figure 2A Cross-sectional view taken along the line X-X).
[0152] The third embodiment is basically the same as the above-mentioned second embodiment, wherein, in the leaf spring 9, the ball-side contact portion 9a is formed at the end of the bent portion of the leaf spring 9, and the contact portion 9b is formed at the end of the leaf spring 9. The middle part of the bent part.
[0153] Also in the same manner as in the second embodiment described above, the bottom surface 3b of the axial groove 3 is separated from the bottom 9d of the leaf spring 9 by a predetermined distance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com