Patents
Literature
1421results about "Elastic bearings" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
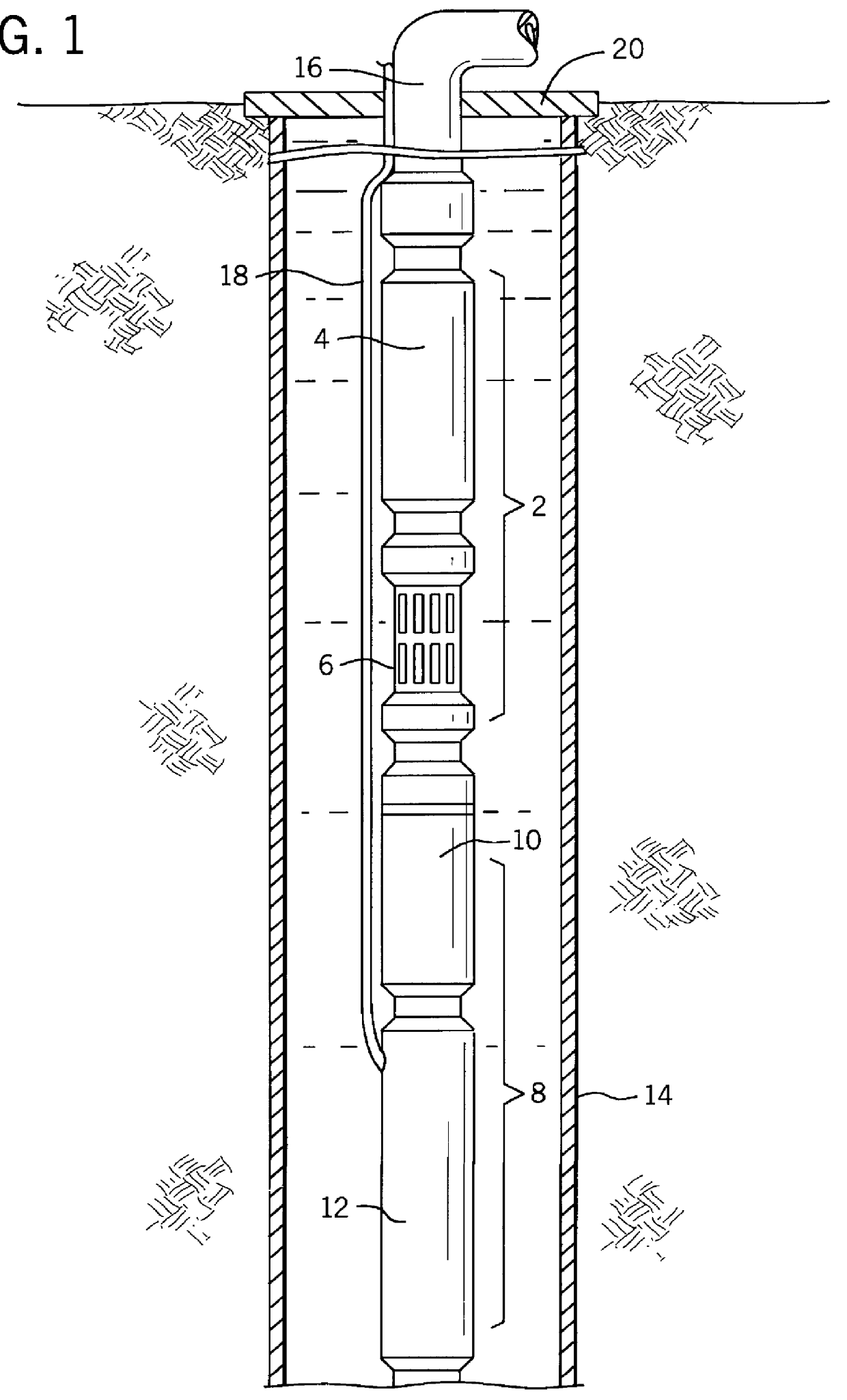
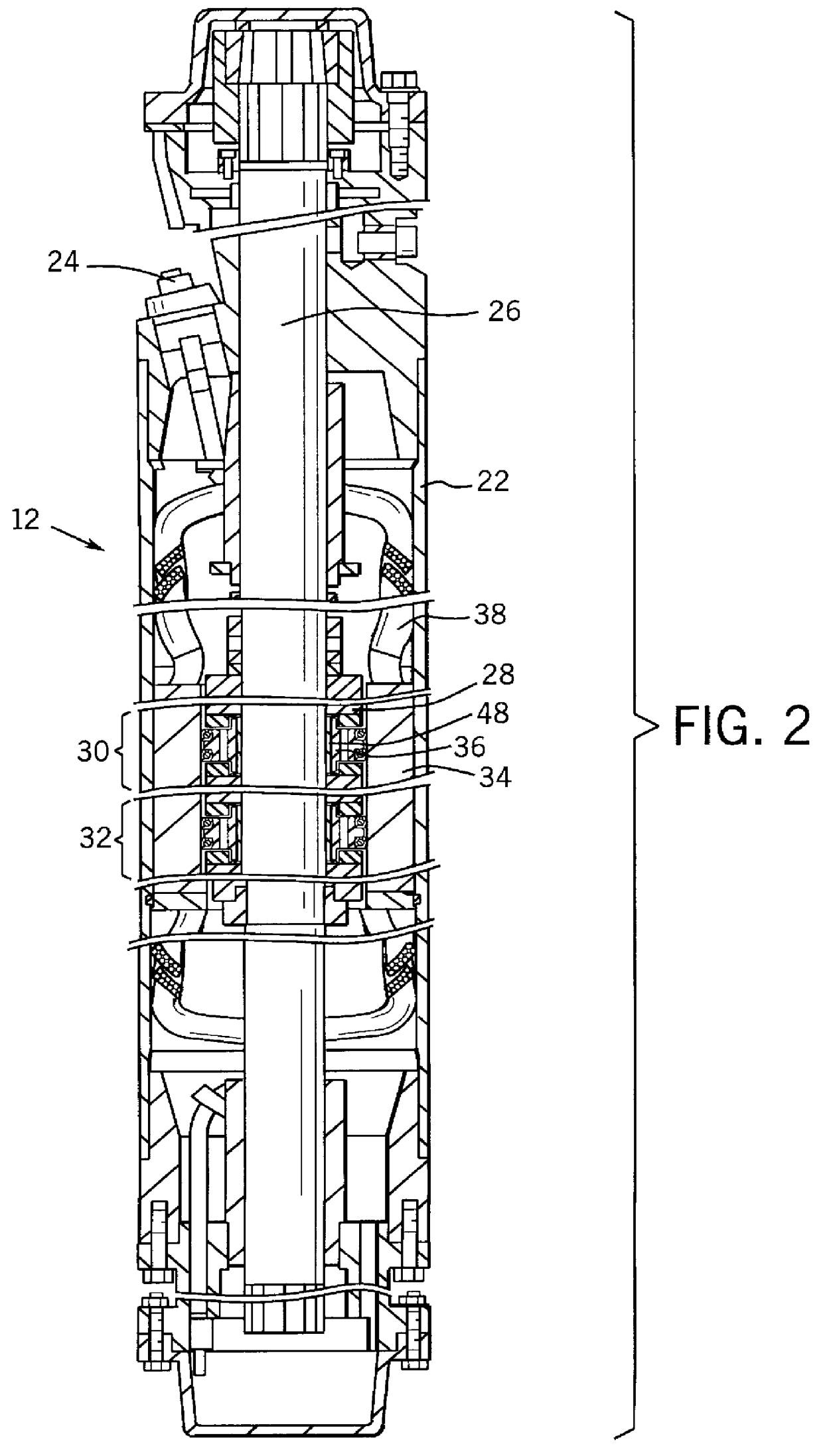
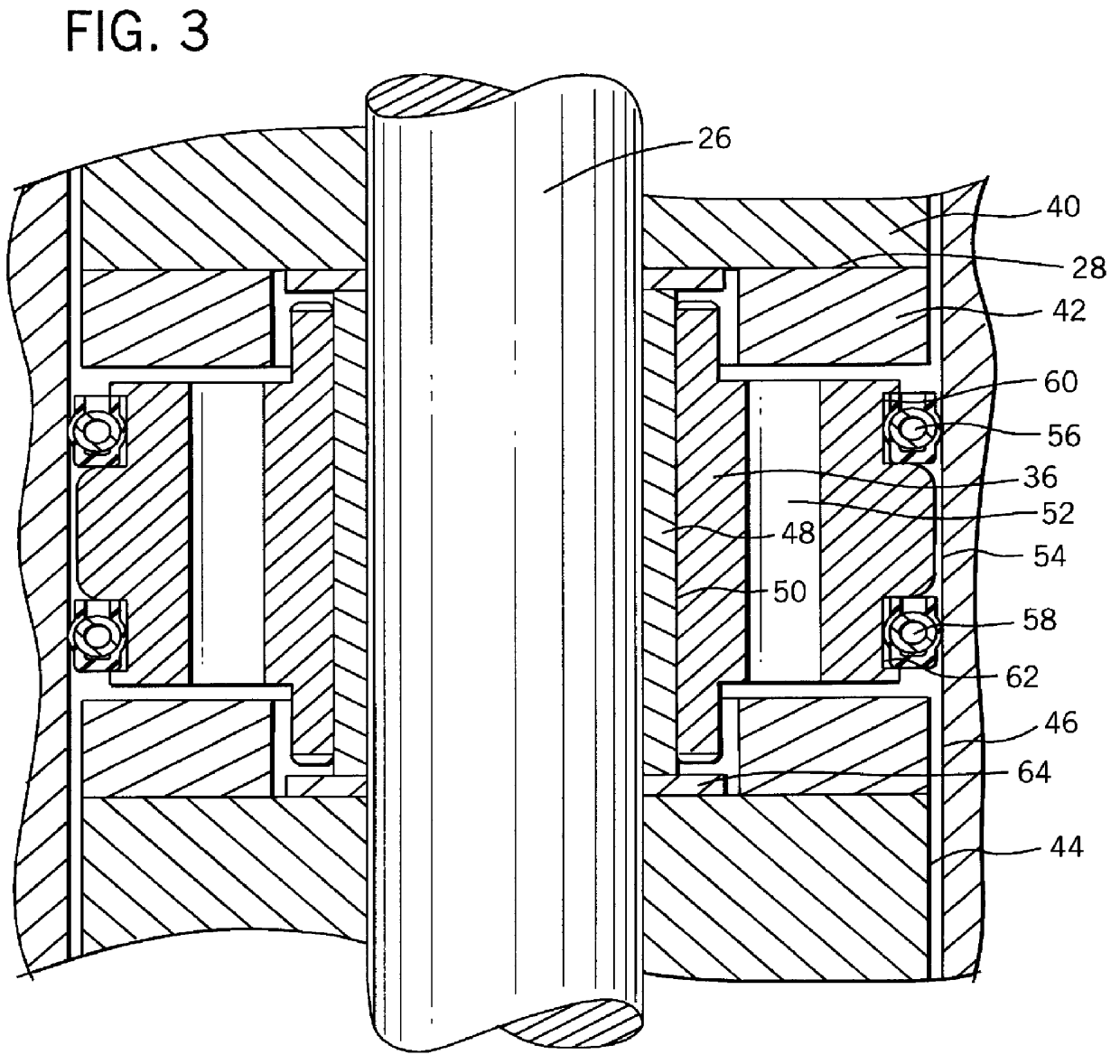
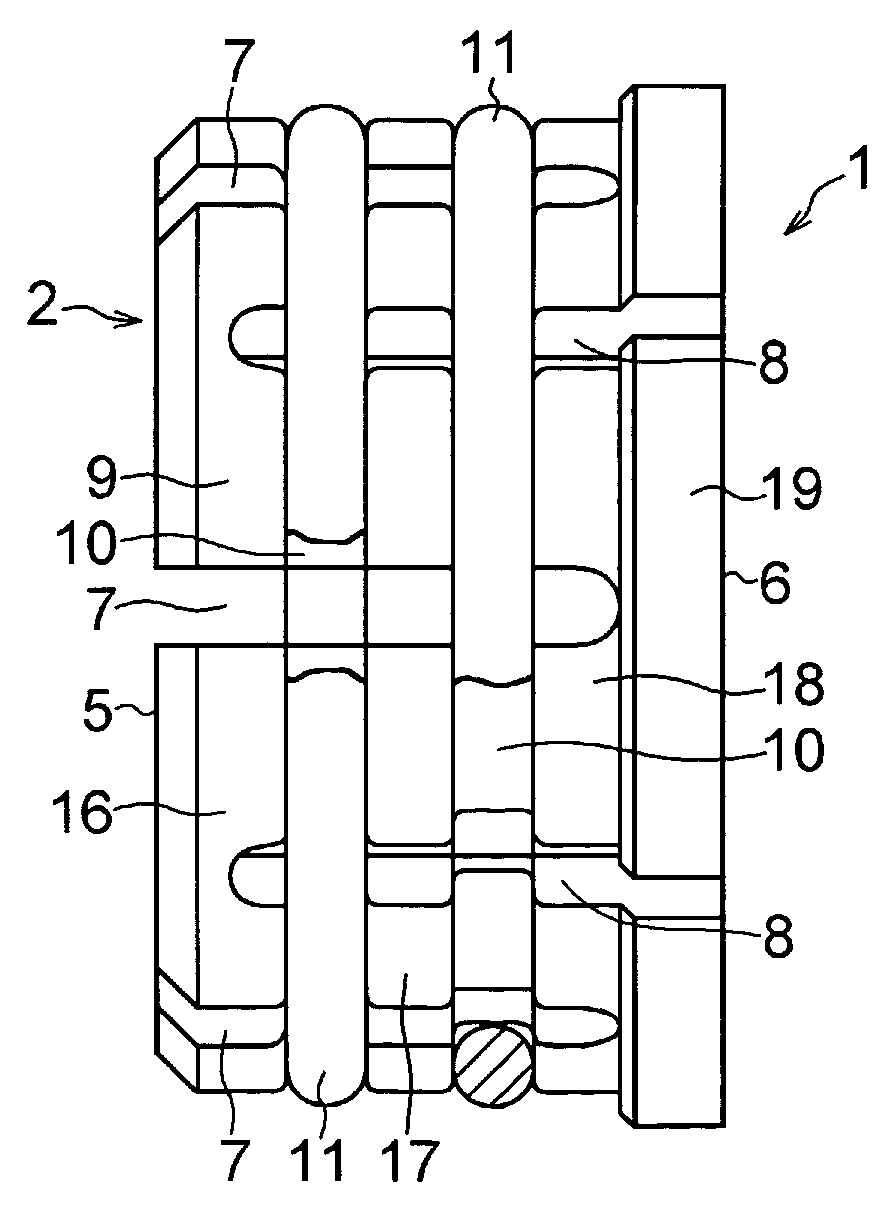
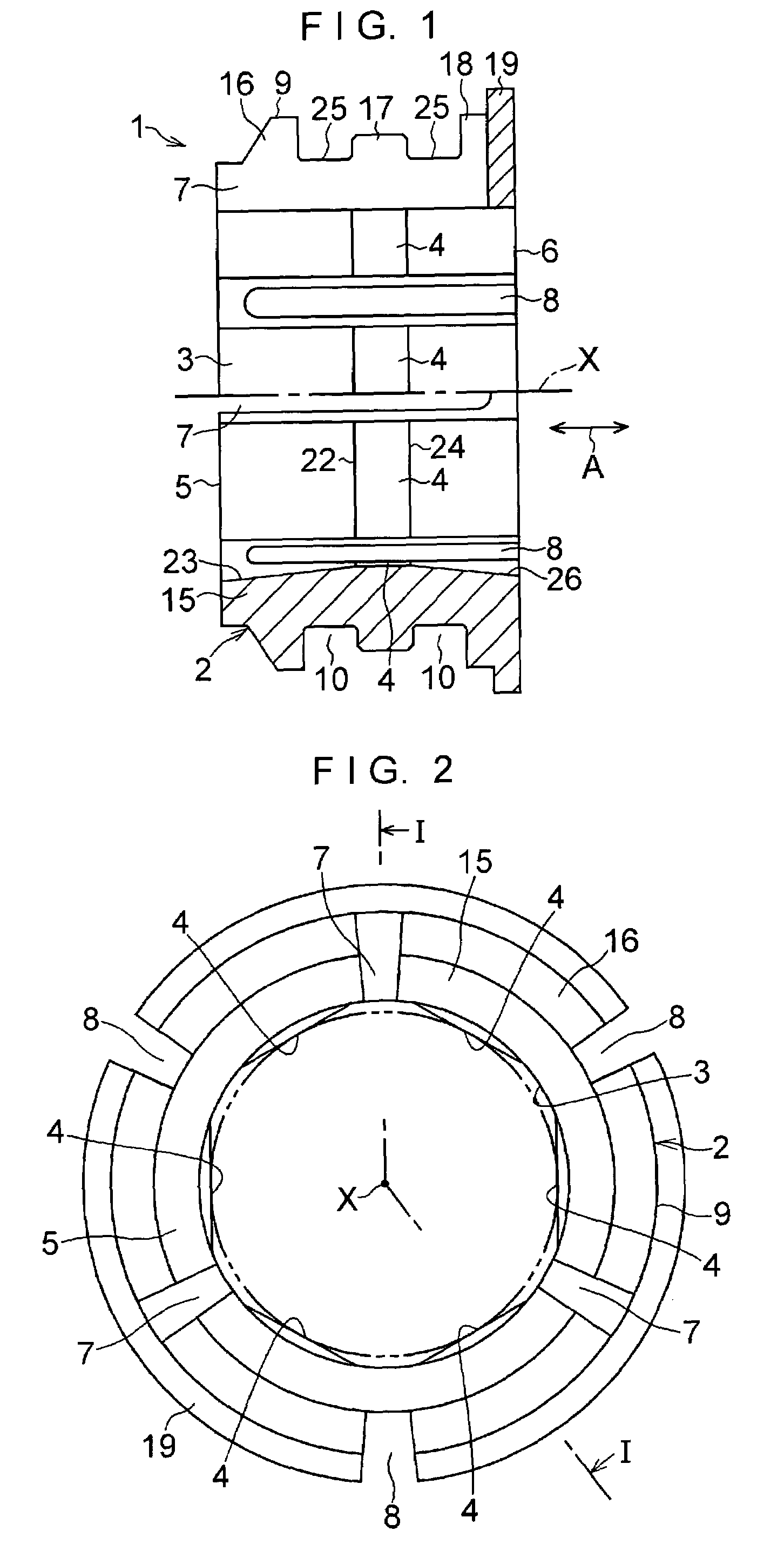
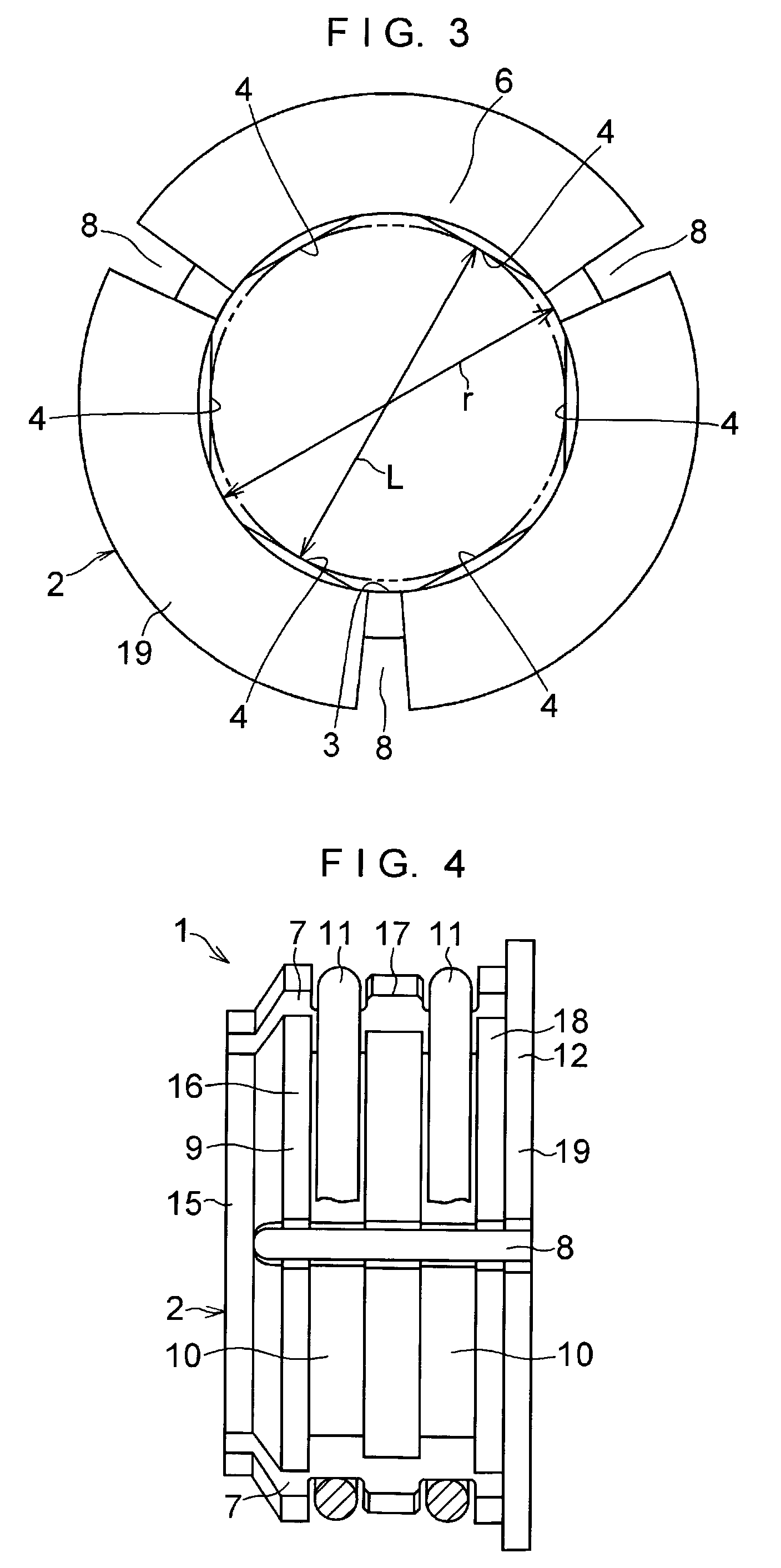
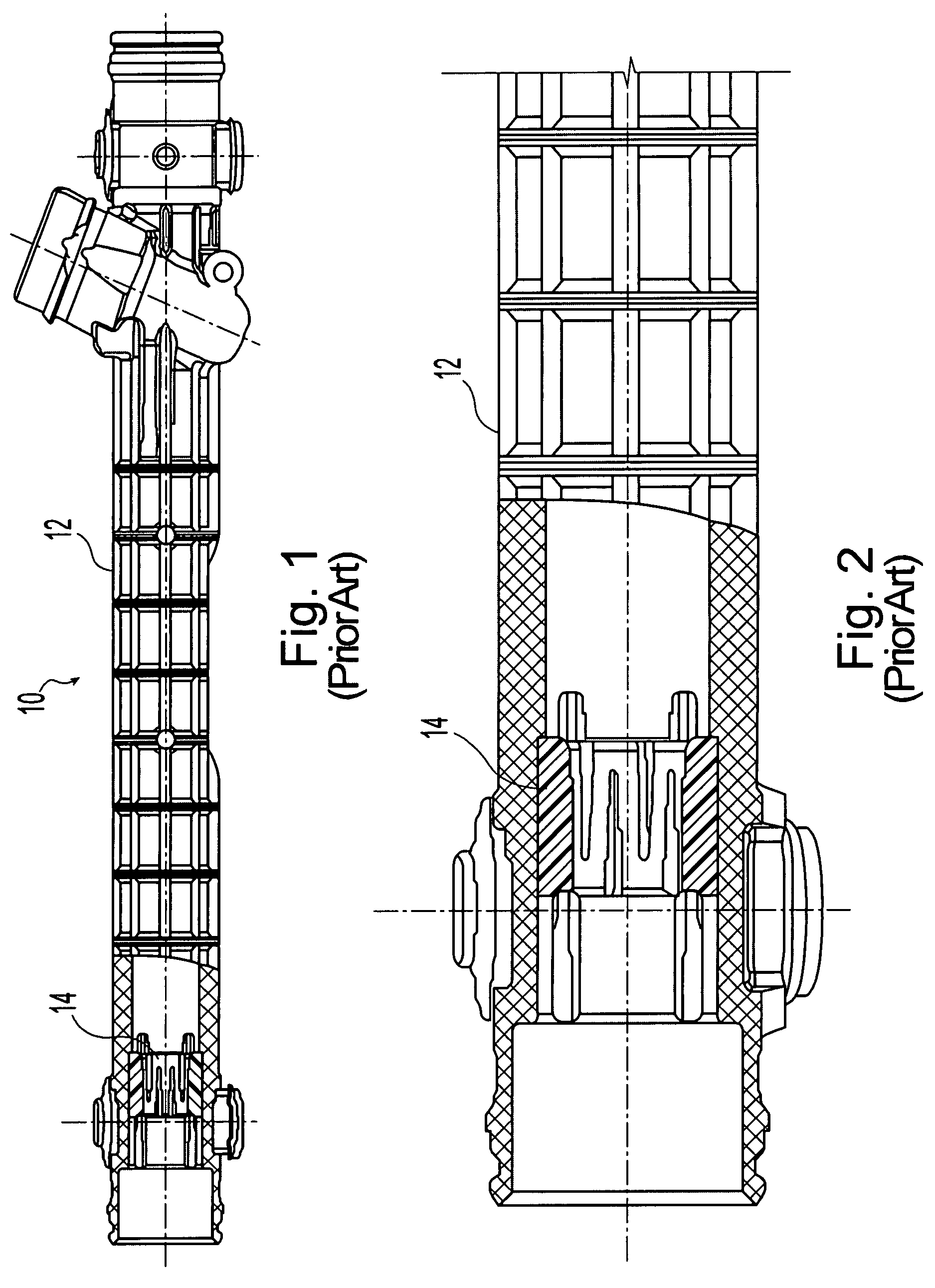
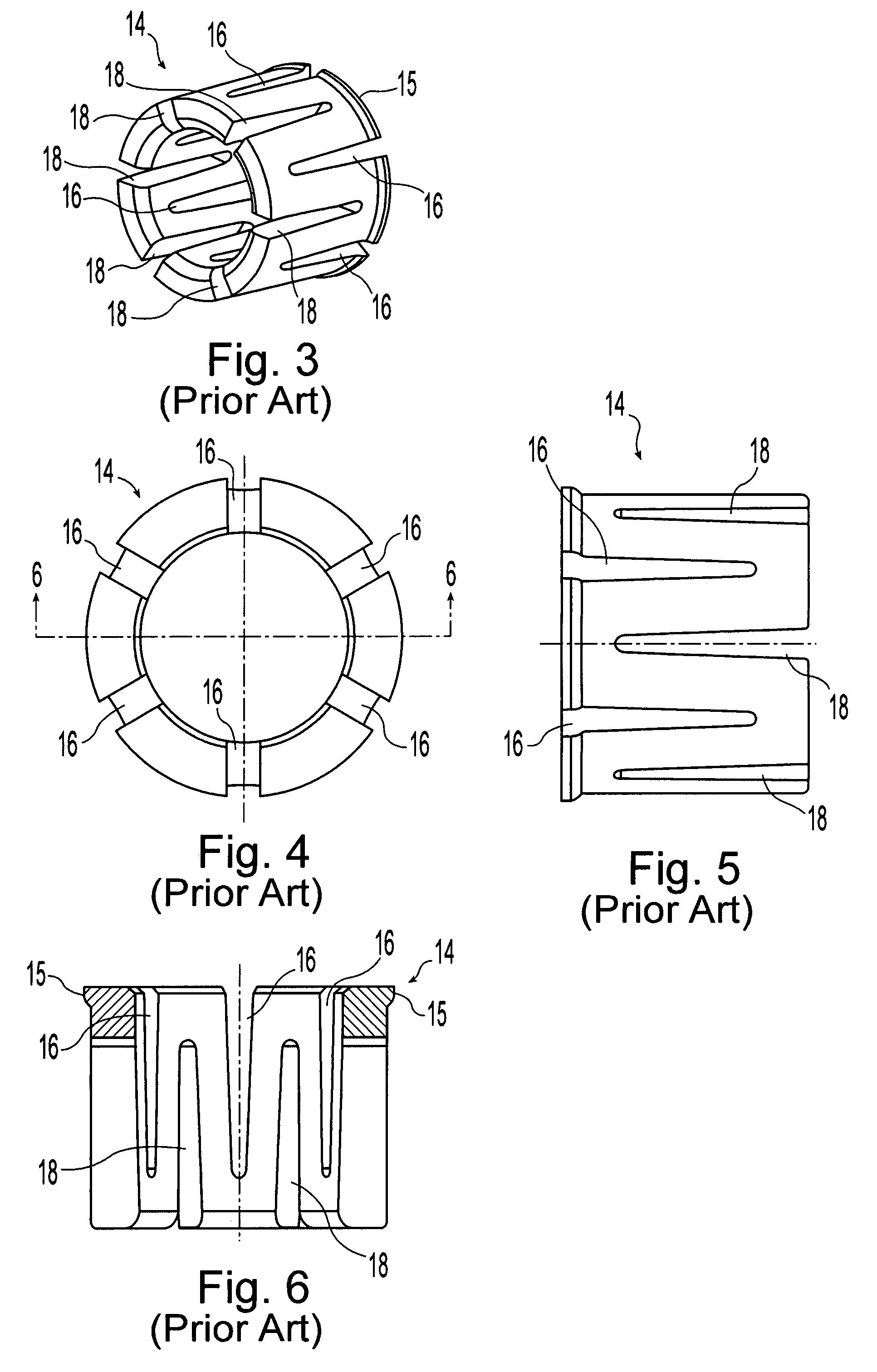
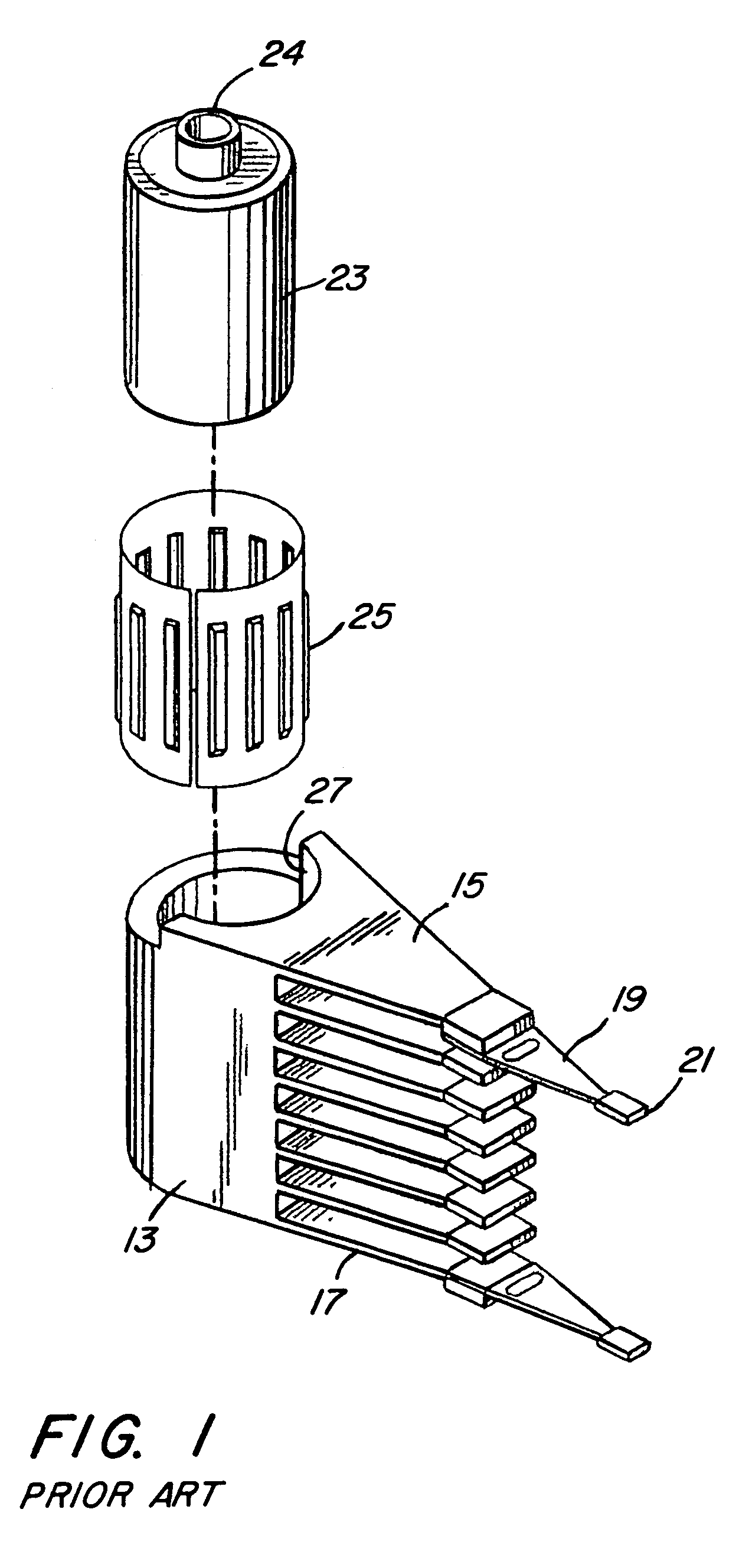
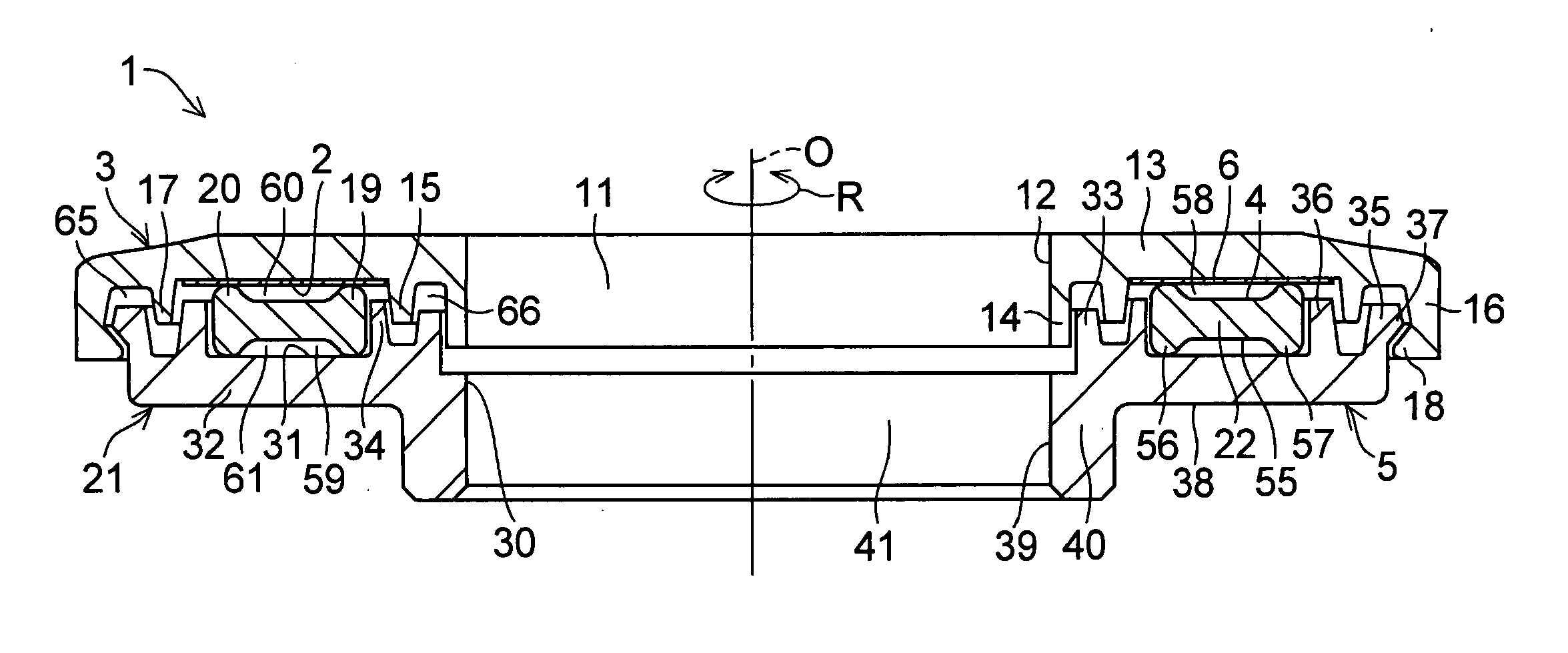
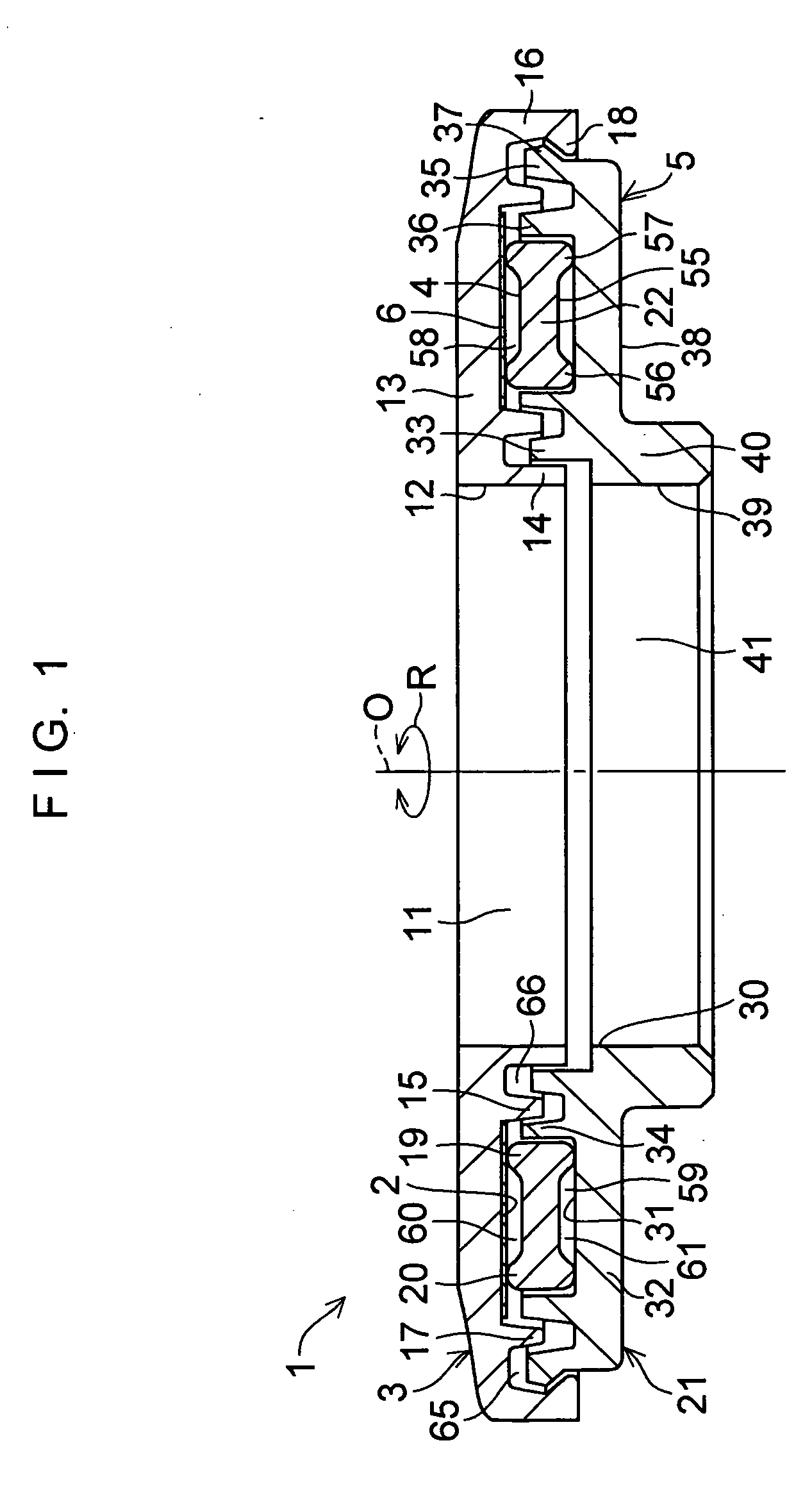
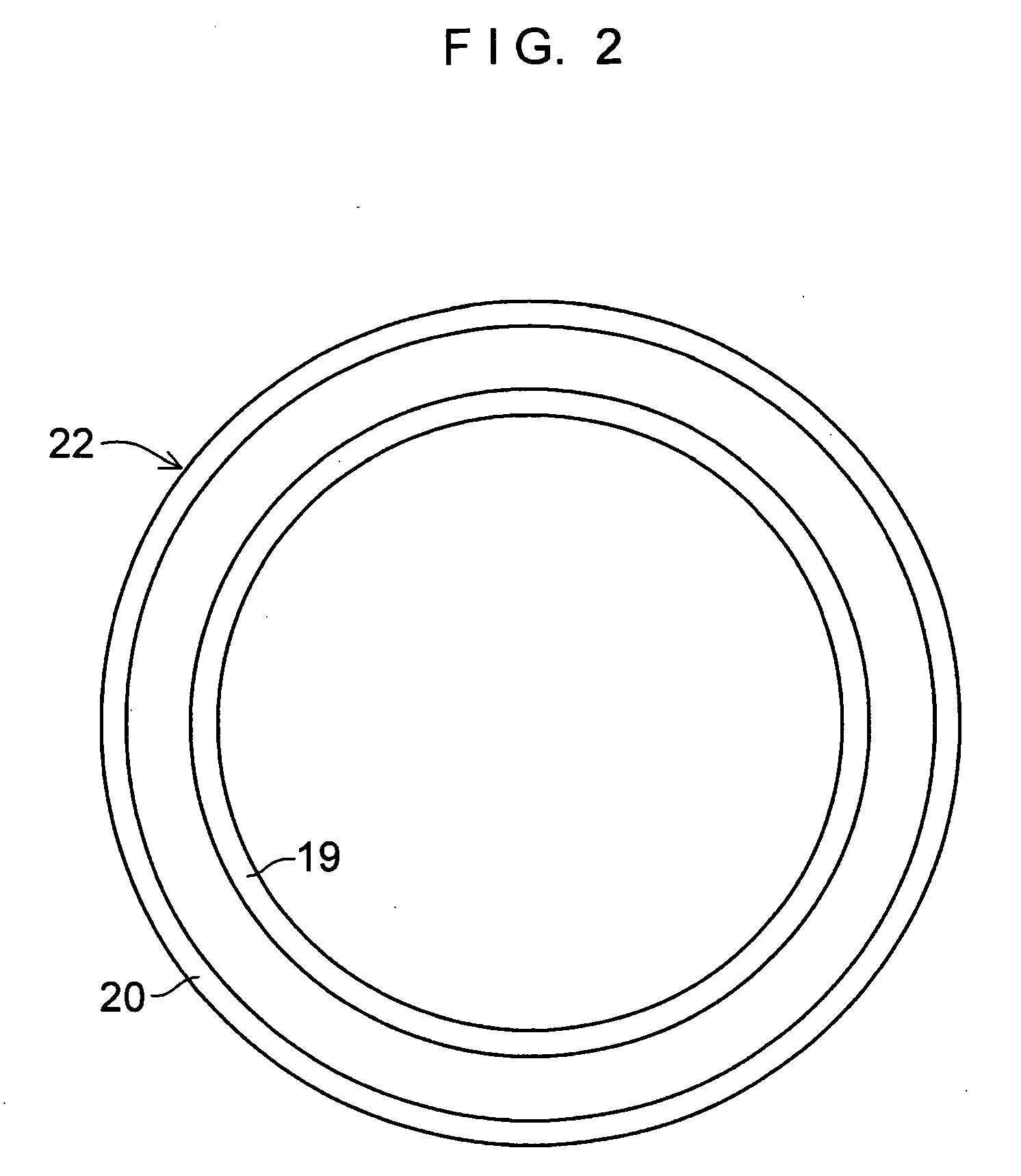
Self-centering rotor bearing assembly for submersible pump motors
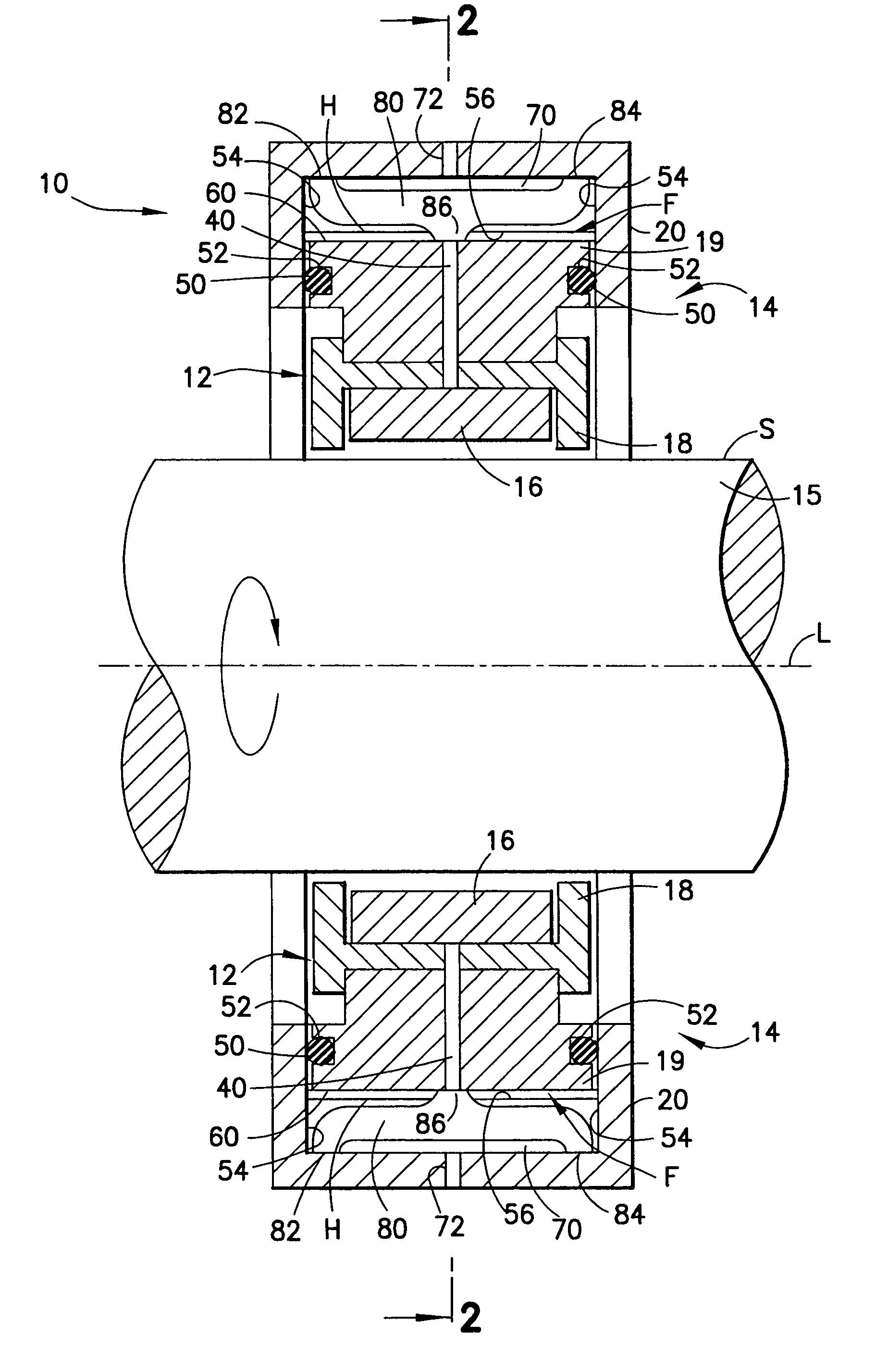
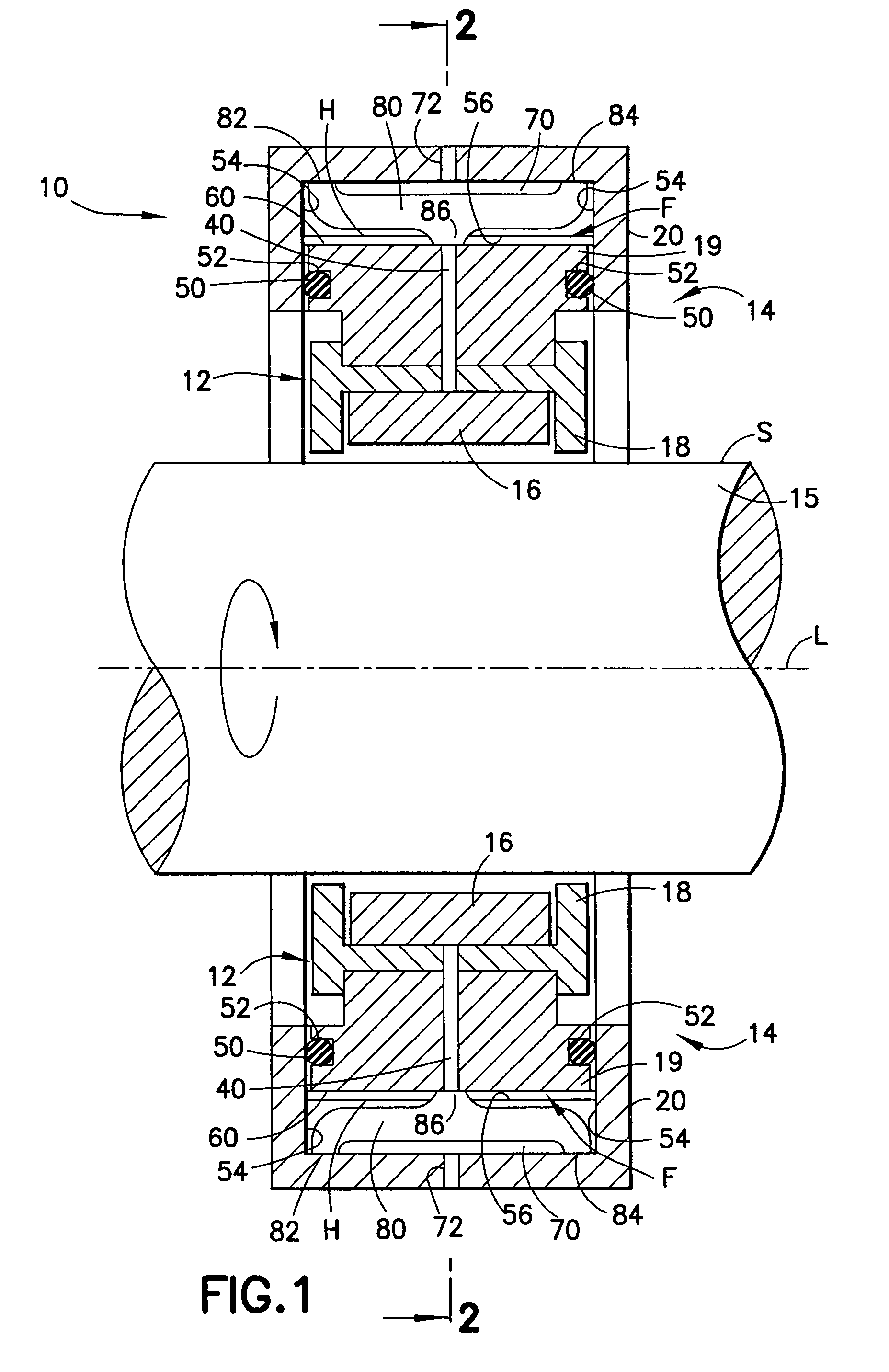
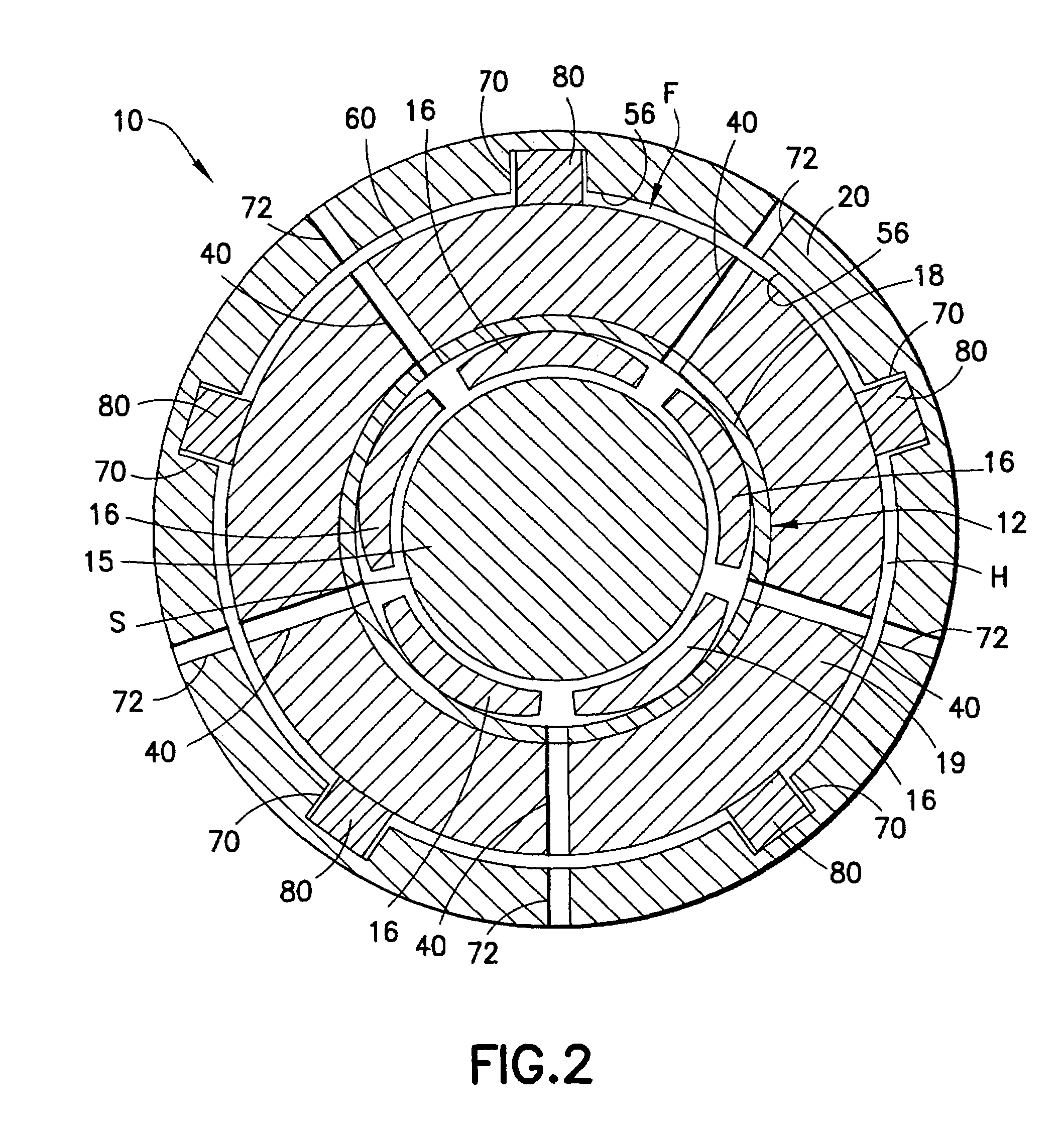
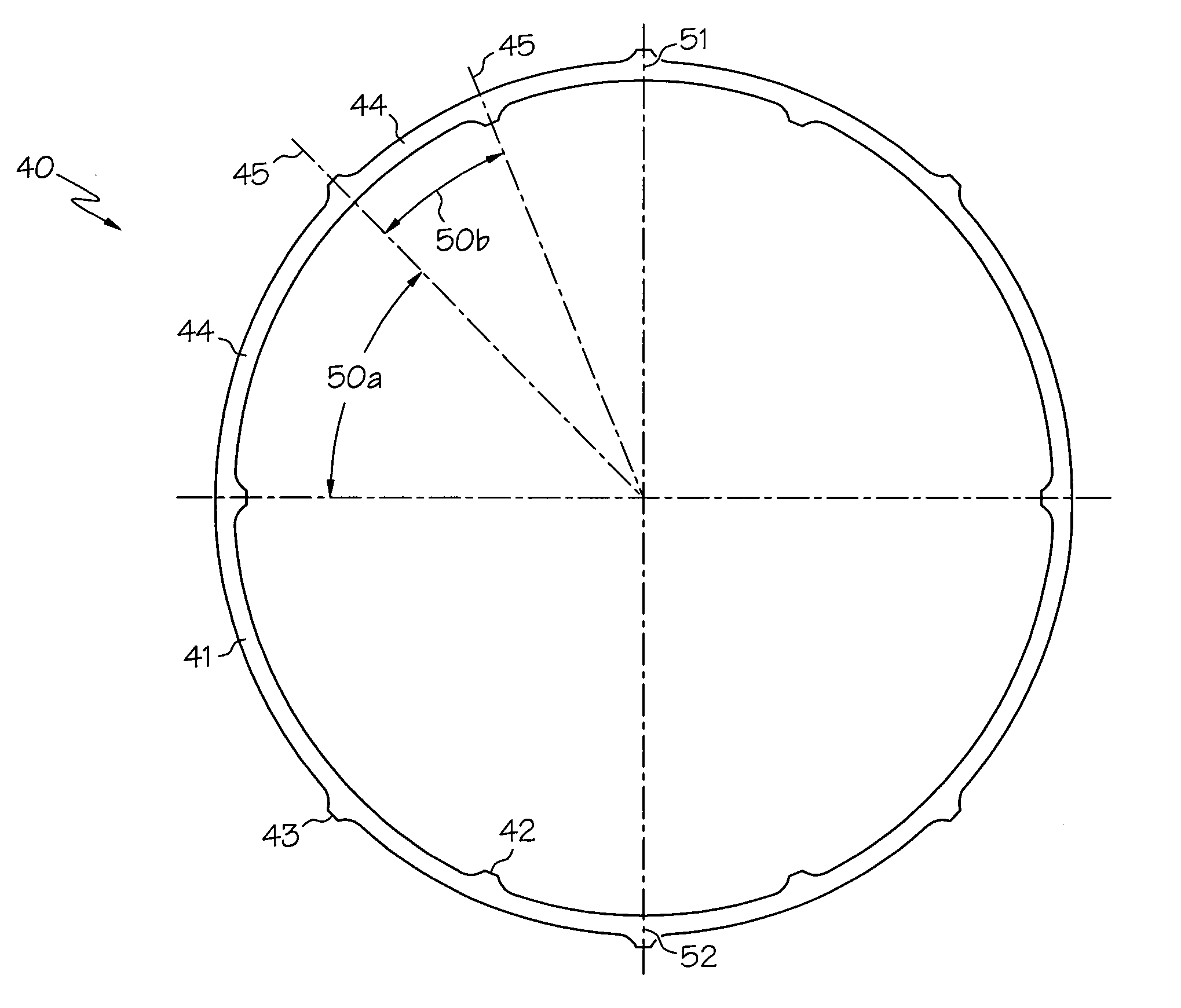
The invention provides a submersible pumping system which includes a motor containing self-centering rotor bearing assemblies. Each rotor bearing assembly in accordance with the present invention includes a sleeve, a journal, and at least two seals. The journal is preferably disposed about the sleeve which is keyed to the power transmission shaft of the motor. The journal has a peripheral surface which is configured to have at least two circumferential support regions which are spaced apart from one another. Each of these circumferential support regions supports a corresponding seal. Each seal includes an interface member and an activating member. When in place in a rotor section of a submersible pump motor, the seals frictionally engage the inner surface of the stator and exert a centering force against the journal and thus against the bearing sleeve and the power transmission shaft. The seals also exert a force against the inner surface of the stator which prevents rotation of the journal when the power transmission shaft is rotating.
Owner:CAMCO INT
Bearing systems for high-speed rotating machinery
InactiveUS20080087018A1Improve performanceMaintain integrityRolling contact bearingsShaftsBall bearingTurbocharger
Bearing systems for high speed rotating shafts, such as turbocharger shafts, include a first ball bearing in one end of an elongated cylinder capable of carrying axial thrust in both directions and a second ball bearing in the opposite end of the elongated cylinder with its outer race slideably mounted in the cylinder against the biasing force of a preload spring. The second ball bearing is free to move axial with the shaft upon axially expansion of the shaft when exposed to high temperature. The inner races of the ball bearings are clamped to and rotate with the shaft as part of the rotating assembly.
Owner:DELGADO LAUREN N
Bearing Assemblies, Bearing Apparatuses Using the Same, and Related Methods
Various embodiments relate to bearing assemblies configured to enable removal and replacement of superhard bearing elements, and bearing apparatuses that may utilize such bearing assemblies. The disclosed bearing assemblies may be used in a number of applications, such as downhole motors in subterranean drilling systems, directional drilling systems, roller-cone drill bits, and many other applications. In an embodiment, a bearing assembly includes a support ring and a retention ring assembled with the support ring. The retention ring includes a plurality of through holes. The bearing assembly further includes a plurality of superhard bearing elements, with each superhard bearing element inserted partially through and projecting from a corresponding one of the through holes of the retention ring. The retention ring and each superhard bearing element are collectively configured to restrict displacement of each superhard bearing element beyond a selected position in a direction away from the support ring.
Owner:US SYNTHETIC CORP
Compliant hybrid gas journal bearing using integral wire mesh dampers
A compliant hybrid gas journal bearing includes compliant hybrid bearing pads having a hydrostatic recess and a capillary restrictor for providing a flow of pressurized gas to the bearing. The bearing also includes an inner rim adjacent the bearing pads, an outer rim and a damper bridge between the inner and outer rims. The damper bridge has an axial length that is less than an axial length of the bearing pads and the outer rim to form a damper cavity on each side of the damper bridge. An integral wire mesh damper is situated within the damper cavity on each side of the damper bridge. Integral centering springs are located between the inner and outer rims to provide radial and rotational compliance to the bearing pads. The oil-free bearing design addresses the low damping and low load capacity characteristics that are inherent in present day compliant air foil bearing designs, while retaining the compliance to changes in rotor geometry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compliant hybrid gas journal bearing using integral wire mesh dampers
A compliant hybrid gas journal bearing includes compliant hybrid bearing pads having a hydrostatic recess and a capillary restrictor for providing a flow of pressurized gas to the bearing. The bearing also includes an inner rim adjacent the bearing pads, an outer rim and a damper bridge between the inner and outer rims. The damper bridge has an axial length that is less than an axial length of the bearing pads and the outer rim to form a damper cavity on each side of the damper bridge. An integral wire mesh damper is situated within the damper cavity on each side of the damper bridge. Integral centering springs are located between the inner and outer rims to provide radial and rotational compliance to the bearing pads. The oil-free bearing design addresses the low damping and low load capacity characteristics that are inherent in present day compliant air foil bearing designs, while retaining the compliance to changes in rotor geometry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
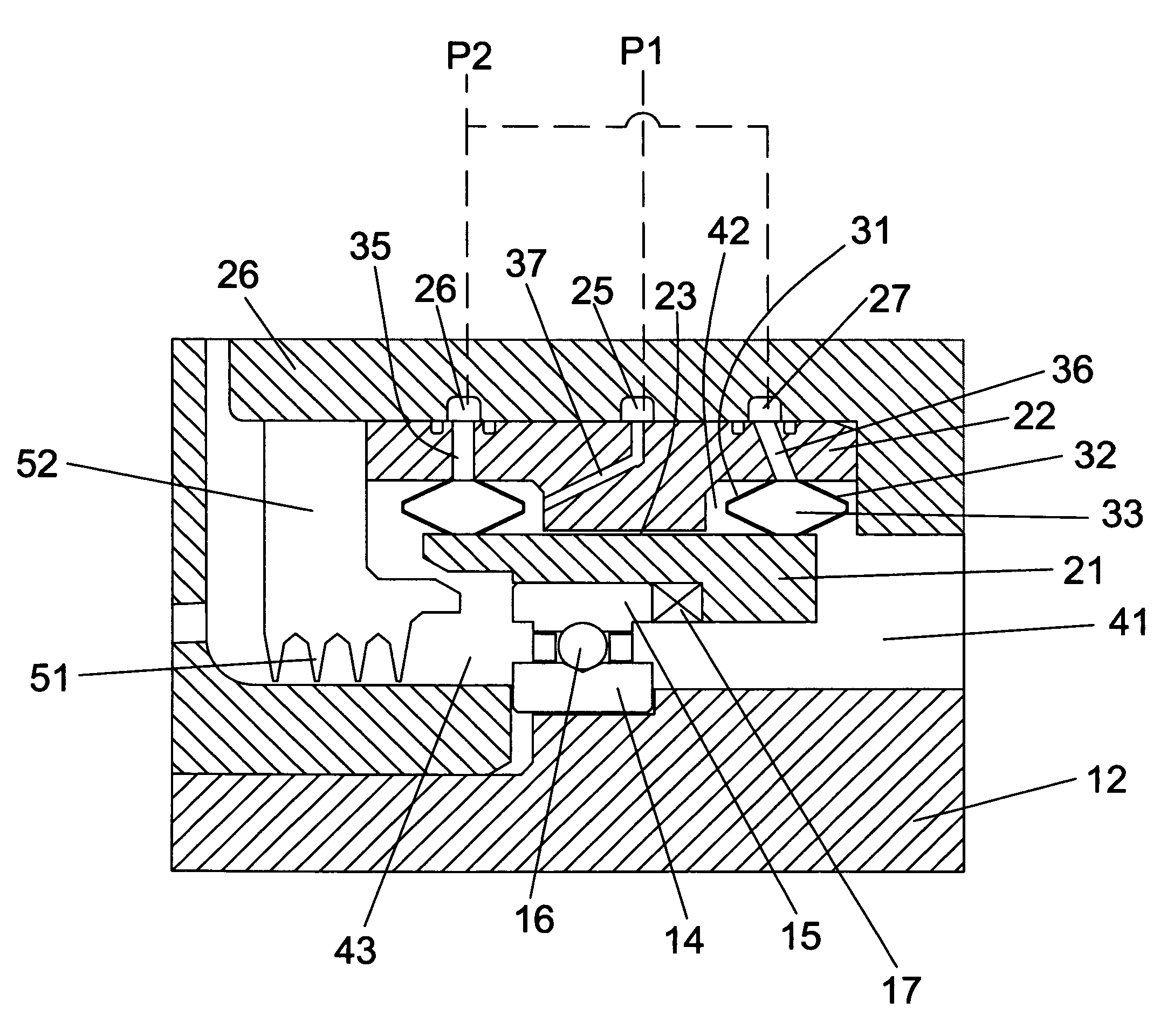
Squeeze film damper with variable support stiffness
A squeeze film damper assembly having a variable stiffness and damping control. The squeeze film damper includes a damper chamber formed by two flexible bellows chambers of the sides. A first pressure source is applied to the damper chamber to regulate the damping. A second pressure source is applied to the flexible bellows chambers to vary the stiffness of the damper. The flexible bellows chambers are secured between an outer member and an inner member of the damper assembly and form the sealed damper chamber. A pressure ratio between the bellows chambers and the damper chamber can vary to control the stiffness of the squeeze film damper.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
Mounting assembly
ActiveUS20080199254A1Less sensitiveEasy to controlRecord information storagePivotal connectionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
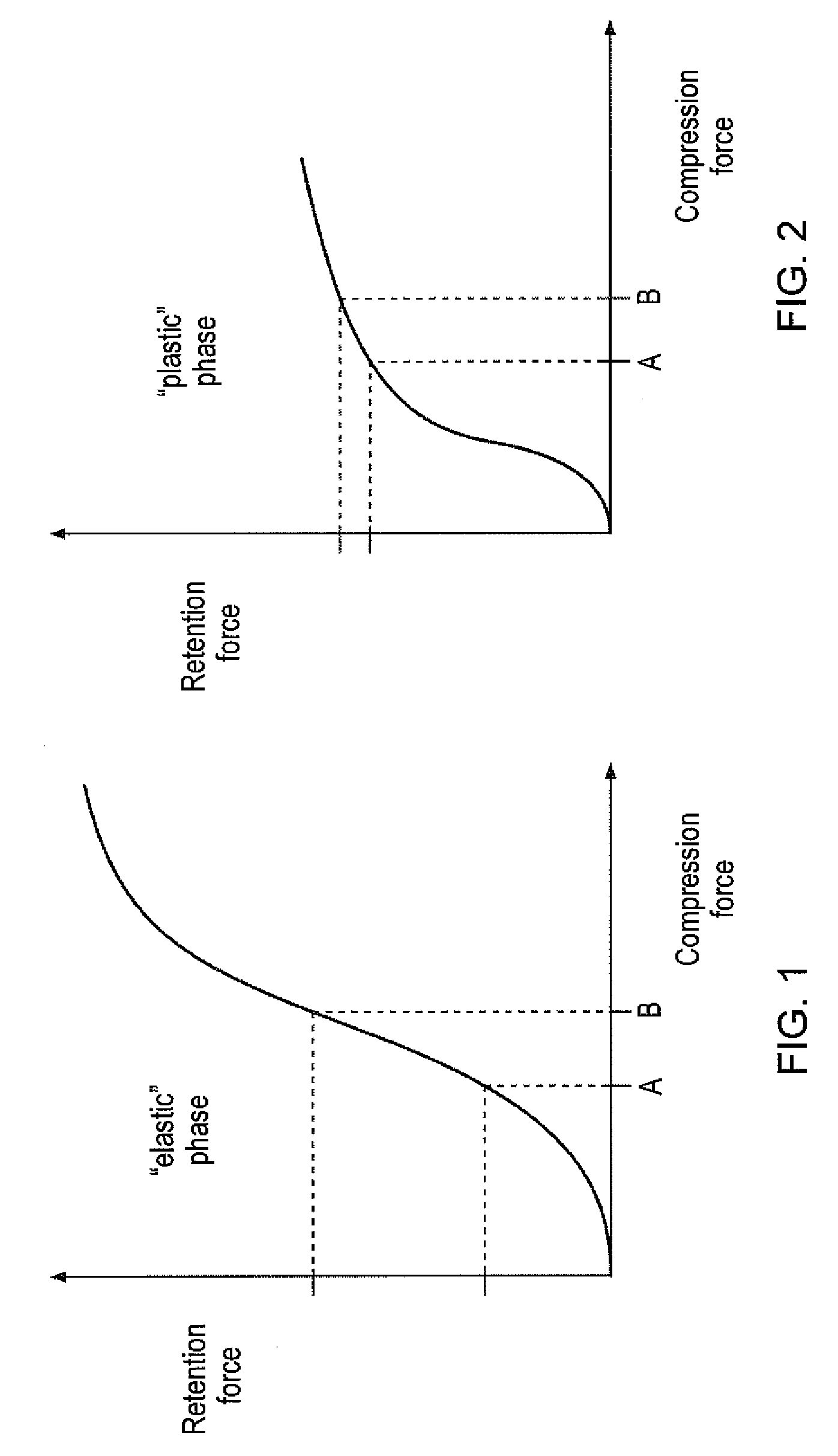
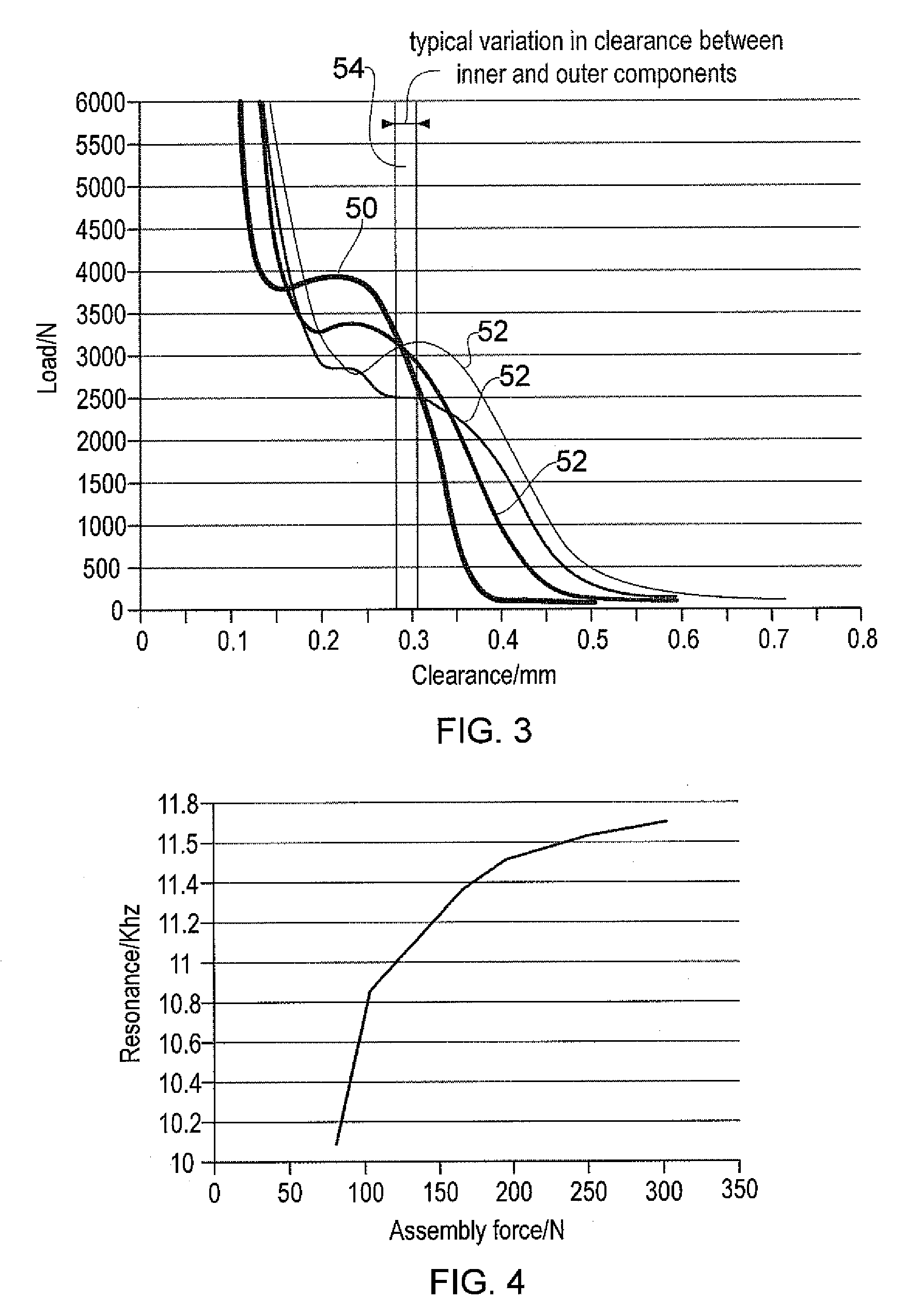
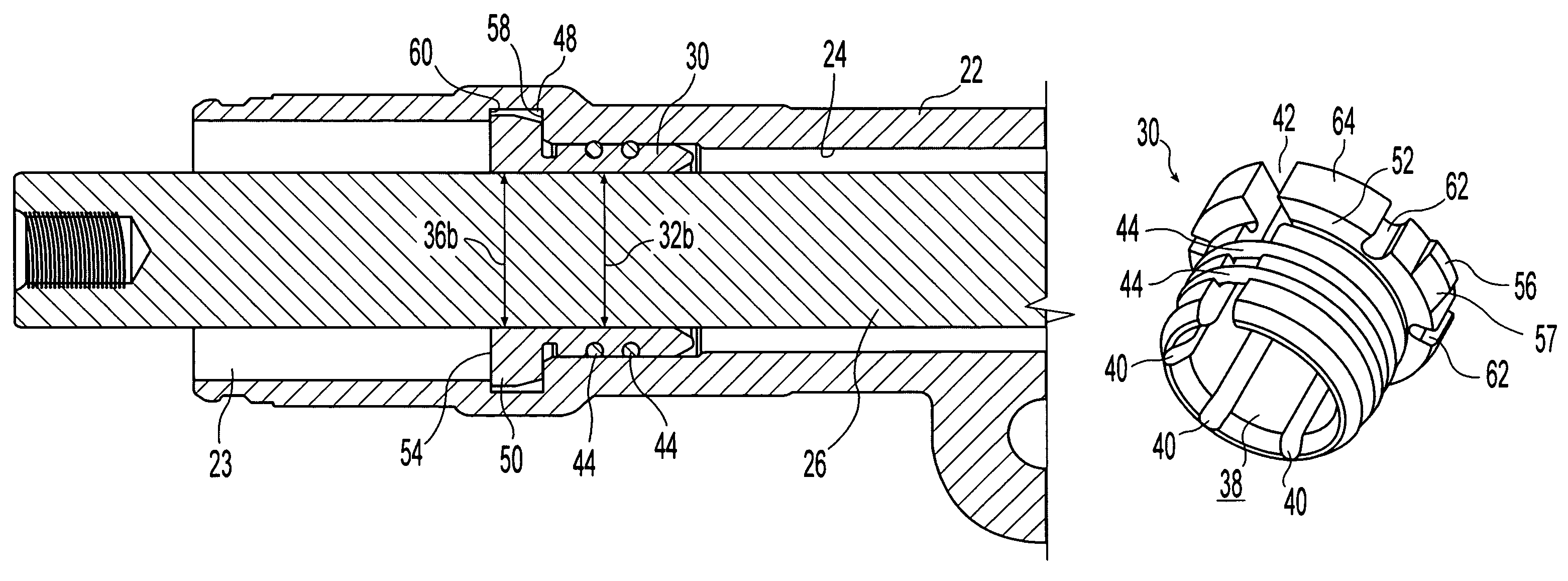
A mounting assembly comprising mating inner and outer components (36, 38) mounted together using a tolerance (20) is disclosed. The tolerance ring (20) has radially extending projections (28) that are configured to cause the tolerance ring (20) to operate into the plastic phase of its compression force / retention force characteristic. This can be achieved by using softer projections than those found in conventional tolerance rings. The force required to mount the tolerance ring and a range of retention forces exhibited by it for a given variance in sizes of mating components is thereby stabilised.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS RENCOL
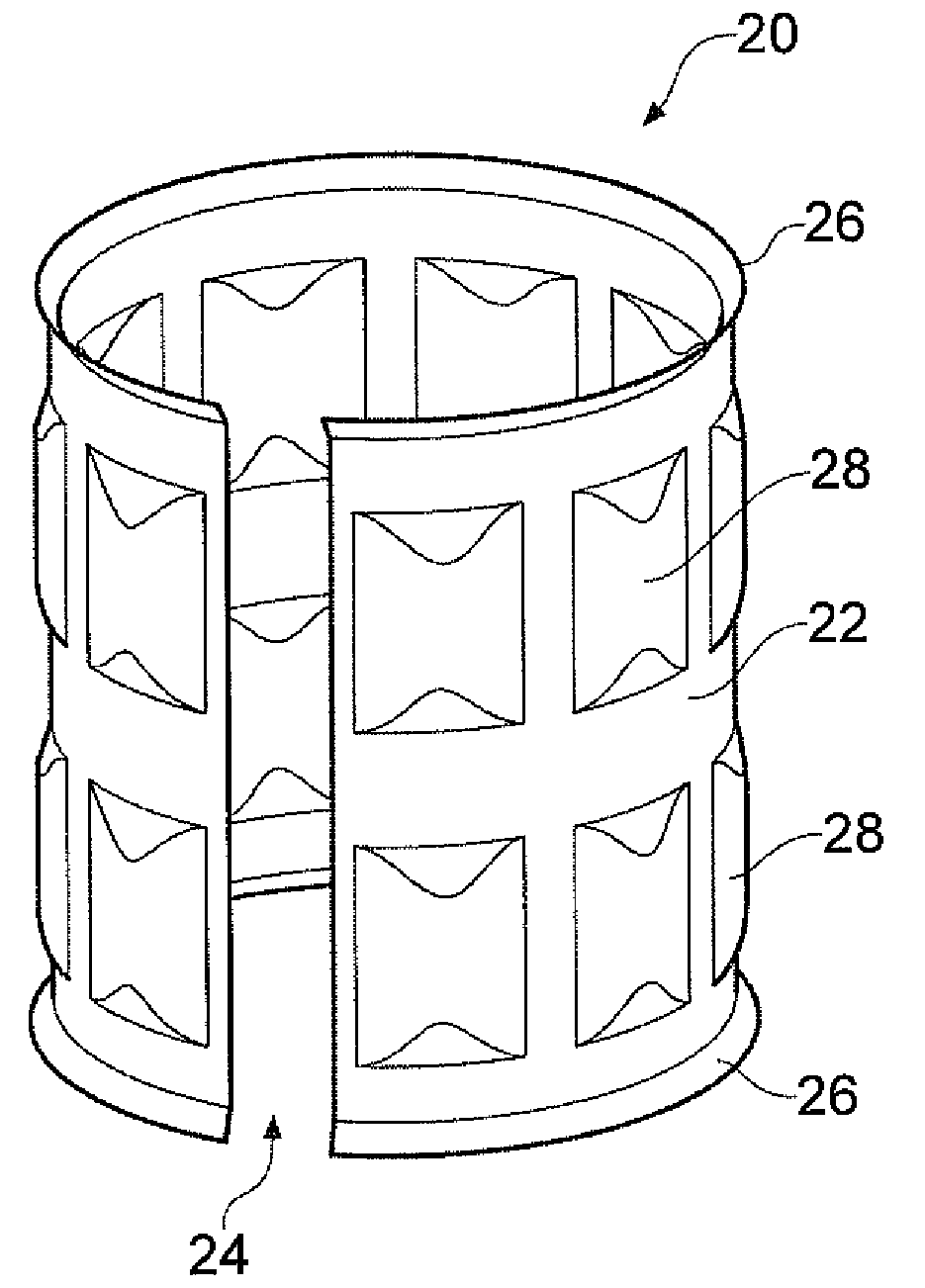
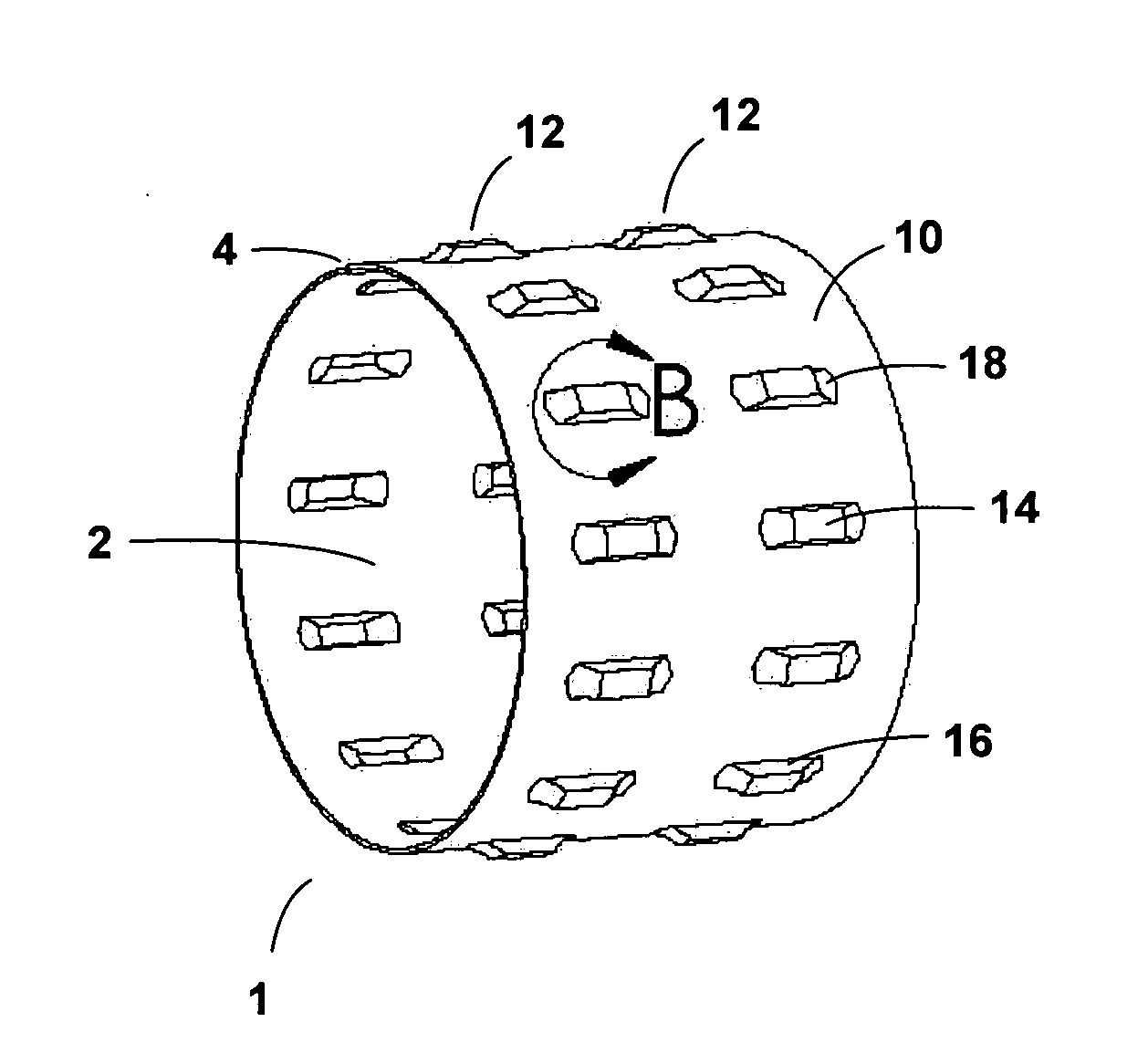
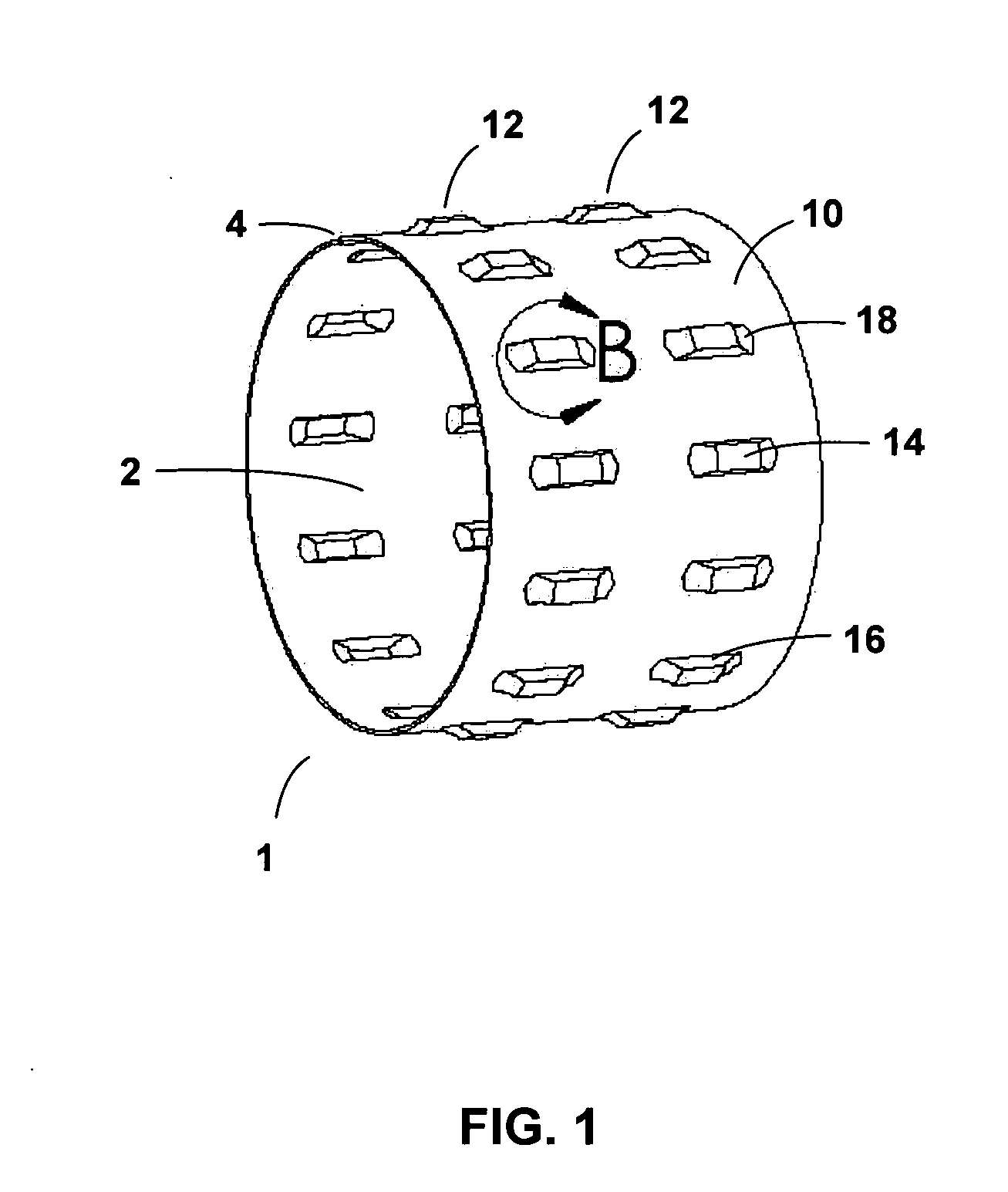
Tolerance ring having variable height and/or assymmetrically located bumps
A tolerance ring configured to reduce torque ripple for a pivot bearing in an actuator arm assembly. The tolerance ring comprises a cylinder having a predetermined length, and a first and a second row of contacting portions arranged around the surface of the cylinder, the contacting portions of the second row are circumferentially displaced with respect to the first row by a distance greater than zero but less than the distance of the contacting portion and the spacing between adjacent contacting portions in the first row.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
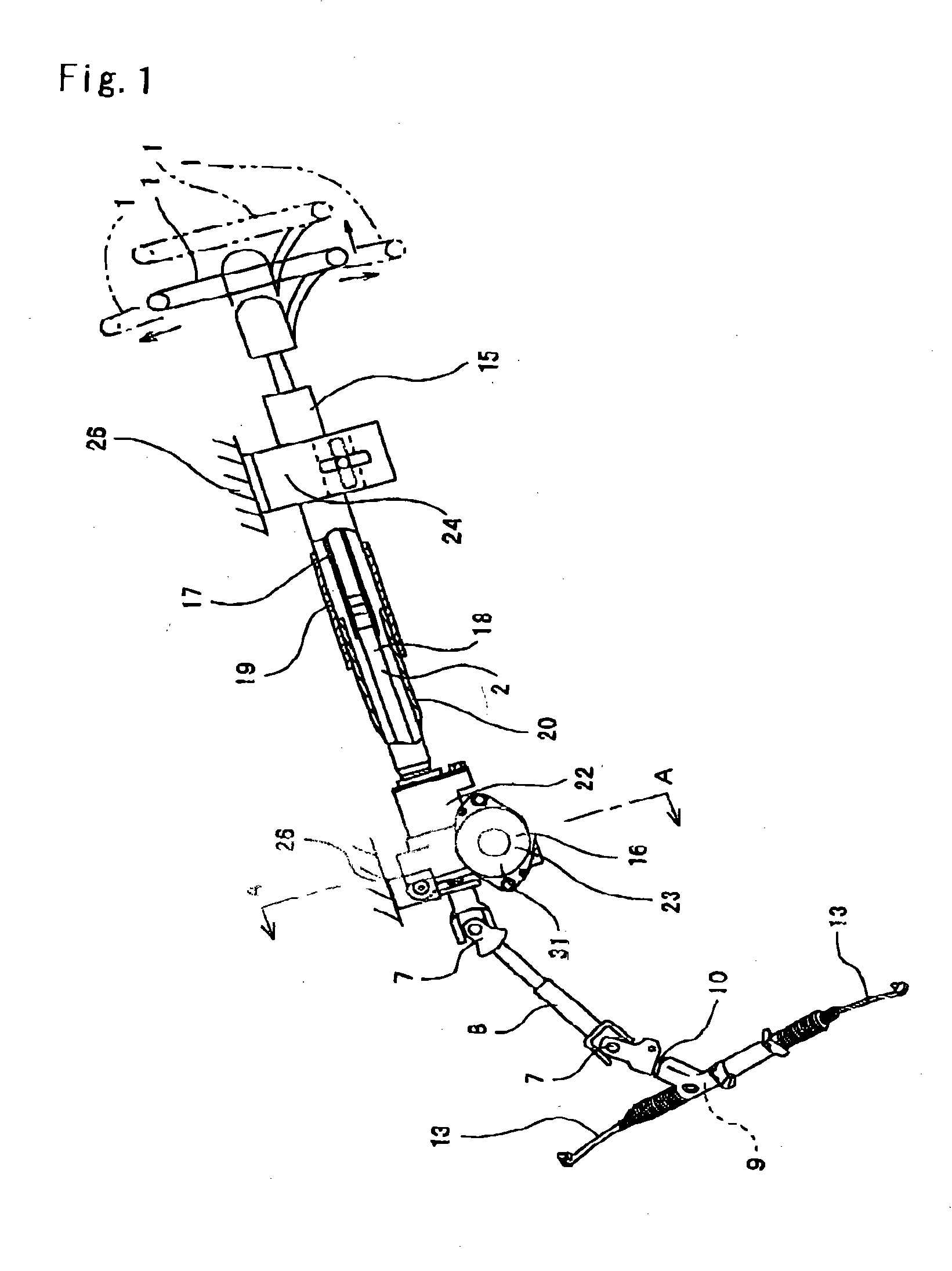
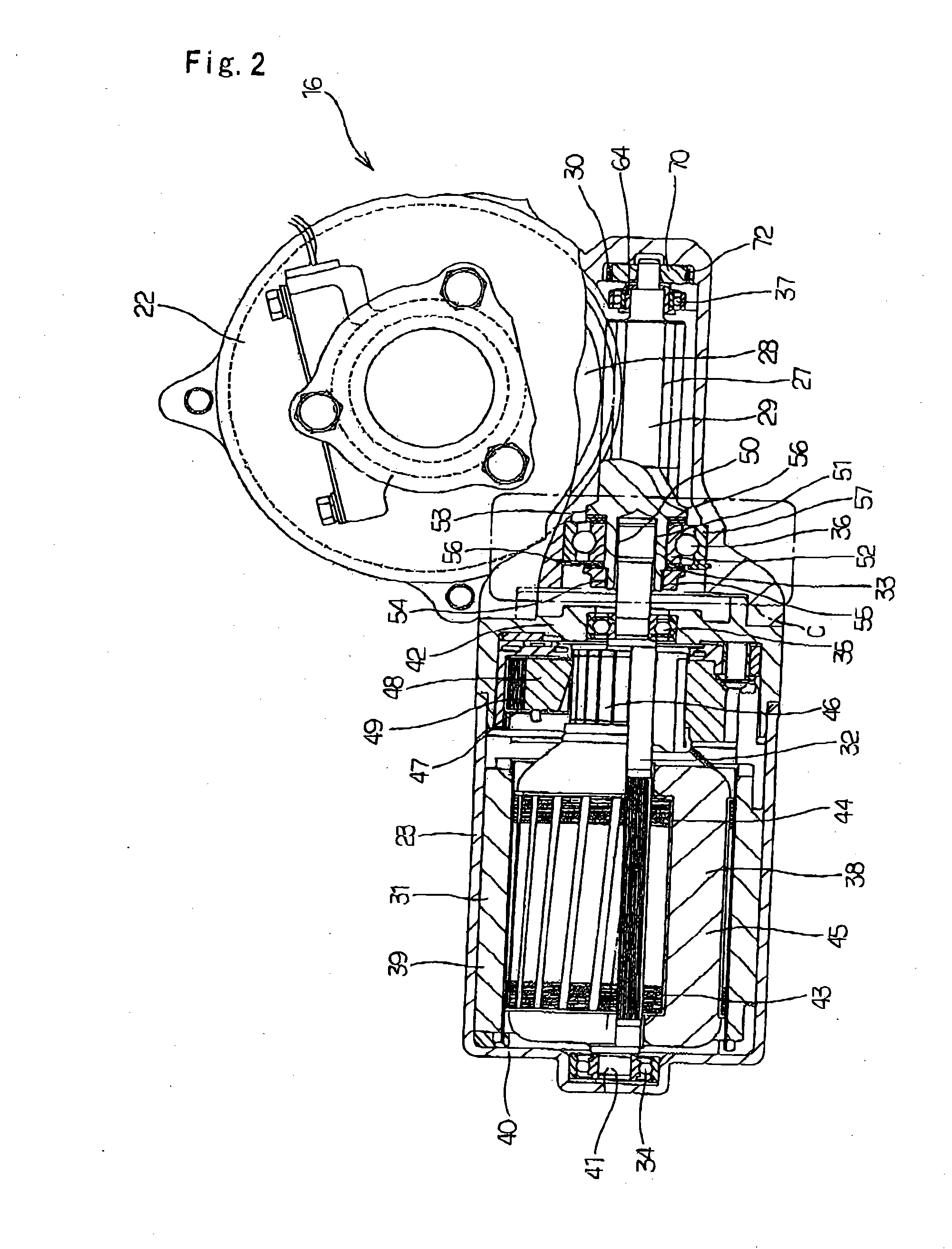
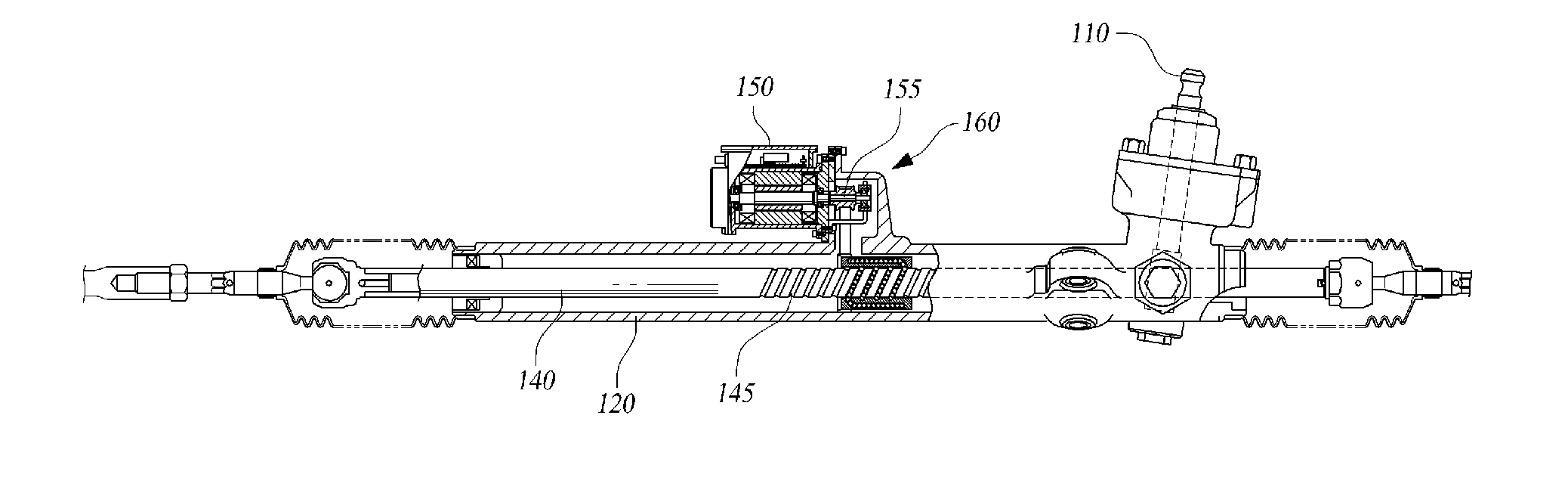
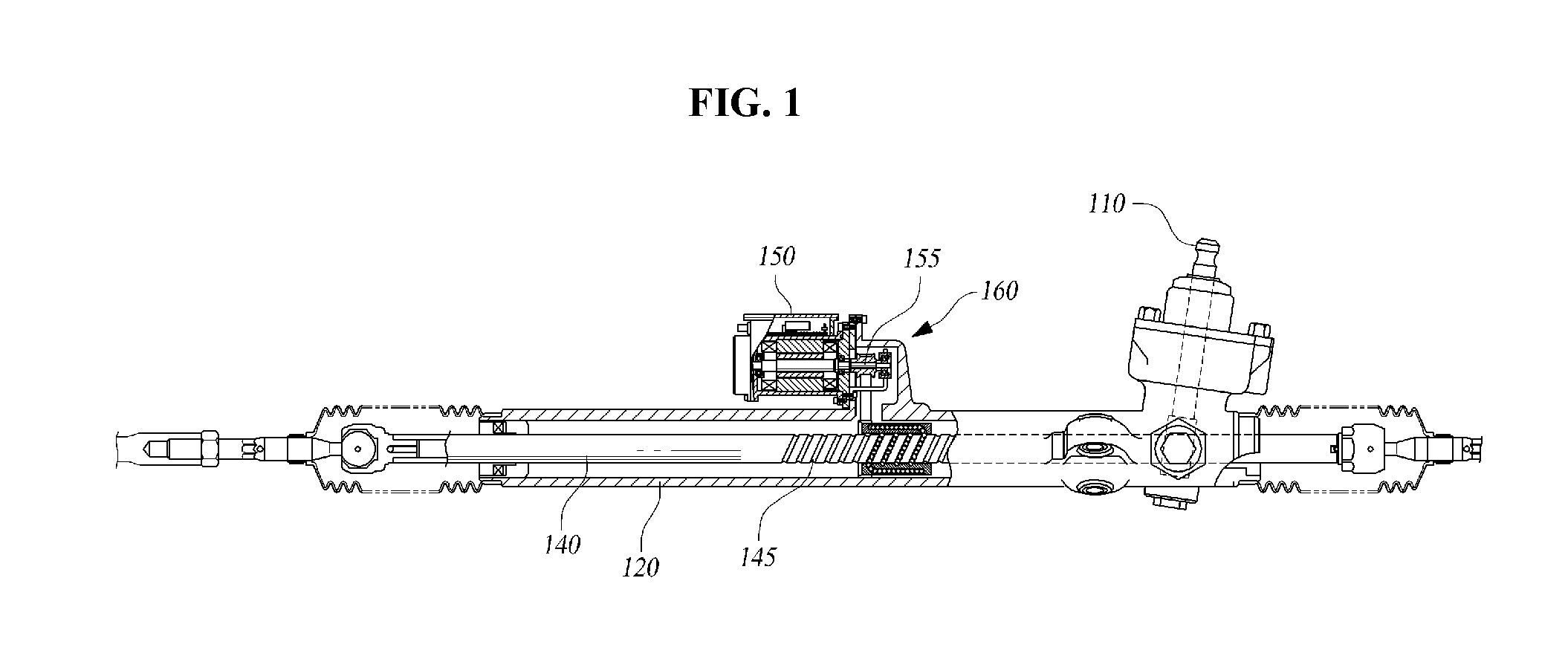
Electric-powered power steering apparatus
InactiveUS20040163879A1InhibitionCheap constructionControlling membersGearboxesElectric power steeringCoil spring
An assist apparatus for electric-powered power steering apparatus is provided to have a torque sensor, steering shaft, preload pad 70, a torsion coil spring 30, and an electric motor 31. With the preload pad 70 and torsion coil spring 30, an elastic force is applied to the worm shaft 29 in the direction toward the worm wheel 28, whereby noises due to colliding teeth are prevented from occurring in the meshing portion between the worm wheel 28 and worm shaft 29.
Owner:NSK LTD
Tolerance ring with debris-reducing profile
A tolerance ring for applications requiring cleanliness has contacting portions having a novel profile that reduces debris generation during installation of the tolerance ring while still providing adequate stiffness after installation. The tolerance ring is suitable for cylindrical interface applications where both a reduction in debris generation and high interface stiffness are desirable, such as the interface between an actuator pivot bearing and an actuator arm in a magnetic hard disk drive.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
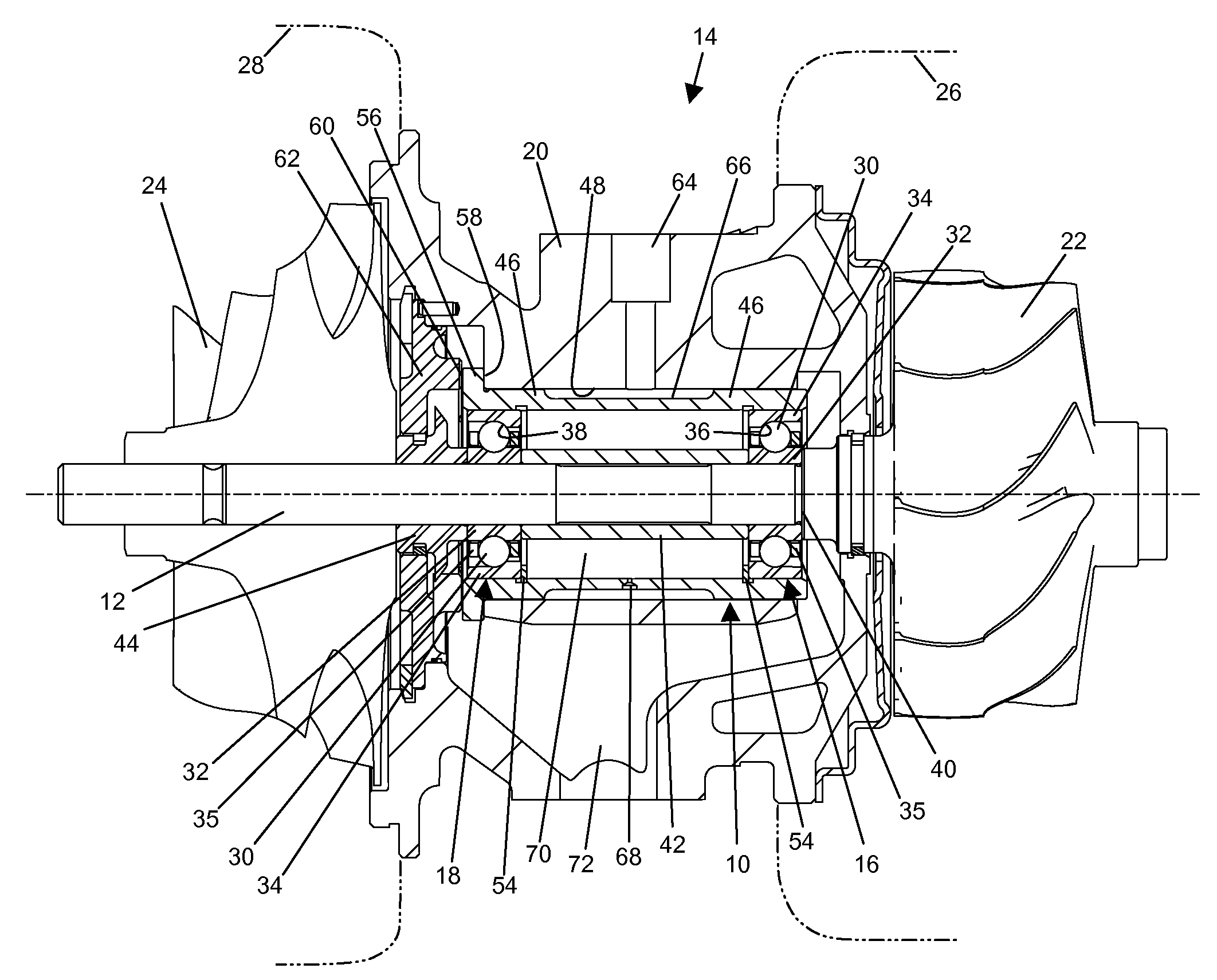
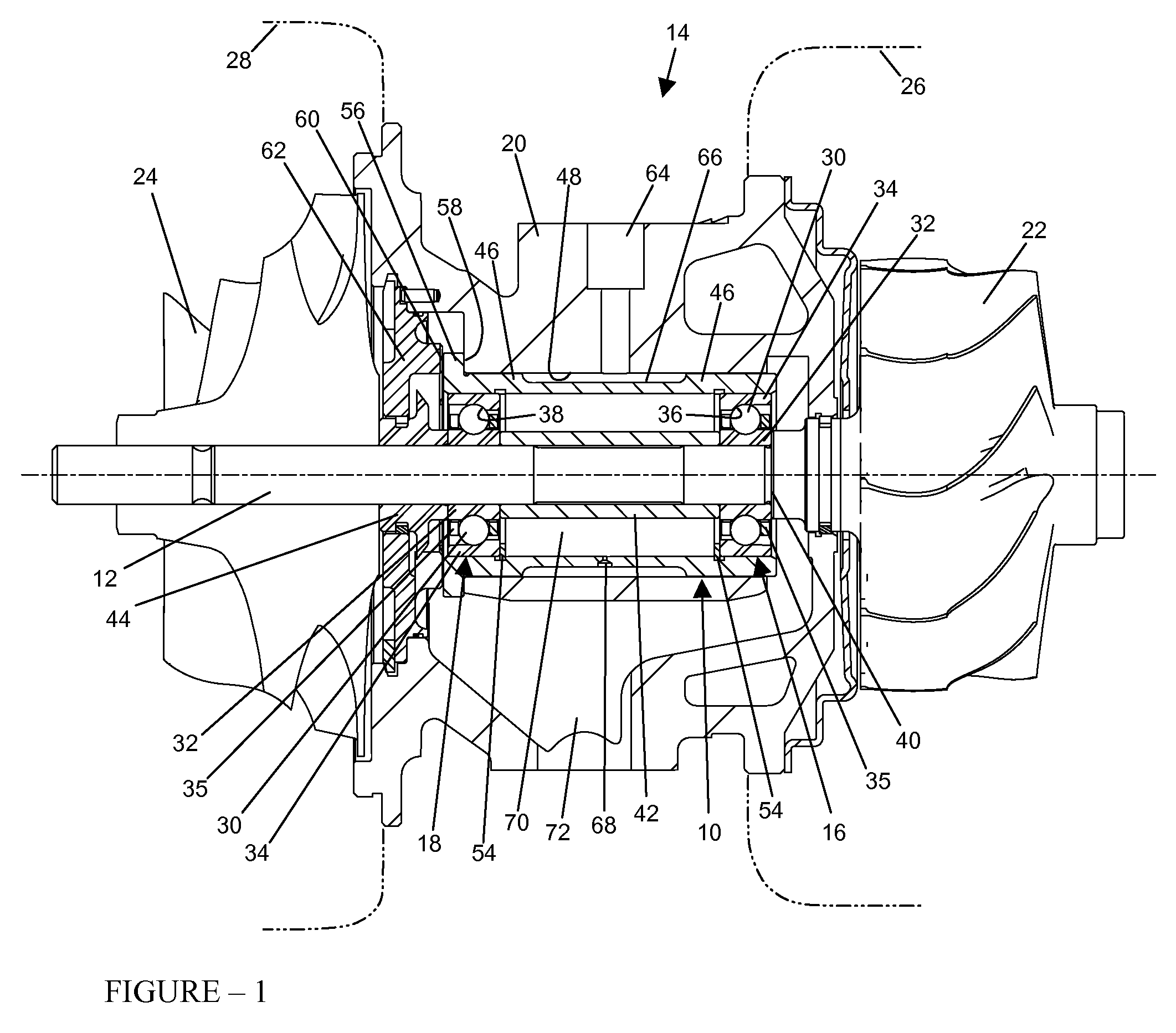
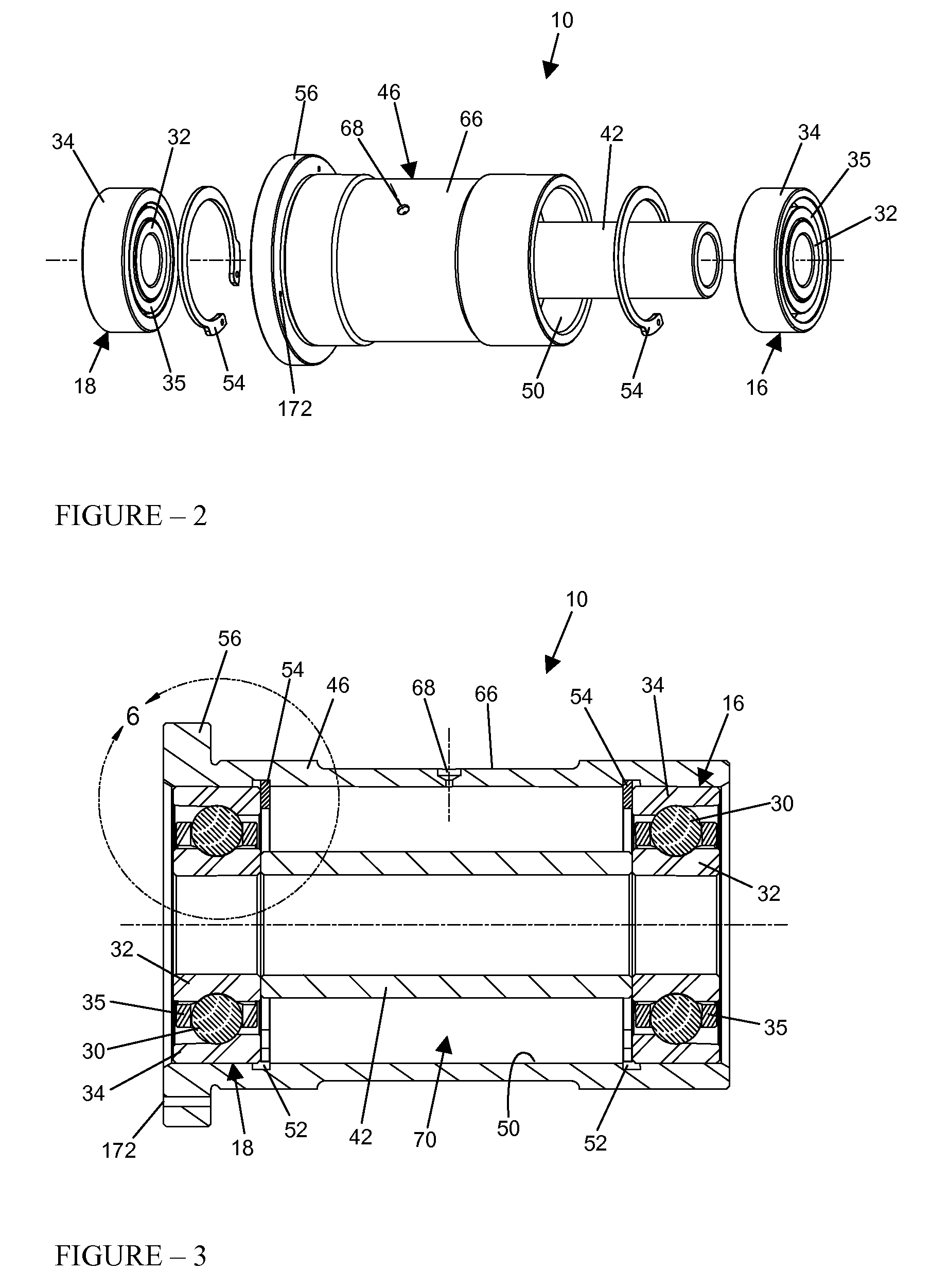
Floating bearing cartridge for a turbocharger shaft
InactiveUS20080019629A1Conducive to stable operationReduced and minimal wearRolling contact bearingsShaftsTurbochargerBearing wear
An improved bearing system for use in high speed rotating machinery, such as a turbocharger, wherein a shaft is rotatably supported by a floating bearing cartridge having axially spaced angular contact bearings each with a set of bearing balls supported between inner and outer races. The bearing cartridge includes an inner spacer sleeve for axially spacing the inner bearing races, and a rotationally floating outer sleeve having a pair of radially inwardly open grooves for removably receiving snap-type retaining rings which engage and axially space the outer bearing races. The axial dimension of the inner spacer sleeve is elongated slightly relative to an axial dimension defined between outboard faces of the installed retaining rings, thereby slightly unloading the sets of bearing balls from their respective outer bearing races. Such slight axial unloading enhances smooth-running operation with minimal bearing wear, while accommodating transient loads during operation.
Owner:CPI HLDG
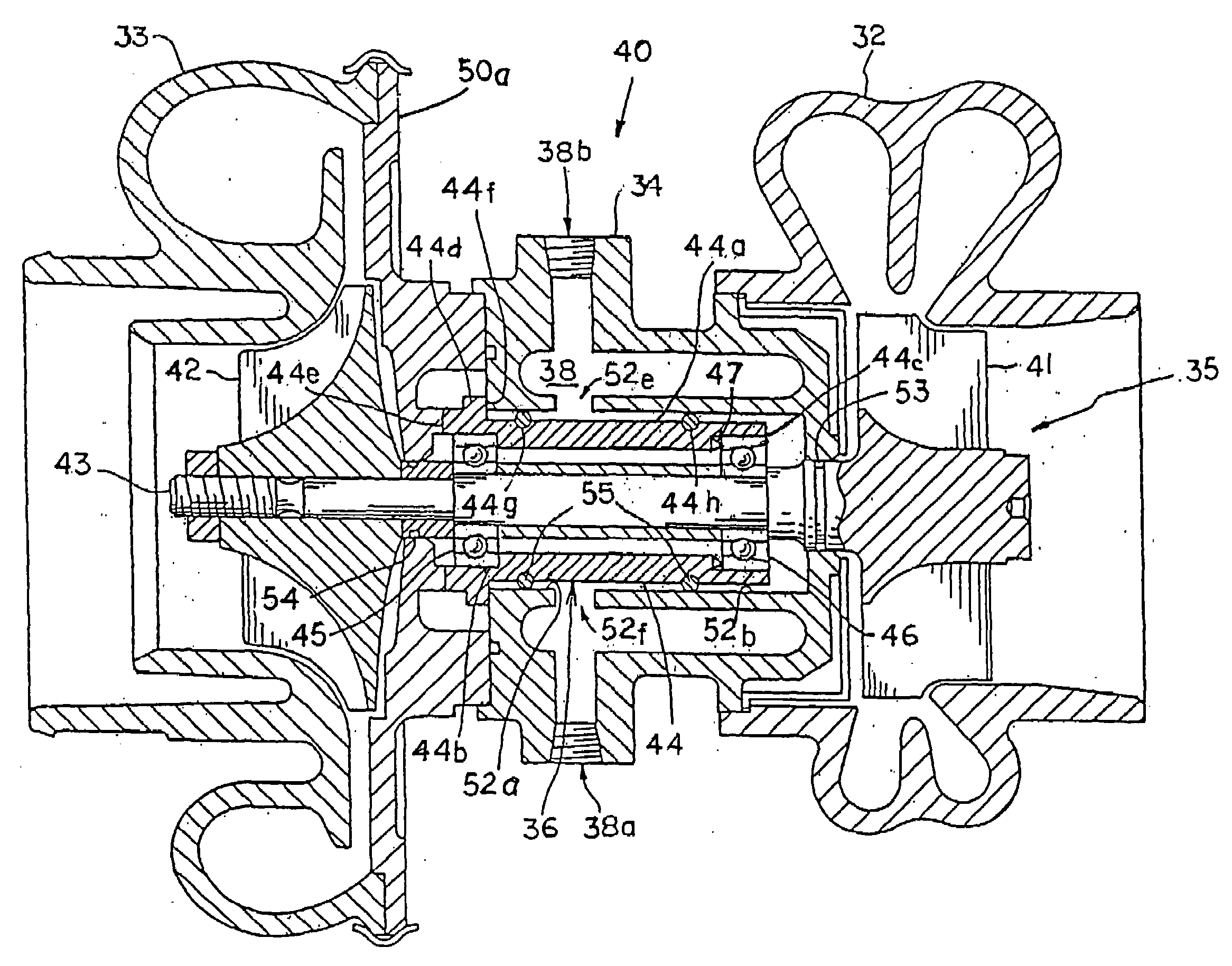
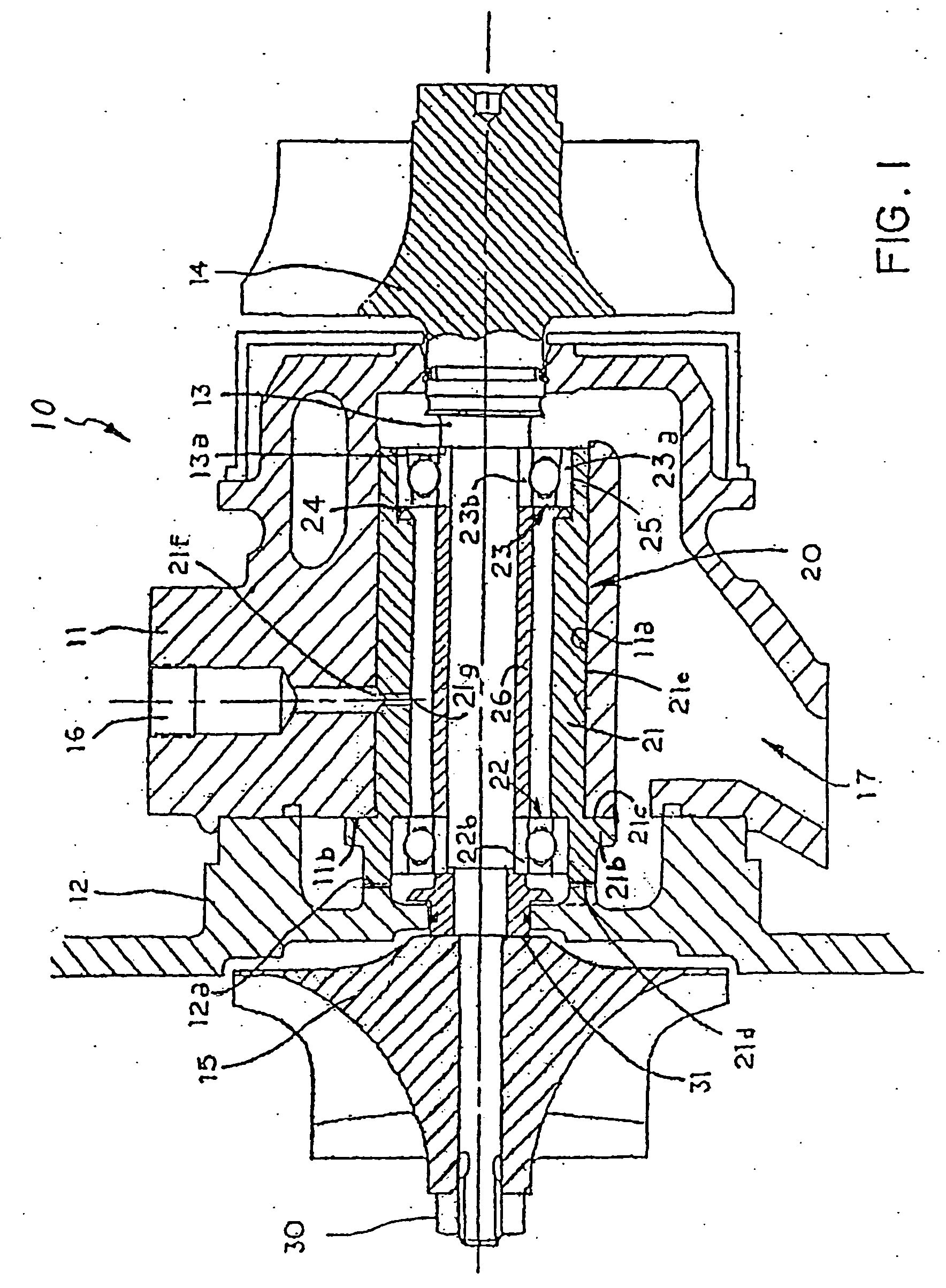
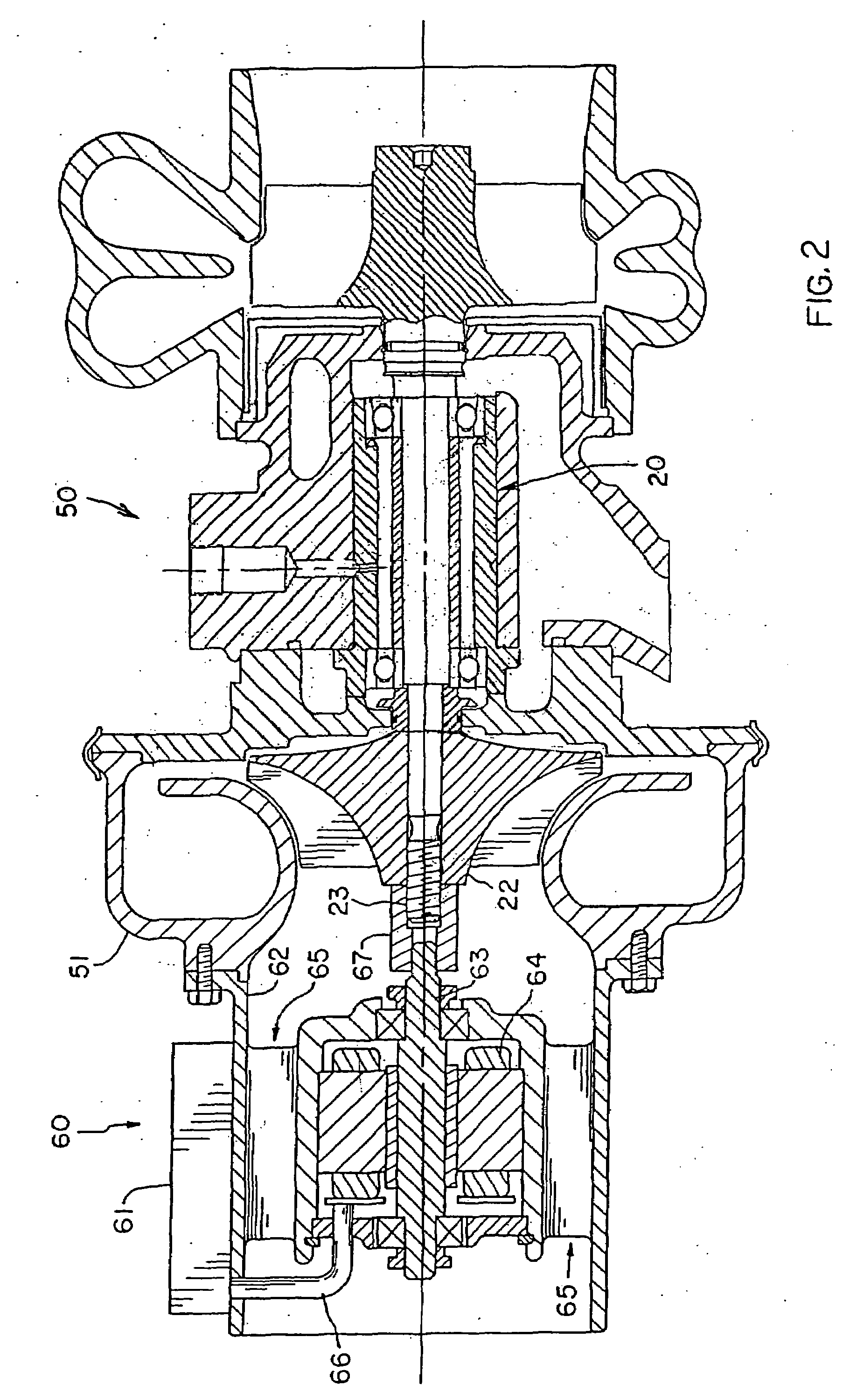
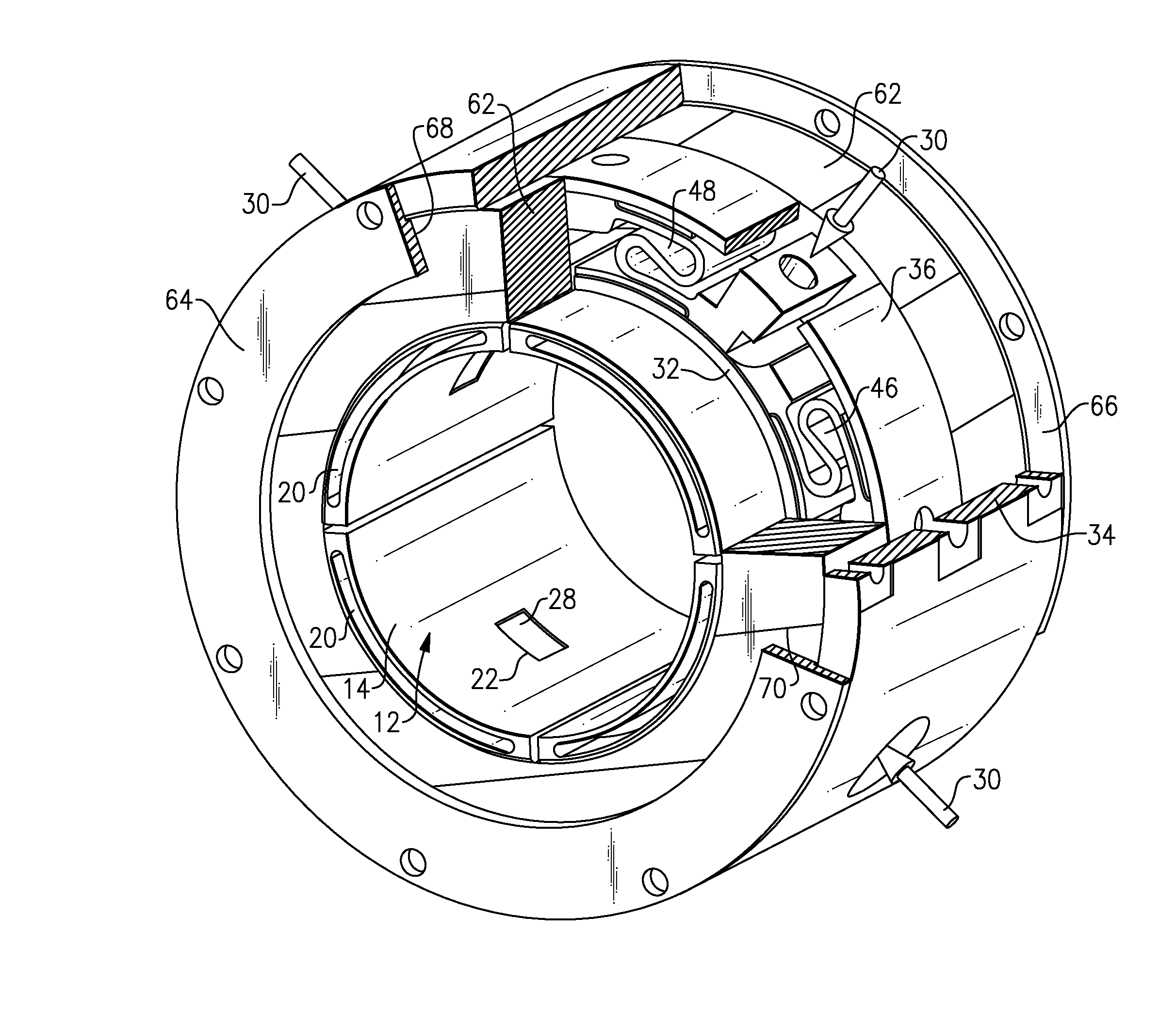
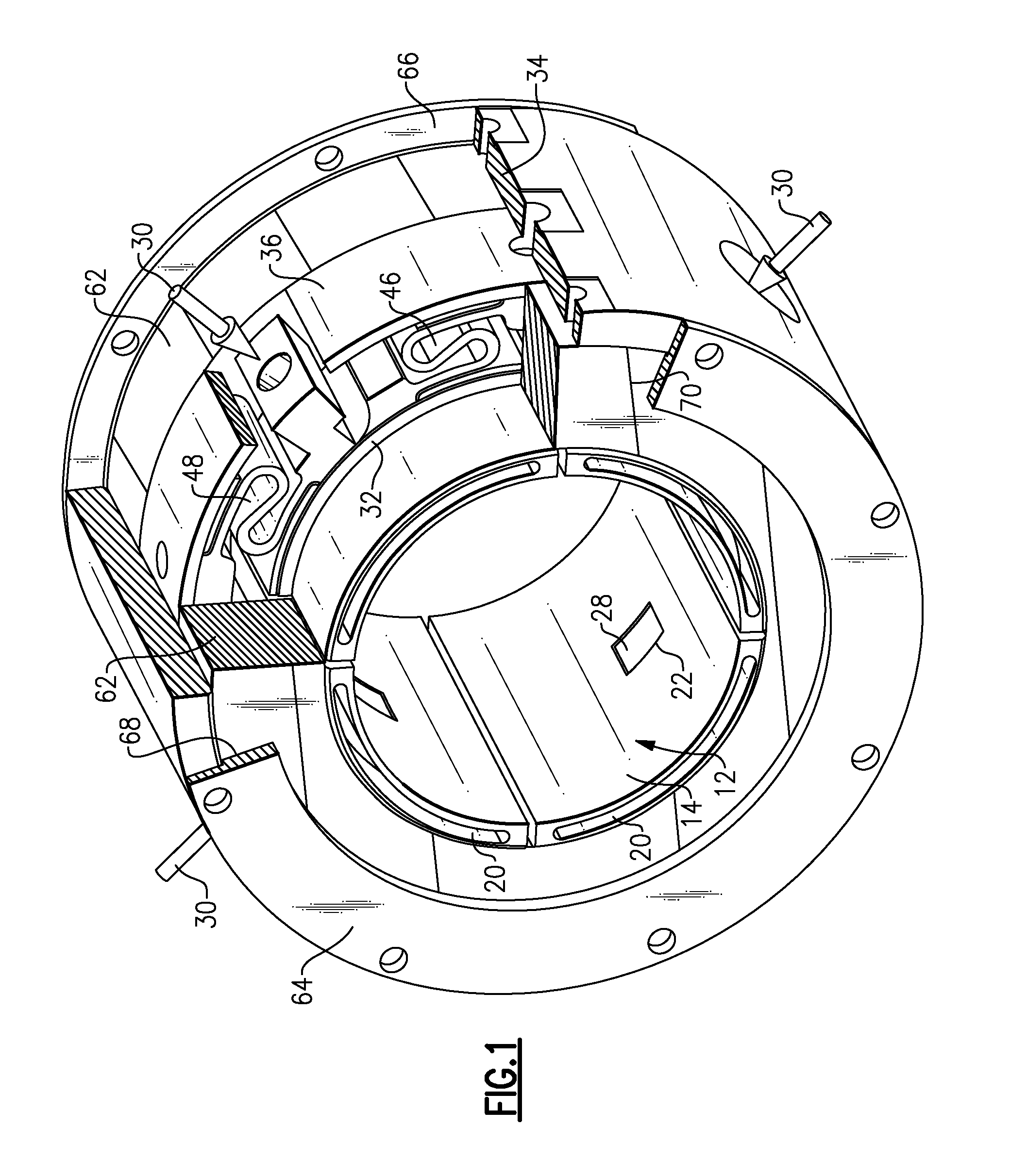
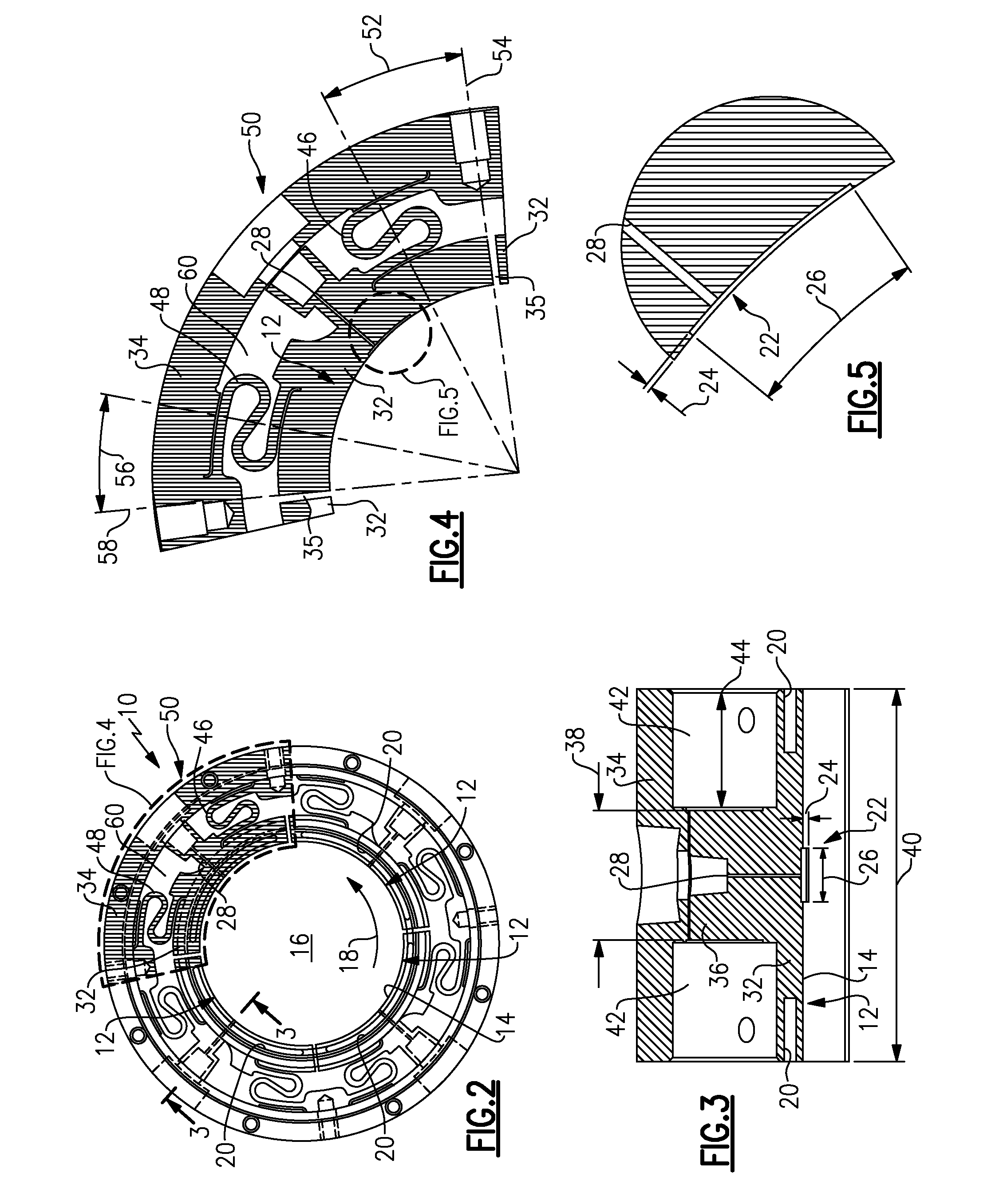
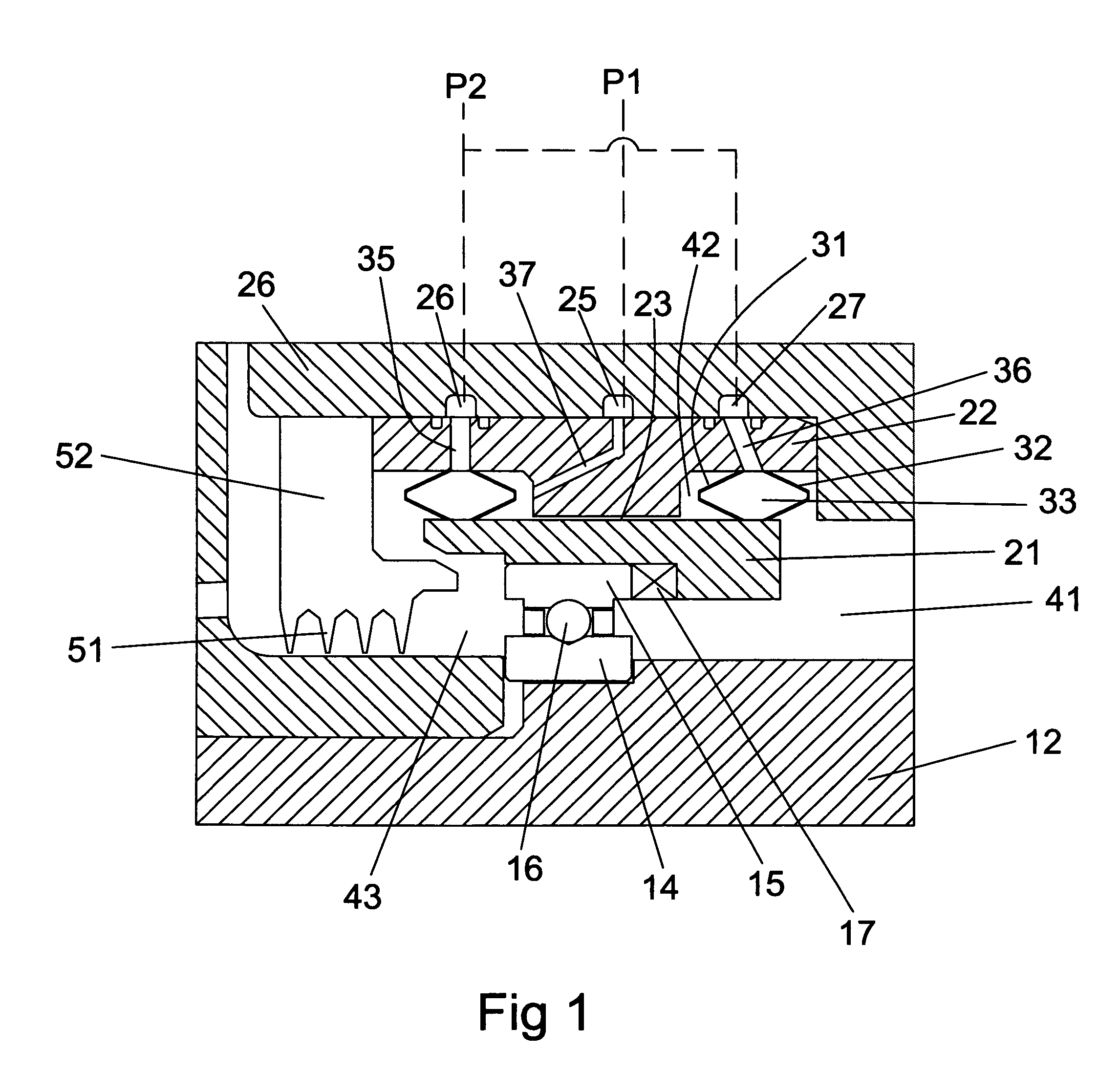
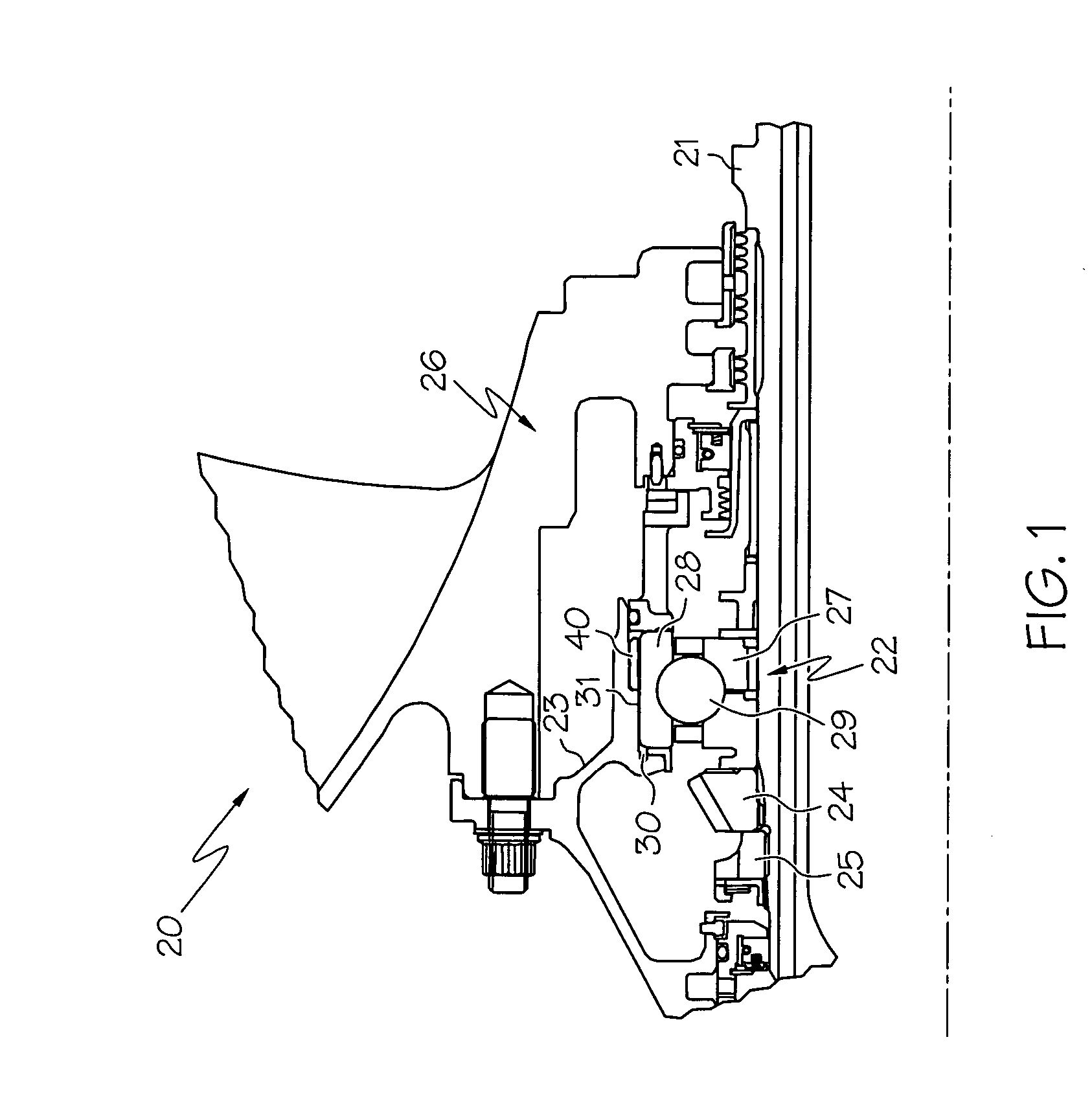
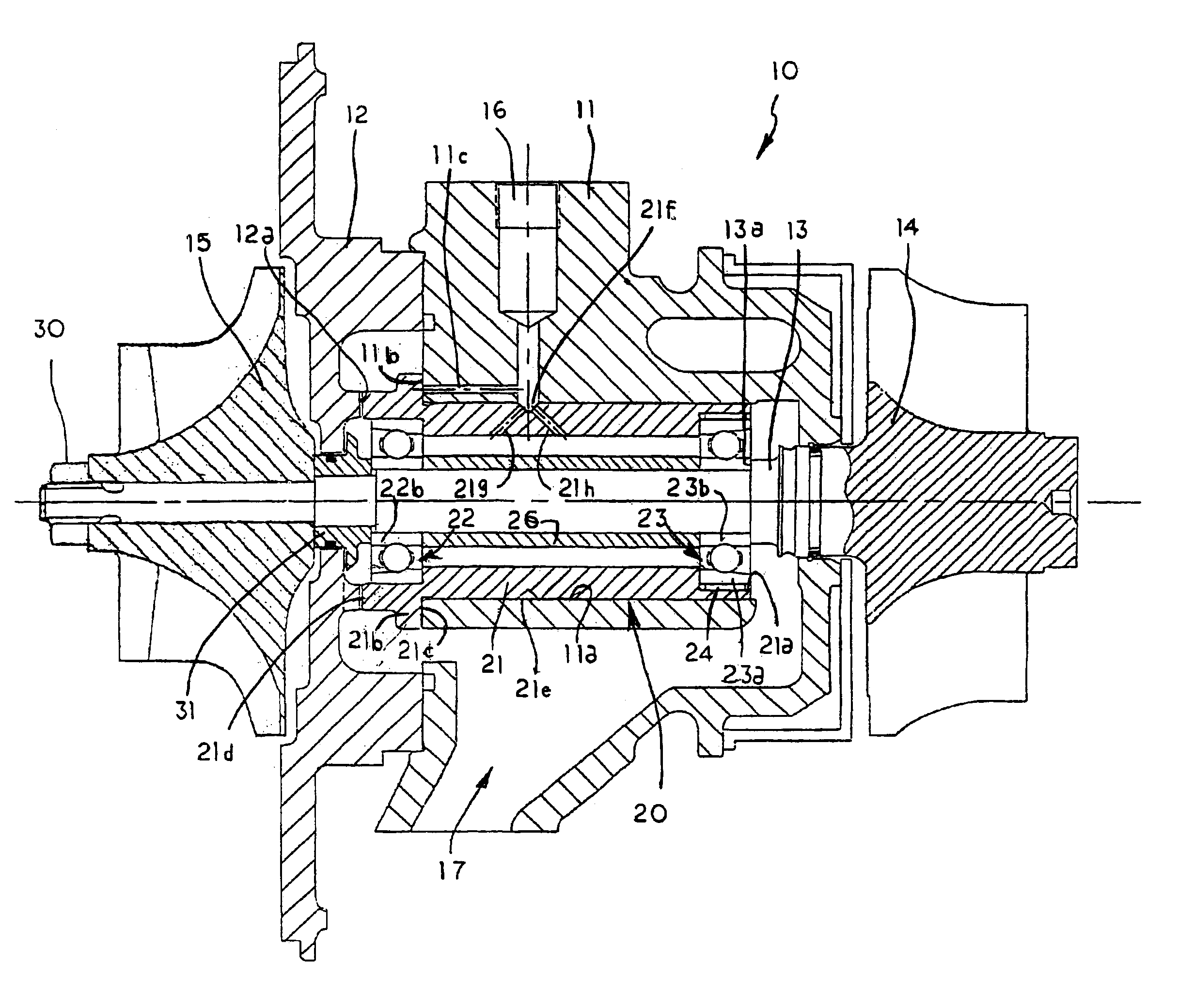
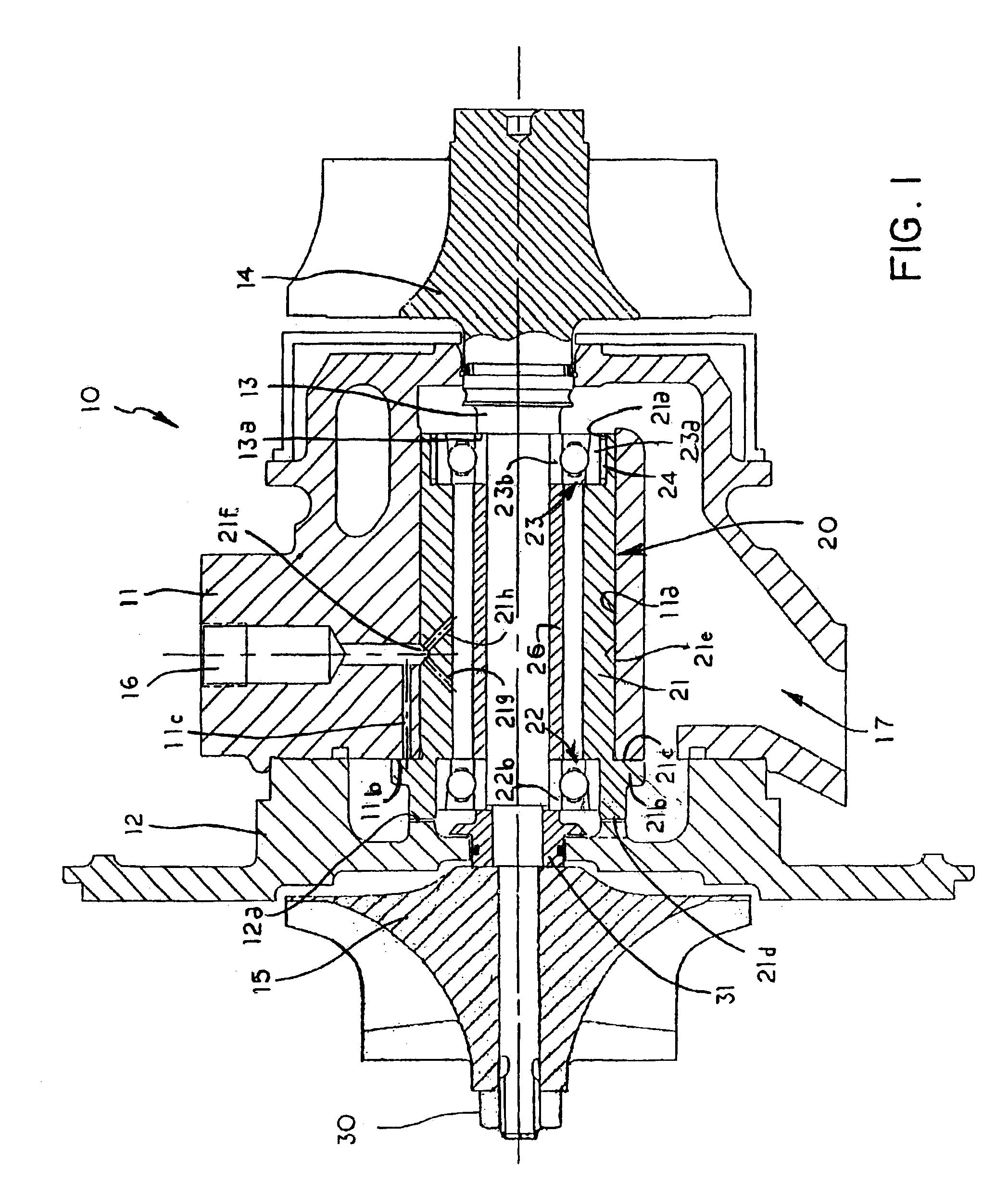
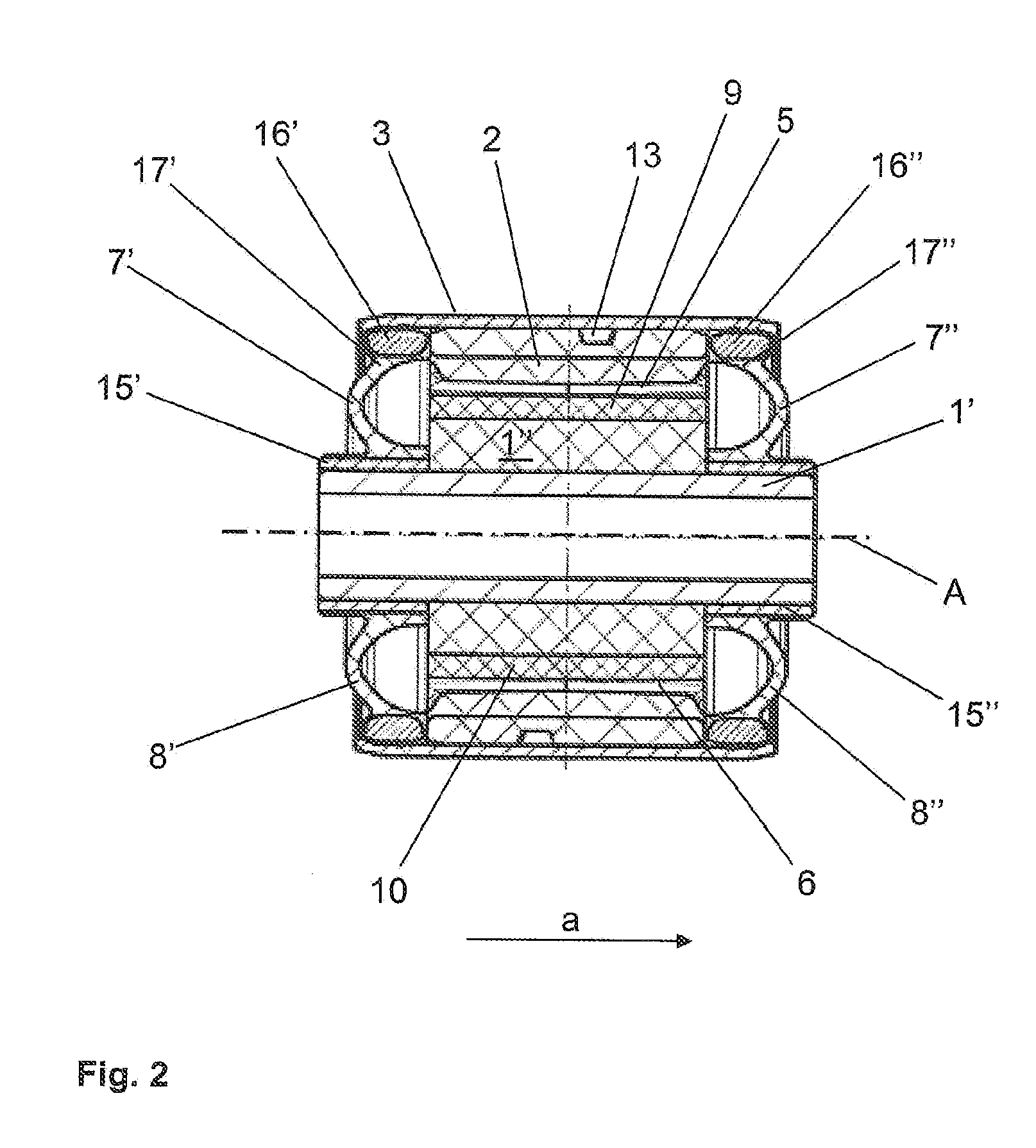
Bearing assembly and centering support structure therefor
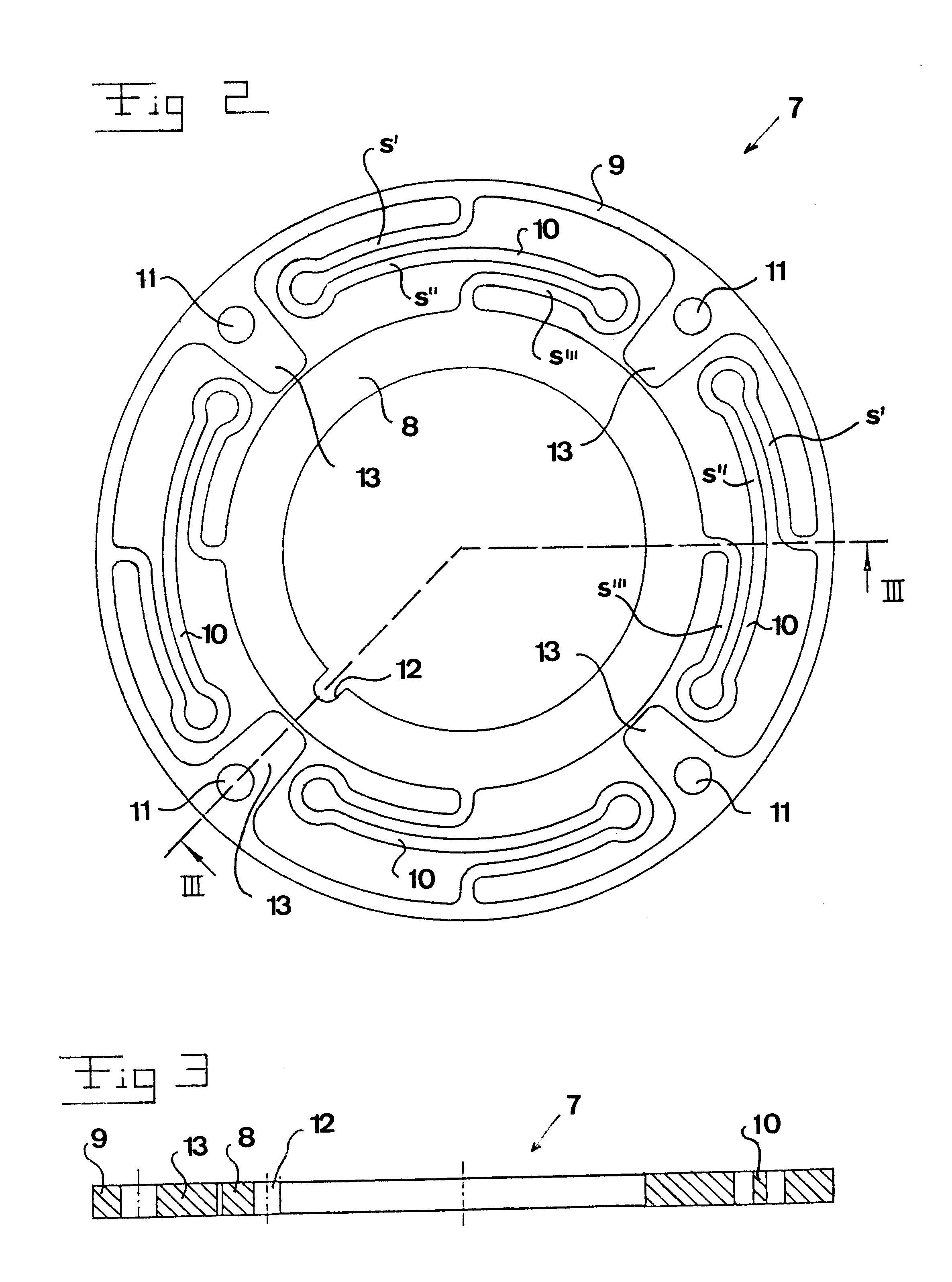
The bearing assembly includes an annular bearing in which the shaft is disposed and a support structure for supporting the bearing. The bearing support is mounted about and radially supports the bearing. The bearing support at least in part defines a squeeze film annulus of the bearing assembly. A plurality of centering elements is associated with the bearing and bearing support and act to center the bearing within the squeeze film annulus. The centering elements are provided at radially spaced locations around the bearing. The centering elements may also be cylinder springs provided at uniformly spaced locations around the bearing. The centering elements may additionally be load cell springs provided at uniformly spaced locations around the bearing. In an alternative embodiment, a singular annular wave spring may be provided in place of the plurality of centering elements.
Owner:ELLIOTT CO
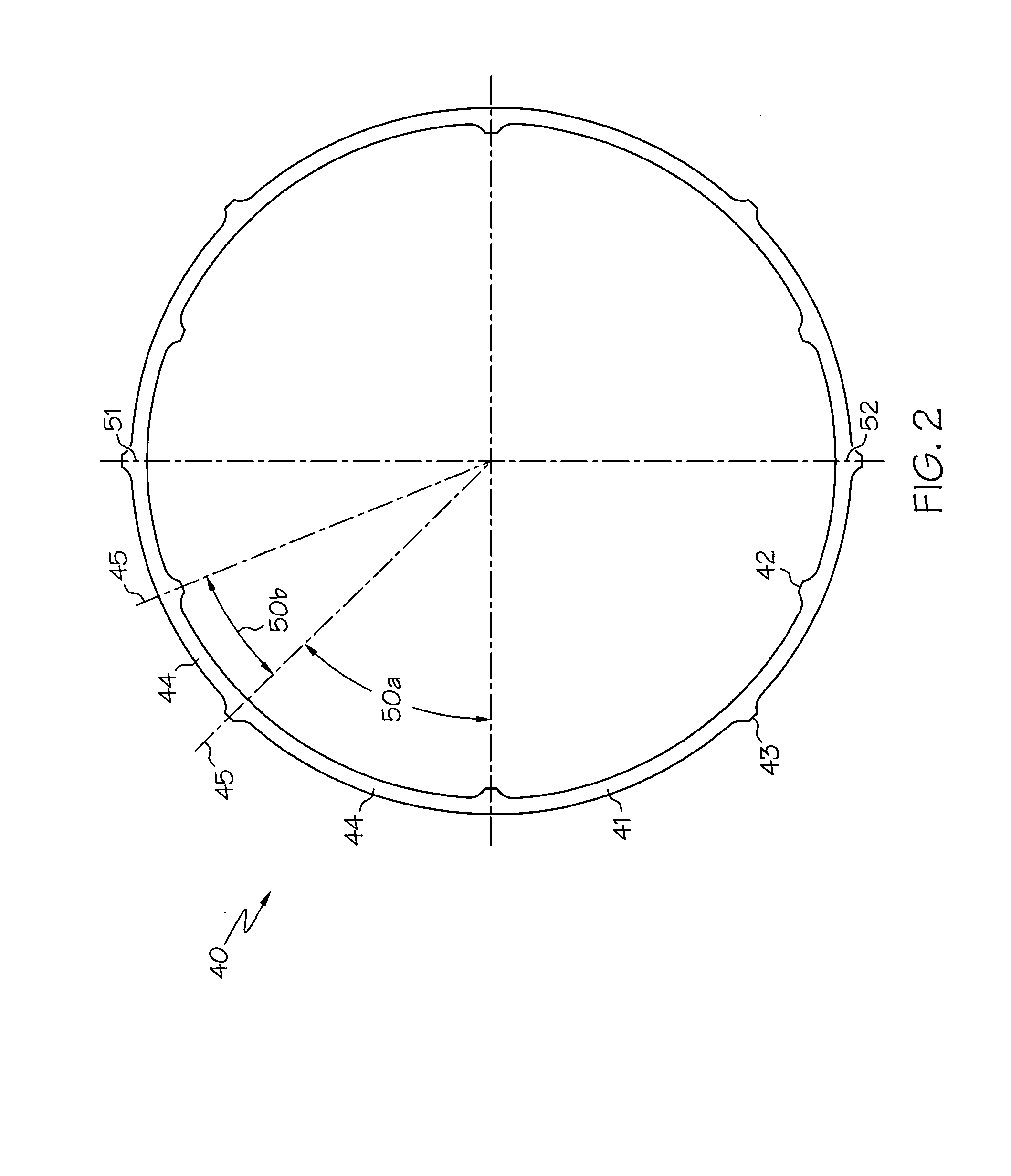
Compact resilient anisotropic support for bearing
InactiveUS20060204153A1Providing some stiffnessEngine manufactureShaftsViscous dampingElastic anisotropy
A support for a bearing comprises a resilient ring having unevenly spaced inner and outer bumpers. The unevenly spaced bumpers provide anisotropy to the rotor to preclude non-synchronous vibration. The inner bumpers can be ground to provide a vertical offset of the rotor centerline to accommodate the deflection due to the rotor weight. A tangential groove in the outer bumper allows oil passage during ring deflection so that oil can be squeezed out under dynamic load, providing additional viscous damping to the rotor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Flexible metal supporting device for a centrifugal separator
InactiveUS6224533B1Simple designSimple structureRolling contact bearingsCentrifugesCentrifuge rotorMetallic materials
A flexible metal support device for a rotatable centrifuge rotor (2) provided in a frame member (1) by a bearing member (4). The support device comprises a support element (7) provided between the bearing member (4) and the frame member (1), and arranged to absorb relative movements between the centrifuge rotor and the frame member. The support element (7) comprises an inner mounting portion, essentially immovable in relation to the bearing member (4), and an outer mounting portion, essentially immovable in relation to the frame member (1). Moreover, the support element (7) comprises three flexible connecting portions which each extends between the inner and outer mounting portions and is arranged to absorb radial and axial relative movements between the centrifuge rotor and the frame member. Furthermore, the inner portion, the connecting portions and the outer portion form an integrated unit manufactured in one piece of metal material.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL AB
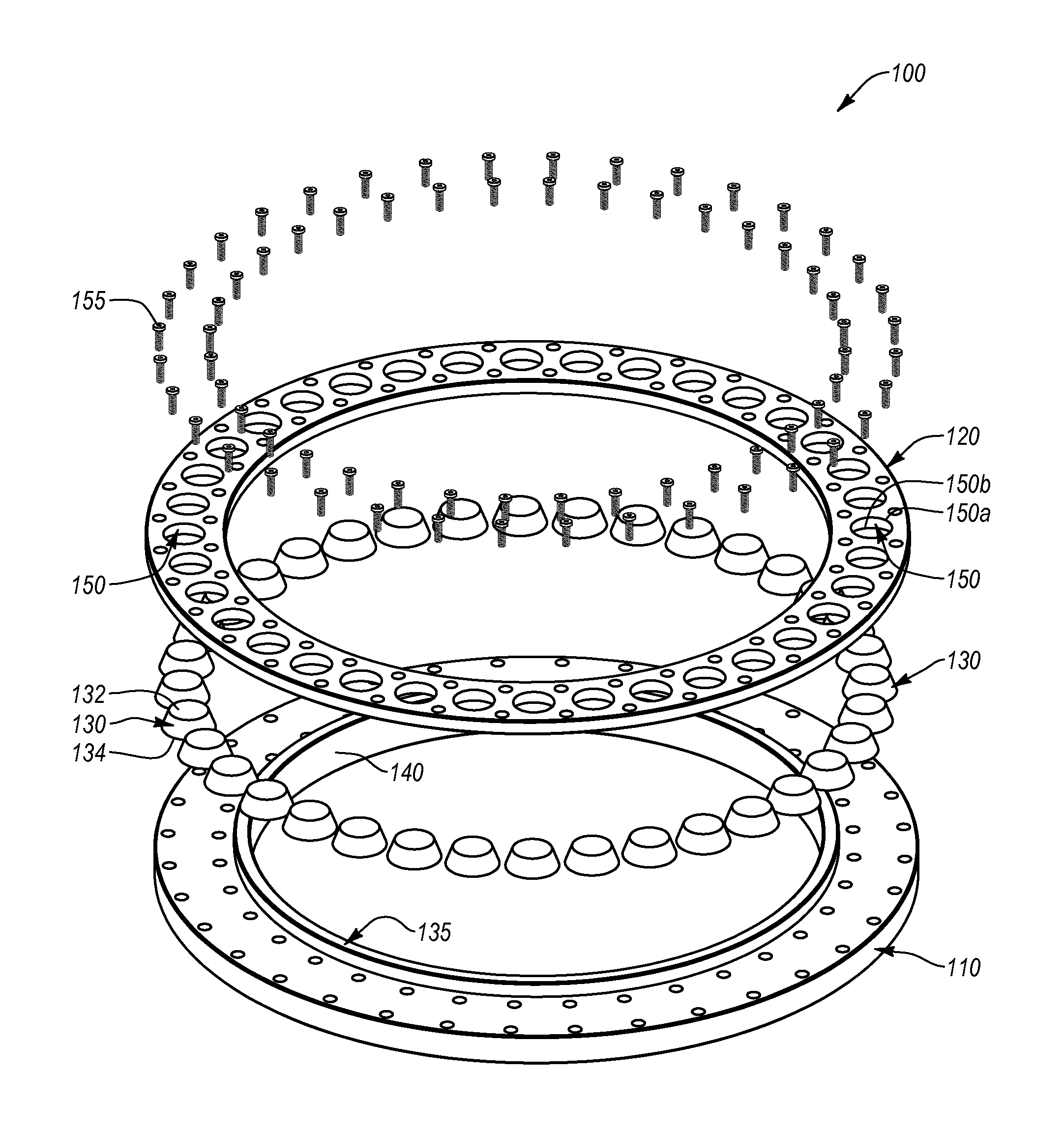
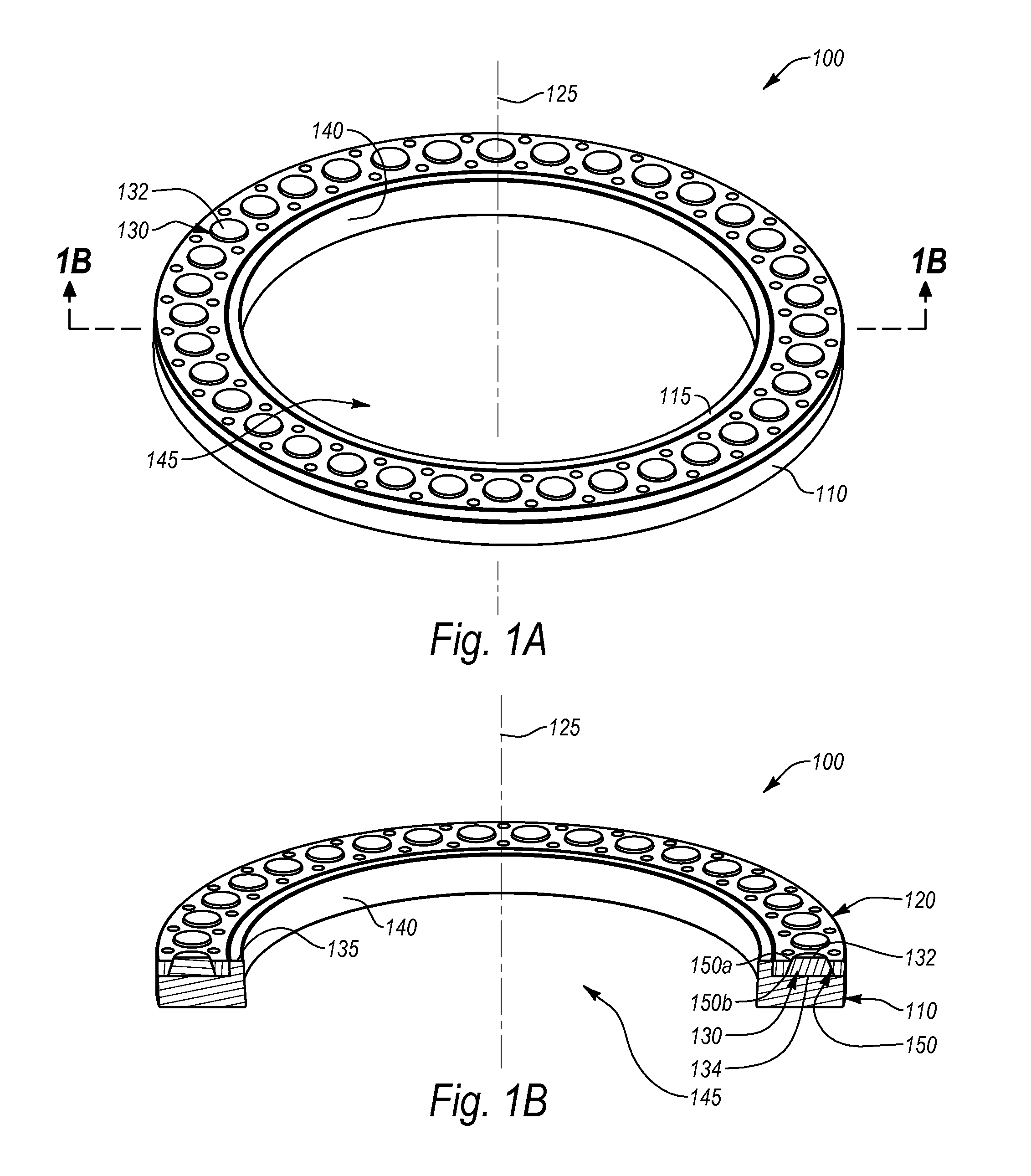
Thrust bearing assembly
ActiveUS20090268995A1Avoiding costly finish-grinding/lappingAccurate locationBearing assemblyShaftsWear resistantThrust bearing
A thrust bearing assembly comprising a bearing runner and a bearing carrier, the carrier defining a plurality of thrust pad sites annularly around the carrier, with a thrust pad disposed at a site and with the carrier limiting movement of the thrust pad in a direction generally radial to the longitudinal axis of the runner while allowing the thrust pad to move in a direction generally parallel to the longitudinal axis. Though the range of movement is limited, the pads can tilt under load to form a hydrodynamic wedge as is known in the art. An embodiment comprises a bearing runner having a wear resistant face and a bearing carrier defining thrust pad sites disposed annularly around the carrier. In one implementation, at each site, a deflection element (e.g., Belleville washer) is disposed in a cavity and a pad is disposed over the deflection element. The pad can be at least partially disposed within the cavity. The wear resistant face contacts the pad. Another embodiment rigidly connects pads disposed oil opposite sides of a stationary bearing carrier. Another embodiment attaches pads to a bearing carrier using pad holder assemblies.
Owner:CERADYNE
Sliding bearing and bearing mechanism having the same
ActiveUS7220056B2Cancel noiseReduce linear-motion frictional resistanceLinear bearingsShaftsSteering columnEngineering
A sliding bearing for a steering column includes: a cylindrical bearing body; flat surfaces formed integrally on an inner peripheral surface of the bearing body; first slits extending from one end face of the bearing body to this side of the other end face of the bearing body; second slits extending from this side of the other end face of the bearing body to the one end face of the bearing body; grooves formed in an outer peripheral surface of the bearing body; and elastic rings which are respectively fitted in the grooves in such a manner as to project from the outer peripheral surface of the bearing body and to reduce the diameter of the bearing body.
Owner:OILES CORP
Method and apparatus for varying the critical speed of a shaft
A system is provided for changing the critical speed of a shaft that includes: a first shaft supported for relative rotational movement with respect to a stationary structure, a forward bearing disposed at the forward end of the shaft, an aft bearing disposed at the aft end of the shaft, at least one active bearing disposed between the forward bearing and the aft bearing, and means for changing the support stiffness of the active bearing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Dampenable bearing
InactiveUS6116784APortable framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BROTZ GREGORY R
Bearing system for high-speed rotating machinery
InactiveUS6877901B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyRotary combination bearingsShaftsBall bearingTurbocharger
A bearing system for a turbocharger shaft includes two angular contact ball bearings mounted in the opposite ends of a lubricated rotatable elongated cylinder, which includes a radially extending flange at one end that cooperates with stationary housing portions and carries the thrust load of the rotor in both directions. The angular contact ball bearing on the turbine end (hot end) of the machine is provided with a radial spring between the outside of its outer race and the elongated cylinder, which prevents rotation of the outer race, but still allows axial movement of the outer race in the elongated cylinder due to axial expansion of the shaft when exposed to high temperature. The inner races of the ball bearings are separated by a spacer, which is clamped in place between the bearings when the rotor assembly lock nut is tightened. Thus, the inner race of the bearings and spacer rotate with the shaft as part of the rotating assembly.
Owner:WOLLENWEBER WILLIAM E
Steering gear assembly having rack bushing
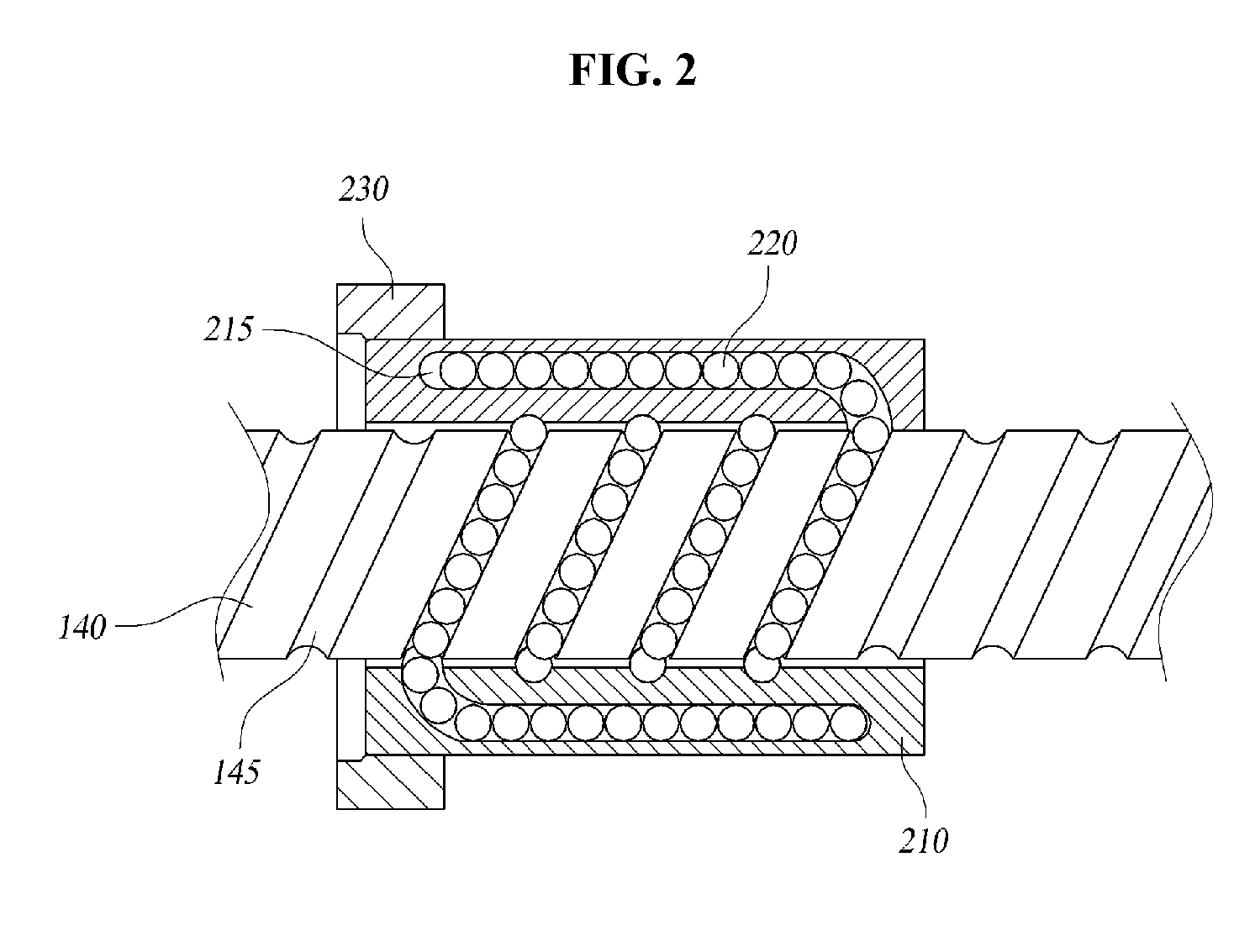
InactiveUS7665747B2Reduce manufacturing costEasy to installLinear bearingsGearingEngineeringRack and pinion
A rack and pinion steering gear assembly including a housing, a rack that is translatably moveable relative to the housing along an axis and a bushing operably disposed between the rack and housing. The bushing defines a gap which extends the entire axial length of the bushing. At least one compressible member may be disposed between the bushing and the housing with the compressible member extending across the gap in the bushing and fully encircling the bushing. The bushing may also include a radial flange that acts as a travel stop. The bushing may also be formed of an acetal material wherein the flange and a tubular portion of the bushing are axially separated by an intermediate portion having a relatively thin radial thickness. Axially extending recesses may be provided to enhance the flexibility of the bushing.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
Tolerance ring having variable height and/or assymmetrically located bumps
A tolerance ring configured to reduce torque ripple for a pivot bearing in an actuator arm assembly. The tolerance ring comprises a cylinder having a predetermined length, and a first and a second row of contacting portions arranged around the surface of the cylinder, the contacting portions of the second row are circumferentially displaced with respect to the first row by a distance greater than zero but less than the distance of the contacting portion and the spacing between adjacent contacting portions in the first row.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
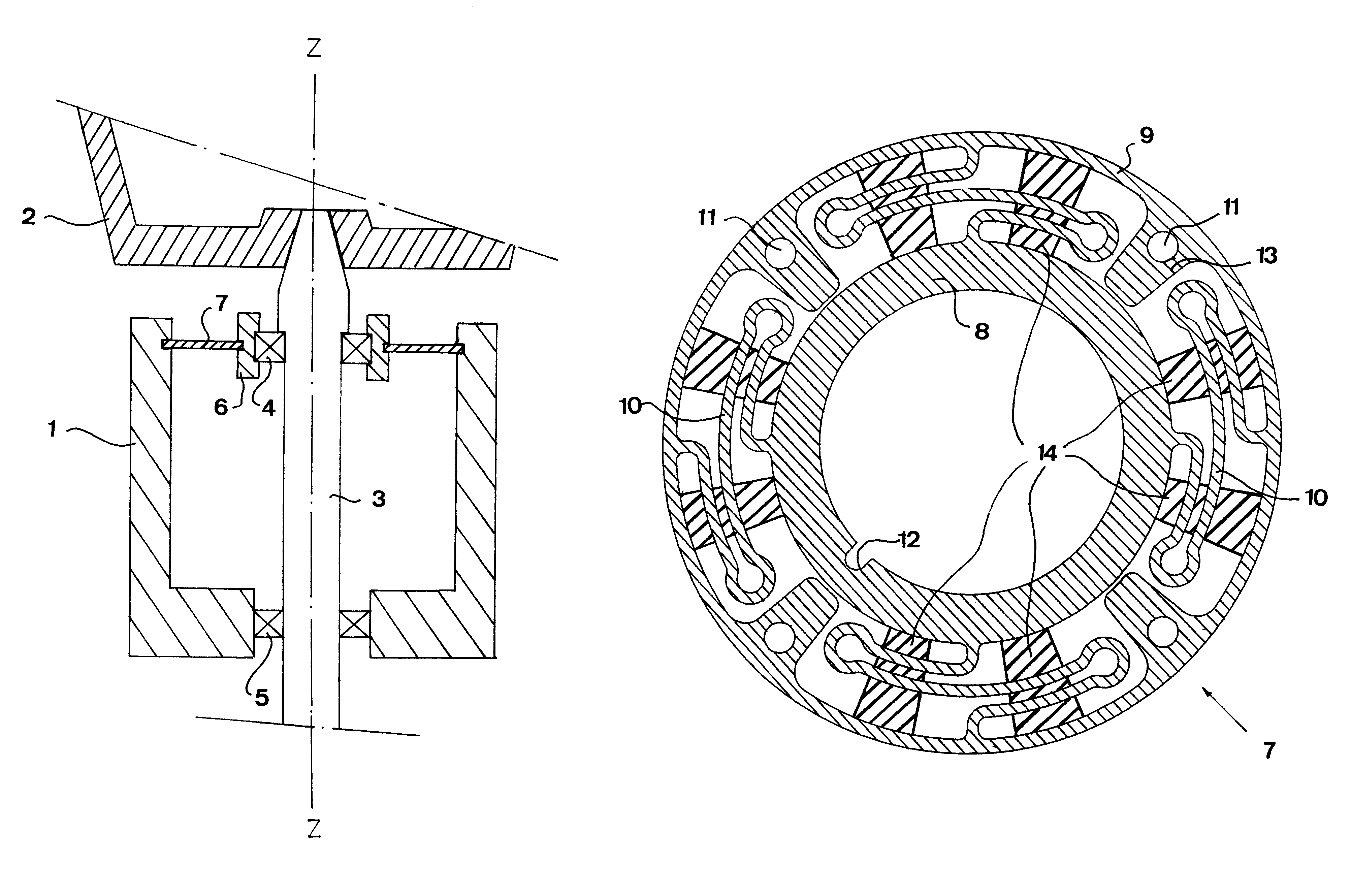
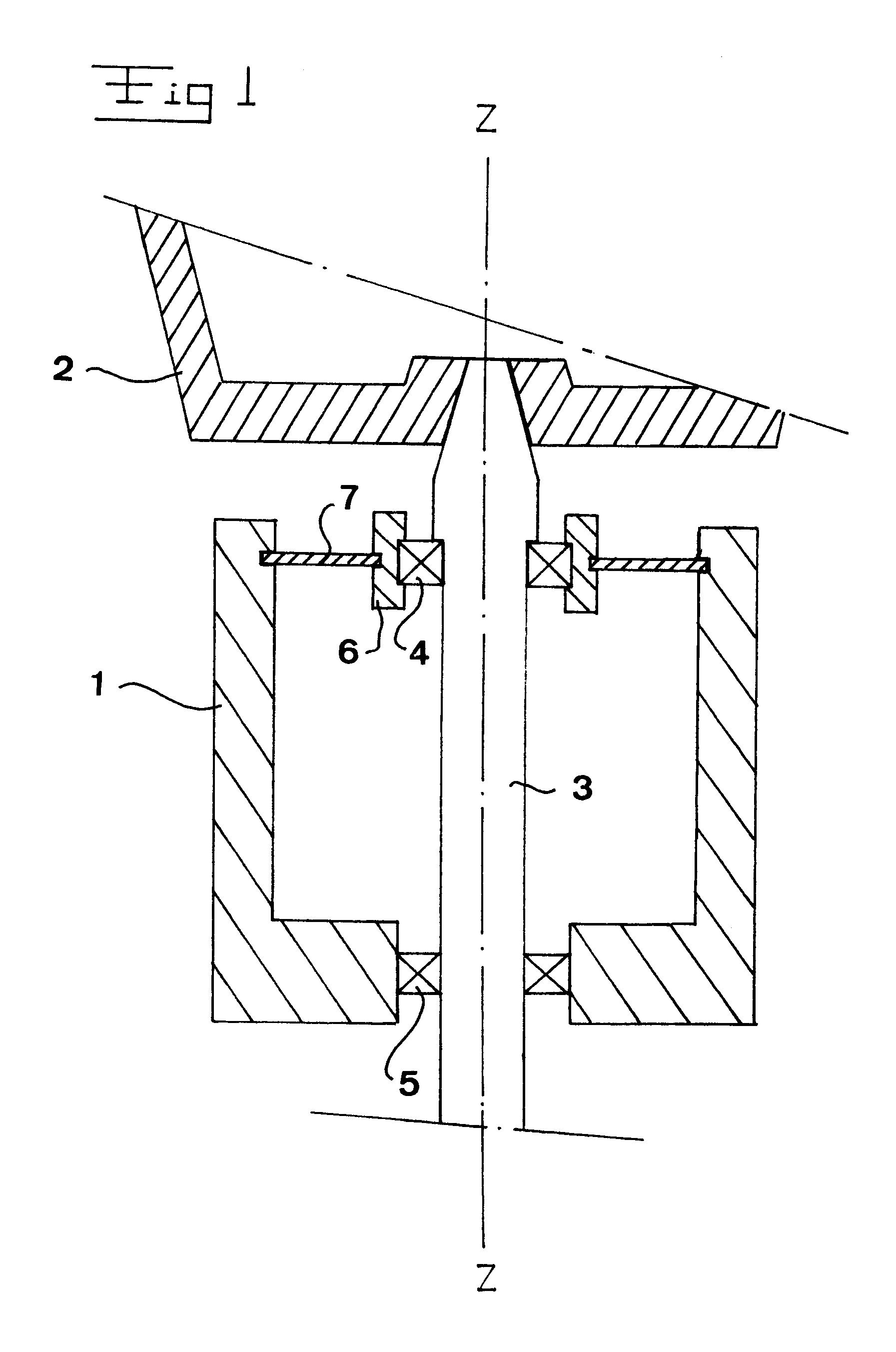
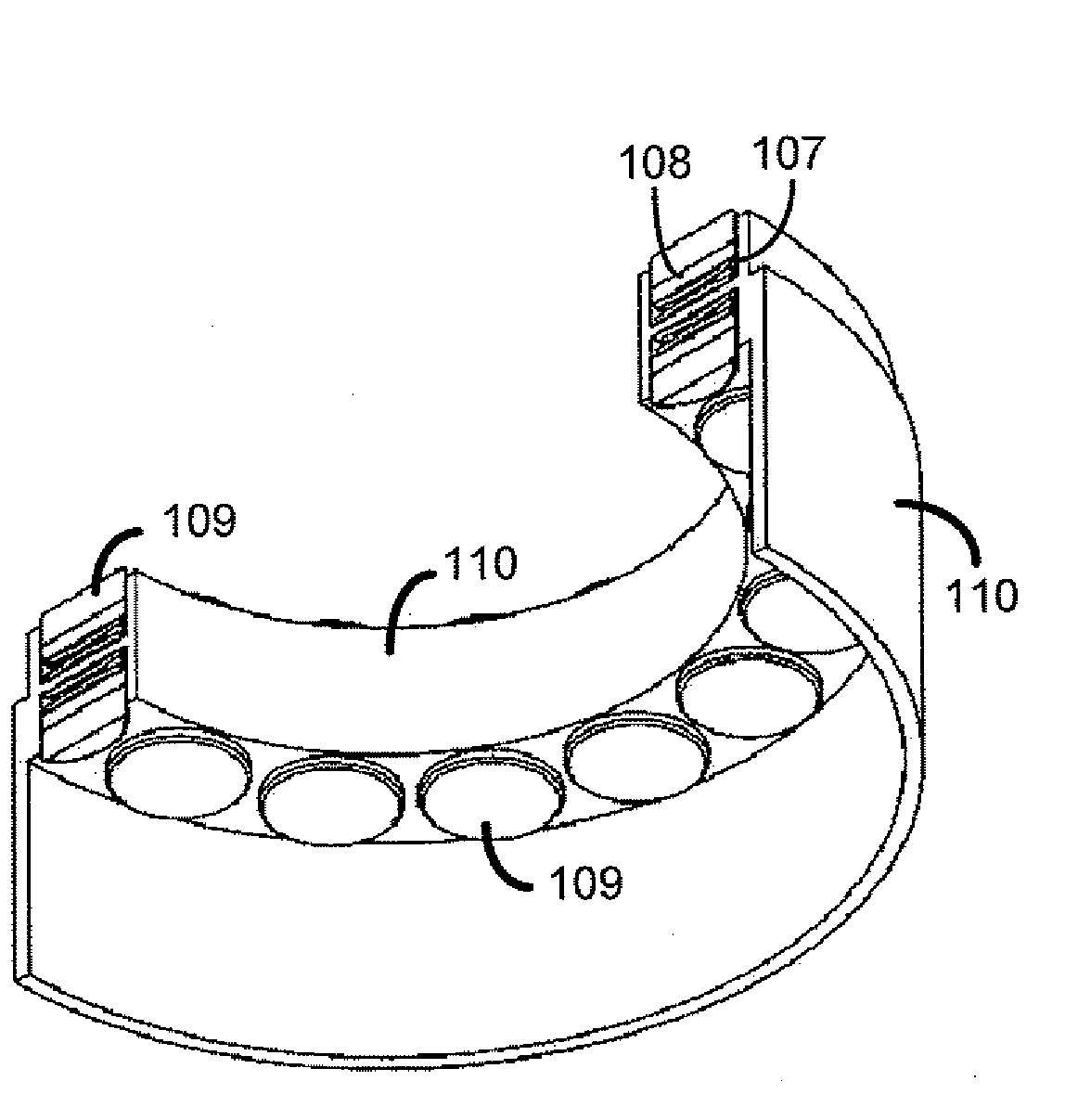
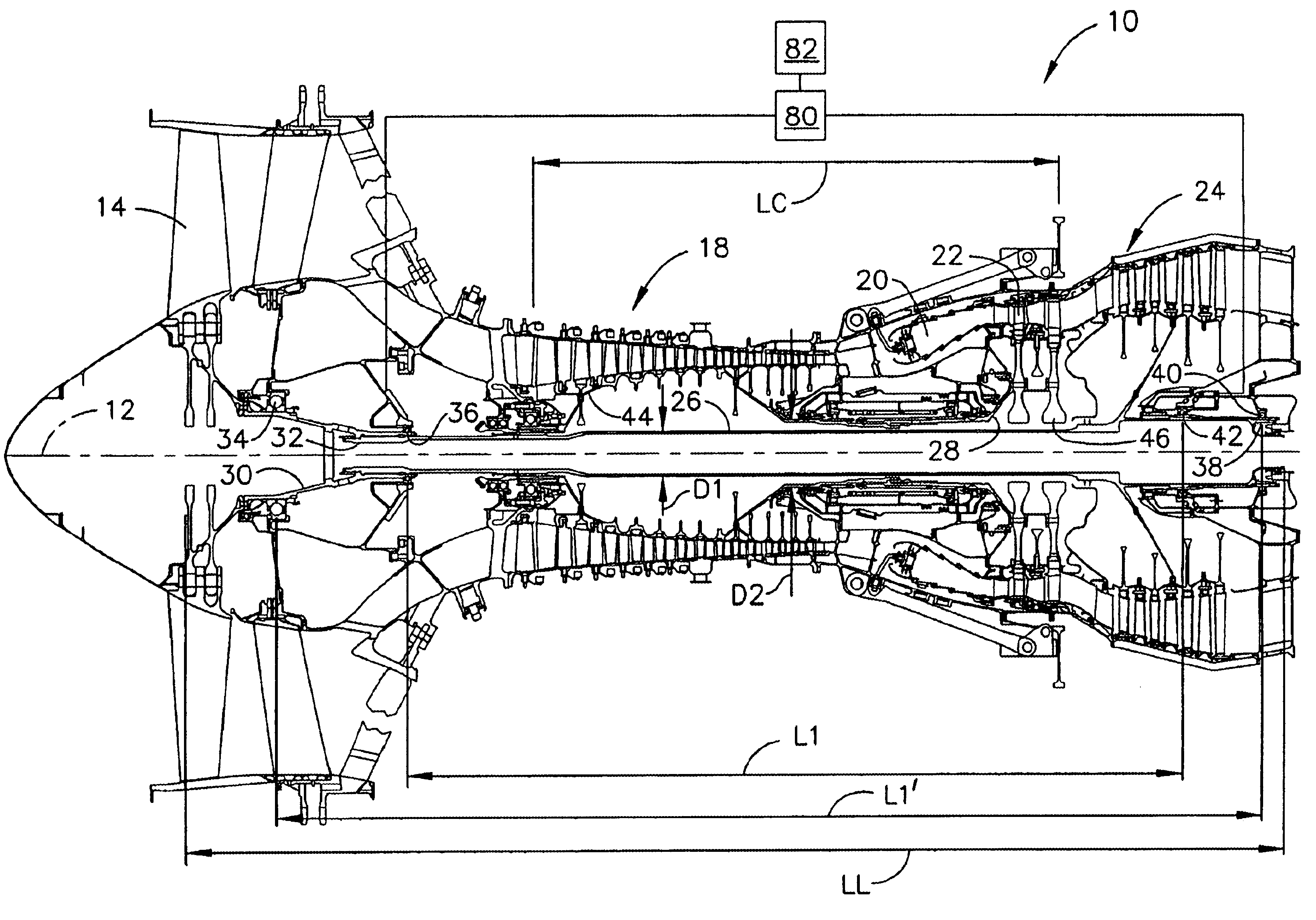
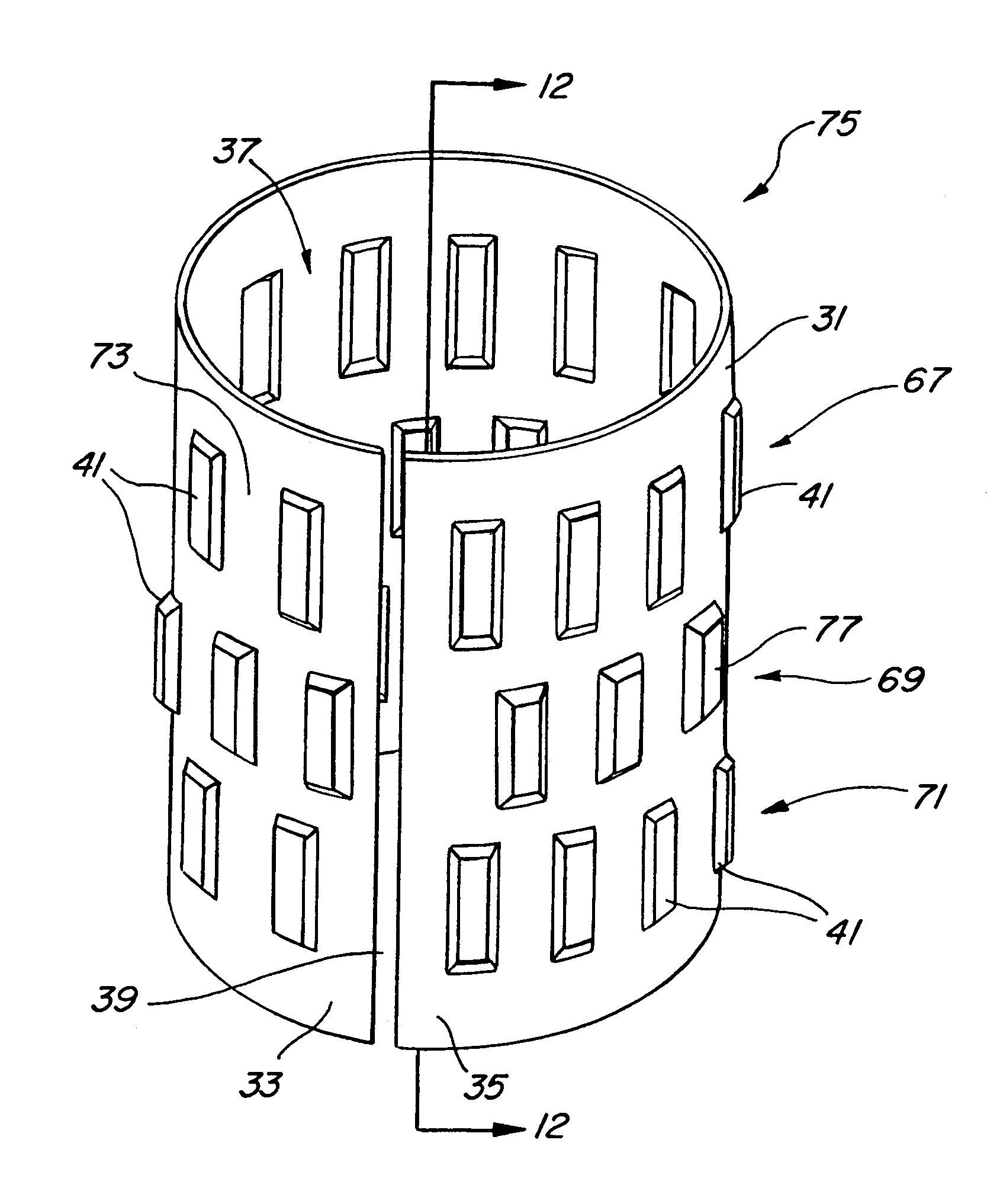
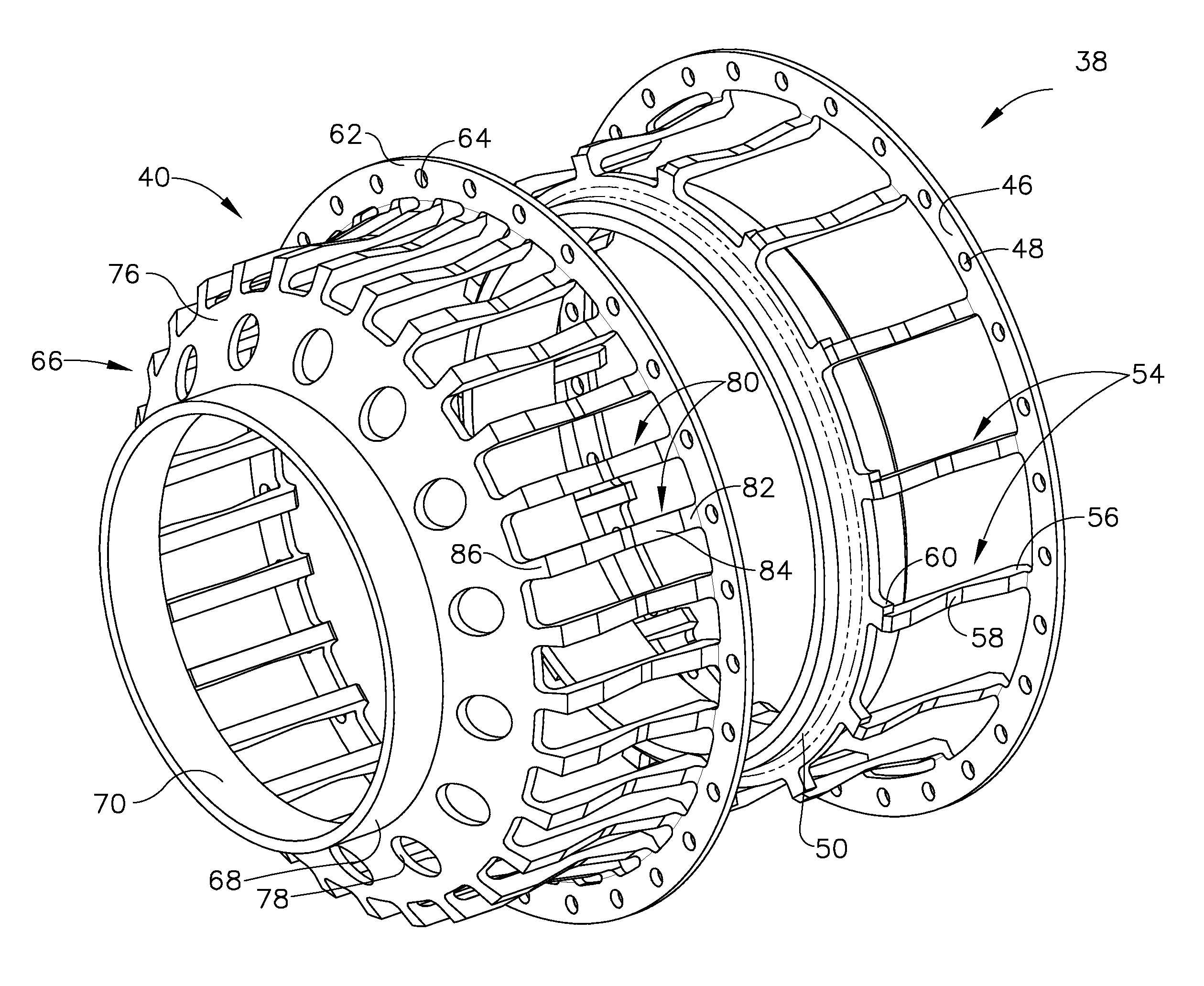
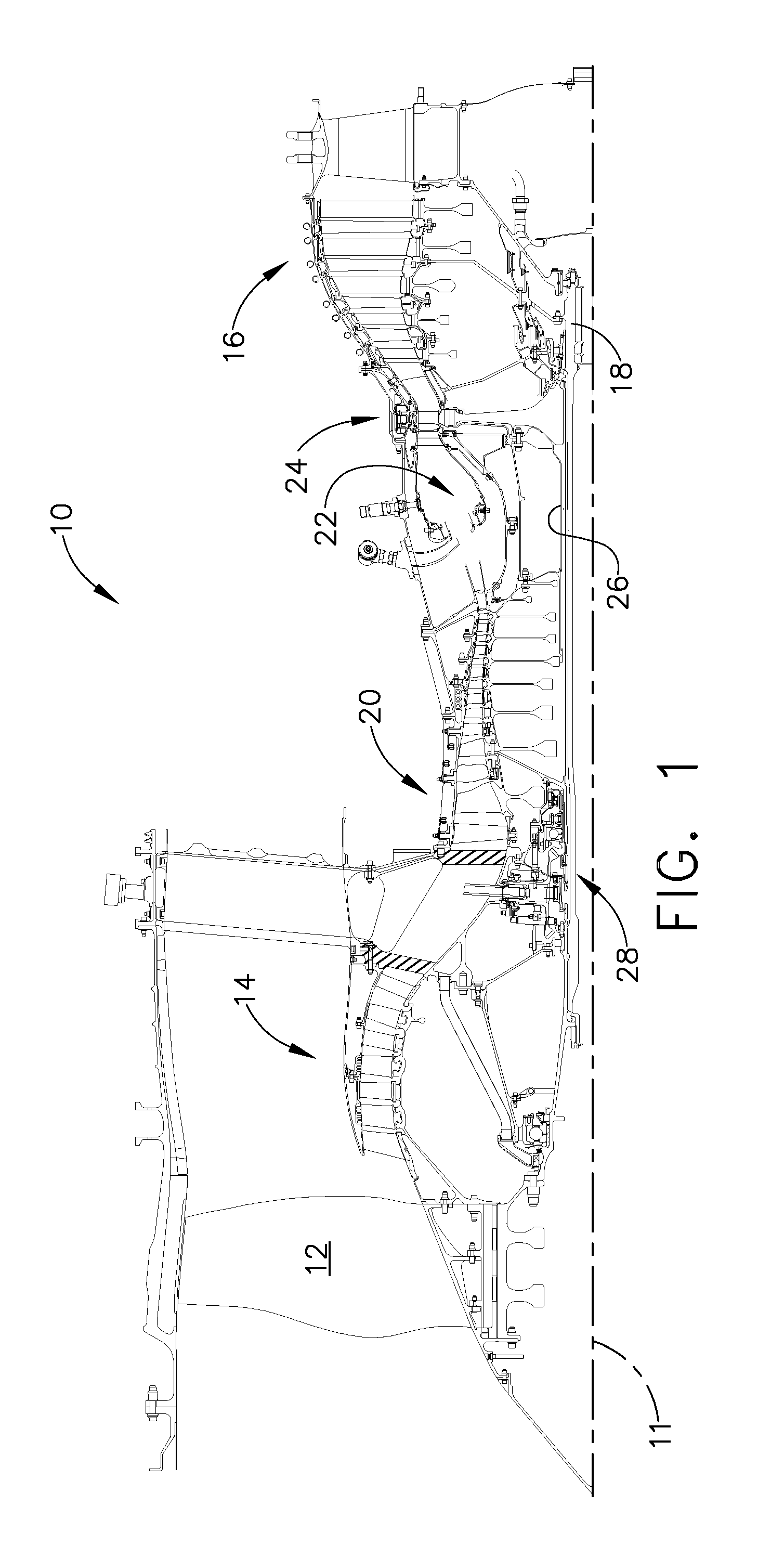
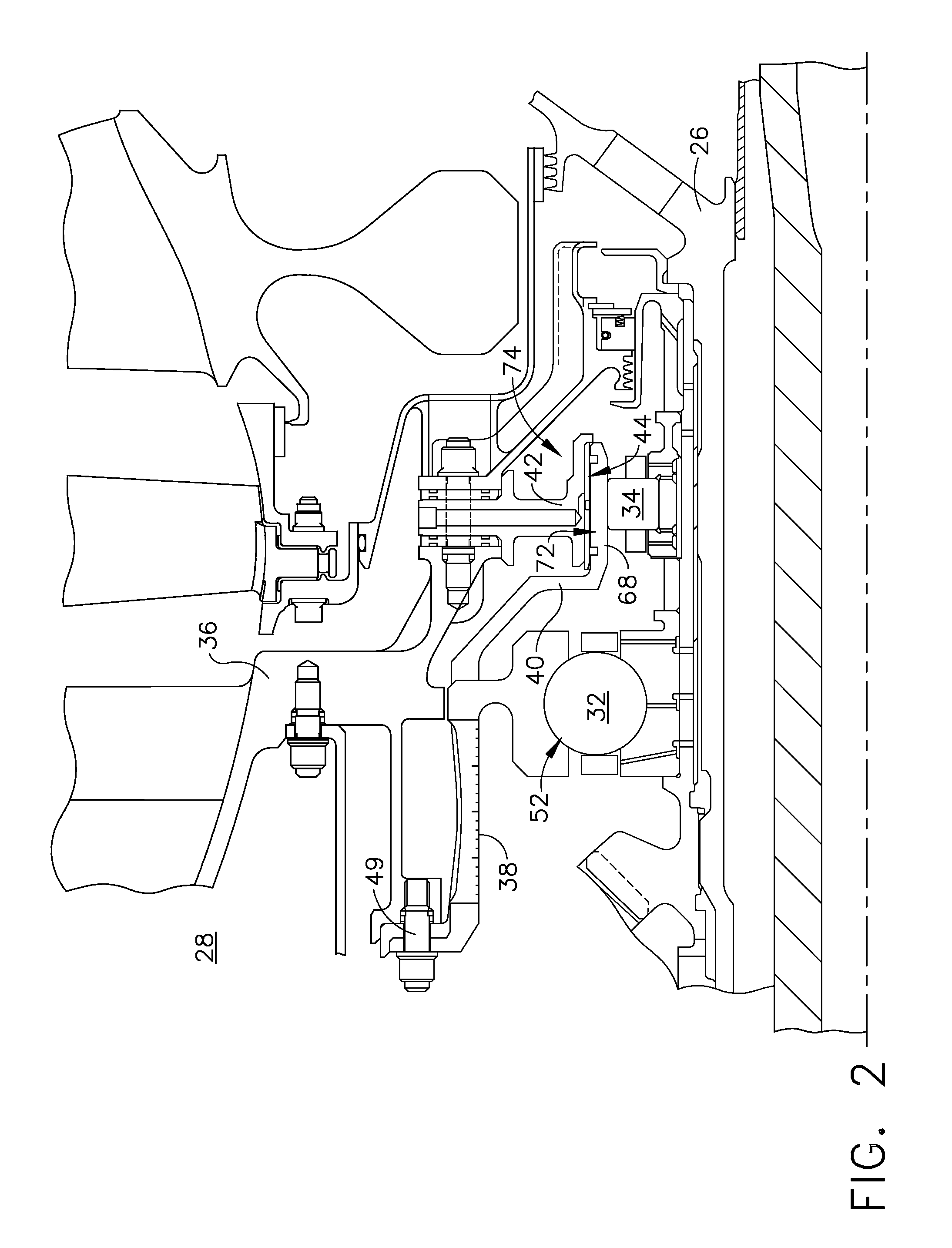
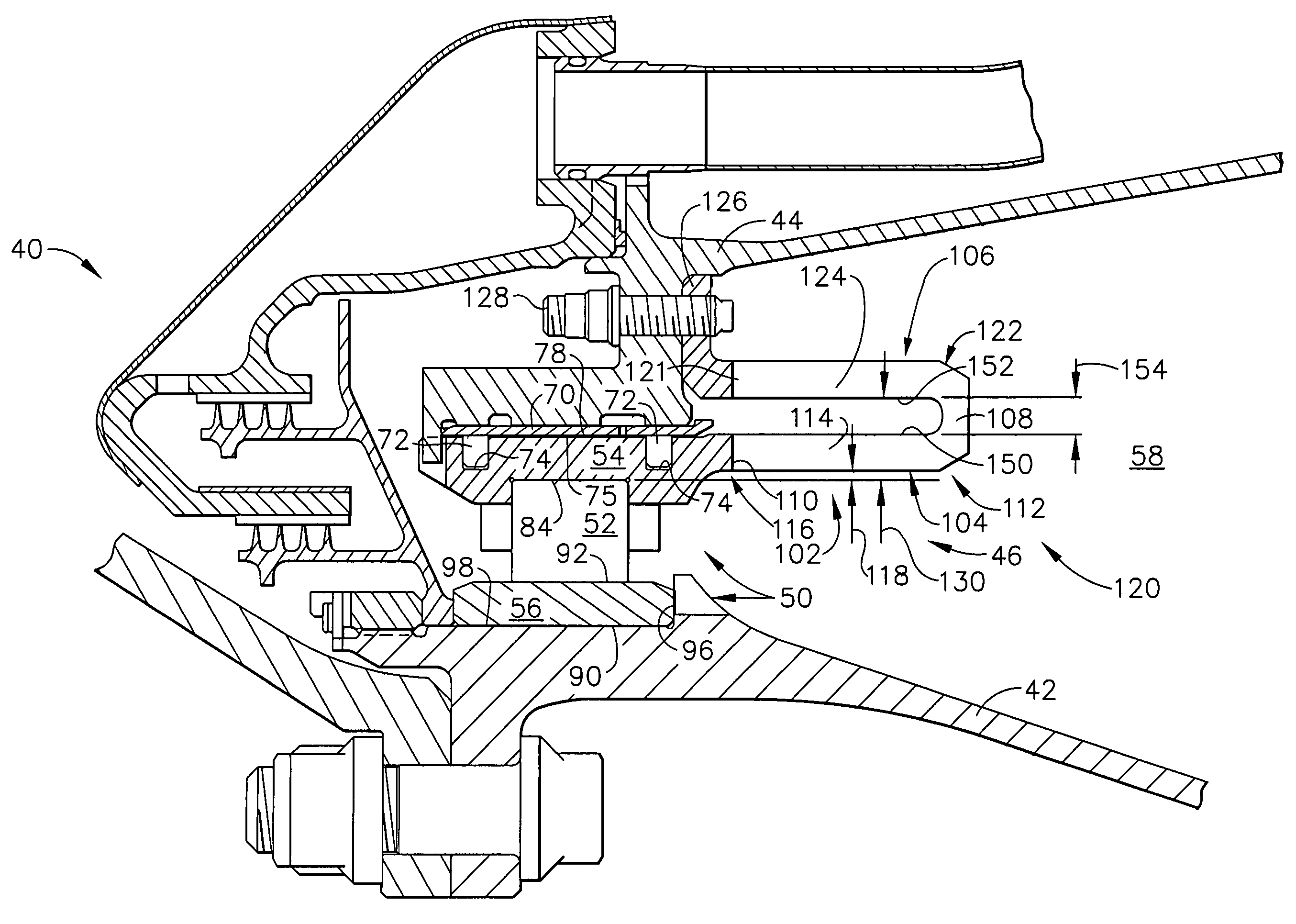
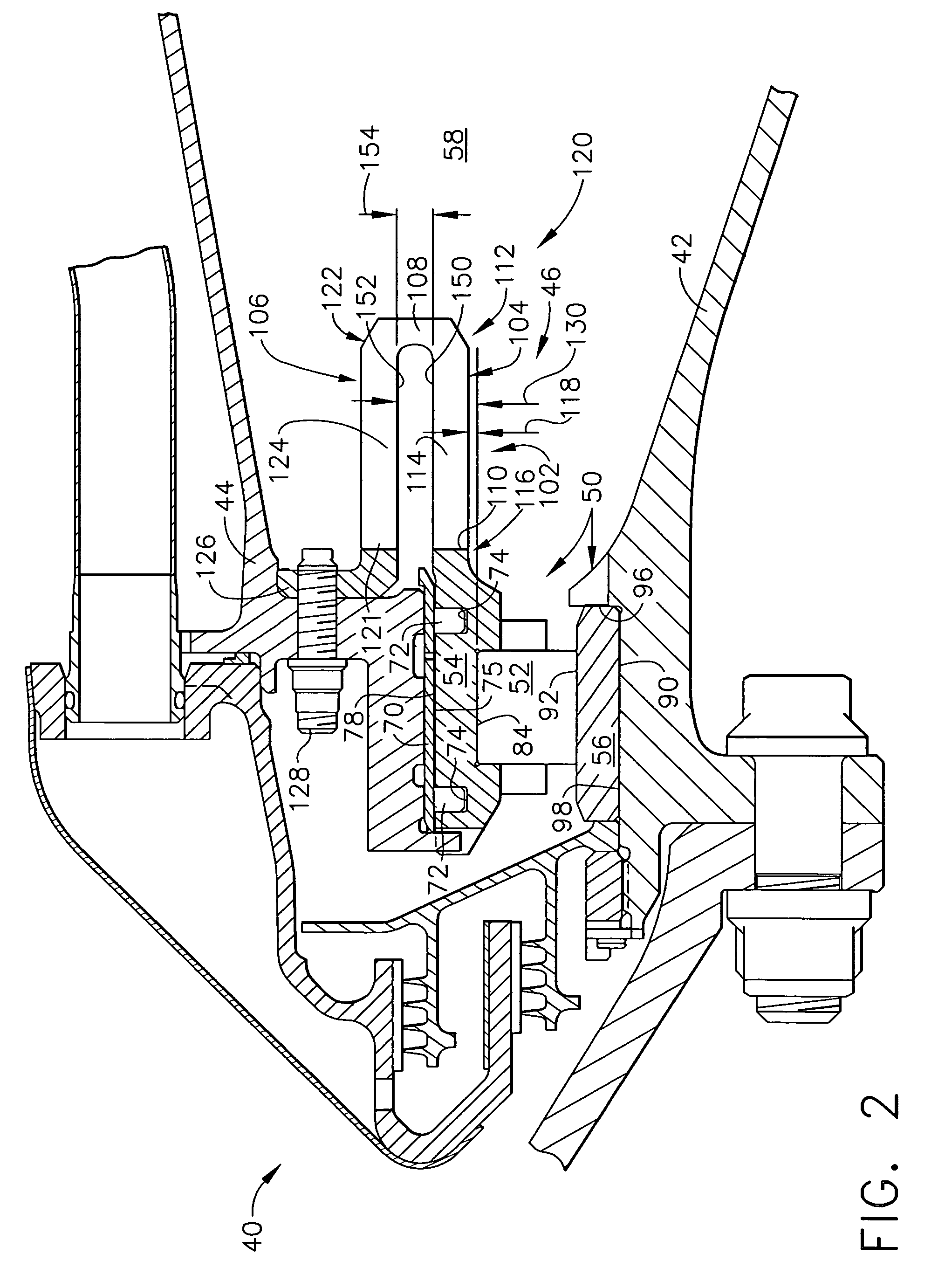
Bearing support apparatus for a gas turbine engine
A bearing support cage includes: an annular forward ring; an annular aft ring; an annular mounting flange disposed between the forward and aft rings; an annular array of axially-extending first spring fingers interconnecting the forward ring and the aft ring; and an annular array of axially-extending second spring fingers interconnecting the mounting flange and the aft ring, wherein the first spring fingers are interdigitated with the second spring fingers. The forward and aft rings, the mounting flange, and the spring fingers are all part of a single monolithic component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rack assist type electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20110127742A1Easy to operateReduce vibrationRolling contact bearingsSteering linkagesElectric power steeringDriver/operator
Disclosed is a rack-assist type electric power steering apparatus, in which when a ball nut slides a rack bar while rotating, a vibration and a noise in the axis direction and the radial direction, generated from the rack bar and a rack housing, are absorbed. This facilitates the operation of the ball nut and the rack bar, and reduces the vibration and the noise, thereby resulting in an effect for providing a comfortable steering feeling to a driver.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Bearing damper with spring seal
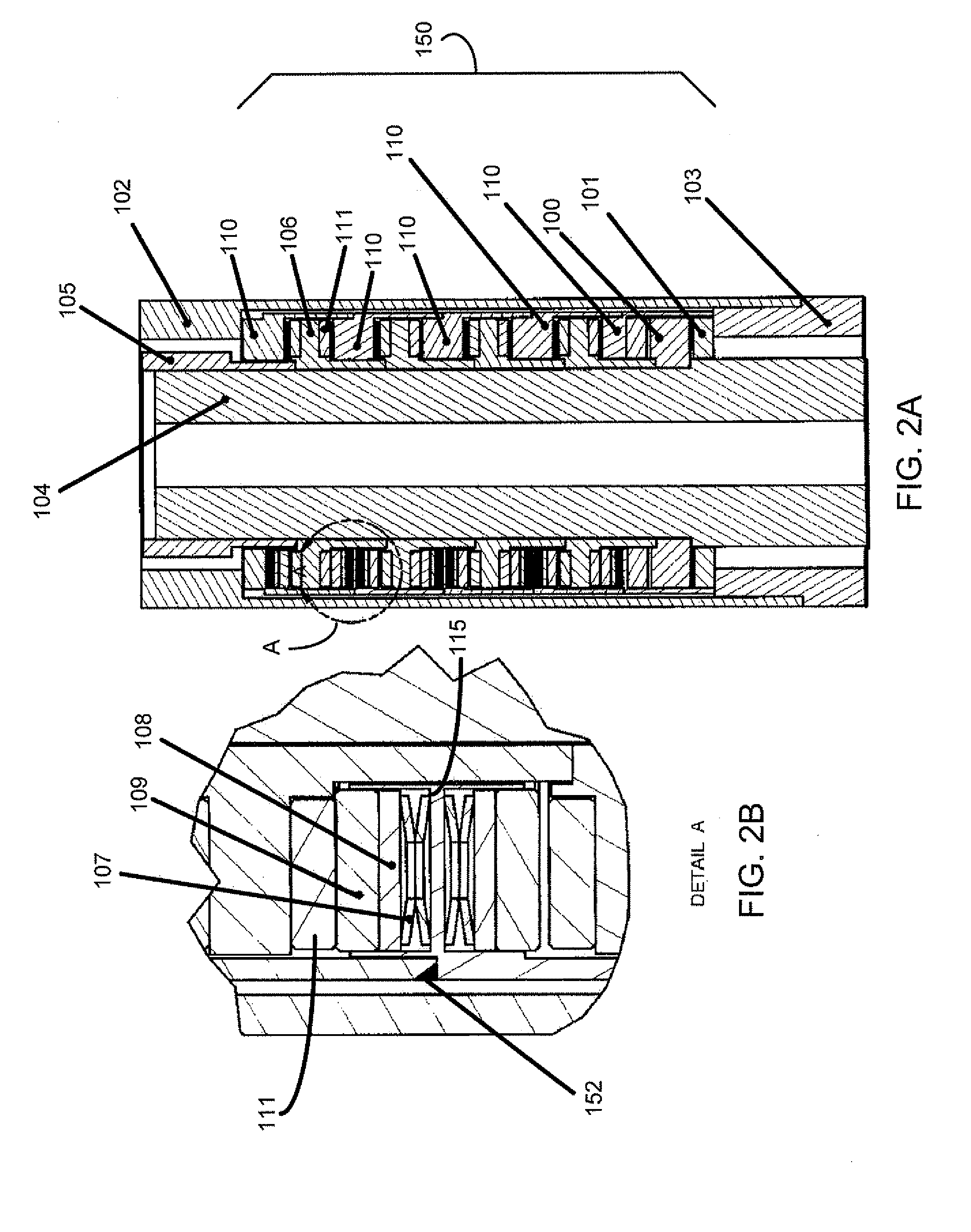
A bearing damper includes: (a) an annular sleeve having spaced-apart grooves formed in a radially-facing surface therein; (b) an annular bearing race received in the sleeve; and (c) a resilient seal ring disposed in each of the grooves, wherein the seal rings cooperate with the sleeve and a radially-facing surface of the bearing race to define a closed annular gap, and further wherein the seal rings are sized so as to urge the bearing race towards a coaxial position relative to the sleeve.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Hydraulically Damping Bushing Bearing
InactiveUS20110188790A1Without limiting the damping comfort of the bearing and its long-term performanceEasy to wearSpringsShock absorbersElastomerEngineering
Chambers for a bushing bearing with damping means include outer sleeve and inner bearing part, accommodated in the outer sleeve with rigid bearing core and elastomeric bearing body surrounding the core. The expanding walls of the chambers are disposed transversely to the bearing axis (A). The inner bearing part is segmented with respect to the longitudinal axis (A) of the bearing and includes a center main segment with bearing core and bearing body and two end segments, each having an inner ring, an outer ring, and an interposed elastomeric element forming expanding wall of a chamber. The end segments are pressed with inner ring onto axial ends of the bearing core so that the material overlaps between the elastomeric elements of the end segments and the ribs of the bearing body. The channel is formed outside of the bearing body in a channel carrier element.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
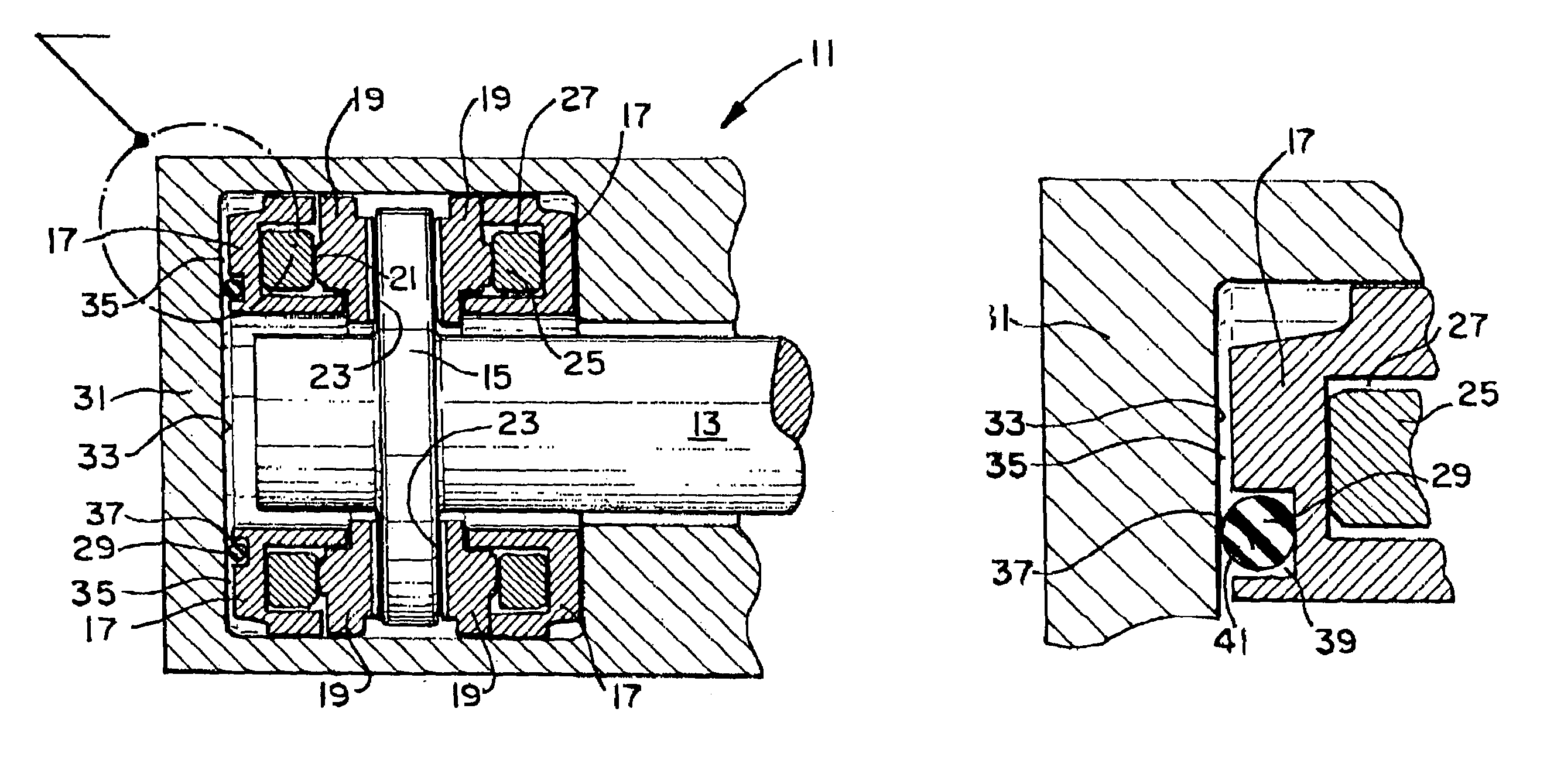
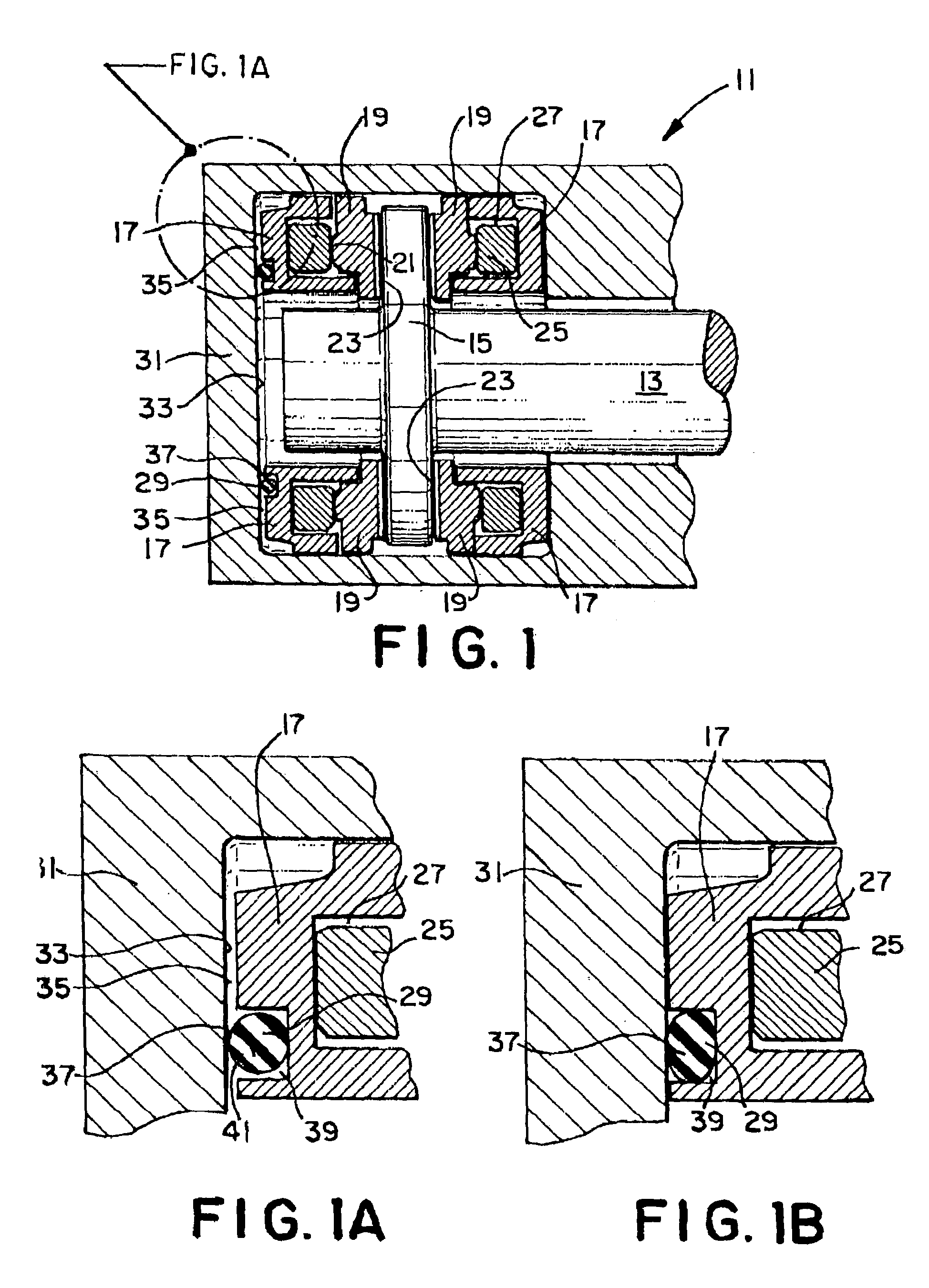
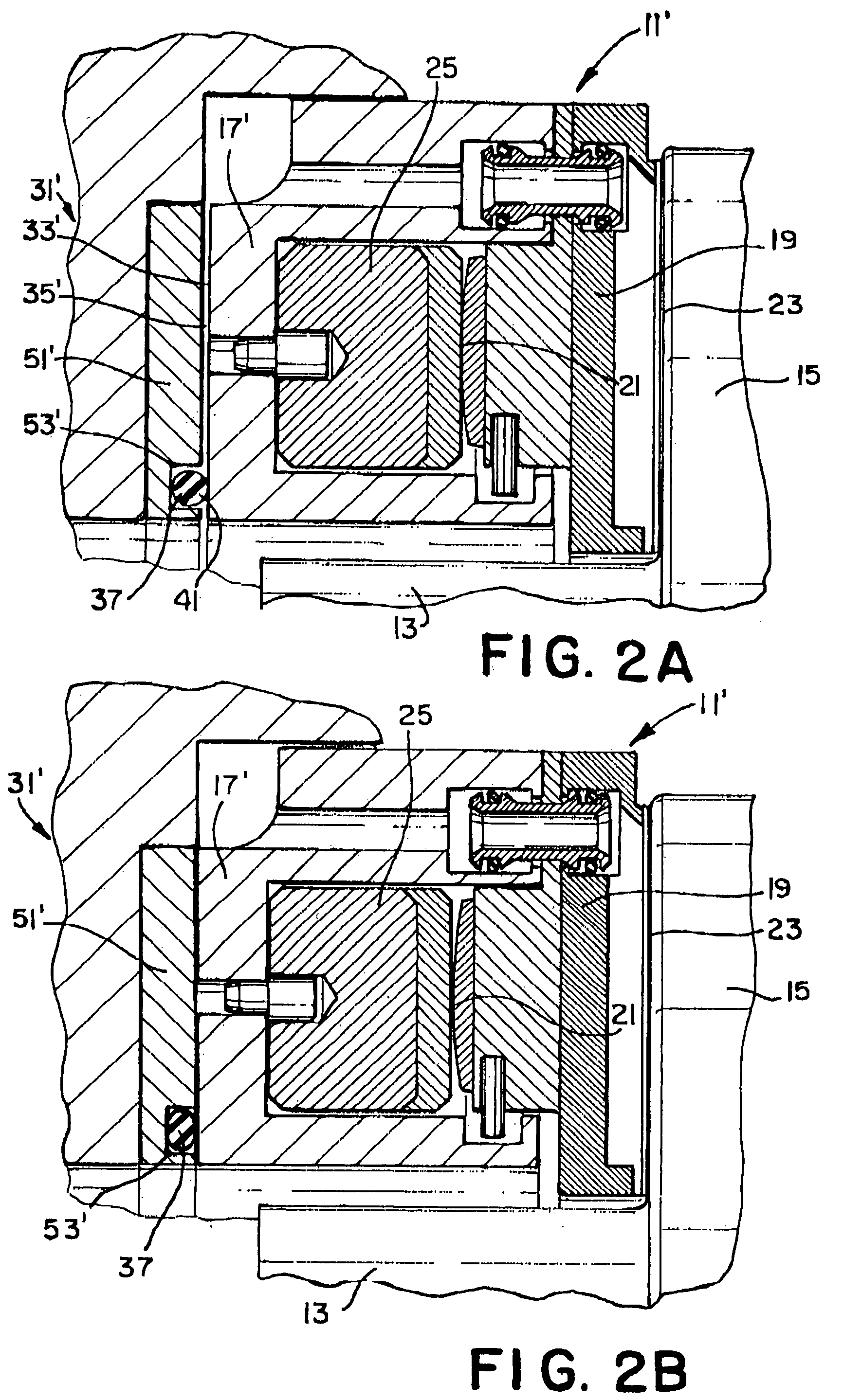
Thrust bearing
InactiveUS7063465B1Eliminates vibration of shaftReduce forceSliding contact bearingsElastic bearingsNormal loadThrust bearing
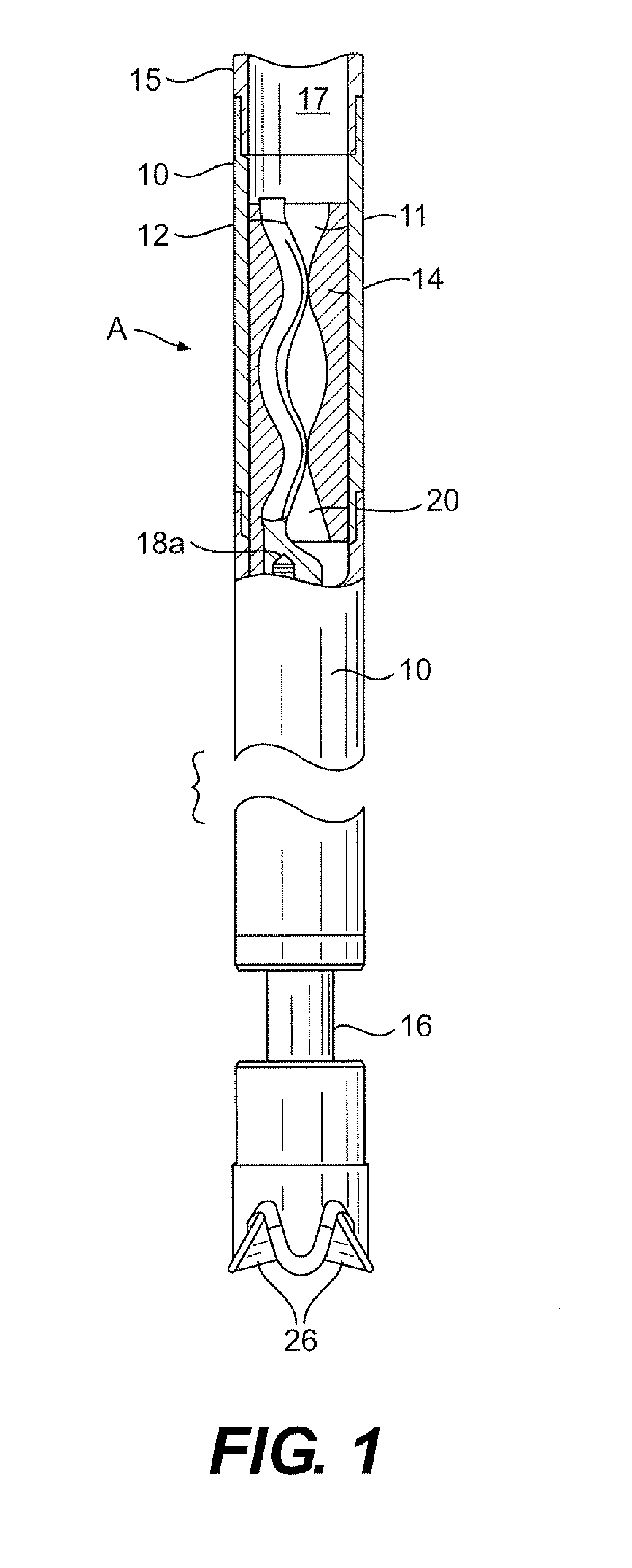
A thrust bearing 11 for use with a shaft 13 having a collar 15 mounted the shaft 13 and rotatable therewith has a base ring 17, a series of shoes 19 positioned on the base ring 17, and a compressible resilient spacing member 29 positioned between the base ring 17 and a housing 31 for the thrust bearing 11. The spacing member 29 supports the thrust bearing 11 when the shaft 13 is rotating during no-load operating conditions, as well as dampens the forces placed on the thrust bearing 11 by the shaft 13 when the shaft 13 is rotating during no-load conditions. The spacing member 29 is sufficiently stiff that it supports the thrust bearing 11 when the shaft 13 is rotating under no-load conditions, but is sufficiently compressible to be compressed to the extent that the gap 33 between the base ring 17 and the housing 31 is eliminated due to the forces placed on the thrust bearing 11 by the shaft 13 bringing the base ring 17 into contact with the housing 31 during normal load operating conditions.
Owner:KINGSBURY INC
Sliding bearing
InactiveUS20060215944A1Easy to adjustReduce coefficient of frictionShaftsRotary machine partsEngineeringSynthetic resin
A sliding bearing (1) includes an upper casing (3) which is made of polyacetal resin as a synthetic resin, has an annular surface (2), and serves as a first bearing body; a second bearing body (5) which is made of a synthetic resin, is superposed on the upper casing (3) so as to be rotatable about an axis (O), and has an synthetic resin-made annular surface (4) opposed to the annular surface (2); and a synthetic resin-made annular sheet (6) which is interposed between the annular surfaces (2) and (4) and slidably abuts against at least one of the upper casing (3) and the bearing body (5).
Owner:OILES CORP
Nested bearing cages
A gas turbine engine bearing cage assembly includes: a first bearing cage having: an annular first bearing support ring; an annular first mounting flange; and an annular array of axially-extending first spring arms interconnecting the first bearing support ring and the first mounting flange, the first spring arms defining an outer diameter; and a second bearing cage having: an annular second bearing support ring; an annular second mounting ring, the second mounting ring defining an inner diameter greater that the outer diameter; and an annular array of axially-extending second spring arms interconnecting the second bearing support ring and the second mounting ring, the second spring arms defining spaces therebetween. The bearing cages are sized such that the first bearing cage can be received within the second bearing cage. The spaces are positioned to receive the first spring arms, permitting independent flexing motion of the first and second spring arms.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
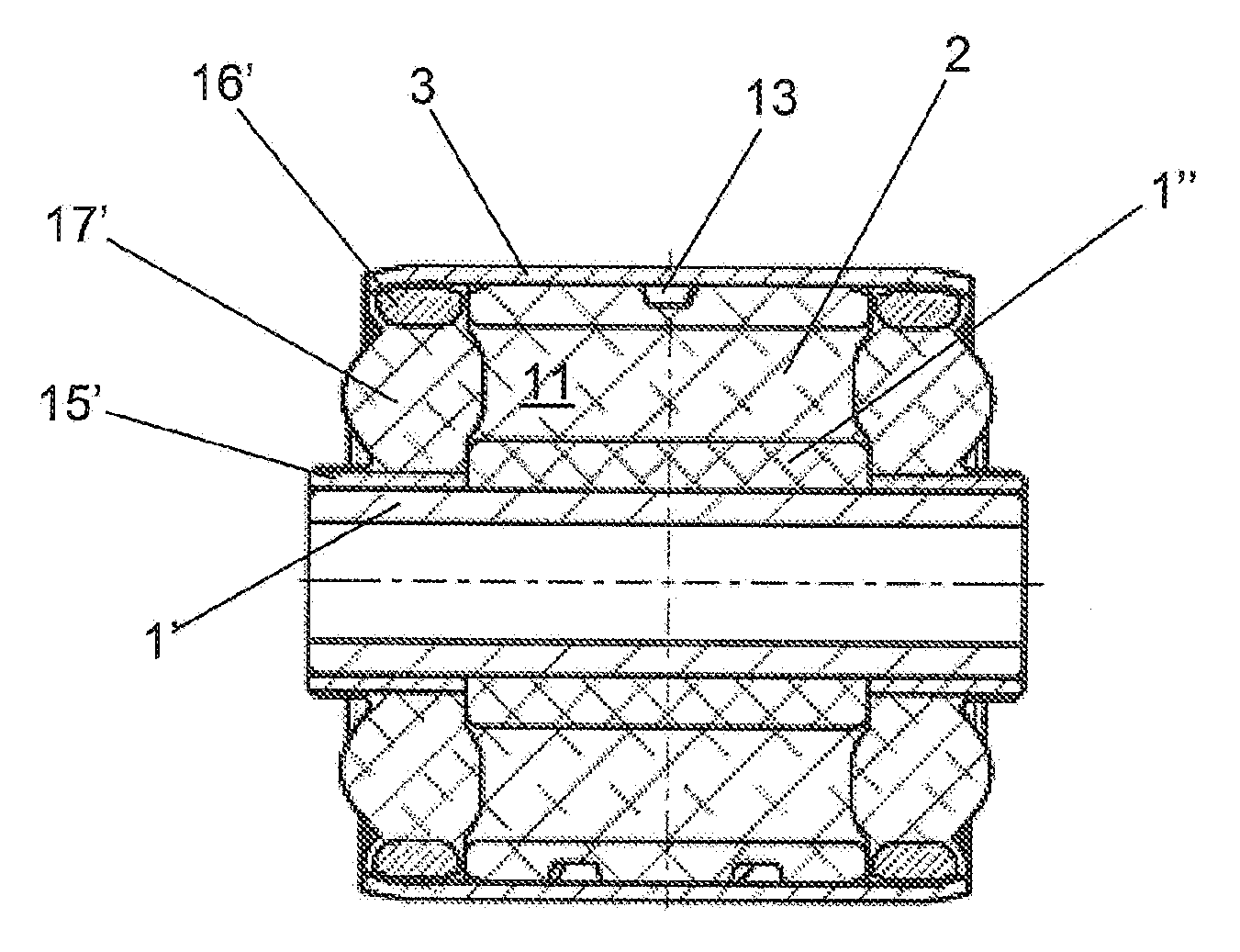
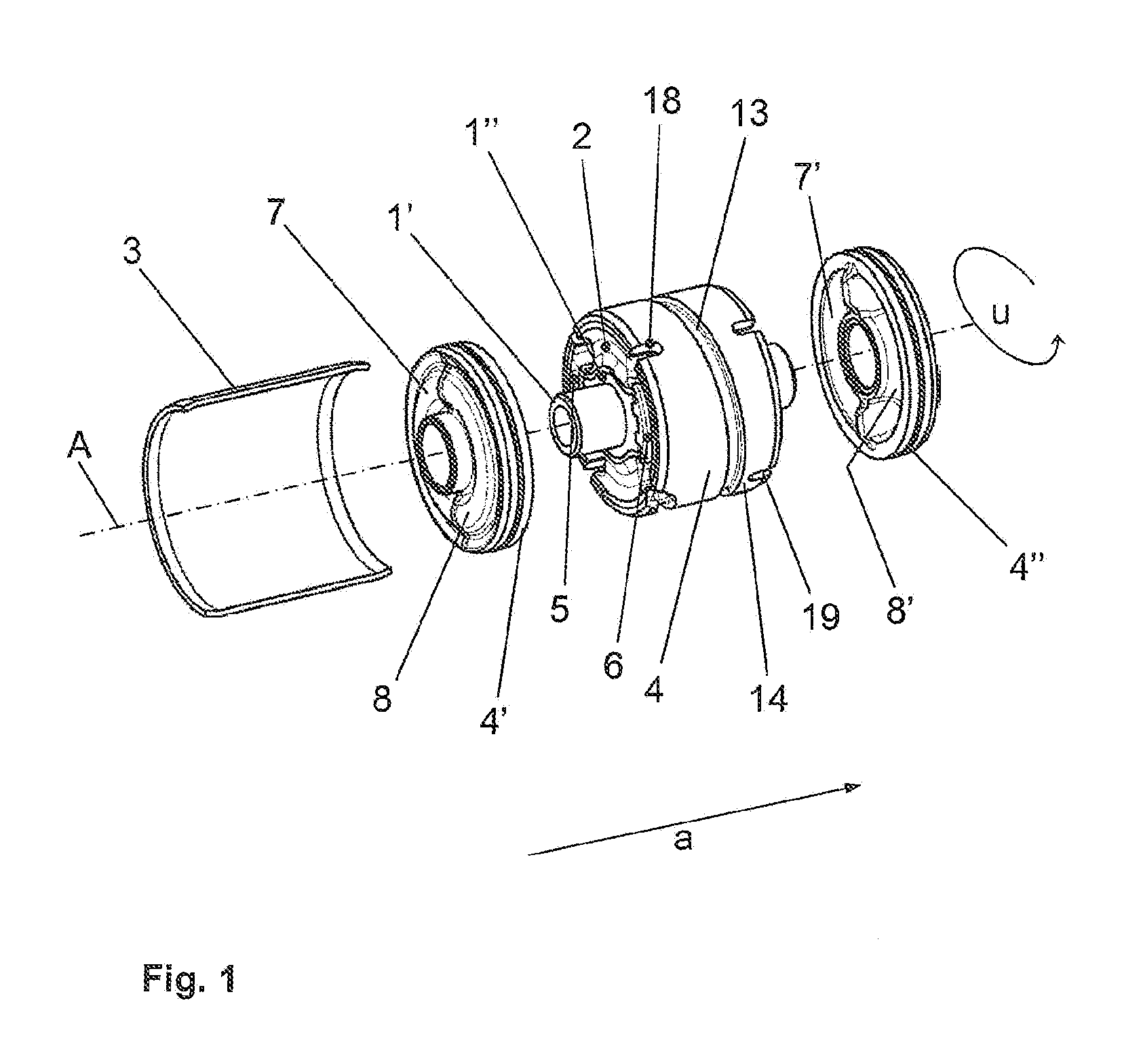
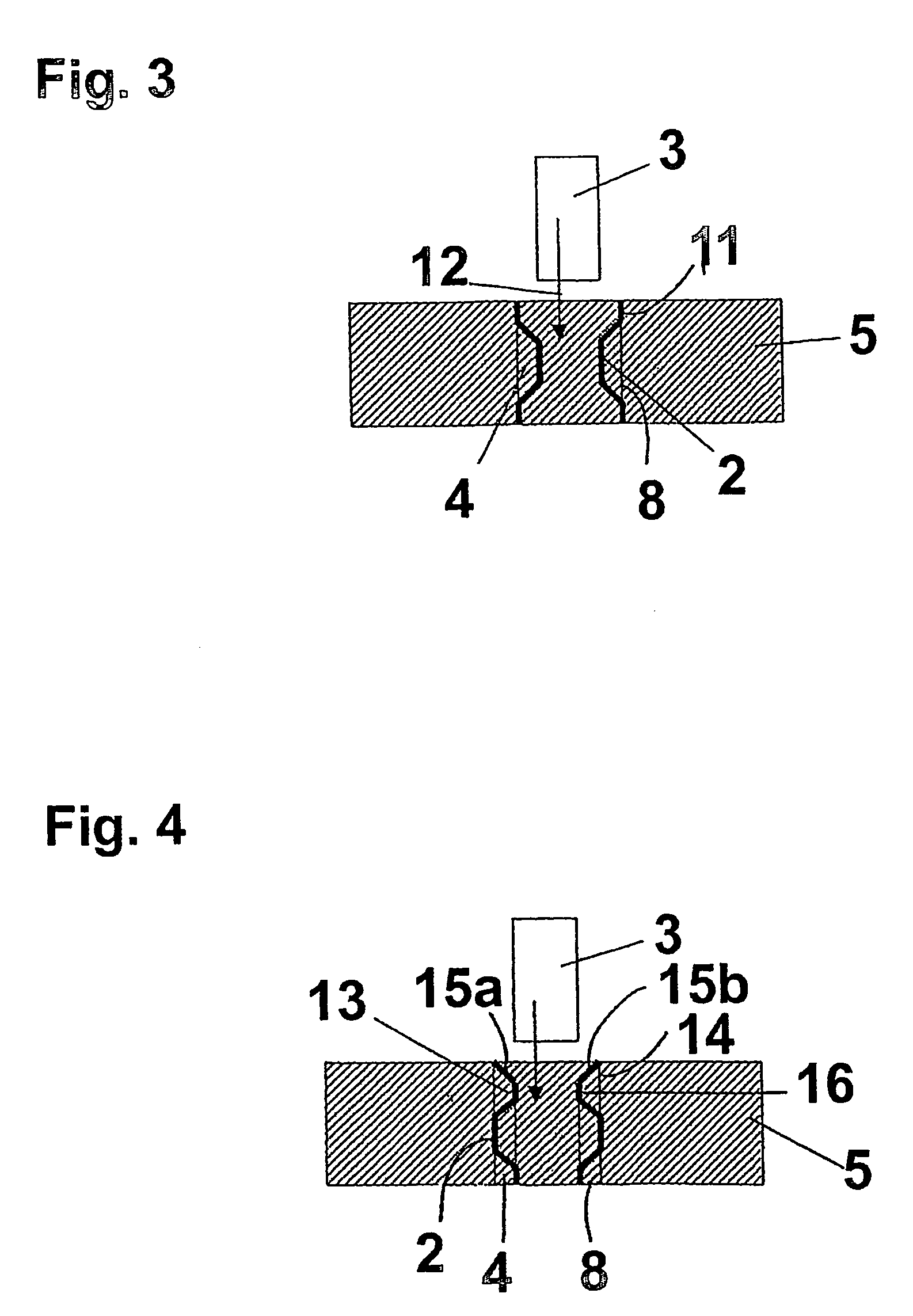
Tolerance ring assembly
ActiveUS20060228174A1Assembly precisionRecord information storageFriction grip releasable fasteningsBiomedical engineering
A tolerance ring has a band (16) with outwardly extending corrugated protrusions forming waves (2) which engage a surface (8) of the bore (4) in a housing (5). At one end of the tolerance ring is an outwardly flared guide surface (15a, 15b) extending axially from the band (16). The guide surface (15a, 15b) acts as an enlarged entrance to the band (16) for a shaft (3) to be mounted in the bore (4) by insertion into the tolerance ring. The use of the guide surface (15a, 15b) assists assembly and reduces or eliminates particle production. It is also possible for the corrugated portions to extend inwardly, for the guide surface to be inwardly flared, and for the tolerance ring to be mounted on the shaft prior to insertion in the bore.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS RENCOL
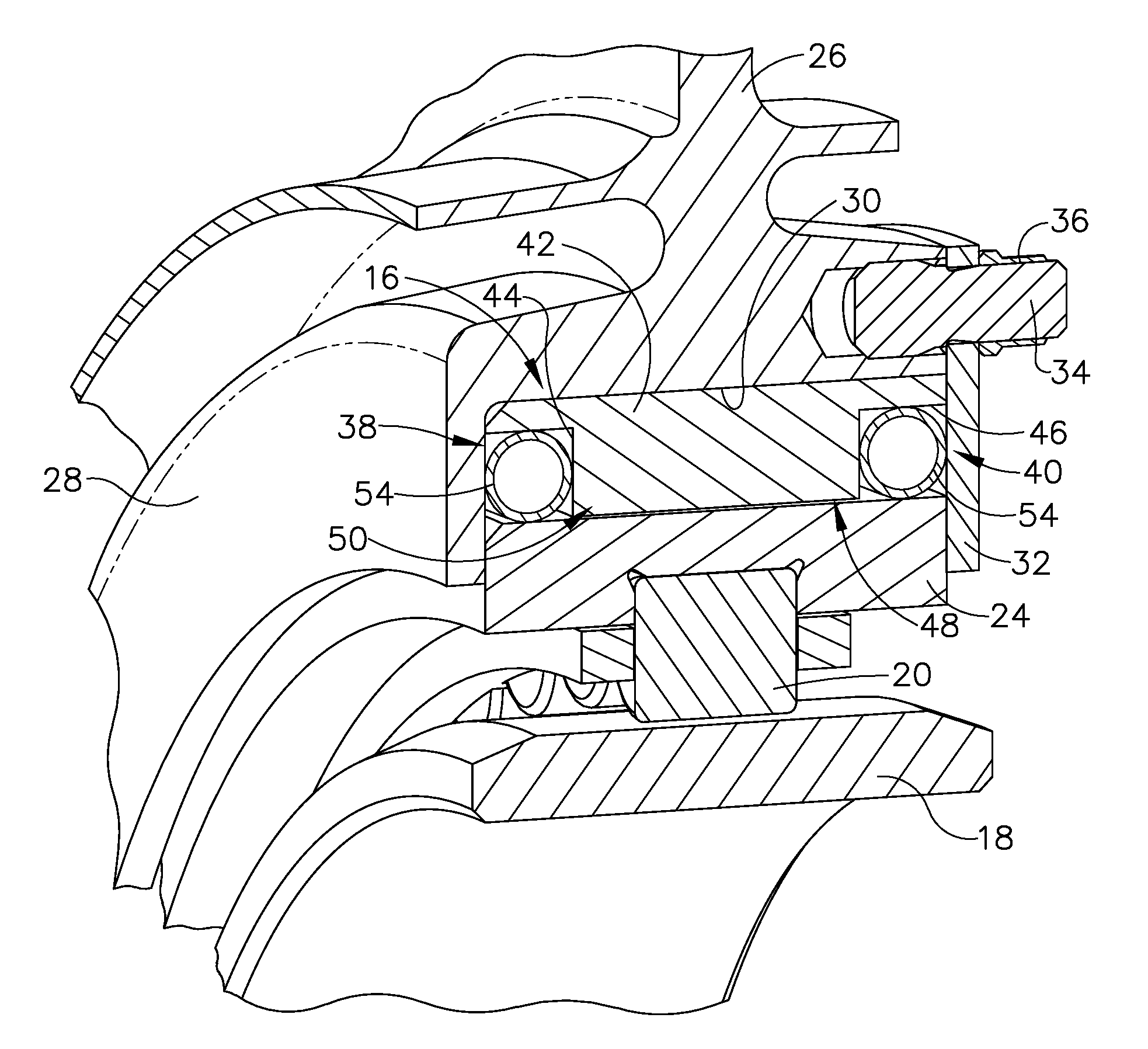
Apparatus for centering rotor assembly bearings
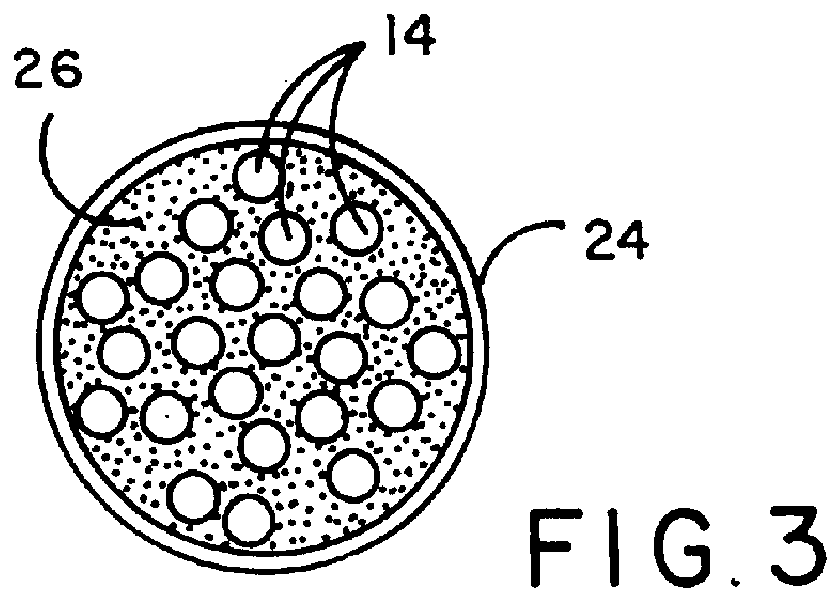
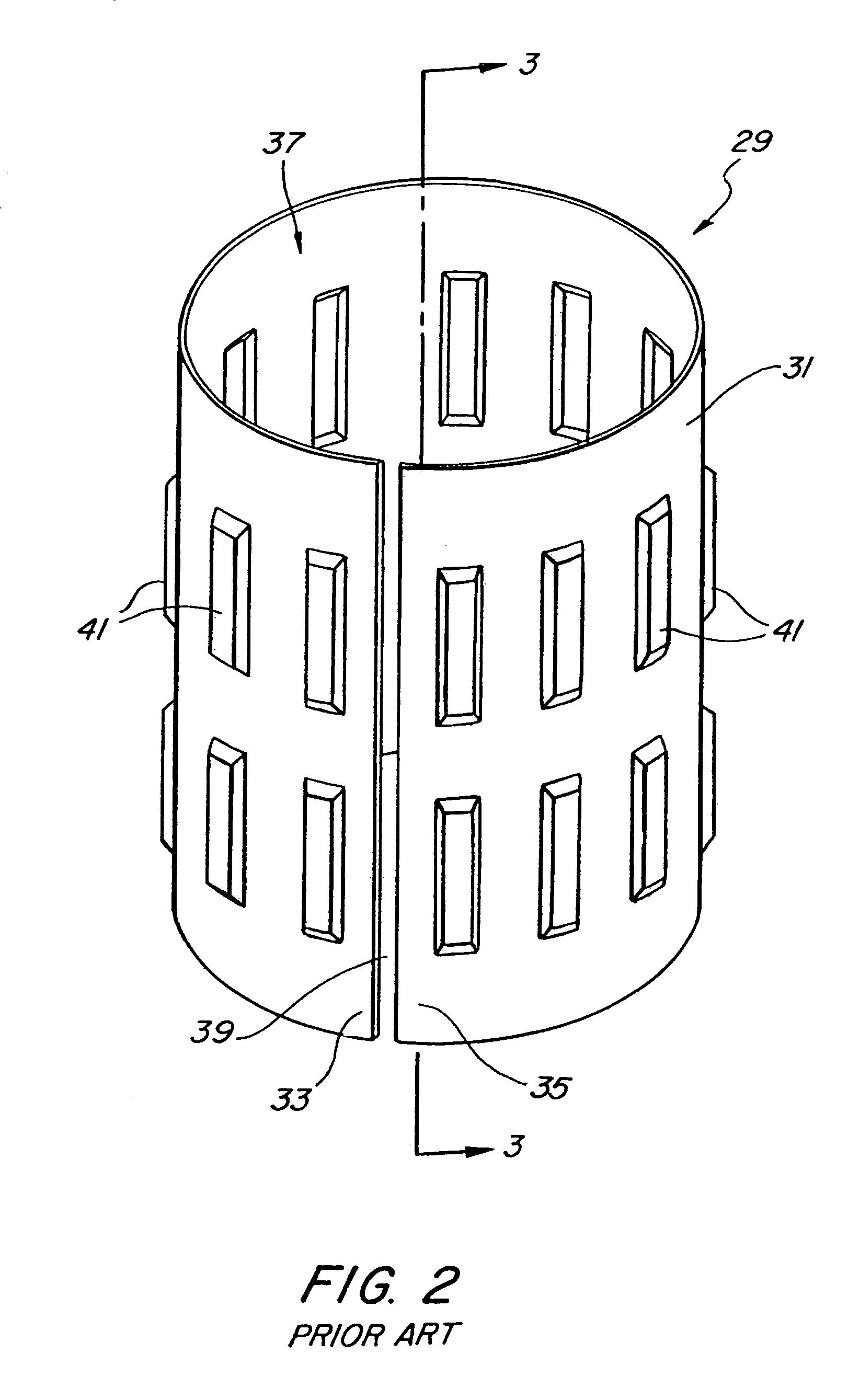
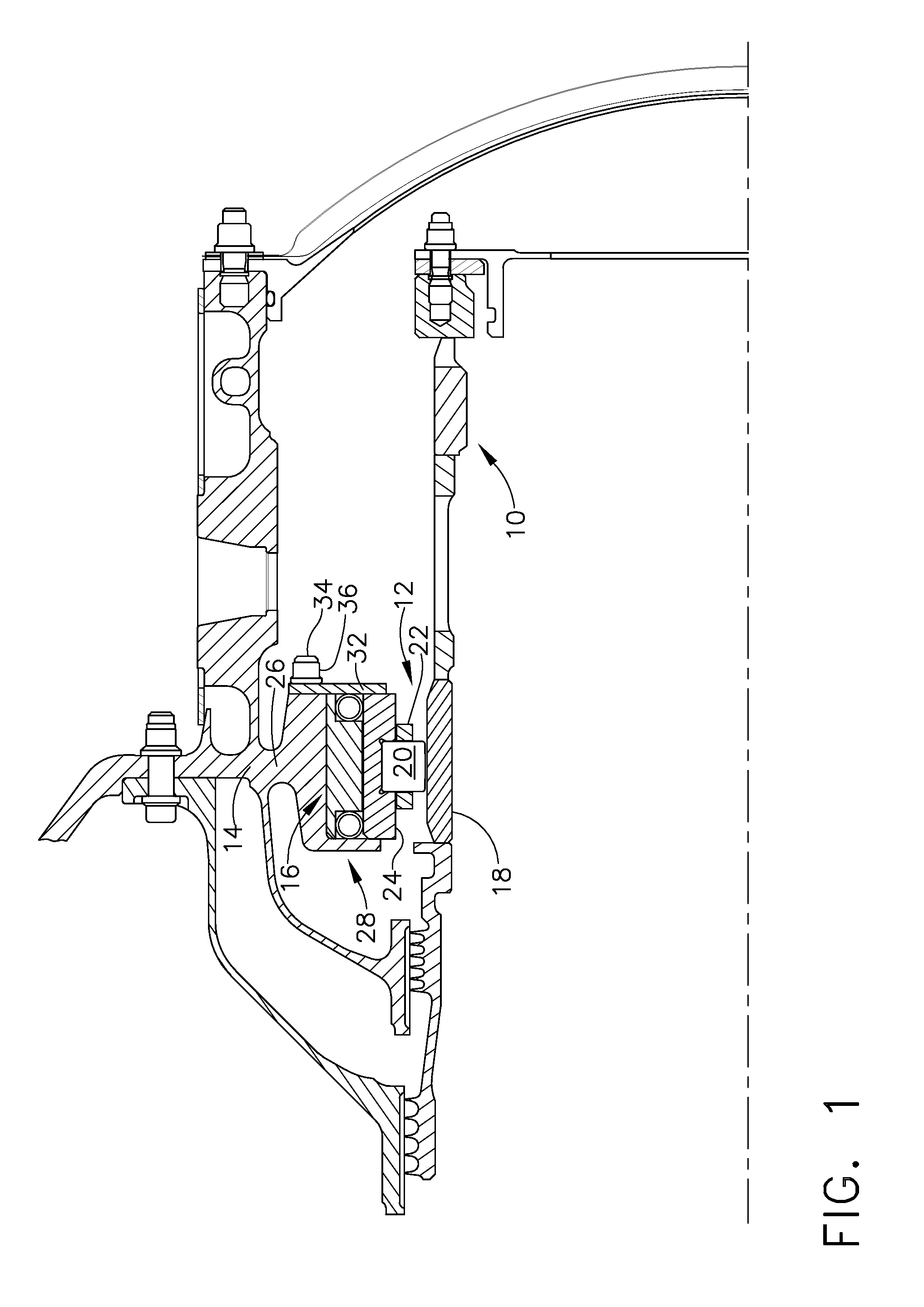
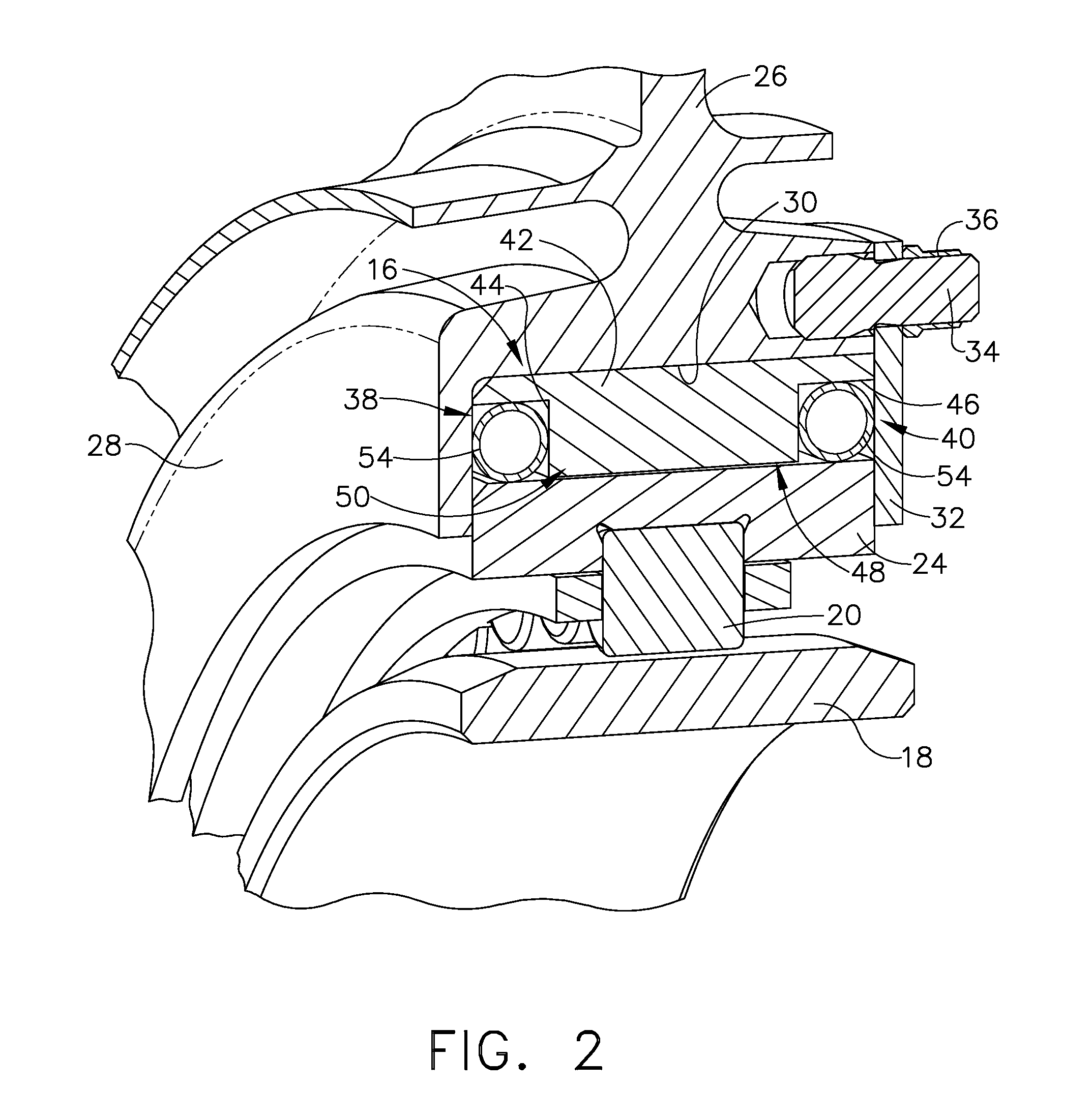
A bearing assembly for a gas turbine engine rotor includes, in an exemplary, an inner race, an outer race assembly, and a rolling element. The outer race assembly includes a body, a plurality of first springs attached to the body, and a plurality of second springs. Each first spring is radially aligned with a corresponding second spring forming a spring pair. The outer race assembly also includes a plurality of connecting members. Each connecting member extends between and connects a first end of the first spring and a first end of the second spring of said spring pair. The outer race assembly further includes a flange with each second spring attached to the flange.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com