Voltage-controlled oscillator
A technology of voltage-controlled oscillators and piezoelectric vibrators, applied in power oscillators, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as narrow frequency variable range, large capacitance value, and inability to switch voltage settings by capacitance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
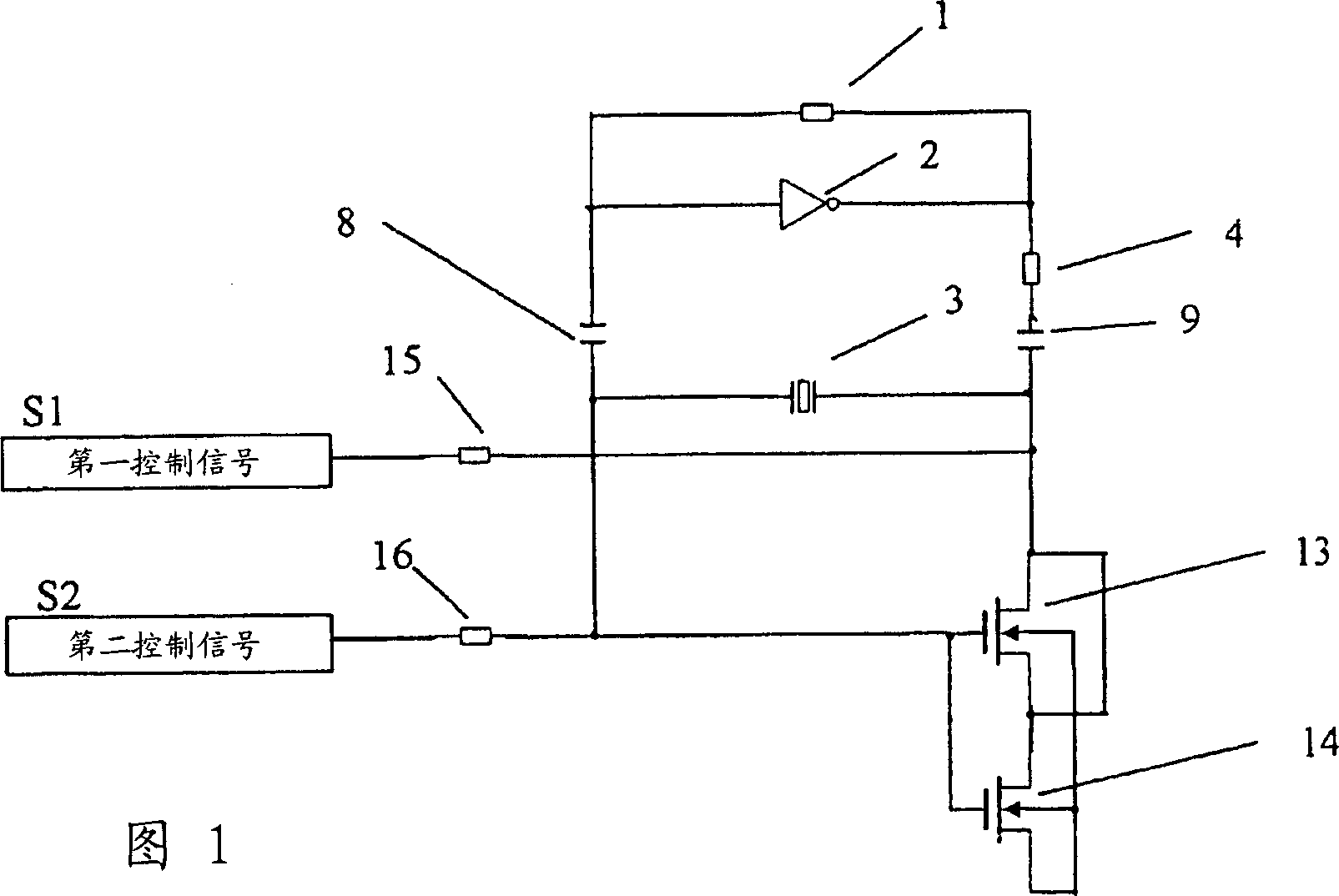
[0047] In the voltage controlled oscillator of Embodiment 1, for example, the first MOS transistor 13 as a variable capacitor is provided, and its source and drain terminals are short-circuited, and the second MOS transistor 14 is connected to the first MOS transistor 13 at its source terminal. The source and drain terminals are shorted. The first and second MOS transistors 13 , 14 have back-gate terminals which are short-circuited to the source terminal of the second MOS transistor 14 . Meanwhile, the first and second MOS transistors 13, 14 have gate terminals shorted together. Therefore, a variable capacitance device is constituted using capacitance between the source and drain terminals of the first MOS transistor 13, the drain terminal of the second MOS transistor 14, and the gate terminals of the first and second MOS transistors.
[0048] That is, the voltage controlled oscillator shows an oscillator circuit composed of an amplifier having a feedback resistor 1 and an in...
Embodiment 2
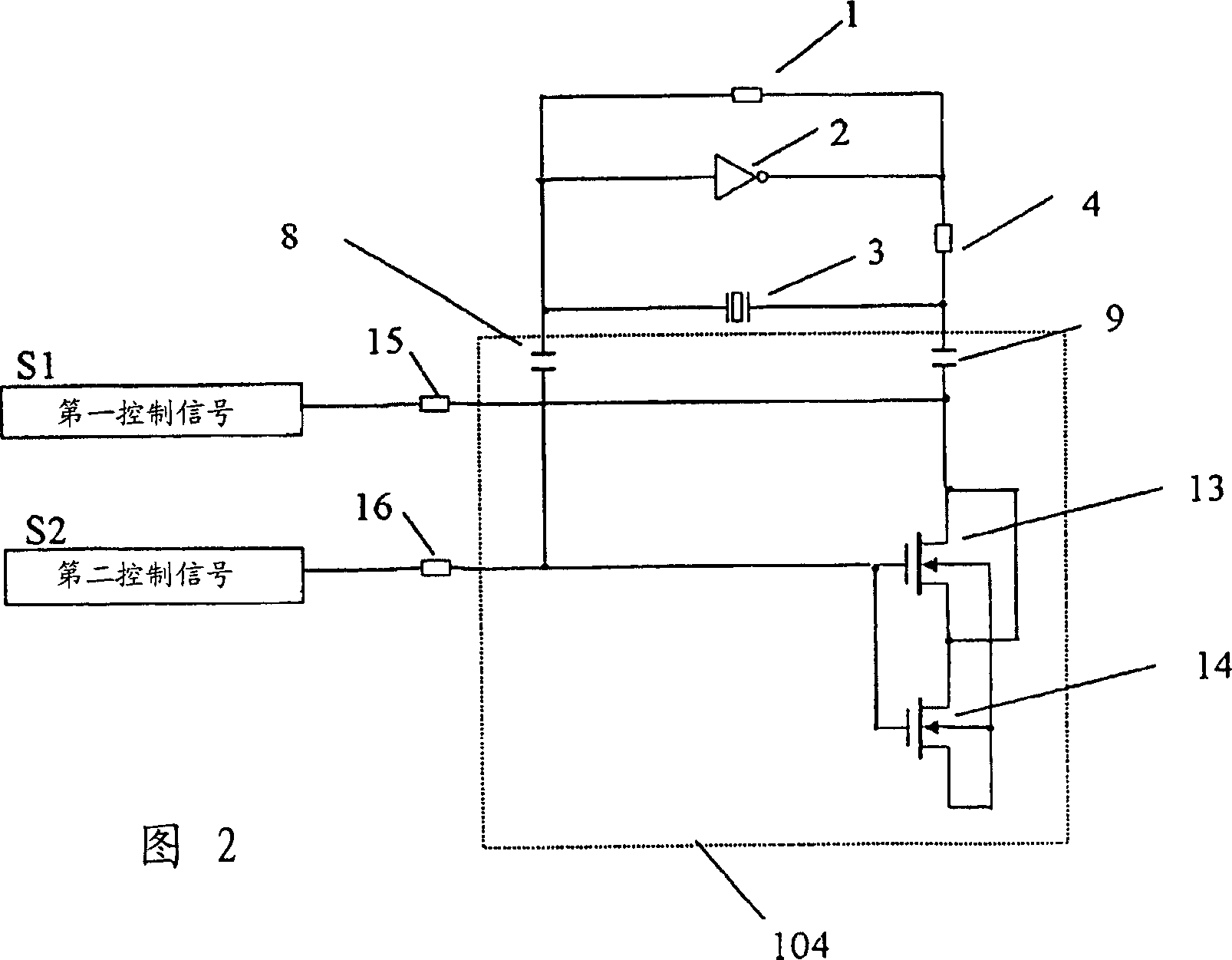
[0053] FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram showing a schematic configuration of a voltage-controlled oscillator in Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0054] Embodiment 2 shows an oscillating circuit composed of a feedback resistor 1, an amplifier 2, and a quartz oscillator 3 forming a feedback circuit. A series connection 104 with a direct connection of the first DC blocking capacitor 8 , the variable capacitor formed by the MOS transistors 13 , 14 of the above-described embodiment and the second DC blocking capacitor 9 is used as the load capacitor.
[0055] At the same time, the first and second MOS transistors 13, 14 as capacitors have a gate terminal and a source-drain terminal, and the MOS transistor threshold value is input to the gate terminal and the source-drain terminal through the high-frequency removal resistors 15, 16 Any one of control signal or temperature compensation control signal and external voltage frequency control signal.
[0056] The others are similar t...
Embodiment 3
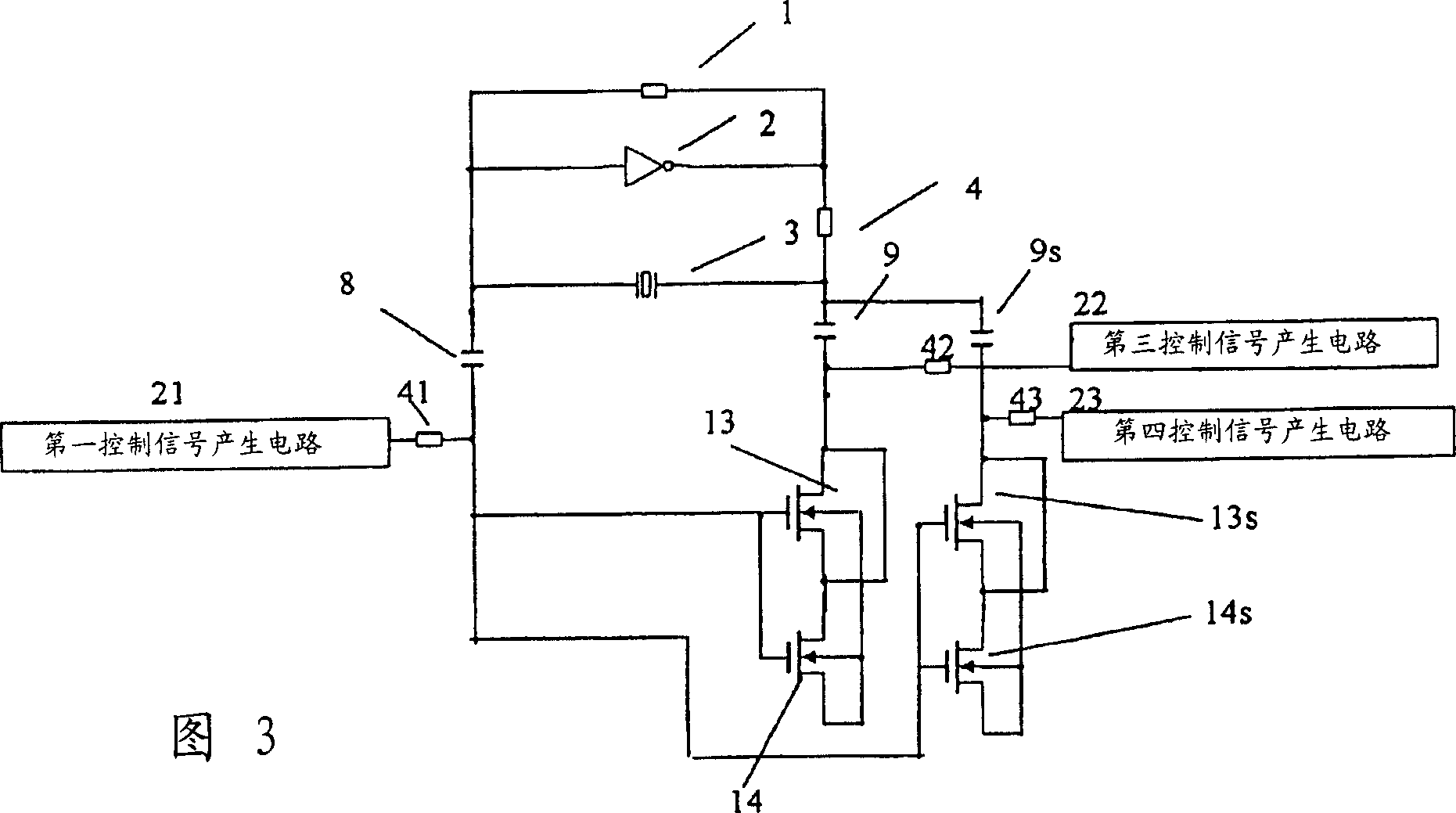
[0061] Embodiment 3 is characterized in that the MOS transistor is divided into a plurality, as shown in FIG. 3, so as to form two sets of variable capacitors, and this configuration enables While the control is similarly performed, the capacitive switching voltage is independently controlled by the temperature compensation control signal and the external voltage frequency control signal.
[0062] In this embodiment, in addition to Embodiment 2, a variable capacitance element formed of the first MOS transistor 13 and the second MOS transistor 14 is provided as the first variable capacitance. At the same time, the third MOS transistor 13S is short-circuited at its source terminal S3 and drain terminal D3 to further short-circuit it with the drain terminal D4 of the fourth MOS transistor 14S. The back gate terminals BG3, BG4 of the third and fourth MOS transistors 13S, 14S are short-circuited with the source terminal S4 of the fourth MOS transistor 14S. At the same time, the ga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com