Fast lavandulol regeneration
A lavender, fast technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of easy variation in morphological and chemical characteristics, high cost of planting lavender, slow reproduction speed, etc., and achieve the effects of shortening production cycle, strong practical value, and fast growth rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
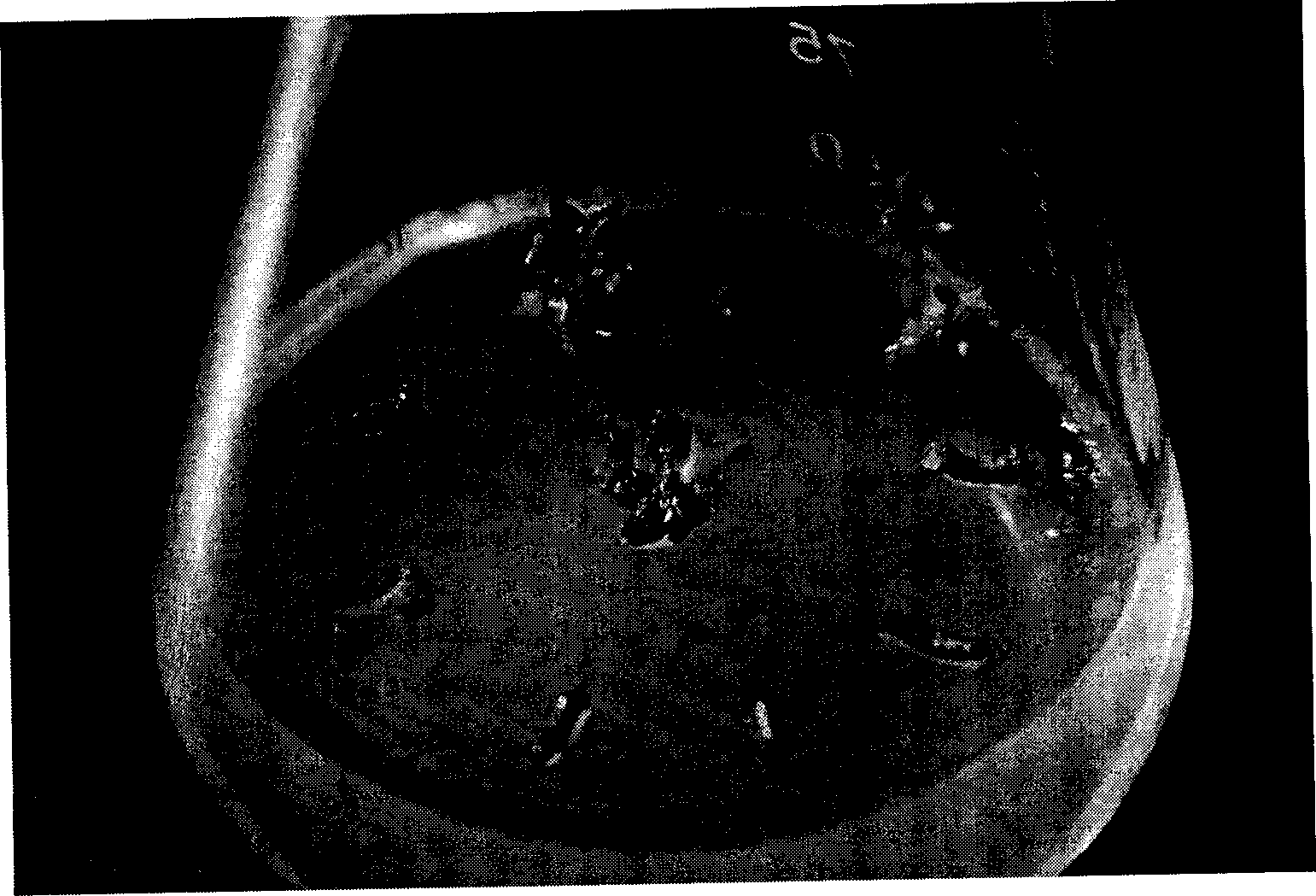
[0028] Obtaining Lavender Hypocotyl Explants
[0029] a. Pick plump lavender seeds, soak them in warm water at 40°C, continue to soak for 24 hours after the water cools, rinse the soaked lavender seeds with running water for 30 minutes, rinse them with 75% ethanol for 25 seconds, rinse them once with sterile water, and rinse them with 0.2% ethanol Soak in sodium dichloroisocyanurate (UCl) solution for 20 minutes, then rinse with sterile water 4-5 times, inoculate the seeds in 0.4% agar-solidified MS solid medium, place at 25±1°C, light for 8 hours, The culture was carried out under dark culture conditions for 16 hours, and the light intensity was 1500 lx. After 15-20 days, the seeds began to germinate, and the germination rate was 53%.
[0030] Direct Differentiation of Lavender Hypocotyl Explants to Adventitious Buds
[0031] b. Take the hypocotyls of the sterile seedlings that have undergone seed germination and cut them into small sections of ab...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Obtaining Lavender Hypocotyl Explants
[0037] a. Pick plump lavender seeds, soak them in warm water at 40°C, continue to soak for 24 hours after the water cools, rinse the soaked lavender seeds with running water for 30 minutes, rinse them with 75% ethanol for 25 seconds, rinse them once with sterile water, and rinse them with 0.2% ethanol Soak in sodium dichloroisocyanurate (UCl) solution for 20 minutes, then rinse with sterile water 4-5 times, inoculate the seeds in 0.4% agar-solidified MS solid medium, place at 25±1°C, light for 8 hours, The culture was carried out under dark culture conditions for 16 hours, and the light intensity was 1500 lx. After 15-20 days, the seeds began to germinate, and the germination rate was 53%.
[0038] Direct Differentiation of Lavender Hypocotyl Explants to Adventitious Buds
[0039] b. Take the hypocotyls of the sterile seedlings that have undergone seed germination and cut them into small sections of abo...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Obtaining Lavender Hypocotyl Explants
[0045] a. Pick plump lavender seeds, soak them in warm water at 40°C, and continue soaking for 24 hours after the water cools down. Rinse the soaked lavender seeds with running water for 30min, rinse with 75% ethanol for 25s, rinse once with sterile water, soak for 20min with 0.2% sodium dichloroisocyanurate (euchlorozine) solution, and then rinse with sterile water 4-5 times, the seeds were inoculated in 0.4% agar-solidified MS solid medium, placed at 25±1°C, 8h light, 16h dark culture conditions, and the light intensity was 1500lx. After 15-20 days, the seeds began to germinate. The germination rate was 53%.
[0046] Direct Differentiation of Lavender Hypocotyl Explants to Adventitious Buds
[0047] b. Take the hypocotyls of the sterile seedlings that have undergone seed germination and cut them into small sections of about 5mm, place them horizontally, and insert 0.5% agar to solidify MS+IAA 0.1mg·L ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com