Method of error compensation in a coordinate measuring machine
A technology for measuring value and coordinate positioning, which is applied to measuring devices, mechanical measuring devices, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of time-consuming and complicated calibration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
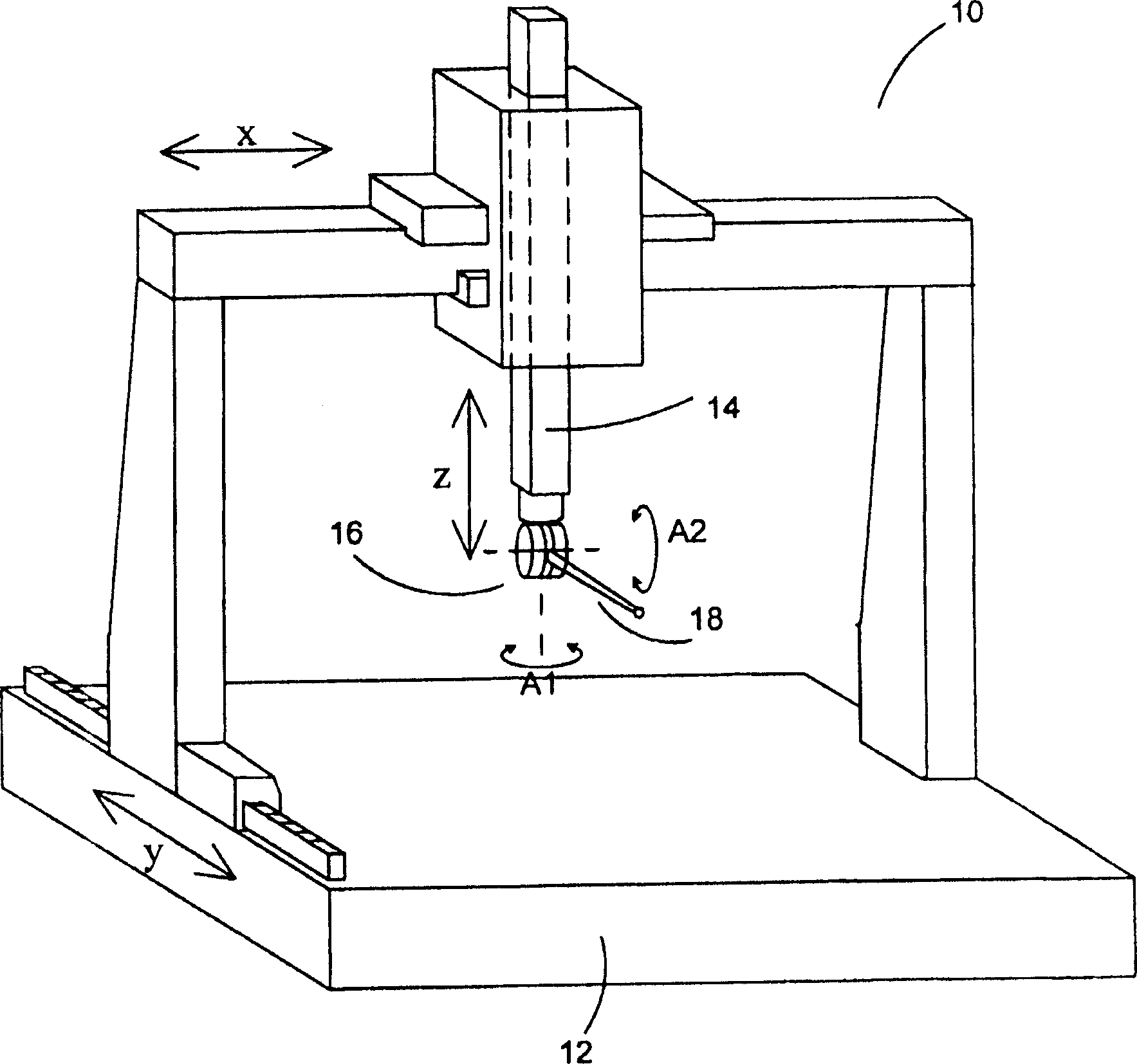
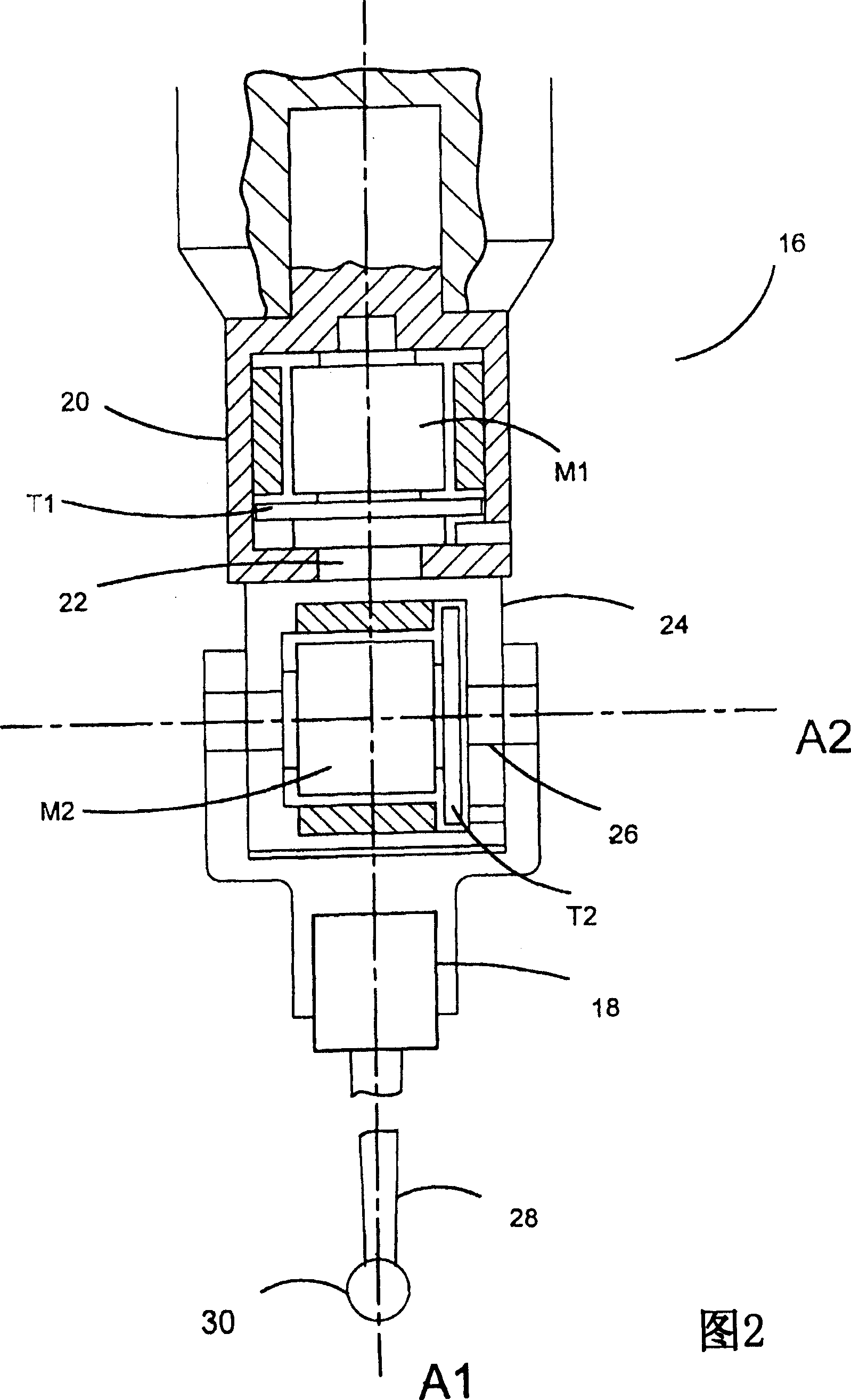
[0044] figure 1 Shown is the articulating probe mounted on a CMM. The coordinate measuring machine 10 includes a platform 12 on which a workpiece can be placed and an arm 14 movable in X, Y and Z directions relative to the platform 12 . An articulated probe 16 is mounted on the arm 14 of the coordinate measuring machine (CMM). The articulating probe head 16 allows a workpiece measurement probe 18 mounted thereon to rotate about two substantially perpendicular axes A1 and A2.
[0045]The robotic arm 14 is thus movable in the X, Y and Z directions by the X, Y and Z drives (not shown) of the CMM. Scale means (not shown) on X, Y and Z indicate the immediate coordinates of where the arm 14 is located. A rotary drive (not shown) located in the articulated probe enables movement of the probe around the two axes of rotation A1 and A2. This motion is measured by a rotary scale (not shown) located within the articulating probe 16 . The signal from the probe 18 indicative of deflect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com