Use of core process models in model predictive controller
A process model and controller technology, applied in the direction of adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., can solve the problems of unreliable and sound prediction of process value, unclear working status of MPC controller, and controllability And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
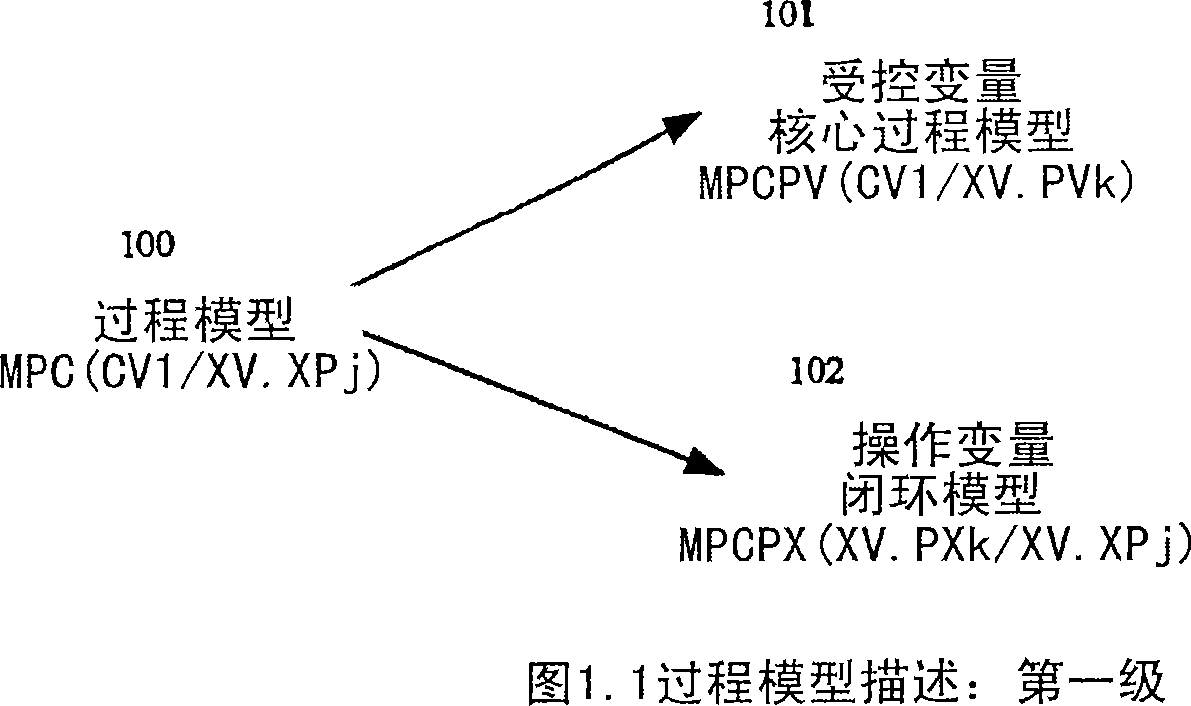
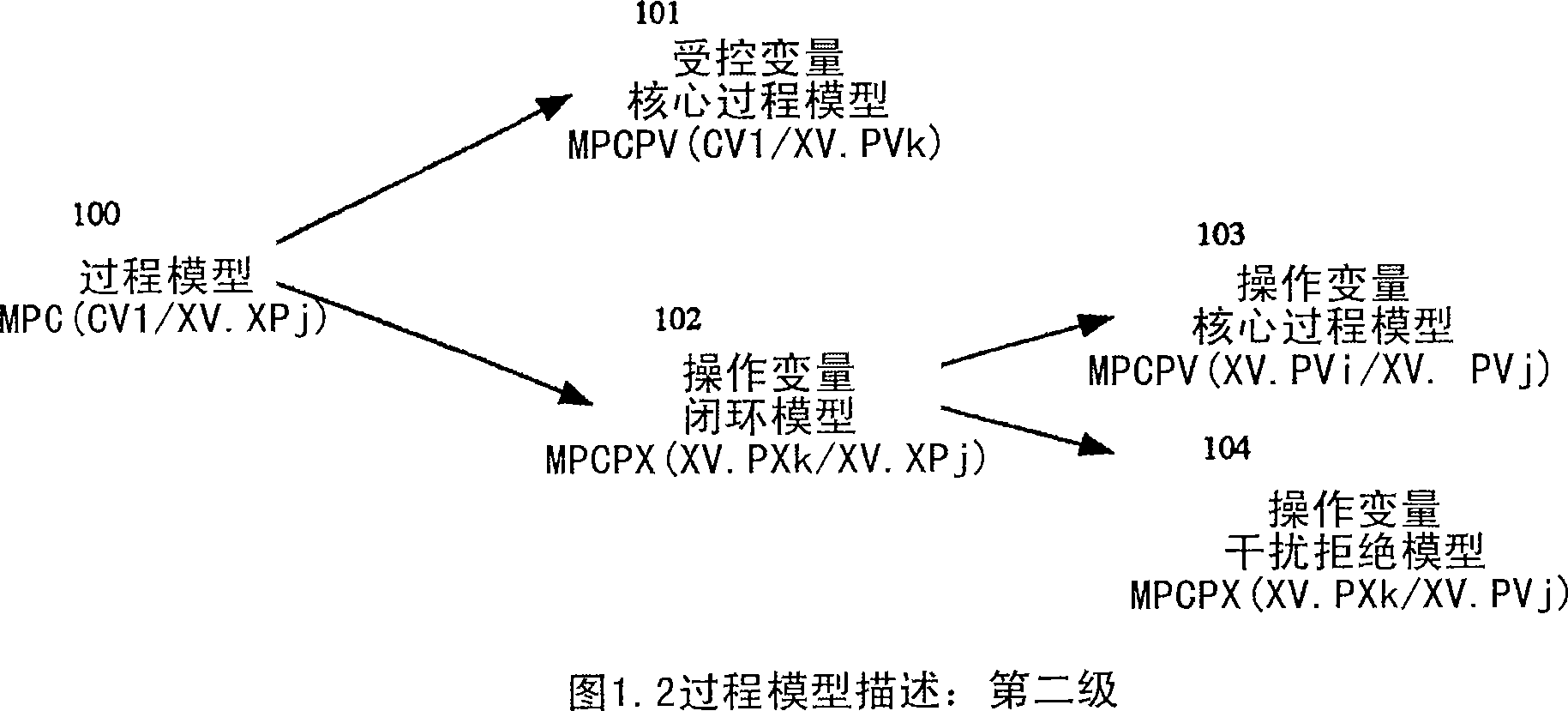
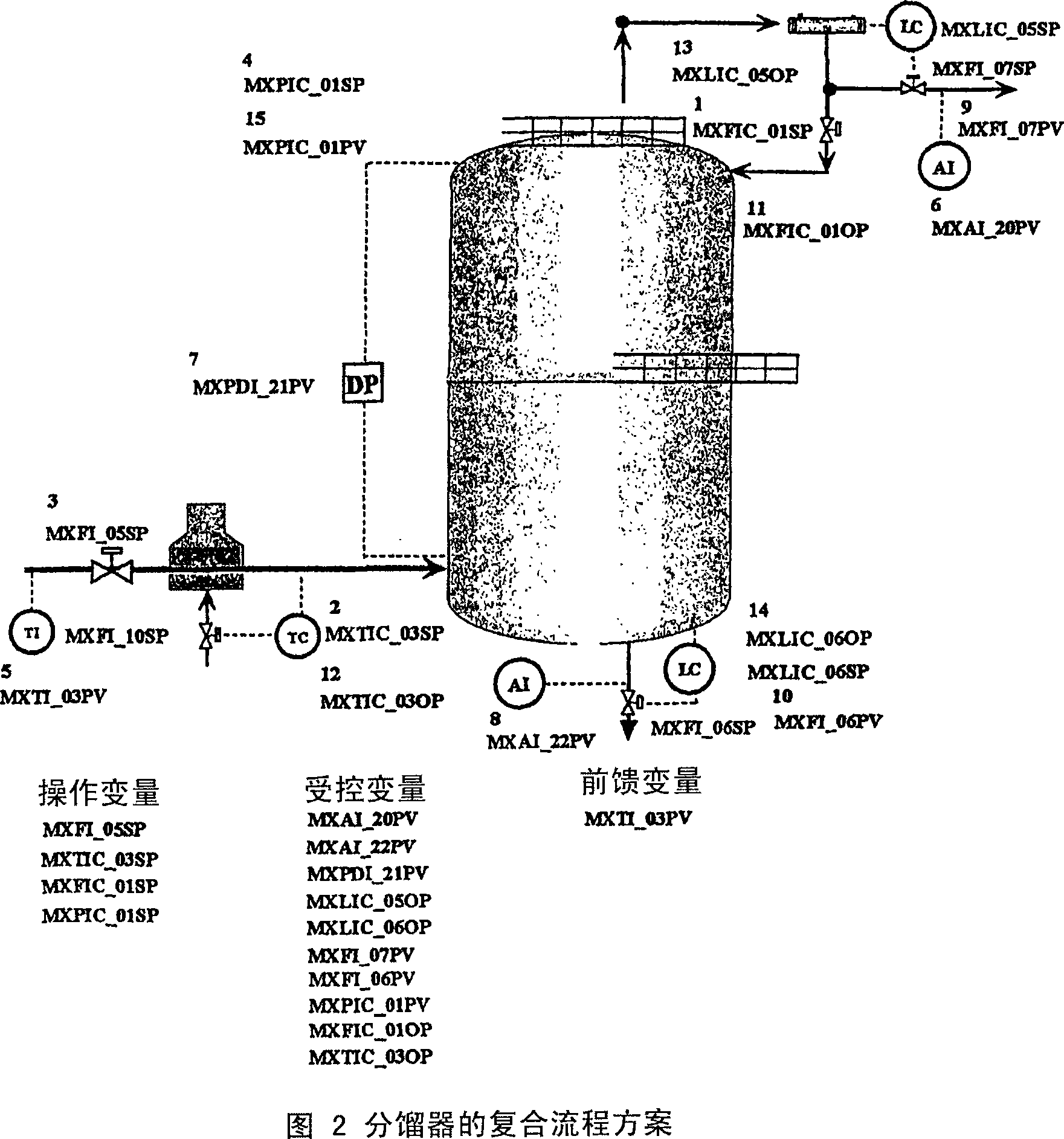
[0041] The present invention describes a dynamic process model that involves a controlled variable relative to a manipulated variable set point, including the defined set of subprocess models described herein. Figure 1.1 and Figure 1.2 represent the two-level process model description disclosed in the present invention. The sub-process model described below provides an unambiguous method for updating the process model with minimal or no additional model validation upon manipulation of variable adjustments / configuration changes and when working in conjunction with an appropriate simulator.
[0042] The invention presented here seeks to describe the potential dynamic effects due to the interaction of manipulated variable adjustment controllers and subelements, in order to update the entire set of process models used in a model predictive controller, only the revalidation of the model's Subset. Basically, when changing the manipulated variable set point, the manipulated variable...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com