Method and device for equalizing tension in parallel yarns
A technology of parallel fiber and operating mode, which is applied in the direction of transportation and packaging, other manufacturing equipment/tools, textiles and paper making, and can solve problems such as uneconomical and inability to adjust creel tension
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
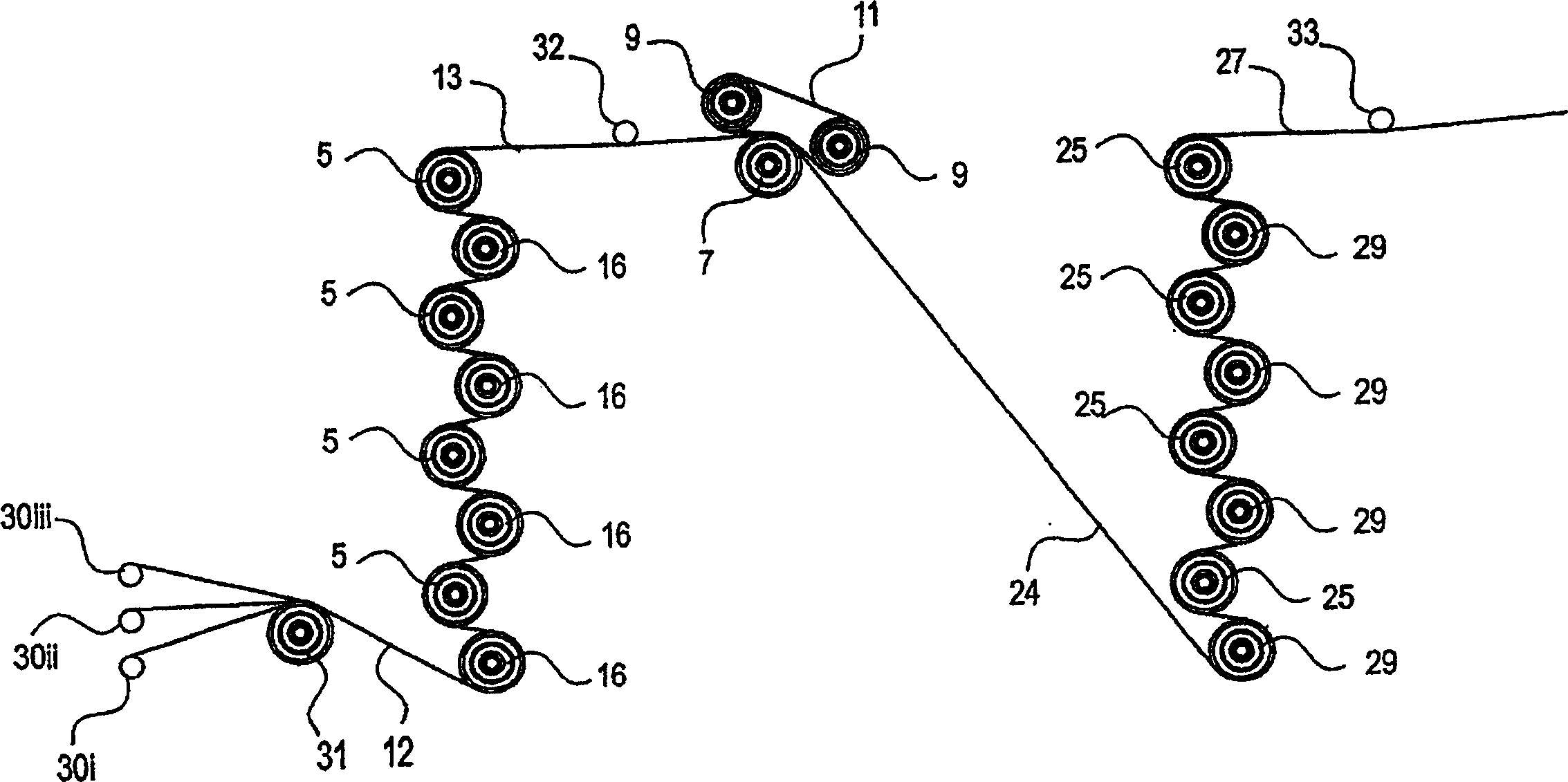
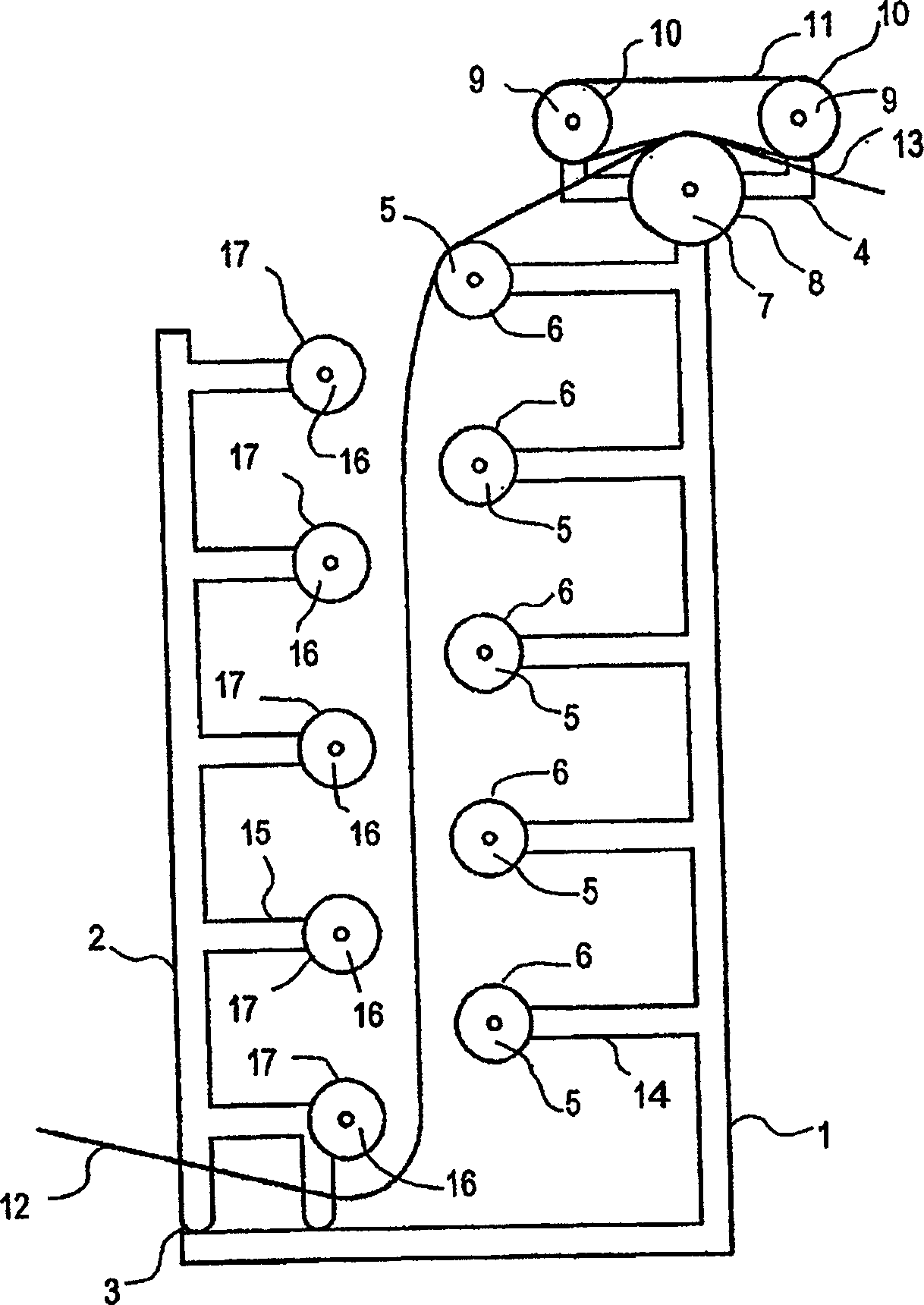
Embodiment Construction
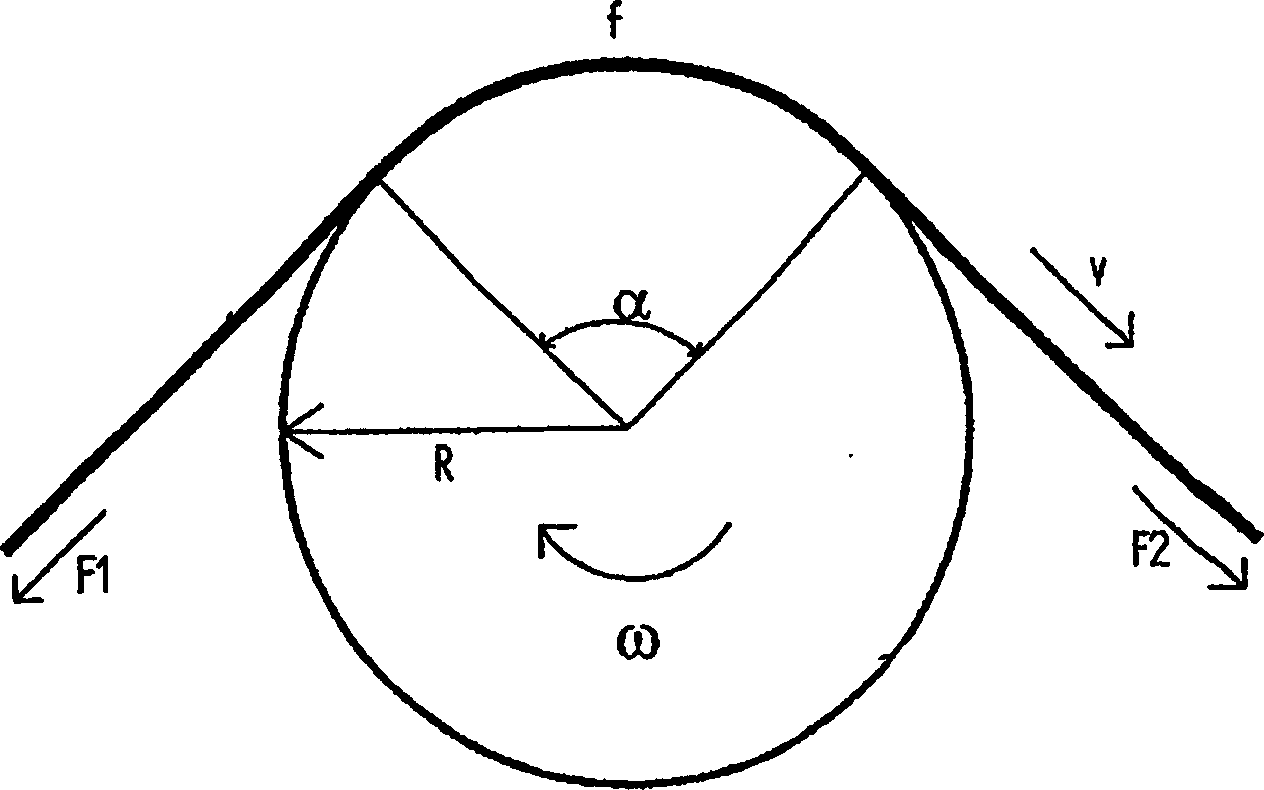
[0056] figure 1 The fiber tow is shown moving at a specific velocity (v) on a driven roller while the fiber tow partially surrounds the roller at an angle (α). The roller rotates at a peripheral speed (ω×R) and in the direction shown on the diagram. The friction coefficient of the roller surface is (f). F1 is the tension of the fiber bundle in front of this roller. F2 is the tension of the fiber bundle behind the roller
[0057] One of three things will now happen:
[0058] 1. (ω×R) > v
[0059] The peripheral speed of the roller is greater than that of the fiber bundle, so the tension on the fiber bundle is reduced. Since sliding friction and sliding velocity are independently separated, the difference in velocity between the fiber and the roller surface is not important. This phenomenon occurs at the tension reducing device.
[0060] (F1>F2).
[0061] 2. (ω×R)=v
[0062] The peripheral speed of the roller is equal to the speed of the fiber bundle, and the fiber bund...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com