A low bending loss superfine low water peak fiber
A technology of bending loss and low water peak, applied in cladding optical fiber, optical waveguide and light guide, etc., can solve the problems of failure to provide optical fiber, achieve excellent bending resistance, improve bending loss performance, and increase the length of optical fiber
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
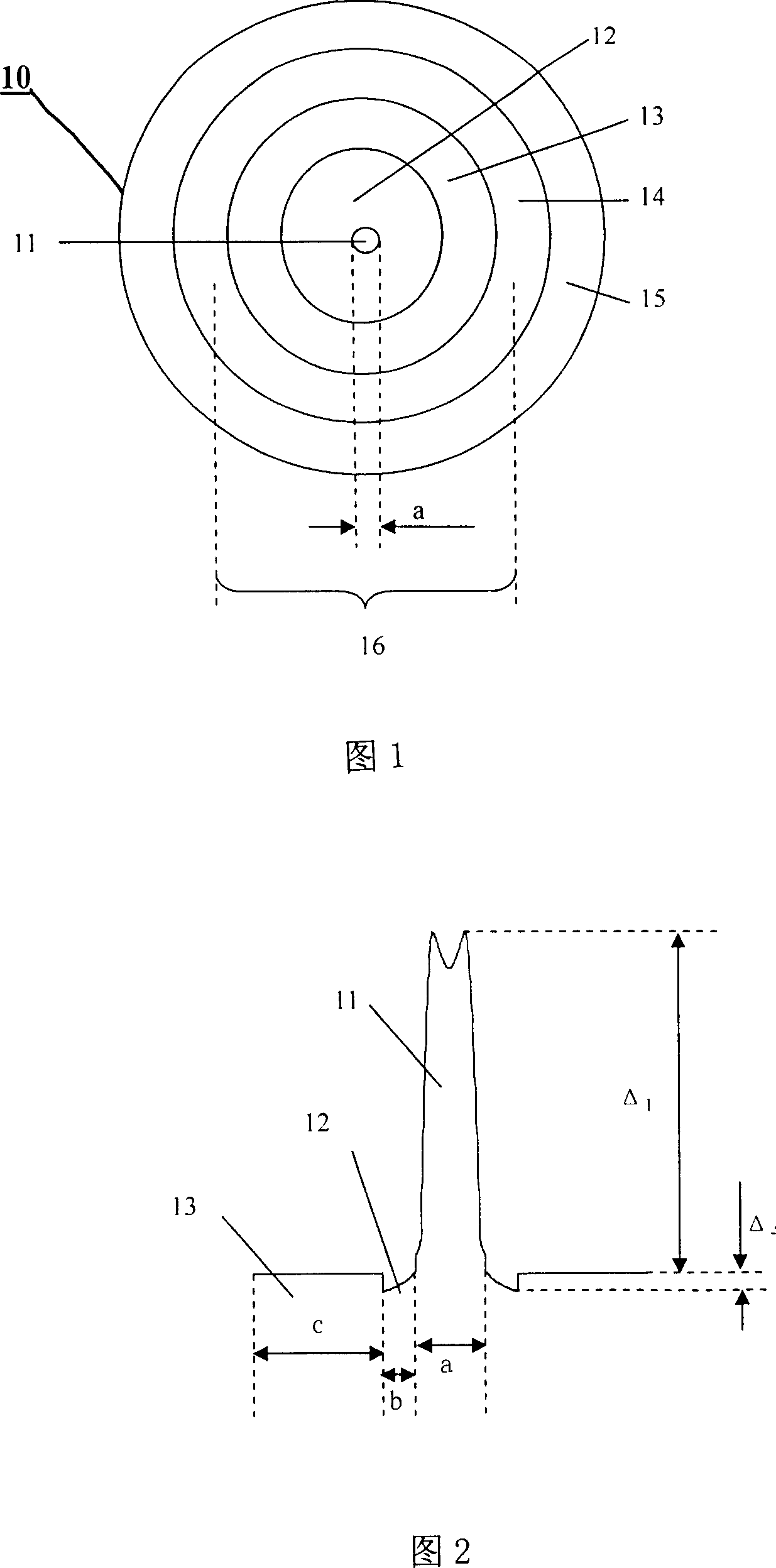
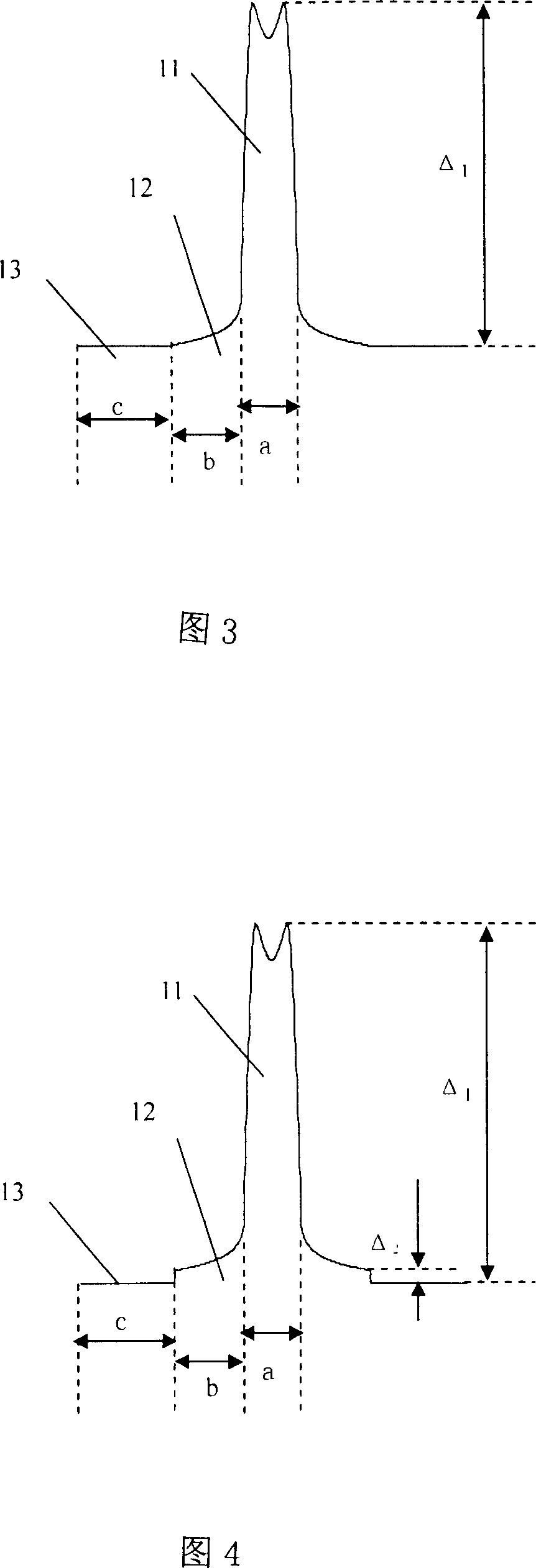
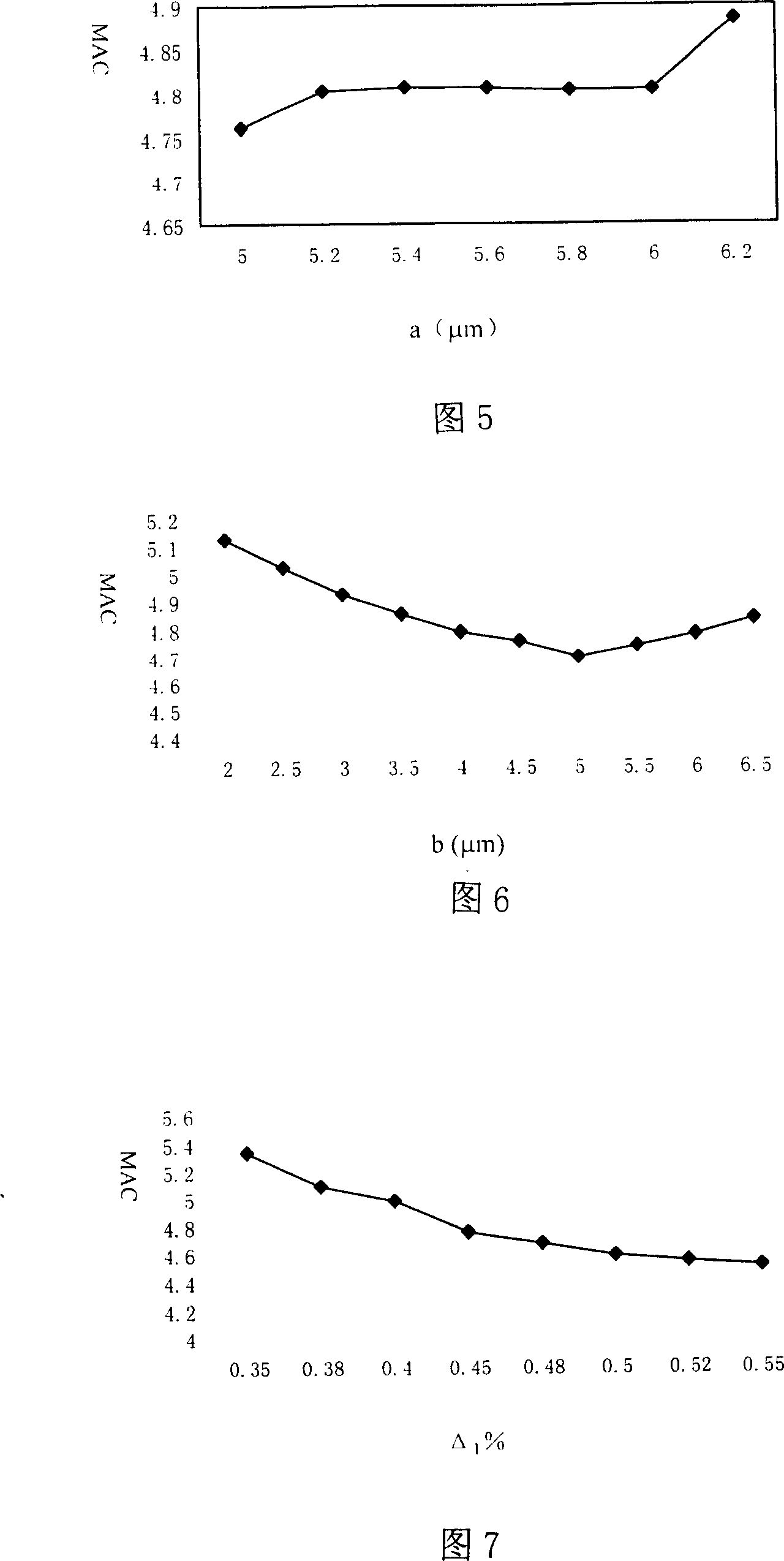
[0060] by the core SiO 2 The method of doping Ge in the medium makes Δ1 between 0.39% and 0.50% at a wavelength of 632.8nm; doping F in the SiO2 of the first cladding layer makes Δ2 between -0.070% and -0.014% at a wavelength of 632.8nm ;The thickness of the core layer and the first cladding layer is controlled by controlling the flow rate of the VAD blowtorch, which are between 2.8-3.2m and 2.5-6.0μm respectively; the thickness of the second cladding layer is between 8.5-13.0μm; by controlling The diameter of the optical fiber is controlled at 80±5μm by wire drawing speed and dropper temperature; the thicknesses of the two coating resins are guaranteed to be about 20 and 10μm respectively; the diameter of the final finished optical fiber is 140±5μm; the first The Young's modulus of the coating 14 and the second coating 15 are about 1.2 MPa and 760 MPa respectively, and the elastic modulus are 1.1 MPa and 1400 MPa respectively. The cross-sectional shape of this fiber can be s...
Embodiment 2
[0067] By doping Ge in the core layer SiO2, Δ1 is between 0.55% and 0.63% at a wavelength of 632.8nm; the first cladding layer is not specially doped, and its refractive index distribution is freely distributed under the influence of the first blowtorch; The thickness of the core layer and the first cladding layer are controlled by controlling the flow rate of the VAD blowtorch, which are between 2.3-3.0 μm and 3.5-5.6 μm respectively; the thickness of the second cladding layer is between 9.4-12.3 μm; by controlling the wire drawing Control the fiber diameter at 80μm±5μm by speed, dropper temperature, etc.; ensure that the thicknesses of the two coating resins are about 20 and 10μm respectively; the final product fiber diameter is 140±5μm; the first coating The Young's modulus of the layer 14 and the second coating 15 are about 1.2 MPa and 760 MPa respectively, and the elastic modulus are 1.1 MPa and 1400 MPa respectively. The cross-sectional shape of this optical fiber can be...
Embodiment 3
[0074] By doping Ge in the core layer SiO2, Δ1 is between 0.43% and 0.63% at a wavelength of 632.8nm, and Δ2 is between 0.03% and 0.07%. The core layer and the first The thickness of the cladding is between 2.5-2.7μm and 4.0-6.5μm respectively; the thickness of the second cladding is between 8.8-11.5μm; the fiber diameter is controlled at 80μm± by controlling the drawing speed, dripper temperature, etc. 5 μm; ensure that the thicknesses of the two coating resins are about 20 and 10 μm respectively; the diameter of the final finished optical fiber is 140±5 μm; the Young’s modulus of the first coating 14 and the second coating 15 are controlled by the resin and assimilation conditions They are about 1.2MPa and 760MPa respectively, and the elastic modulus are 1.1MPa and 1400MPa respectively. The cross-sectional shape of this optical fiber can be shown in FIG. 4 . The geometric parameters and performances of several typical optical fibers obtained in this embodiment are shown in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com