Wind turbine blade handling aboard a vessel
a technology for wind turbine blades and vessels, which is applied in the direction of waterborne vessels, engine fuctions, renewable energy products, etc., can solve the problems of wasting already limited space on board the vessel, affecting the operation of the vessel, so as to improve the handling method and improve the transportation configuration. , the effect of increasing safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
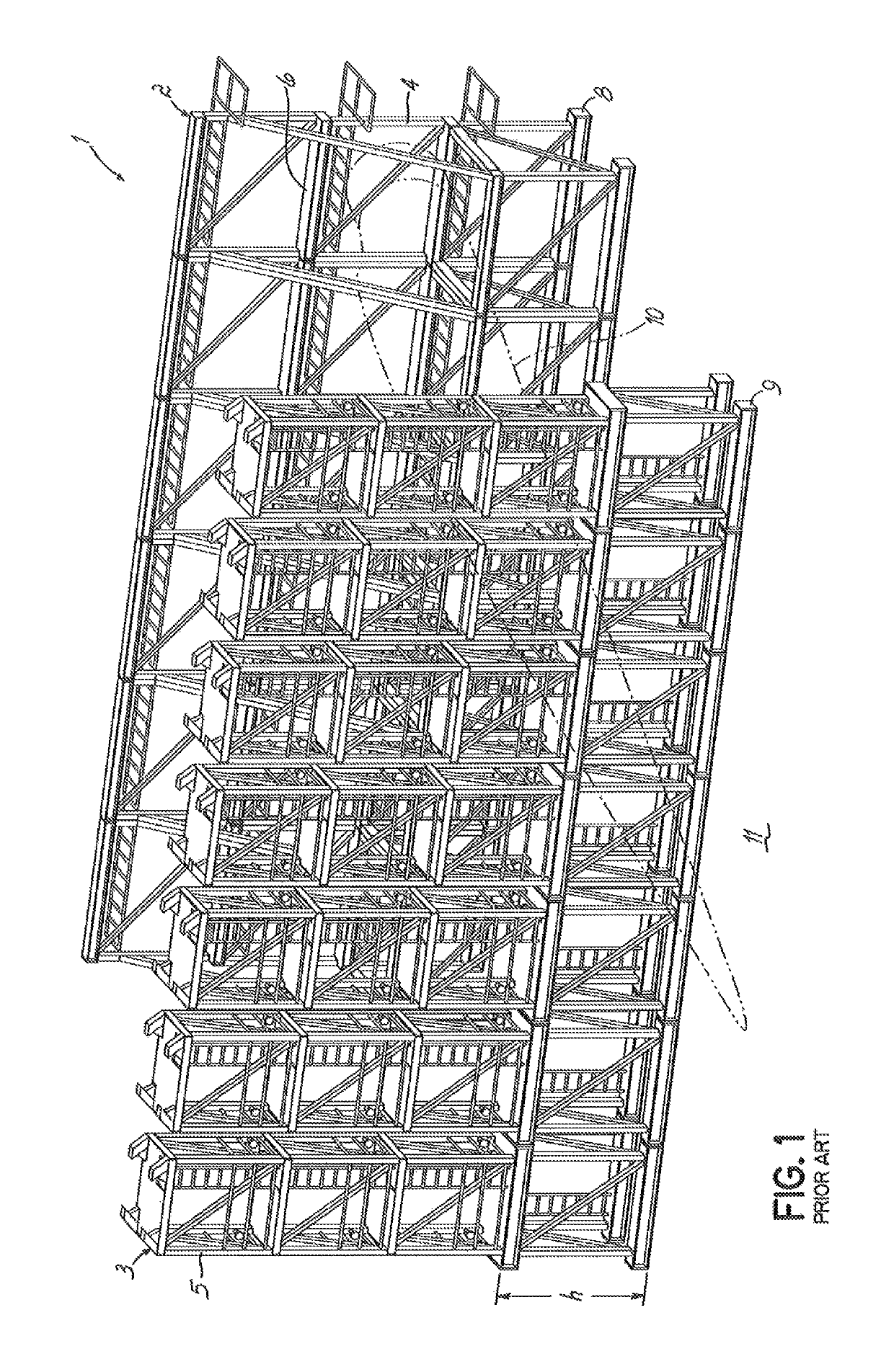
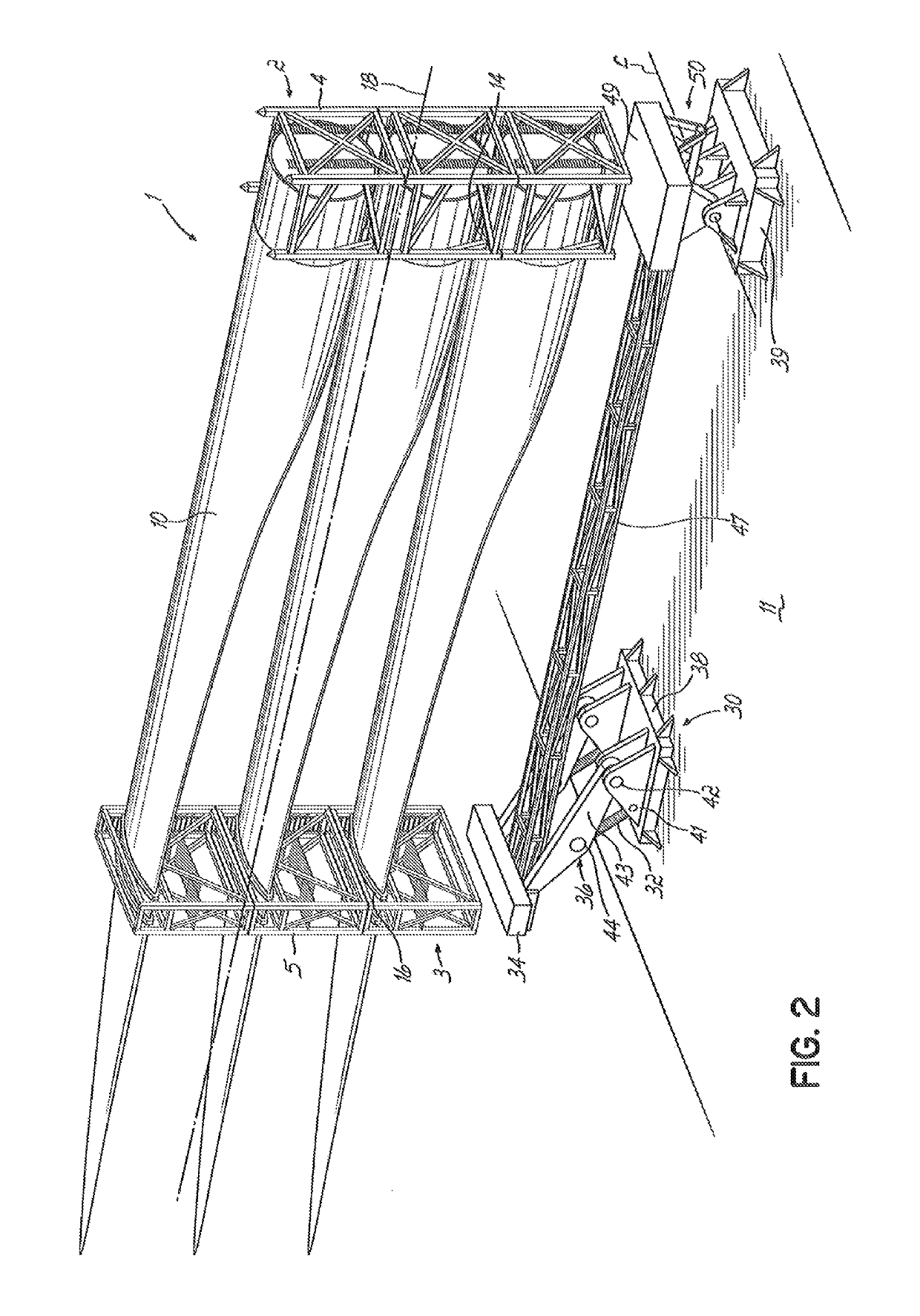
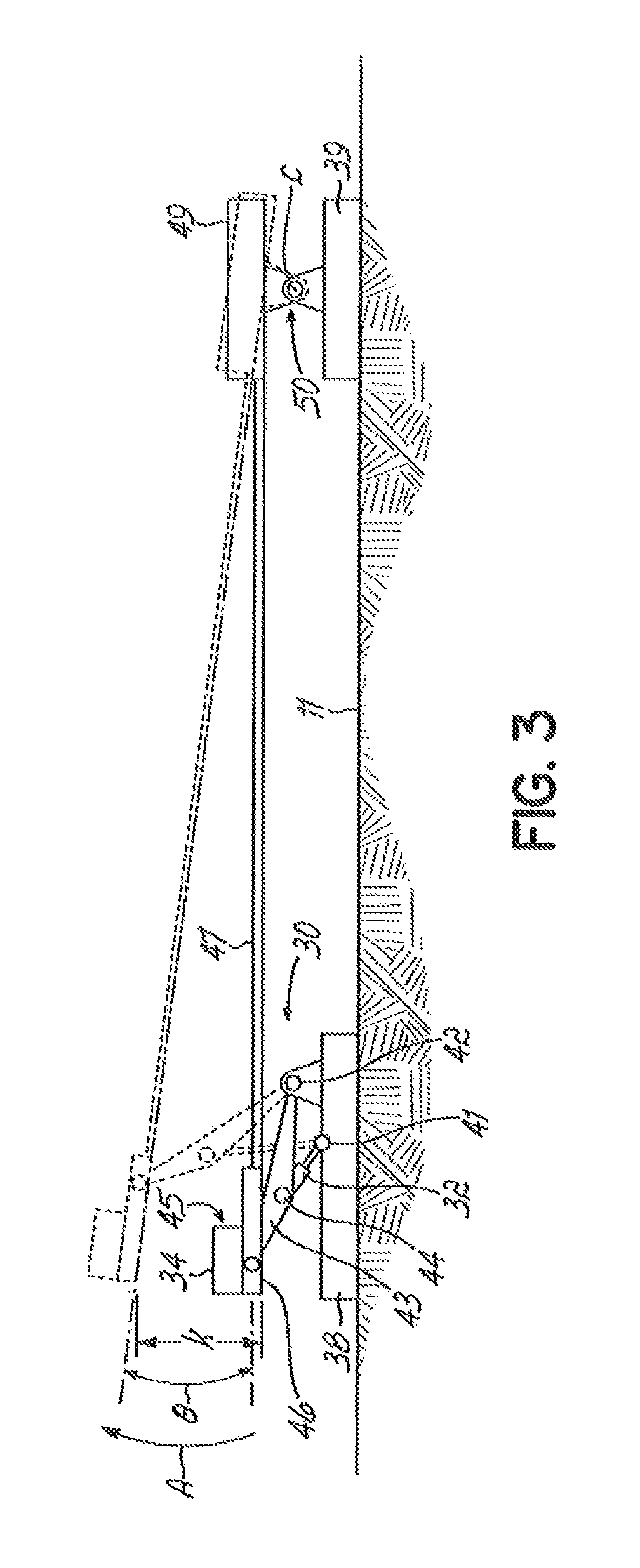
[0029]The term “rack arrangement” is a collective term intended to denote a blade storage construction providing a support structure for wind turbine blades with support elements at or towards the blades' root ends and at or towards their tip ends in the form of a respective, facing root and tip rack. So-called “tip end” support may in particular be provided by means of a tip frame or tip rack at or near a mid-portion of a blade, towards the blade tip. So-called “root end” support may in particular be provided by means of a root frame or root rack at or near a root end of a blade. Preferably, a root end support frame or root rack is provided at the blade root end. A root or tip rack may be unitary or modular although the modular type may be preferred. Each blade may preferably be stored in a frame pair. A root or tip rack may be established by providing one or more frames in a fixed arrangement on a working platform such as on a loading deck of a vessel. The rack arrangement may be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com