Weaving loom for producing a leno fabric
a weaving loom and fabric technology, applied in the direction of looms, leno shedding mechanisms, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of three separate drives, the control of conventional warp threads requires substantial effort and expense for its construction, and the leno threads are no longer positively guided in the slant slots of the heald or shaft frame. to achieve the effect of improving the control or guiding of the leno threads
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
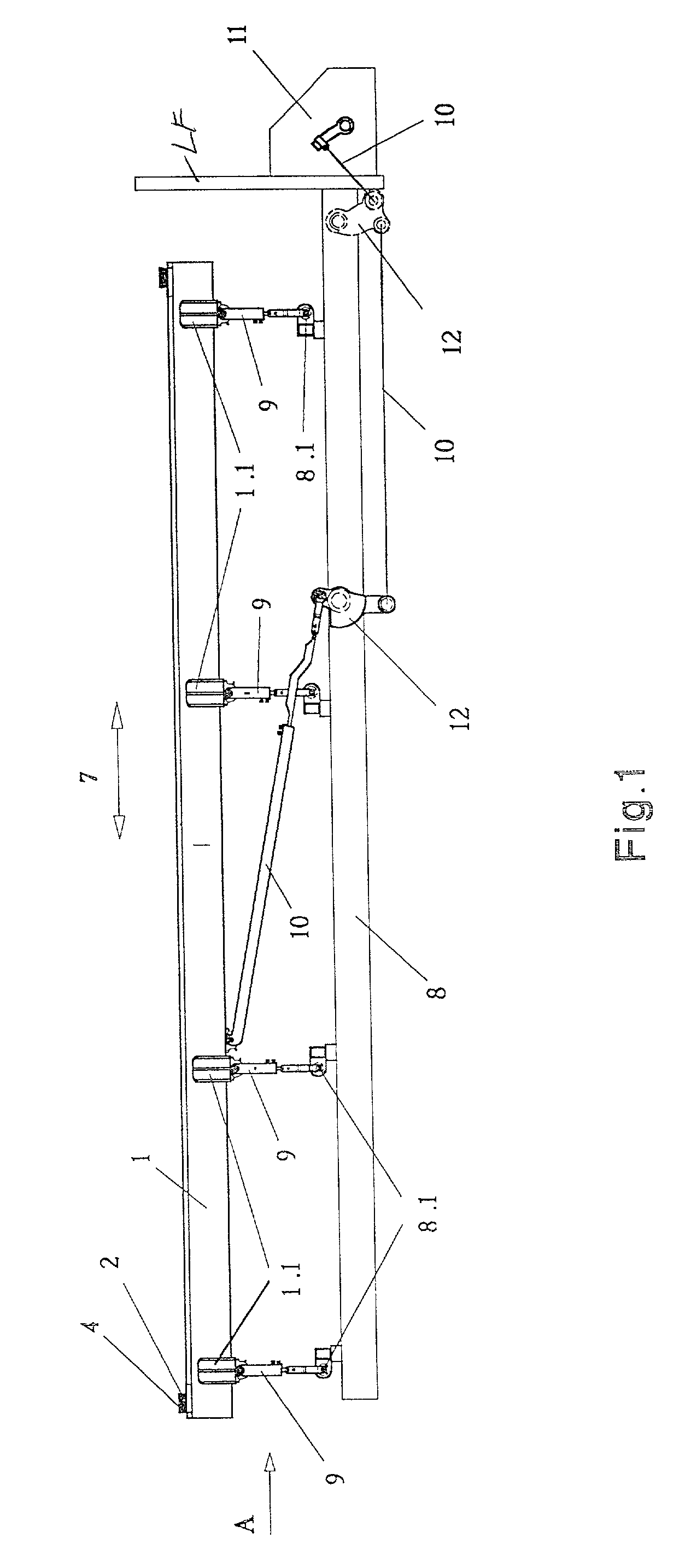
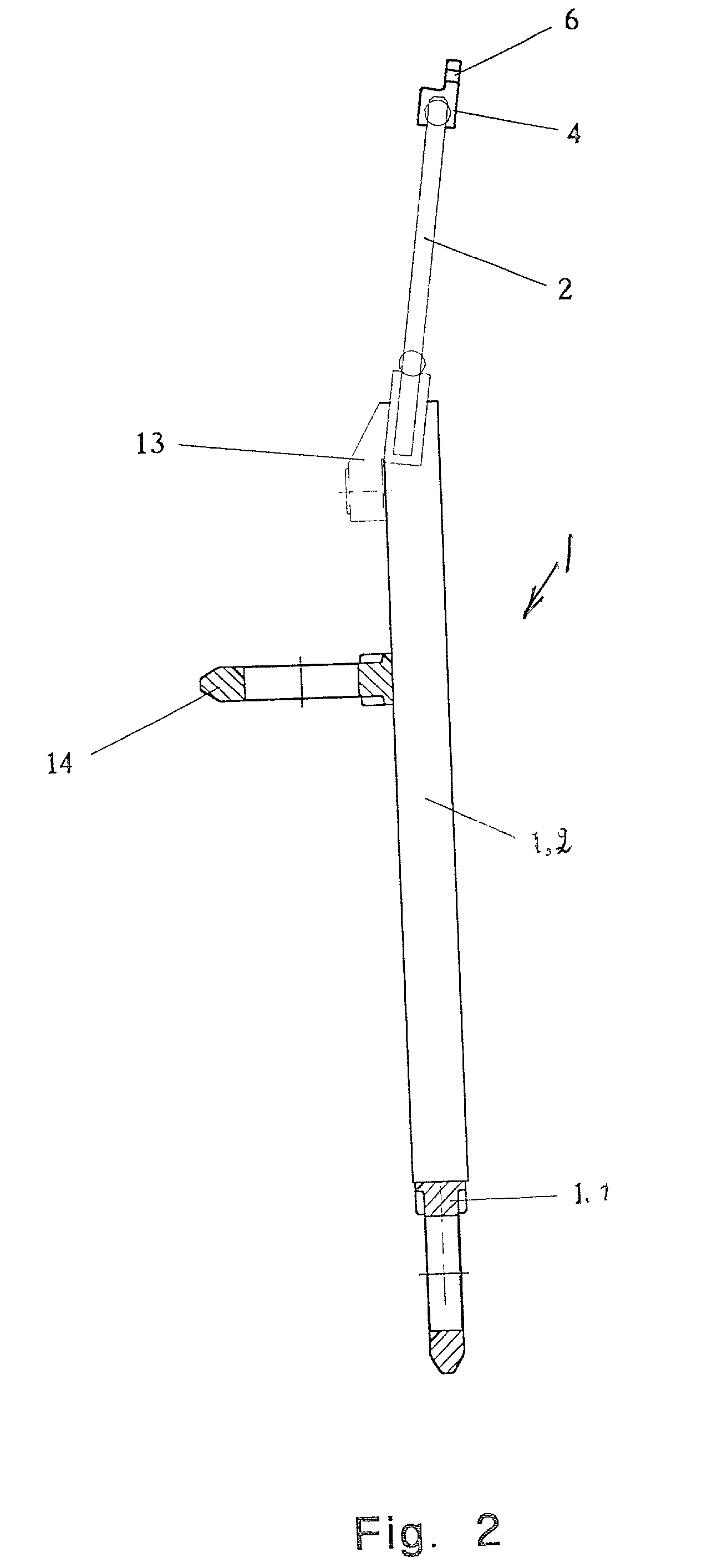
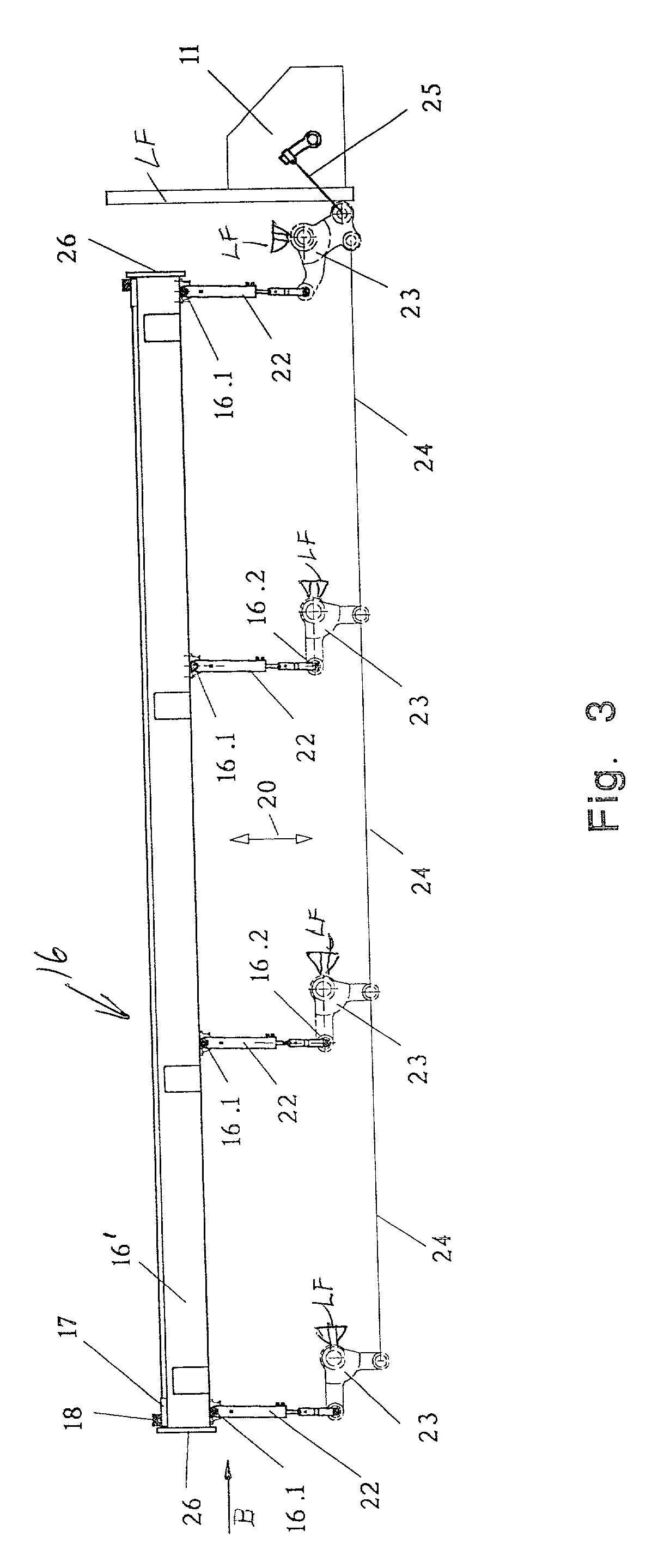
[0036] FIG. 1 shows the first embodiment according to the invention illustrating the first warp control section 1 constructed as a frame structure having a horizontal length extending over the weaving width of a loom. The first section 1 includes a guide member 2 for guiding the leno threads 3 and a guide bar 4 for guiding the ground threads 5 as seen in more detail in FIGS. 6 and 8. The guide element 2 comprises a reed type thread guide connected to the frame structure of the first warp control section 1. The guide bar 4 comprises a multitude of passages 6 extending axially and parallel relative to each other. One passage 6 is provided for each ground thread. The passages 6 may be optionally upwardly open or closed.
[0037] The first section 1 is connected to a drive 11 through a drive transmission to be described below for driving a horizontal oscillatory motion as indicated by the arrow 7. This motion is limited to a few millimeters which are adequate to properly guide the ground t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com