Method and apparatus for preventing the friction induced rotation of non-rotating stabilizers
a non-rotating stabilizer and friction induced technology, which is applied in the direction of drilling rods, drilling casings, drilling pipes, etc., can solve the problems of low curvature rate and/or low bit weight, preventing the use of conventional rotary steerable systems on many directional drilling applications, and high frictional rotation ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
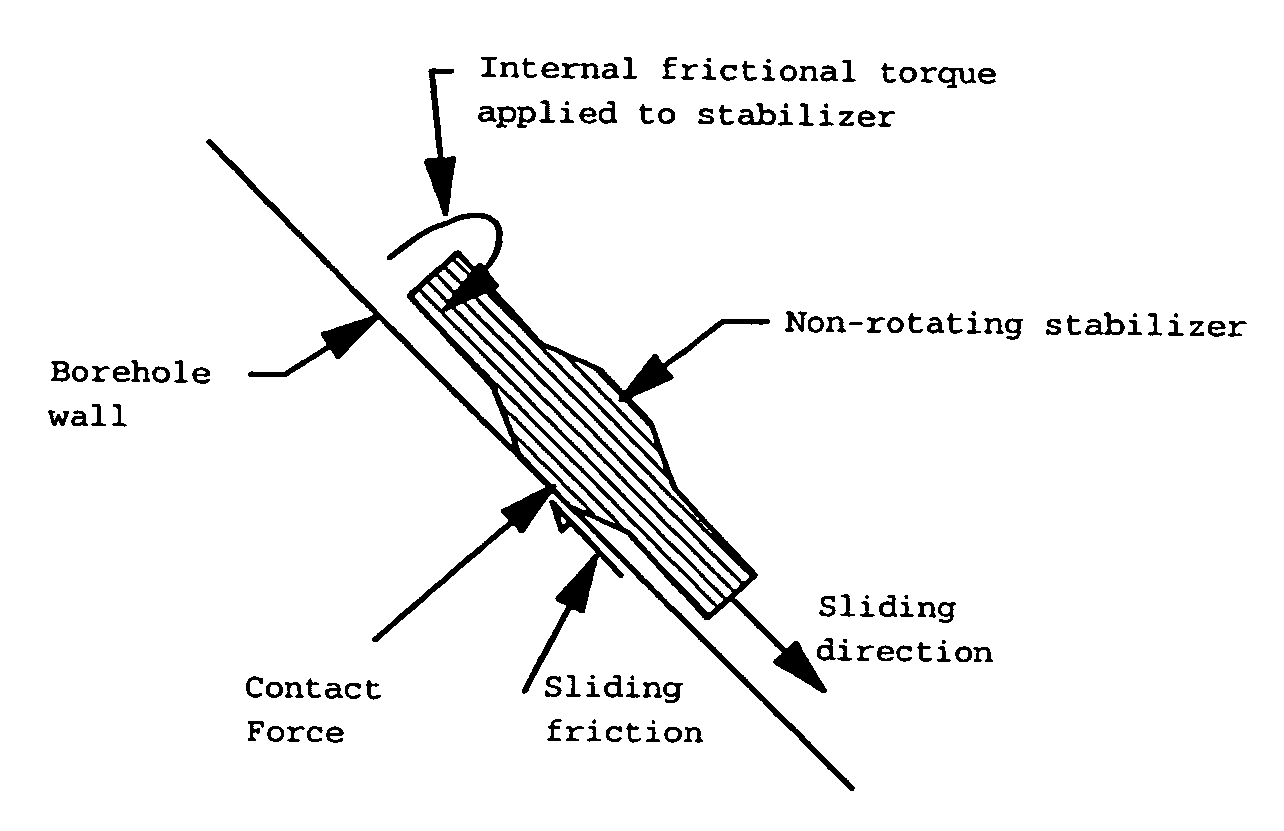
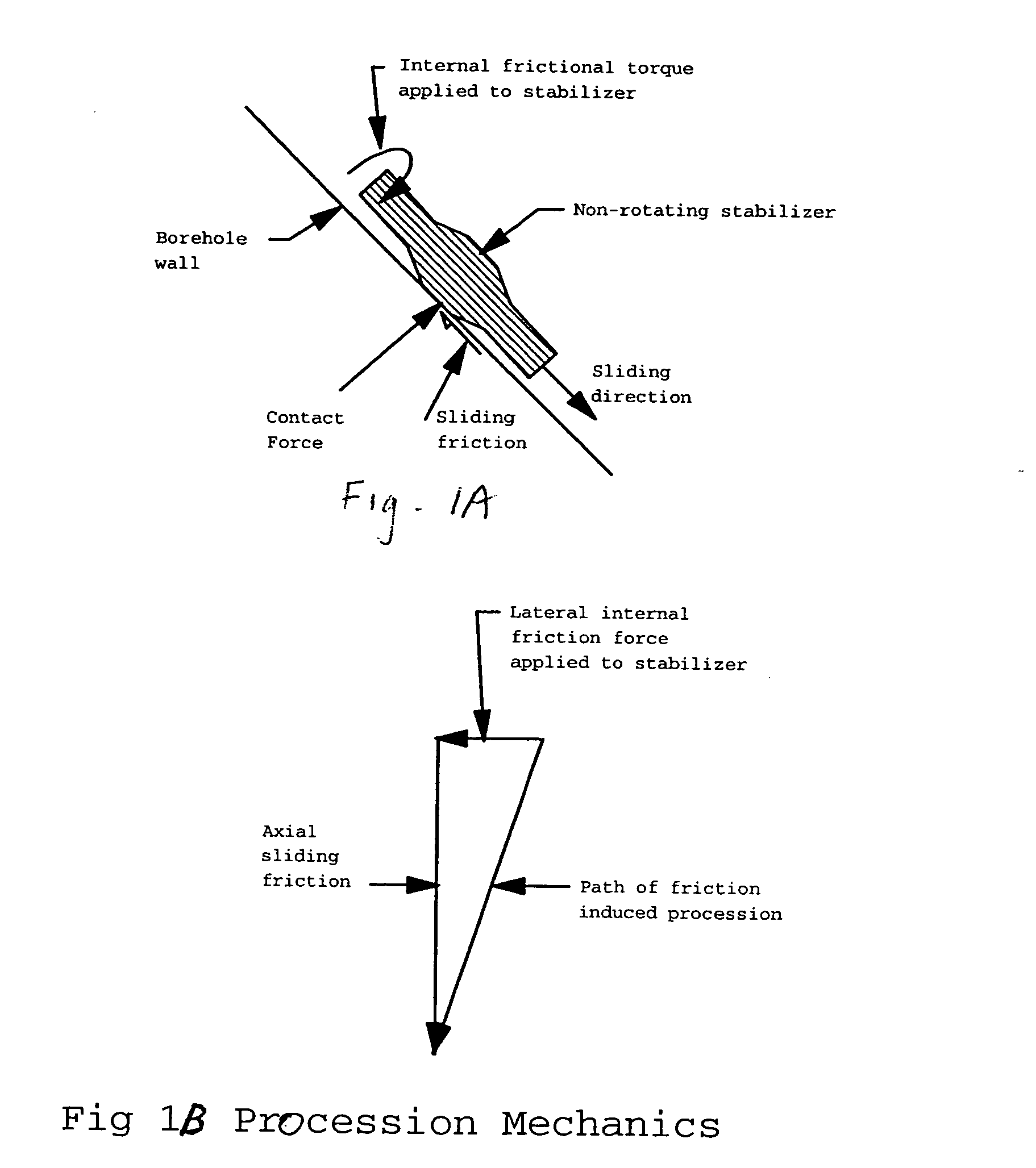
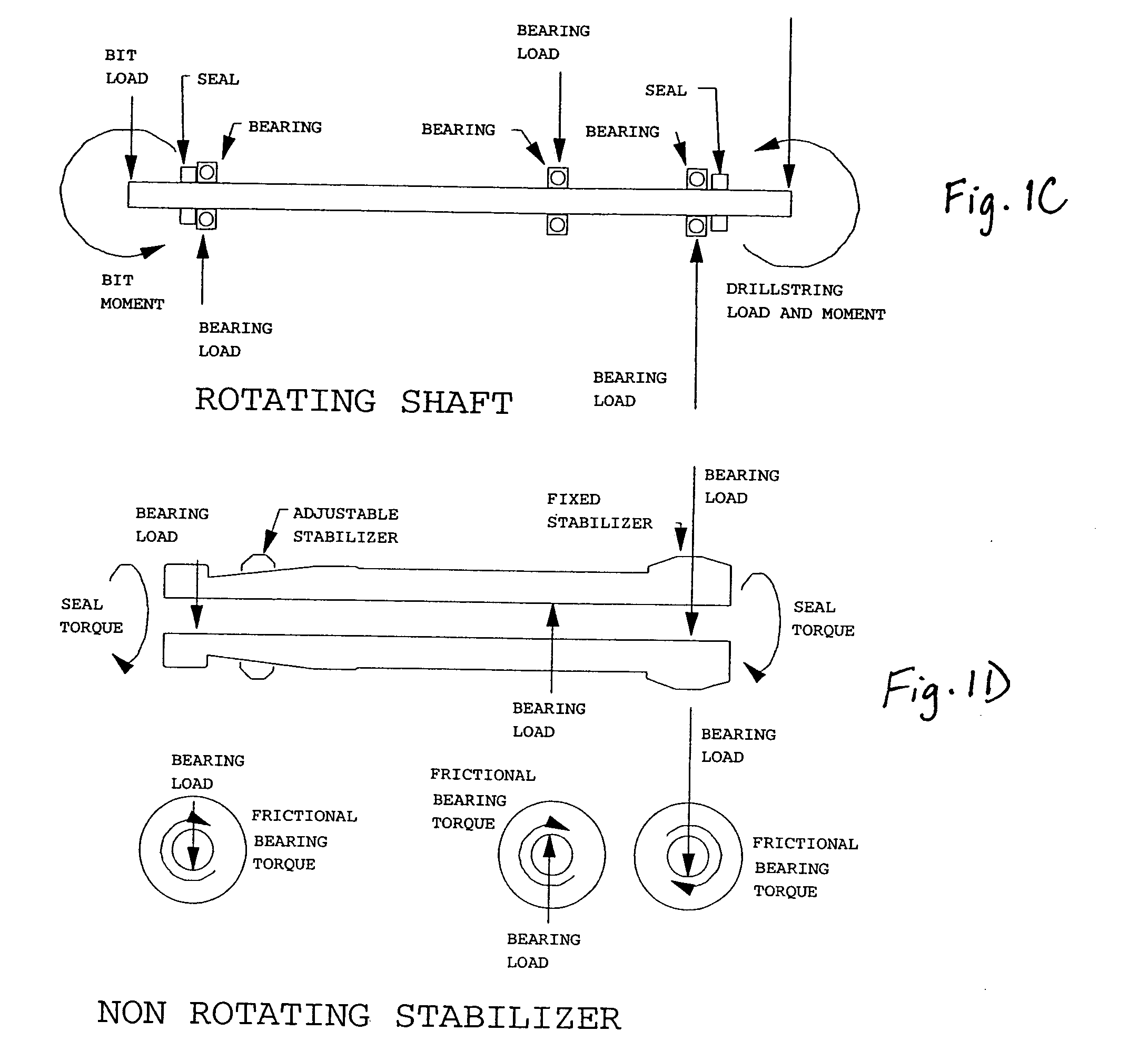
[0011] Referring to the accompanying Figures, a preferred embodiment of the invention is described as follows.
[0012] Referring to FIGS. 1A-1D, the present inventor determined that the mechanics of frictional rotation are defined generally by the following equations: RDT=bd·ff·SBF2+2·st(1)
[0013] Where:
RDT = Rotational driving torquein lbs.bd = Shaft bearing diameterin.ff = Bearing friction factor*SBF = Sum of all the bearing forceslbs.st = Rotating seal torquein lbs
[0014] The present invention is specifically applicable to drilling tools including two to four bearings. However, the invention may be applied to a drilling tool with a different number of bearings as long as the summation of the lateral forces on the bearings (SBF) is taken into account. The rotational driving torque comes from the frictional torque in the Kalsi seals and the lateral contact forces in the bearings between the shaft and the (non-adjustable stabilizer) (NAS). The resisting forces are generated by the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com