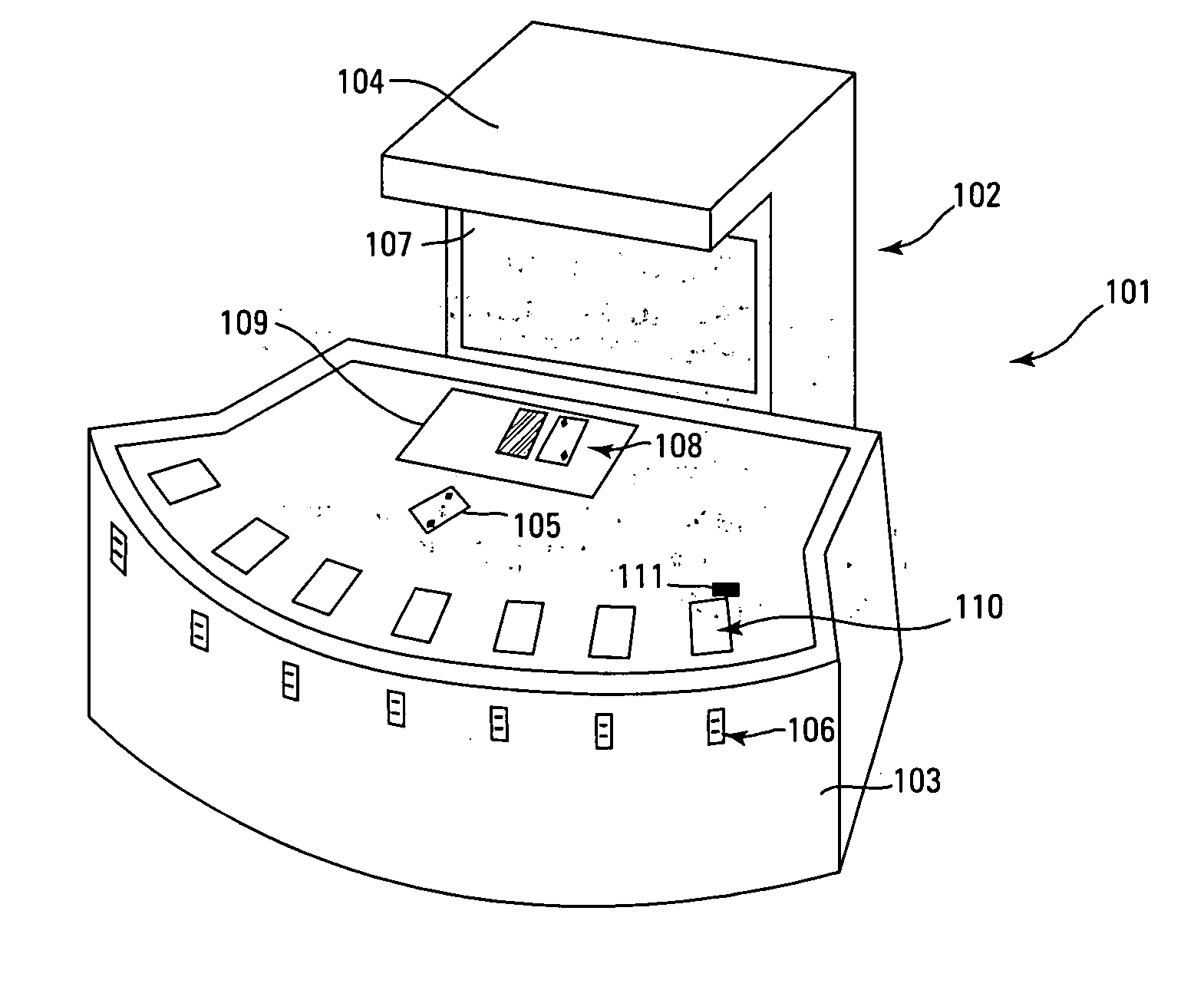
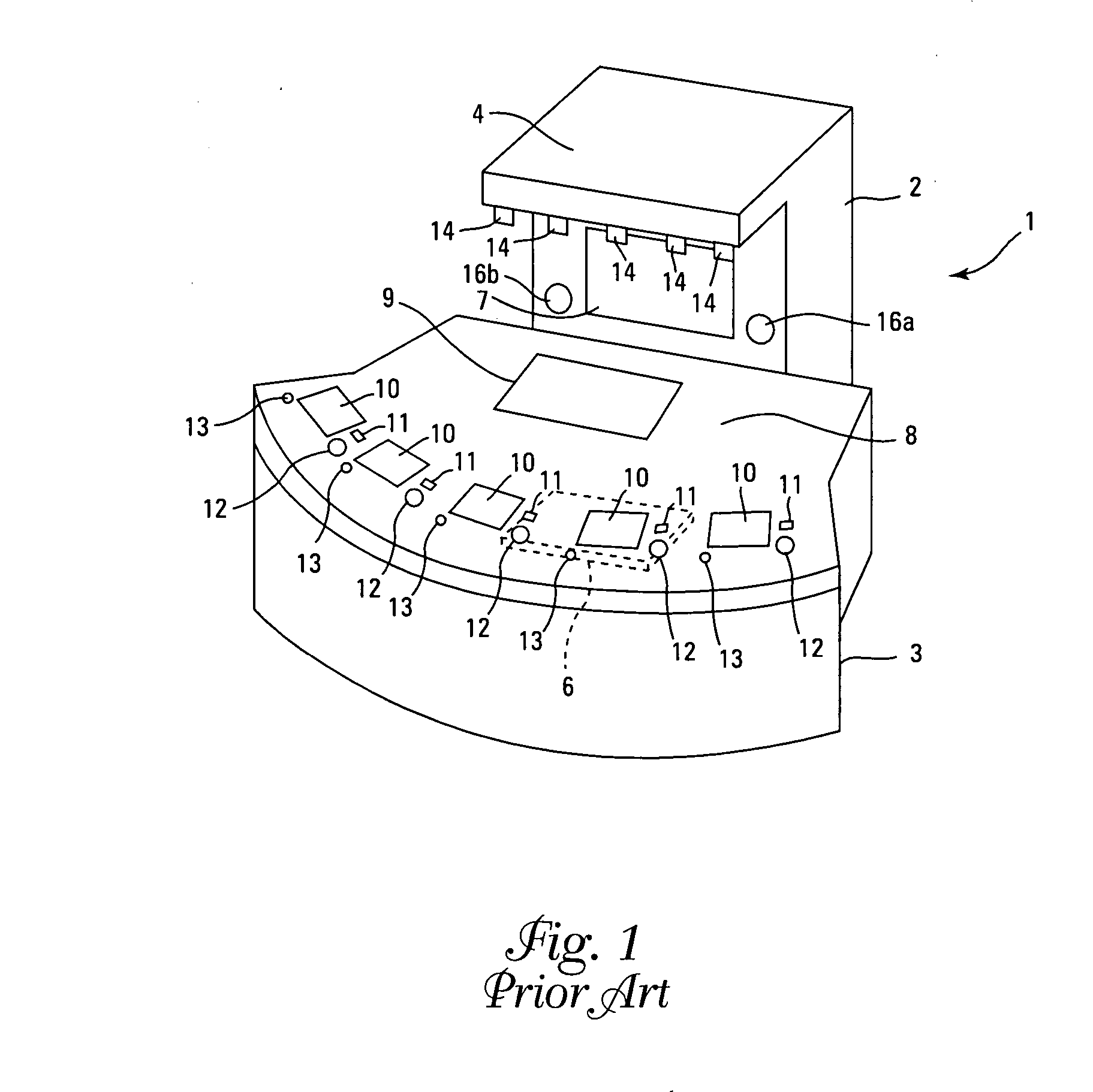
The use of playing cards provided by a live dealer has a number of associated limitations and disadvantages that have long plagued the casino industry.
Others are problems associated with the use of playing cards in particular games.
The use of playing cards at live table games typically involves several
operational requirements that are time-consuming.
These manipulations take time and are not typically appreciated by either the dealer or players as enhancing the play and entertainment value of the game.
The use of physical cards also adds a regular cost to play of the game in the wear on decks of cards that must be replaced every few hours.
When
shuffling is needed, it involves a break in the action of the table game and consumes a significant amount of time.
Thus, earnings are limited by the number of hands that can be played per hour.
Accomplishing this without detracting from the players' enjoyment and desire to play the game is a challenging and longstanding issue with casino owners and consultants in the gaming industry.
The amount of time consumed by collecting,
shuffling and dealing is also of significance in private card games because it also delays action and requires some special effort to perform.
In private games there is also some added complexity due to card players remembering or figuring out which player had previously dealt and who should now shuffle and re-deal the cards as needed.
In addition to the time
delay and added activity needed to collect, shuffle and deal cards, there is typically some time devoted to
cutting the
deck of cards which have been shuffled and which are soon to be dealt.
Although
cutting the
deck does not require a large amount of time, it does take some time.
In the gaming industry there is also a very significant amount of time and effort devoted to security issues that relate to play of the casino games.
Part of the security concerns stem from frequent attempts to cheat during play of the games.
The amount of
cheating in card games is significant to the casino industry and constitutes a major security problem that has large associated losses.
The costs of efforts to deter or prevent
cheating are very large and made on a daily basis.
This approach is disadvantaged by the fact that not all cards dealt are easily imaged from a camera position above the table because some or all of the cards are not dealt face-up, or are hidden by overlying cards.
Although many blackjack games are sufficiently revealing to later determine the order of dealt cards, others are not.
Even where cameras are used, their use may not be effective.
Such cameras may require time-consuming and tedious human analysis to go over the videotapes or other recordings of table action or require the use of
software that is complex and imprecise.
Such human analysis is costly and cannot economically be used to routinely monitor all action in a casino card room or table game pit.
For the above reasons, the
video camera monitoring techniques have found very limited effectiveness as a routine approach for identifying
cheating.
There has also been relatively limited use as a serious analytical tool because of the difficulty of analysis.
Such camera surveillance techniques are also of only limited effectiveness as a deterrent because many of the people involved with cheating have a working knowledge of their limitations and utilize approaches which are not easily detectible by such systems.
More routine and
general screening to detect cheating has remained a difficult and continuing problem for casinos.
This increases the cost of the cards and may not fully resolve the problems and difficulties in obtaining accurate information concerning sequence information.
The
automated data collecting card shoes also do not have an inherent means for collecting data on the assignment of the card to a particular player or the dealer.
They further do not collect data on the amounts bet.
However, it has been found that multiple decks are not sufficient to overcome the skilled gambler's ability to track cards and turn the
advantage against the house.
Sequential card tracking can be devastating to a casino since a player taking
advantage of such information can bet large in a winning situation and change the
odds in favor of the player and against the casino.
There is also a long-standing problem in the play of blackjack which concerns the situation when the dealer receives a blackjack hand in the initial two cards dealt.
If the hand is fully played out, and the dealer then reveals that the dealer has received a blackjack hand, then a significant amount of time has been wasted.
It also causes players to often be upset when a hand is played out to no avail.
Many casinos do not allow the dealer to look at or inspect the down card until all insurance wagers have been made or declined.
These devices and methods generally add greater costs and slow the play of the game.
The prior attempts have often ended up unacceptable and are removed.
Another notable problem suffered by live table games is the intimidation which many novice or less experienced players feel when playing such games.
These people feel intimidation at a live table game because such games require quick thinking and
decision making while other people are watching and waiting.
A further issue that has developed in the casino business is the public's increasing interest in participating in games that have a very large potential payoff.
These
slot machine systems are relatively more costly to purchase and operate.
For many gamblers, this approach is not particularly attractive.
This lack of attractiveness may be due to the impersonal and solitary nature of playing slot machines.
Table card games have not been able to satisfactorily address this interest.
Further problems associated with live table card games are the costs associated with
purchasing, handling and disposal of paper and plastic playing cards.
In any case, the cost of playing cards for a casino is significant and can easily run in the hundreds of thousands of dollars per year.
In addition to the above problems, there are also significant costs associated with handling and storing the new and worn playing cards.
Thus, the high costs of casino facilities further exacerbate the costs associated with paper and plastic playing cards.
The most significant cost in operation of gaming apparatus is personnel costs.
These machines are common in casinos, but do not duplicate the ambience of the casino table game with multiple players present.
This tends to maximize the cost of the system and tends to provide a slow system with high
processing power demands to keep the operation working at speeds needed to maximize use and profit from the machines.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More